Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain Brief Synapse Final
Brain Brief Synapse Final
Uploaded by
veerraju tv0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThe synapse is the small gap between neurons where neurotransmission occurs, allowing brain cells to communicate. There may be as many as 150 trillion synapses in the human brain. At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and received by receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, transmitting signals between cells and enabling processes like learning and memory. While tiny at 20-40 nanometers wide, synapses allow for bidirectional communication between neurons that is critical to cognitive functions.
Original Description:
brain synapses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe synapse is the small gap between neurons where neurotransmission occurs, allowing brain cells to communicate. There may be as many as 150 trillion synapses in the human brain. At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and received by receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, transmitting signals between cells and enabling processes like learning and memory. While tiny at 20-40 nanometers wide, synapses allow for bidirectional communication between neurons that is critical to cognitive functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesBrain Brief Synapse Final
Brain Brief Synapse Final
Uploaded by
veerraju tvThe synapse is the small gap between neurons where neurotransmission occurs, allowing brain cells to communicate. There may be as many as 150 trillion synapses in the human brain. At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and received by receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, transmitting signals between cells and enabling processes like learning and memory. While tiny at 20-40 nanometers wide, synapses allow for bidirectional communication between neurons that is critical to cognitive functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
BRAIN BRIEFS
Neurotransmission: The Synapse
The brain is responsible for every thought, feeling, and Current estimates are listed somewhere around 0.15
action. But how do the billions of cells that reside in the quadrillion synapses—or 150,000,000,000,000
brain manage these feats? synapses.
They do so through a process called neurotransmission. What is synaptic transmission?
Simply stated, neurotransmission is the way that brain cells
communicate. And the bulk of those communications Generally speaking, it’s just another way to say
occur at a site called the synapse. Neuroscientists now neurotransmission. But it specifies that the communication
understand that the synapse plays a critical role in a occurring between brain cells is happening at the synapse
variety of cognitive processes—especially those involved as opposed to some other communication point. One
with learning and memory. neuron, often referred to as the pre-synaptic cell, will
release a neurotransmitter or other neurochemical from
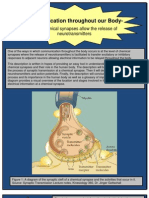
What is a synapse? special pouches clustered near the cell membrane called
synaptic vesicles into the space between cells. Those
The word synapse stems from the Greek words molecules will then be taken up by membrane receptors on
“syn” (together) and “haptein” (to clasp). This might make the post-synaptic, or neighboring, cell. When this message
you think that a synapse is where brain cells touch or is passed between the two cells at the synapse, it has the
fasten together, but that isn’t quite right. The synapse, power to change the behavior of both cells. Chemicals
rather, is that small pocket of space between two cells, from the pre-synaptic neuron may excite the post-synaptic
where they can pass messages to communicate. A single cell, telling it to release its own neurochemicals. It may tell
neuron may contain thousands of synapses. In fact, one the post-synaptic cell to slow down signaling or stop it all
type of neuron called the Purkinje cell, found in the brain’s together. Or it may simply tell it to change the message a
cerebellum, may have as many as one hundred thousand bit. But synapses offer the possibility of bi-directional
synapses. communication. As such, post-synaptic cells can send back
their own messages to pre-synaptic cells—telling them to
How big is a synapse? change how much or how often a neurotransmitter is
released.
Synapses are tiny—you cannot see them with the
naked eye. When measured using sophisticated tools,
scientists can see that the small gaps between cells is
approximately 20-40 nanometers wide. If you consider
that the thickness of a single sheet of paper is about
100,000 nanometers wide, you can start to understand
just how small these functional contact points between
neurons really are. More than 3,000 synapses would fit in
that space alone!
How many synapses are in the human brain?
The short answer is that neuroscientists aren’t exactly
sure. It’s very hard to measure in living human beings. But
current post-mortem studies, where scientists examine the
brains of deceased individuals, suggest that the average
male human brain contains about 86 billion neurons. If
each neuron is home to hundreds or even thousands of
synapses, the estimated number of these communication
points must be in the trillions.
www.dana.org
You might also like
- The MindUP Curriculum Grades 3-5 Brain-Focused Strategies For Learning-And Living PDFDocument162 pagesThe MindUP Curriculum Grades 3-5 Brain-Focused Strategies For Learning-And Living PDFSheena Pago100% (5)
- MigraineDocument20 pagesMigraineveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument369 pagesUntitledveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Perkins Theory of Learnable IntelligenceDocument2 pagesPerkins Theory of Learnable IntelligenceMohd Kamarulzaman OmarNo ratings yet
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Telepathy and The Technology of Mind ControlDocument18 pagesTelepathy and The Technology of Mind Controlbingwazzup100% (2)
- Neurotransmission: The Synapse: What Is Synaptic Transmission?Document2 pagesNeurotransmission: The Synapse: What Is Synaptic Transmission?devdsantoshNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument2 pagesBio ProjectNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Alde Annieska Learning Journal 2Document5 pagesAlde Annieska Learning Journal 2Maria AnnieskaNo ratings yet
- SynapseDocument12 pagesSynapseSweety DhillonNo ratings yet
- (English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)Document8 pages(English) The Nervous System, Part 3 - Synapses! - Crash Course A&P #10 (DownSub - Com)bank townNo ratings yet
- The Processing & Information at Higher Levels: Tutik ErmawatiDocument19 pagesThe Processing & Information at Higher Levels: Tutik ErmawatiApsopela SandiveraNo ratings yet
- Intro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Document97 pagesIntro Animal Physiology Ch-2.1Jojo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drugs and The BrainDocument7 pagesDrugs and The Brainebola123No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument44 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAarohi PatilNo ratings yet
- Concept of The SynapseDocument3 pagesConcept of The SynapseShannon Erika Drew A. EdañoNo ratings yet
- SynapseDocument7 pagesSynapseSinan Sa100% (1)
- 10nervous System 1Document26 pages10nervous System 1Jack OneNo ratings yet
- CNS NoteDocument203 pagesCNS NoteAhmad Khair Ahmad BazliNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesStructure and Function of Nervous SystemFUN FLARE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- General Physiology of SynapsesDocument30 pagesGeneral Physiology of SynapsesSanchezNo ratings yet
- Nervous CoordinationDocument2 pagesNervous CoordinationParty CularNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument81 pagesNervous System - Generalyash rajNo ratings yet
- AsdfgDocument28 pagesAsdfgrerereNo ratings yet
- THE Nervous System: Biology ProjectDocument8 pagesTHE Nervous System: Biology ProjectAravind JChandranNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Its Function February 2014Document4 pagesNeurons and Its Function February 2014Odaine BennettNo ratings yet
- NervousDocument13 pagesNervousJoan GalarceNo ratings yet
- Unit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument37 pagesUnit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMAmrita RanaNo ratings yet
- Neuron SystemDocument17 pagesNeuron Systemdibya patraNo ratings yet
- SynapseDocument1 pageSynapseamorteyNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Synapses of The Nervous System. For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 pagesThis Article Is About Synapses of The Nervous System. For Other Uses, Seeberat90No ratings yet
- 5 SynapsesDocument60 pages5 Synapsesrosario gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Brains Bodies Behaviour (Psychology)Document18 pagesBrains Bodies Behaviour (Psychology)Cassia LmtNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAutonomic Nervous Systemsunil patelNo ratings yet
- Consciousness - Engine of Reason Seat of Soul - Paul Churchland PDFDocument329 pagesConsciousness - Engine of Reason Seat of Soul - Paul Churchland PDFmassimo rossi100% (1)
- 1 - Synapses & Synaptic Transmission (Updated)Document13 pages1 - Synapses & Synaptic Transmission (Updated)abdallaNo ratings yet
- 3 Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument25 pages3 Biological Basis of BehaviorFatima GhaniNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Science Assignment)Document6 pagesNervous System (Science Assignment)Emylya HasnirNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishAish ThangalNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet
- 4.nervous System IDocument12 pages4.nervous System IPatricia TeyeNo ratings yet
- End - Sem - For MergeDocument42 pagesEnd - Sem - For Mergeমেঘে ঢাকা তারাNo ratings yet
- Biological Relevance of Neurotransmitter ReleaseDocument12 pagesBiological Relevance of Neurotransmitter ReleaseazzaassNo ratings yet
- Technical DescriptionDocument8 pagesTechnical Descriptioncool_comic88100% (1)
- Synaptic ConductionDocument8 pagesSynaptic ConductionRiddhi RavalNo ratings yet
- Histology of Chemical Synapses of The Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of Chemical Synapses of The Nervous SystemAhmed ZanatyNo ratings yet
- Exploring Neuroscience 1-6Document6 pagesExploring Neuroscience 1-6Patricia SusckindNo ratings yet
- Will You Ever Be Able To Upload Your Brain?: Present Vogue Cryogenic PreservationDocument3 pagesWill You Ever Be Able To Upload Your Brain?: Present Vogue Cryogenic PreservationesimezacatencoNo ratings yet
- INTRO Spiking Neural Networks An Introduction-VreekenDocument5 pagesINTRO Spiking Neural Networks An Introduction-VreekenZiom TygaNo ratings yet
- 02 Central Nervous Systemppt396Document63 pages02 Central Nervous Systemppt396Tahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument15 pagesNervous TissueStar ManavNo ratings yet
- Le Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectDocument5 pagesLe Neuron Structure: Reflexes: Sensory Nuerons: Trasmit Info From Sensors That DetectYiboNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomical Divisions of The Nervous SystemDamianNo ratings yet
- University of Pennsylvania Neuroscience ResearchDocument25 pagesUniversity of Pennsylvania Neuroscience Researchapi-495461280No ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument86 pagesGen BioPaul MagbagoNo ratings yet
- Question 3 & 4Document15 pagesQuestion 3 & 4Arslan Muhammad EjazNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument74 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourytsrajalmaharjanNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of NeuronsDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of NeuronsAlkykwyn LiteratoNo ratings yet
- 7 Sensitivity and CoordinationDocument19 pages7 Sensitivity and CoordinationVarun GoseinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System RECORDINGSDocument52 pagesThe Nervous System RECORDINGSKathy Angeli Bel-idaNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument6 pagesNervous TissueAhmed JawdetNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document51 pagesUnit 5JAYANT CH (RA2111004010265)No ratings yet
- BASIC FUNCTIONS of SYNAPSESDocument8 pagesBASIC FUNCTIONS of SYNAPSESJadys Merill DiezNo ratings yet
- 02 Central Nervous Systemppt396Document104 pages02 Central Nervous Systemppt396iqra riazNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of First Seizure and Newly Diagnosed.4Document31 pagesEvaluation of First Seizure and Newly Diagnosed.4veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- CONTINUUM Lifelong Learning in Neurology (Sleep Neurology) August 2023Document292 pagesCONTINUUM Lifelong Learning in Neurology (Sleep Neurology) August 2023veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Premature Cardiovascular Disease and Brain Health in MidlifeDocument11 pagesPremature Cardiovascular Disease and Brain Health in Midlifeveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Neuroimage: Sheng Zhang, Chiang-Shan R. LiDocument15 pagesNeuroimage: Sheng Zhang, Chiang-Shan R. Liveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Evaluation of Stroke Etiology: Review ArticleDocument13 pagesDiagnostic Evaluation of Stroke Etiology: Review Articleveerraju tv100% (1)
- Pilot Product Catalogue 18Document28 pagesPilot Product Catalogue 18veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Acute Metronidazole-Induced NeurotoxicityDocument7 pagesAcute Metronidazole-Induced Neurotoxicityveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- MILLER'S Information Processing TheoryDocument34 pagesMILLER'S Information Processing TheoryDarlen May Dalida100% (1)
- BrainDocument15 pagesBrainŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BrainDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Brainelrasc06No ratings yet
- LL1 - HW Week 5Document2 pagesLL1 - HW Week 5Bích ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Theory of DreamsDocument2 pagesTheory of DreamsJasonNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO Samplex Motor SystemDocument42 pagesPHYSIO Samplex Motor SystemMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SummaryDocument10 pagesChapter 5 SummarykuzmanovicstanaNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Remote Neural Monitoring - A Technology Used For Controlling Human BrainDocument44 pagesStrahlenfolter Stalking - TI - Remote Neural Monitoring - A Technology Used For Controlling Human BrainOlaf-SchmidkeNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Clarke-Stewart & Parke Social Development Chapter 10. Sex and Gender: Vive La Différence?Document11 pagesTest Bank For Clarke-Stewart & Parke Social Development Chapter 10. Sex and Gender: Vive La Différence?NeeshaNo ratings yet
- Lect 12Document70 pagesLect 12fatima shahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan COT 5esDocument8 pagesLesson Plan COT 5esjuneza tagyobonNo ratings yet
- Does WiFi Affect The BrainDocument6 pagesDoes WiFi Affect The BrainrustyNo ratings yet
- HydrocephalusDocument9 pagesHydrocephalusAbdul Rauf Araneta Ramirez100% (1)
- Psychotronic SDocument5 pagesPsychotronic SEyemanProphet100% (1)
- Psychobiological Concepts: - Relationship of Neuroanatomy and - Relationship of Psychiatric Illnesses ToDocument56 pagesPsychobiological Concepts: - Relationship of Neuroanatomy and - Relationship of Psychiatric Illnesses ToRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- Neuroelectrophysiology Paper 2Document6 pagesNeuroelectrophysiology Paper 2Harveen BawaNo ratings yet
- Fluoxetine Treatment For More Than 2 Days Decreases The Cellular Neuroplasticity and Microtubule Plasticity in Differentiated PC12 CellsDocument27 pagesFluoxetine Treatment For More Than 2 Days Decreases The Cellular Neuroplasticity and Microtubule Plasticity in Differentiated PC12 CellsRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Advances in Molecular BiologyDocument8 pagesAdvances in Molecular Biologyfazila zahoorNo ratings yet
- Aptitude 9Document6 pagesAptitude 9khanrules2012No ratings yet
- The MAP Minibook: © MAP Coaching Institute April 2021Document11 pagesThe MAP Minibook: © MAP Coaching Institute April 2021Tiffany Fox100% (1)
- Review Vayu PerspectiveDocument14 pagesReview Vayu PerspectiveRahul JaganNo ratings yet
- NT57-sat TestDocument57 pagesNT57-sat Testhanh dao thuyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PsychologytDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Psychologytravibunga4489No ratings yet
- Ook Reviews: Biophysics of Computation: Information Processing in Single NeuronsDocument2 pagesOok Reviews: Biophysics of Computation: Information Processing in Single NeuronsAsdfgNo ratings yet
- (TEXT) I Just Finished The Online Coursera Course - Learning How To Learn - I Highly Recommend It To Everyone and I Summarized Everything I Learned From It. - GetMotivatedDocument28 pages(TEXT) I Just Finished The Online Coursera Course - Learning How To Learn - I Highly Recommend It To Everyone and I Summarized Everything I Learned From It. - GetMotivatedOni JotaNo ratings yet
- ADHD and Neuropsychology: Developmental Perspective, Assessment, and InterventionsDocument3 pagesADHD and Neuropsychology: Developmental Perspective, Assessment, and InterventionsShiv SookunNo ratings yet