Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformational
Transformational
Uploaded by
Lea Condalo TantaoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformational
Transformational
Uploaded by
Lea Condalo TantaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformational leadership is a theory of leadership where a leader works with teams to
identify needed change, creating a vision to guide the change through inspiration, and executing
the change in tandem with committed members of a group;[1] it is an integral part of the Full
Range Leadership Model. Transformational leadership serves to enhance the motivation,
morale, and job performance of followers through a variety of mechanisms; these include
connecting the follower's sense of identity and self to a project and to the collective identity of
the organization; being a role model for followers in order to inspire them and to raise their
interest in the project; challenging followers to take greater ownership for their work, and
understanding the strengths and weaknesses of followers, allowing the leader to align followers
with tasks that enhance their performance. Transformational leadership is a theory
of leadership where a leader works with teams to identify needed change, creating a vision to
guide the change through inspiration, and executing the change in tandem with committed
members of a group;[1] it is an integral part of the Full Range Leadership Model.
Transformational leadership serves to enhance the motivation, morale, and job
performance of followers through a variety of mechanisms; these include connecting the
follower's sense of identity and self to a project and to the collective identity of the organization;
being a role model for followers in order to inspire them and to raise their interest in the project;
challenging followers to take greater ownership for their work, and understanding the strengths
and weaknesses of followers, allowing the leader to align followers with tasks that enhance their
performance.
According to Bass,[5] transformational leadership encompasses several different
aspects, including:
Emphasizing intrinsic motivation and positive development of followers
Raising awareness of moral standards
Highlighting important priorities
Fostering higher moral maturity in followers
Creating an ethical climate (share values, high ethical standards)
Encouraging followers to look beyond self-interests to the common good
Promoting cooperation and harmony
Using authentic, consistent means
Using persuasive appeals based on reason
Providing individual coaching and mentoring for followers
Appealing to the ideals of followers
Allowing freedom of choice for followers
Transformational leaders are described to hold positive expectations for followers,
believing that they can do their best. As a result, they inspire, empower, and stimulate
followers to exceed normal levels of performance. Transformational leaders also focus
on and care about followers and their personal needs and
development.[6]Transformational leaders fit well in leading and working with complex
work groups and organizations, where beyond seeking an inspirational leader to help
guide them through an uncertain environment, followers are also challenged and feel
empowered; this nurtures them into becoming loyal, high performers.
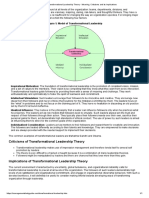
There are 4 components to transformational leadership, sometimes referred to as the 4
I's:
Idealized Influence (II) - the leader serves as an ideal role model for followers; the leader "walks
the talk," and is admired for this. A transformational leader embodies the qualities she wants in her
team.
Inspirational Motivation (IM) - Transformational leaders have the ability to inspire and motivate
followers through having a vision and presenting that vision. Combined, these first two I's are what
constitute the transformational leader's charisma.
Individualized Consideration (IC) - Transformational leaders demonstrate genuine concern for
the needs and feelings of followers and help them self-actualize. This personal attention to each
follower assists in developing trust among the organization's members and their authority
figure(s). This is an important element because teams are able to rely on and work together so
decisions can be made more quickly, the transformational leader increases their buy-in[7]
Intellectual Stimulation (IS) - the leader challenges followers to be innovative and creative, they
encourage their followers to challenge the status quo. A common misunderstanding is that
transformational leaders are "soft," but the truth is that they constantly challenge followers to
higher levels of performance.[6]
Transformational leadership is said to have occurred when engagement in a group
results in leaders and followers raising one another to increased levels of motivation
and morality.[5] It is not enough to make the correct choice, but to make the moral
choice.
You might also like
- Trauma ChecklistDocument2 pagesTrauma ChecklistMohammed Ezz El Regal100% (2)
- Transformational LeadershipDocument16 pagesTransformational LeadershipFaHEEM DILAWAR75% (8)
- Case Study 1Document3 pagesCase Study 1asuvaniNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument5 pagesTransformational LeadershipMikkey Jane DelgraNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Leadership Development (Industrial Psychology)Document11 pagesAssignment On Leadership Development (Industrial Psychology)Jaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument12 pagesTransformational LeadershipCapt . Naif AlhamdNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership. VKDocument6 pagesTransformational Leadership. VKAdityaNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership ConceptDocument2 pagesTransformational Leadership Concepteyaluayssa10qNo ratings yet
- Leadership Assignment 1 - Transformational Leadership Theory PDFDocument11 pagesLeadership Assignment 1 - Transformational Leadership Theory PDFIsaac Chinhengo100% (1)
- Lesson 5.1: Transformational LeadersDocument8 pagesLesson 5.1: Transformational LeadersAnthony Añora 2No ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument2 pagesTransformational LeadershipRayhan AriqNo ratings yet
- Module IIIDocument15 pagesModule IIIMichelle SoguilonNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument10 pagesDocumentBushra FeroziNo ratings yet
- What Is Transformational LeadershipDocument7 pagesWhat Is Transformational LeadershipJohn Lenard MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument2 pagesTransformational LeadershipTSN InternetNo ratings yet
- What Is Management and LeadershipDocument5 pagesWhat Is Management and LeadershipMaricel BacatanNo ratings yet
- Transformational and Authentic LeadershipDocument9 pagesTransformational and Authentic LeadershipAdeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Describe The Following Leadership Theories: (A) Transformational Leadership, (B) SituationalDocument16 pagesDescribe The Following Leadership Theories: (A) Transformational Leadership, (B) Situationalqis 2008No ratings yet
- Transformational LeadersDocument14 pagesTransformational Leadersakii ramNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument24 pagesTransformational LeadershipAhmed YinkaNo ratings yet
- Ision Empower Followers To Meet Higher Standards Others Want To Trust Them, and Who Give Meaning To Organizational LifeDocument2 pagesIsion Empower Followers To Meet Higher Standards Others Want To Trust Them, and Who Give Meaning To Organizational Lifethamnguyen304No ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership StyleDocument21 pagesTransformational Leadership Styleeyaluayssa10qNo ratings yet
- Transformational Theory of LeadershipDocument9 pagesTransformational Theory of LeadershipJohn Glenn BalacanoNo ratings yet
- PPM UNIT 4 LeadershipDocument3 pagesPPM UNIT 4 LeadershipJitendra PavanNo ratings yet
- c5 Hbo Leadership EffectivenessDocument7 pagesc5 Hbo Leadership EffectivenessiamamayNo ratings yet
- The Goal of Transformational LeadershipDocument1 pageThe Goal of Transformational Leadershipeugene123No ratings yet
- Top 7 Benefits of Developing Strong Leadership SkillsDocument5 pagesTop 7 Benefits of Developing Strong Leadership SkillsRomana ChangeziNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument14 pagesTransformational LeadershipPandesal with EggNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership Theory - Meaning, Criticisms and Its ImplicationsDocument1 pageTransformational Leadership Theory - Meaning, Criticisms and Its ImplicationsSatyam SachanNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument2 pagesLeadershipNurul IzyanNo ratings yet
- Leadership Training: Prepared and Presented by Group 3Document20 pagesLeadership Training: Prepared and Presented by Group 3Nathaniel LozanoNo ratings yet
- Transactional Vs TransformationalDocument2 pagesTransactional Vs TransformationalΛthul pràkáshNo ratings yet
- Models of Educational Leadership and ManagementDocument34 pagesModels of Educational Leadership and ManagementGoshen ShamaSelahNo ratings yet
- Transformational Vs Transactional LeadershipDocument5 pagesTransformational Vs Transactional LeadershipKrezielDulosEscobarNo ratings yet
- Master in Management Major in Public AdministrationDocument11 pagesMaster in Management Major in Public AdministrationJohn Michael TalanNo ratings yet
- Unit07 Transformational Vs Transactional Leadership SVDocument19 pagesUnit07 Transformational Vs Transactional Leadership SVVi LeNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Who Is A Leader? Abdul Hasib SafiDocument16 pagesLeadership: Who Is A Leader? Abdul Hasib Safimassoud ahadiNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Transformational Leadershi-1Document8 pagesThe Impact of Transformational Leadershi-1jamaelarham720No ratings yet
- Assignment On ": Course Title: Leadership in Organization (HRM 6406)Document25 pagesAssignment On ": Course Title: Leadership in Organization (HRM 6406)Adib ShakilNo ratings yet
- Leadership TheoriesDocument10 pagesLeadership TheoriesCephas KariukiNo ratings yet
- Transfomational Leadership (Tharmaraj Subramaniam)Document7 pagesTransfomational Leadership (Tharmaraj Subramaniam)stharmaraj06100% (1)
- Final Report (Leading Change)Document23 pagesFinal Report (Leading Change)Karen May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- A Closer Look at The Effects of Transformational LeadershipDocument3 pagesA Closer Look at The Effects of Transformational LeadershipzainuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2Azhar ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document32 pagesUnit 5inaadhikari98No ratings yet
- The Importance of Leadership Quality PDFDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Leadership Quality PDFGuidoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document4 pagesTopic 1Yen Kim12No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 LeadershipDocument41 pagesChapter 6 LeadershipSiputs Sedut100% (1)
- Transformational LeadershipDocument15 pagesTransformational LeadershipMichael Phan100% (11)
- On Becoming A Transformational LeaderDocument13 pagesOn Becoming A Transformational LeaderKyle Harry Magdasoc100% (1)
- Notes Topic 10Document4 pagesNotes Topic 10norsuriahazniNo ratings yet
- On Becoming A Transformational LeaderDocument21 pagesOn Becoming A Transformational LeaderJohnVanMagnoBalazuela50% (2)
- Leadership & CEO Traning - Module 1Document29 pagesLeadership & CEO Traning - Module 1yamoka2001No ratings yet
- Difference Between Transactional and Transformational LeadershipDocument16 pagesDifference Between Transactional and Transformational Leadershipalkjgh100% (2)
- Lean-Agile Leadership - Scaled Agile FrameworkDocument1 pageLean-Agile Leadership - Scaled Agile FrameworkYitaoNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument18 pagesLeadershipRashid MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Michelle MartinNo ratings yet
- The Art of Strategic Leadership: A Brief Guide to Becoming a Great LeaderFrom EverandThe Art of Strategic Leadership: A Brief Guide to Becoming a Great LeaderNo ratings yet
- ML 4Document5 pagesML 4Ali HasanNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument10 pagesTransformational LeadershipMa. Theresse Cathlene Alyzon TorlaoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Transformational LeaderDocument24 pagesElements of Transformational LeaderShengNo ratings yet
- Magallanes Juan Sebastián ElcanoDocument2 pagesMagallanes Juan Sebastián ElcanoLea Condalo TantaoNo ratings yet
- Transformational Leadership Theory: Thursday, March 18Th, 2010 - Comments Off - ShareDocument1 pageTransformational Leadership Theory: Thursday, March 18Th, 2010 - Comments Off - ShareLea Condalo TantaoNo ratings yet
- TransactionalDocument4 pagesTransactionalLea Condalo TantaoNo ratings yet
- Situational Leadership Theory: Thursday, February 25Th, 2010 - Comments Off - ShareDocument4 pagesSituational Leadership Theory: Thursday, February 25Th, 2010 - Comments Off - ShareLea Condalo TantaoNo ratings yet
- Volunteer BrochureDocument2 pagesVolunteer BrochureLong JosephNo ratings yet
- Single-Sex vs. Co-Ed Schools: A Study of Communication SkillsDocument44 pagesSingle-Sex vs. Co-Ed Schools: A Study of Communication SkillsShah RaiderNo ratings yet
- PsikometrikDocument20 pagesPsikometrikaidawardhananti100% (1)
- NSTP Project Proposal Group 1 La TrinidadDocument6 pagesNSTP Project Proposal Group 1 La TrinidadBlessy Garce JuanNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Students and TeachersDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Students and TeachersLucian GiscaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1578376317494Document48 pagesOrca Share Media1578376317494cHrisSa pAsCua0% (1)
- V. The Filipinization of Personality TheoryDocument28 pagesV. The Filipinization of Personality TheorylfhippocampusNo ratings yet
- Sched and CodesDocument1 pageSched and CodesCyriz Matthew MontesNo ratings yet
- Canadian Model Standards For TelepsychologyDocument3 pagesCanadian Model Standards For TelepsychologyJohn GavazziNo ratings yet
- Areas of SociologyDocument4 pagesAreas of SociologyNavasca Jhey AnnNo ratings yet
- HRM QuizDocument63 pagesHRM QuizC Rani100% (1)
- Literary Criticism About The Sea SANZ D.Document3 pagesLiterary Criticism About The Sea SANZ D.DivineFalalimpaSanzNo ratings yet
- Who Am I in The Cyber World. Digital SelfDocument24 pagesWho Am I in The Cyber World. Digital SelfAlessandra ArutaNo ratings yet
- Social Style InventoryDocument11 pagesSocial Style Inventoryapi-488799211No ratings yet
- Grace AbellaDocument5 pagesGrace AbellaAnne FenisNo ratings yet
- BASB 19 Live Session 1 ChatDocument80 pagesBASB 19 Live Session 1 Chatclonary9No ratings yet
- Counseling Psychology vs. Clinical PsychologyDocument3 pagesCounseling Psychology vs. Clinical PsychologyDivyaDeepthi18No ratings yet
- Modul PPG 2 PKB 3105topic6Document7 pagesModul PPG 2 PKB 3105topic6masitahNo ratings yet
- Fathers' Experiences in Caring For A Young Child With Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument33 pagesFathers' Experiences in Caring For A Young Child With Autism Spectrum DisorderlauraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basic ConceptsDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Basic ConceptsJericoNo ratings yet
- Prelim Physio PsychDocument28 pagesPrelim Physio PsychRM April AlonNo ratings yet
- 006 Section 5 Phase 3 - Dream Control NotesDocument19 pages006 Section 5 Phase 3 - Dream Control NotesRamovic Elvir-Beli100% (1)
- Y. Satyanarayana - Ethics-Pearson Education (2009)Document281 pagesY. Satyanarayana - Ethics-Pearson Education (2009)SADAF KHAN100% (1)
- Violence Assessment ToolDocument1 pageViolence Assessment ToolmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Howard 2020Document15 pagesHoward 2020Maggý MöllerNo ratings yet
- Social Influence NotesDocument14 pagesSocial Influence Notessukhi07100% (1)
- Helicopter Parents HomeworkDocument5 pagesHelicopter Parents Homeworkafmtfanym100% (2)
- STUDENT RESEARCH TITLE PROPOSAL FORM Google Docs 1Document3 pagesSTUDENT RESEARCH TITLE PROPOSAL FORM Google Docs 1Rosales Keian G.No ratings yet