Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Montelukast Training Manual
Montelukast Training Manual
Uploaded by
Faisal ZaheerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Montelukast Training ManualDocument24 pagesMontelukast Training ManualFaisal Zaheer100% (1)
- Asthma Management & MontelukastDocument43 pagesAsthma Management & Montelukastامتیاز ہاشم بزنجوNo ratings yet
- Natural AllergenDocument28 pagesNatural Allergengaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1Document55 pagesRespiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1ahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- Asthma 160424141552Document54 pagesAsthma 160424141552almukhtabir100% (1)
- Sams Guide 2nd Edition 2016 10Document361 pagesSams Guide 2nd Edition 2016 109s2ntk5ywpNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectCrazy about Jungles88% (32)
- Bronchial Asthma ManagementDocument55 pagesBronchial Asthma ManagementBirhanu AyenewNo ratings yet
- Agriculture PoisoningDocument30 pagesAgriculture PoisoningBhagabati BhusalNo ratings yet
- O P Poisoning AnithaDocument56 pagesO P Poisoning AnithaAnitha NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesAsthma Cheat SheetervinalisdayaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesDrugs For Disorders of The Respiratory SystemkwennybiangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological GroupsDocument96 pagesPharmacological GroupsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Asthama VireshDocument34 pagesAsthama VireshVarun MahajaniNo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCOPD Case PresentationNaresh JeengarNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medical Services Agency Lessons Learned: To: AlDocument4 pagesEmergency Medical Services Agency Lessons Learned: To: AlMega MuzdalifahNo ratings yet
- 7 - PesticidesDocument10 pages7 - Pesticidesghada.k.elsamanNo ratings yet
- Kodex LDocument48 pagesKodex Lamitdwivedi11No ratings yet
- 2.3 (Mfa) Toxic Hazards of ChemicalsDocument12 pages2.3 (Mfa) Toxic Hazards of ChemicalsTEY NuwansaraNo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument44 pagesCOPD Case PresentationNaresh JeengarNo ratings yet
- Xylene MsdsDocument11 pagesXylene Msdssheqarayzan0% (1)
- Opthalmology DrugDocument52 pagesOpthalmology Drugrayx323No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Therapy Antihistamine Oral On Rhinitis AlergiDocument7 pagesTherapy Antihistamine Oral On Rhinitis AlergiElizabeth Joan SalimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT 2 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 2 UNIT 2 PDFTanay ManeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Document63 pagesDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument107 pagesHypersensitivity ReactionsKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- ALLERGIESDocument13 pagesALLERGIESpravisankar1978No ratings yet
- Flash Cards Common MedicationDocument58 pagesFlash Cards Common MedicationJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorDocument40 pagesDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaNo ratings yet
- Opc PoisoningDocument57 pagesOpc PoisoningJanthonyNo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document21 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Sadam ArigaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology 2021Document41 pagesClinical Toxicology 2021abc aptNo ratings yet
- National Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidDocument55 pagesNational Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidMarvinGarciaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Respiratory DrugsDocument51 pagesPharmacology Respiratory DrugsAngel DamoNo ratings yet
- Rasionalitation in Anti-Asthma Drugs: Nurfatimah I.R. (030100088) Pipi Malindo H. (030100092) Deyvia Daulay (030100094)Document31 pagesRasionalitation in Anti-Asthma Drugs: Nurfatimah I.R. (030100088) Pipi Malindo H. (030100092) Deyvia Daulay (030100094)Vita DesriantiNo ratings yet
- PesticidesDocument30 pagesPesticidesahmedzohair2005No ratings yet
- Usa Safety Data Sheet: LORD Corporation 111 LORD Drive Cary, NC 27511-7923 USADocument7 pagesUsa Safety Data Sheet: LORD Corporation 111 LORD Drive Cary, NC 27511-7923 USAErnesto PadillaNo ratings yet
- Therapy Basics AsthmaDocument82 pagesTherapy Basics AsthmaShrestha BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Adult Nursing - The Final PresentationDocument70 pagesAdult Nursing - The Final Presentationក្មេងប្រុស ល្ងីល្ងើNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity: A Damage To Host Mediated by Immunity To Self or Foreign AntigenDocument54 pagesHypersensitivity: A Damage To Host Mediated by Immunity To Self or Foreign Antigenapi-19916399No ratings yet
- SDS - GP Cleaner C-Y1Document6 pagesSDS - GP Cleaner C-Y1Sophie TranNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument33 pagesPDFIvanes IgorNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Synthesis Lab Report Last OgDocument11 pagesAcetaminophen Synthesis Lab Report Last Ogandrewriberakurora15No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pharmacology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document4 pagesChapter 7 Pharmacology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Akhilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disease 2..for PrintingDocument9 pagesDrug Therapy of Respiratory Disease 2..for Printingstanleyofforbuike54No ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3 Unit 3Document20 pagesPharmacology 3 Unit 3Akshay ShindeNo ratings yet
- 20) Unit V Natural AllergensDocument32 pages20) Unit V Natural AllergensAnuj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaDocument47 pagesDrugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaNavlika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of AsthmaDocument4 pagesSymptoms of AsthmaAthina Maricar CabaseNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On Pathophysiology and Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disorders. byDocument34 pagesAn Assignment On Pathophysiology and Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disorders. byShaik ShoaibNo ratings yet
- OrganophosphatesDocument6 pagesOrganophosphatesDhruboNo ratings yet
- GRP 1 Report 1Document13 pagesGRP 1 Report 1SOFIA YVONNE ZANONo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials and Cytotoxic Drugs: DR Caroline Tetteyfio Koney 37 Military Hospital Accra Feb 2012Document58 pagesAntimicrobials and Cytotoxic Drugs: DR Caroline Tetteyfio Koney 37 Military Hospital Accra Feb 2012Fred OseiNo ratings yet
- JZ Asthma and Copd FinalDocument65 pagesJZ Asthma and Copd Finalapi-745571307No ratings yet
- Shifting Exam (Environmental Peadiatric Poisoning and Toxidromes)Document14 pagesShifting Exam (Environmental Peadiatric Poisoning and Toxidromes)GrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- ToxicDocument16 pagesToxicنوف الحربي.No ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Air and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthFrom EverandAir and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pandey Et Al 2014 The 7th Japan Korea Chemical Biology Symposium Chemical Biology of Natural Bioactive MoleculesDocument5 pagesPandey Et Al 2014 The 7th Japan Korea Chemical Biology Symposium Chemical Biology of Natural Bioactive MoleculesISHIKA GHOSH 20093No ratings yet
- Brochure SoothexDocument2 pagesBrochure SoothexRojas Evert AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Antiallergic AgentsDocument56 pagesAntiallergic AgentsTazrian FarahNo ratings yet
- Leukotriene B4Document6 pagesLeukotriene B4activnetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Clove Oil (Eugenol)Document47 pagesChapter 6-Clove Oil (Eugenol)jimmyboy111No ratings yet
- Lipids: Structure and ClassificationDocument83 pagesLipids: Structure and ClassificationGOT7 ł IGOT7 TRUSTNo ratings yet
- Genetic Factors in Drug MetabolismDocument9 pagesGenetic Factors in Drug MetabolismGloria Adetokunbo OjoNo ratings yet
- RISPDocument149 pagesRISPDessu AshagrieNo ratings yet
- AutacoidDocument28 pagesAutacoidPKay RecordsNo ratings yet
- 2 Bloktiene Actavis Montelukast DR Budhi AntariksaDocument36 pages2 Bloktiene Actavis Montelukast DR Budhi AntariksaAbd UaNo ratings yet
- H-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityDocument72 pagesH-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityShing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Boswellia Serrata, A Potential Antiinflammatory AgentDocument7 pagesBoswellia Serrata, A Potential Antiinflammatory AgentSunny GuptaNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument124 pagesAutacoidsMuhammad Modu BulamaNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Parasitology 50) - Academic Press (2001)Document275 pages(Advances in Parasitology 50) - Academic Press (2001)Stoian GoranovNo ratings yet
- Article WJPR 1513745964Document12 pagesArticle WJPR 1513745964Sivakumar LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis (OA) - CM Plex Cream Study by DR KraemerDocument9 pagesOsteoarthritis (OA) - CM Plex Cream Study by DR KraemerHisWellnessNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- Garcinol - Mini-Review - Liu Et Al - Cancer Letters 362 (2015) 8-14Document7 pagesGarcinol - Mini-Review - Liu Et Al - Cancer Letters 362 (2015) 8-14Phan Do Dang KhoaNo ratings yet
- PLT APRESFLEX Product Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPLT APRESFLEX Product Sheet PDFVic Veeraj GoyaramNo ratings yet
- Advances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchDocument243 pagesAdvances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchCarmen PopaNo ratings yet
- Insight and Control of Infectious Disease in Global Scenario - P. Roy (Intech, 2012) WWDocument454 pagesInsight and Control of Infectious Disease in Global Scenario - P. Roy (Intech, 2012) WWgoutham sivasailamNo ratings yet
- Kamatou, G. P. P., Viljoen, A. M. (2009). A Review of the Application and Pharmacological Properties of α-Bisabolol and α-Bisabolol-Rich Oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 87(1), 1–7Document7 pagesKamatou, G. P. P., Viljoen, A. M. (2009). A Review of the Application and Pharmacological Properties of α-Bisabolol and α-Bisabolol-Rich Oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 87(1), 1–7VIỆT NAM NUHANCIAMNo ratings yet
- 2010 Drug AllergyDocument78 pages2010 Drug AllergyEve Methaw100% (1)
- 411 PDFDocument9 pages411 PDFAmmar Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Bioisosterism A Rational Approach in Drug DesignDocument30 pagesBioisosterism A Rational Approach in Drug DesignFrancy FeltNo ratings yet
- Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine 20th Ed-2544-2694Document151 pagesHarrison's Principle of Internal Medicine 20th Ed-2544-2694EstellaNo ratings yet
- Ginger: A Functional Herb: January 2013Document30 pagesGinger: A Functional Herb: January 2013marutheshNo ratings yet
- EJMC1999Document1,011 pagesEJMC1999Mini MinuteNo ratings yet
- (RSC Drug Discovery Series, 26) Jeremy I Levin - Stefan Laufer - Anti-Inflammatory Drug Discovery (2012, Royal Society of Chemistry)Document545 pages(RSC Drug Discovery Series, 26) Jeremy I Levin - Stefan Laufer - Anti-Inflammatory Drug Discovery (2012, Royal Society of Chemistry)Cosmina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
Montelukast Training Manual
Montelukast Training Manual
Uploaded by
Faisal ZaheerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Montelukast Training Manual
Montelukast Training Manual
Uploaded by
Faisal ZaheerCopyright:
Available Formats
TRAINING MANUAL
AIRFLO
(MONTELUKAST SODIUM)
Qazi Faisal Zaheer
B. Pharm.
Assistant Product Manager,
Amson – Blue
CONTENTS
Preface : 02
SECTION I
Respiratory System in brief : 03
Allergy : 04
Asthma : 06
Allergic rhinitis : 07
Leukotrienes : 08
Introduction : 08
Production / synthesis : 09
Mode of action : 11
Role / effects : 11
SECTION II
Treatment Options : 12
Montelukast : 14
Brief Description : 14
Introduction : 14
Chemistry : 14
Physical Appearance : 14
Approved Indications : 15
Pharmacodynamics : 15
Action : 15
Effects : 15
Pharmacokinetics : 15
Onset of Action : 15
Absorption : 15
Distribution : 16
Metabolism : 16
Half Life : 16
Excretion : 16
Interactions : 16
Adverse effects : 17
Posology : 17
Warnings : 18
Precautions : 18
Airflo portfolio : 19
Challenge : 20
Glossary : 22
***-^-***
1
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
PREFACE
This product manual is designed for Airflo that is a newly launched product by Amson
Vaccines and Pharma (Pvt) Ltd.
This manual contains two sections. First section contains brief details of the indications of
Airflo, a slight insight into their molecular basis and the mechanisms involved in the overall
picture of these indications.
The second section covers the different treatment options for asthma and finally the
Pharmacology i.e., Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetics and other necessary information
about Airflo.
We are sure that this manual will help in easy understanding of the product.
With Best wishes for Airflo
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
SECTION I
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IN BRIEF
The human respiratory system is an
essential system of the body. It is
divided into two sections:
The upper Respiratory Tract
It consists of nostrils, Nasal Cavity,
Larynx and Pharynx.
The Lower Resp. Tract
It consists of the Trachea, the
Bronchi and the two lungs. The
bronchi divide and subdivide inside
the lungs to bronchioles which end
up in small bags like structures
known as alveoli or air sacs. They
occur in a bunch like grapes. They
are the primary site where the
exchange of CO2 and O2 occurs
between the blood and air inside the
sacs.
Lungs lie in the chest cavity which is
separated from the abdominal cavity
through a strong skeletal muscle i.e., diaphragm. Diaphragm helps in breathing.
Breathing is simply the mechanical process of movement of air into and out from lungs.
The breathing in of air into the lungs is called Inspiration and the breathing air out of the
lungs is called expiration.
Respiration is the complex chemical process that involves exchange of gases both at
alveolar level at the cellular level.
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
ALLERGY
Introduction
The word allergy is derived from the Greek word “alol”
which means “to change the original state”.
Allergies are exaggerated reactions of the immune system to
certain foreign invaders that it mistakes as a threat to the
body. With an allergy, the immune system incorrectly
identifies a harmless substance (e.g. pollen, animal dander, eggs, and milk) as
dangerous.
Allergic cascade:
This misidentification stimulates a series of events known as an allergic cascade
resulting in allergic reaction and uncomfortable allergy symptoms.
There are three basic phases of an allergic cascade:
1. The immune system first encounters a substance that it decides is threatening. In
response the body produces specific antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE). In
other words, the person becomes sensitized to the allergen.
2. The person encounters the allergen again and IgE antibodies trigger the release of
histamines and other chemicals into the bloodstream.
3. Allergy symptoms appear. They may be localized (only in the area where these
chemicals were first released) or systemic (throughout the entire body). Chemicals
released during an allergic reaction mainly affect the blood vessels, mucous glands
and bronchial tubes.
Causes:
The substances that cause allergy are collectively called allergens. These include
Pollens, Dust mites, Mold spores, Pet dander, Food, Insect stings, Medicines.
Categories:
Indoor allergies (e.g., dust, mold, dander)
Outdoor allergies (e.g., pollen, plants, sun, cold)
Food allergies
Animal allergies or insect sting allergies
Cosmetic allergies or other chemical allergies
Drug allergies (over-the-counter or prescription medications)
The most severe kind of allergic response an individual can have is anaphylaxis,
which is a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction. Symptoms include
shortness of breath, tightness in the chest, swelling (of the lips and face), vomiting,
diarrhea and lowered blood pressure.
Many types of allergens are triggers for asthma.
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Mediators and Blood cells involved in Allergy:
Cells involved:
• Mast cells
When activated, they release histamine, prostaglandin D2, Cytokines and
Leukotriene C4.
• T – Cells
They secreted cytokines after binding to B – Cells. The cytokines stimulate
the gathering of further T – Cells and macrophages to the site.
• B – Cells
They play their role in preparing antibodies against the antigens.
• Basophils
After activation, they release histamine, proteoglycans and proteolytic
enzymes. They also secrete Leukotrienes and several cytokines.
• Activated Eosinophils.
Mediators:
Following chemical substances are involved in causing symptoms of allergy:
• Histamine
• Prostaglandins
• Leukotrienes
• Proteases
• Cytokines
Affected organs and sign and symptoms:
Affected Organ Symptoms
Nose Swelling of the nasal mucosa, Allergic Rhinitis
Sinuses Allergic Sinusitis
Eyes Redness and itching of the conjunctiva,
Allergic conjunctivitis
Airways Sneezing, Bronchoconstriction, wheezing,
dyspnea, outright attacks of asthma,
anaphylaxis (severe cases)
Ears Feeling of fullness possible pain, impaired
hearing due to lack of Eustachian tube
drainage
Skin Rashes, eczema and urticaria
GIT Abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting, nausea,
hyperacidity
5
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
ASTHMA
Introduction
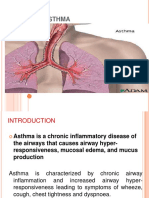
The word asthma is derived from a Greek word “aazien” means “sharp breath”. Asthma is a
clinical condition that is associated with narrowing of the airway passages and that results in
difficulty in breathing. It is a
condition that involves the
respiratory system in which there is
occasional narrowing of the airway. Asthmatic airway Normal airway
Asthma is the result of immune
response in the bronchial airways
during which there is obstruction
to the passage of air during
breathing due to sensitization to
environmental stimulants such as
smoke, dust or pollen and as a
result the airways narrow and
produce excess mucus, making it
difficult to breathe.
This obstruction to the passage of air may be due to any of the following:
1. Inflammation
Incase of inflammation, the airways get irritated, red and swollen and may
produce more mucus. Asthmatic patient will usually have some inflammation all
the time and if this condition is left untreated, the symptoms may exacerbate and
the airway becomes more sensitive which may lead to life threatening conditions.
2. Bronchoconstriction
The muscles surrounding the airway becomes more sensitized and causing the
airway to twitch and tighten i.e., narrows. Eventually it is this narrowing that
causes difficulty in breathing. Bronchoconstriction usually occurs because
the inflammation is not treated.
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Other factors that may initiate bronchoconstriction or asthma include environmental
stimulant (or allergen) such as:
cold air,
warm air,
moist air,
exercise or exertion,
Or emotional stress.
In children, the most common triggers are viral illnesses such as those that cause the
common cold.
ALLERGIC RHINITIS
Introduction
It is also known as hay fever, cause cold-like symptoms such as a runny nose, congestion,
and sneezing or sinus pressure. Unlike cold, it is not caused by a virus; instead it is caused by
an allergic response to specific substances in
environment. It may occur and worsen at a
particular time of year, initiated by tree pollen,
grasses or weeds. Sensitivity to indoor
allergens such as dust mites, cockroaches,
mold or pet dander, may also cause allergic
rhinitis that may occur any time a year.
Sign and Symptoms:
Sign and symptoms range from mild to severe.
In mild conditions, there may be brief,
infrequent episodes of a runny nose and itchy,
watery eyes. In severe states, there may be persistent, severe symptoms that last for more
than four days a week or longer than four weeks at a time. Chronic congestion may cause
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
facial pressure and pain, alter sense of taste and smell, and affect appearance. The skin under
eyes may swell and turn bluish (sometimes called allergic shiners). Symptoms usually develop
immediately after exposure to specific allergens.
Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, cockroaches, mold and pet dander.
Sometimes, exposure to irritants such as perfume and tobacco smoke can trigger or worsen
symptoms. Signs and symptoms of allergic rhinitis may include:
Runny nose
Watery eyes
Congestion
Frequent sneezing
Itchy eyes, nose, roof of mouth or throat
Swollen, blue-colored skin under the eyes (allergic shiners)
Cough
Facial pressure and pain
Allergic rhinitis can also cause:
Sleeplessness
Fatigue
Irritability
LEUKOTRIENES
Introduction
Leukotrienes are the chemical substances that belongs to Eicosanoid class of unsaturated
fatty acids. They are characterized by having 3 or 4 conjugated double bonds. Originially, the
eicosanoids are derived from essential fatty acids.
Classification
They are divided into two classes:
a) Chemoattractants; the Di-hydroxy acids (e.g. the LTB4), they attract other
chemical substances to the site of inflammation, (chemical attractants).
b) Smooth Muscle Contractants; the Cysteinyl conjugated Leukotrienes LTD4
and LTE4
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Production / Synthesis
Leukotrienes are synthesized during an allergic response.
They are synthesized from Arachidonic acid through Lipoxygenase pathway. As the name
suggests, they are mainly formed in leukocytes since the lipoxygenase pathway is active in
these cells. These also include mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, monocytes and basophils.
After stimulation, the enzyme Phospholipase A2 converts the phospholipids of the cell
membrane to Arachidonic acid.
The enzyme 5-Lipoxygenase converts the Arachidonic acid into Leukotriene A4,
which is an unstable epoxide.
The LTA4 hydrolase enzyme (found in neutrophils and monocytes) converts LTA4
into LTB4.
LTC4 synthase enzyme (found in eosinophils and mast cells) converts the LTA4 into
LTC4. LTC4 is the first of the Cysteinyl Leukotrienes.
Outside the cell, the LTC4 is gradually converted into LTD4 and then into LTE4.
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Stimulus
Membrane
Phospholipids
Phospholipase A2
Arachidonic Acid
5-Lipoxygenase
Leukotriene A4
LTA4
LTA4 hydrolase
LTB4
LTC4 synthase
LTC4
LTD4
Outside the cell
LTE4
Diagrammatic illustration of Leukotriene synthesis
10
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Mechanism of action:
These cysteinyl Leukotrienes act at CysLT1 and CysLT2 receptors on target cells to contract
bronchial and vascular smooth muscle to increase permeability of small blood vessels, and
thus enhances the secretion of mucus in the airway and gut and attract further leukocytes to
the sites of inflammation.
Role of Leukotrienes in Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis:
Leukotrienes play important role in asthma and allergic responses. The cysteinyl
Leukotrienes initiate the symptoms of asthma and allergic responses i.e.,
bronchoconstriction, edema and mucus secretion.
LTB4 is known as the promoter of Leukocyte gathering and activation and is thought to
contribute to the chronic inflammation that can occur in the asthmatic patient.
Stimulant
Phosphoplipase A2 in cell membranes
Phospholipids
COX
Prostaglandins Arachidonic Acid
5-Lipoxygenase
Symptoms of Asthma,
bronchoconstriction, edema,
Cysteinyl Leukotrienes
difficulty in breathing, allergic
rhinitis.
Diagrammatic Summary
11
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
SECTION II
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ASTHMA *
The different treatment options available for curing asthma are as follows:
1. Quick Relief Medications (QRM)
2. Medication for Allergy Induced Asthma (MAIA)
3. Long Term Control Medications (LTCM)
Drug Brief Side effects
Drugs
category description
Short acting Beta-2 Cannot prevent symptoms from
agonists, e.g. albuterol reappearing.
Oral and IV Cannot be used for long term treatment.
Corticosteroids, Causes serious side effects, including
cataracts, loss of bone mineral
Short acting, for (osteoporosis), muscle weakness, decreased
QRM
quick relief. resistance to infection, high blood pressure
and thinning of the skin.
Anticholinergics, Absorption of Ipratropium is poor and
(Muscarinic doesnot readily enter the CNS.
antagonists)
Ipratropium
Immunotherapy Not same effect in every individual, not
universal. Sensitivity to the allergen can be
lost. Risk of allergic reaction to the shot.
Life threating reactions can also occur
Focuses on
(rare).
treating allergic
MAIA
triggers of
Anti-IgE (For children over 12years of age)
asthma
monochlonal Possibility of severe reaction within two
antibodies, hours of receiving the shot, blood clotting
(Omalizumab) problems and a possible link to cancer.
Inhaled Side effects associated with inhaled
corticosteroids, corticosteroids can include hoarseness or
Usually taken on
Fluticasone , loss of voice, oral yeast infections (thrush),
daily basis for
Budesonide, and cough. Long-term use of inhaled
LTCM long time to
Triamcinolone, corticosteroids may slightly increase the risk
treat persistent
Flunisolide and of skin thinning, bruising, osteoporosis, eye
asthma
Beclomethasone pressure and cataracts. In children, inhaled
corticosteroids may slow growth.
Long Term Beta-2 These medications may increase the risk of
Agonists, severe asthma episodes and possibly death
The Bronchodilators. if a severe asthma episode occurs, (FDA,
Salmterol, Nov’ 18, 2005).
Formoterol,
12
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Cromolyn and Not same effect in every individual, not
Nedocromil universal. No effect on airway smooth
muscles and does not reverse asthmatic
bronchospasm. Only of value when taken
prophylactically.
Methylxanthines, Nervousness, insomnia, convulsions.
Theophylline, Theophylline has been successfully used in
Theobromine, suicidal attempts.
Caffiene
Leukotriene (Montelukast approved for as young as 6
modifiers, years of age)
a) LT syntesis Safe to use.
inhibitors
b)LT Antagonists
* Ref:
a) www.mayoclinic.com
b) Basic and Clinical Pharmacology by Katzung, Edition 9th, 2004.
13
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
MONTELUKAST SODIUM
INTRODUCTION:
Approved by the FDA in 1998, Montelukast is an oral therapy for asthma and allergic
rhinitis. It belongs to the sub-class Leukotriene Antagonist of class Leukotriene modifiers
which are used for Long Term Control of asthma.
Leukotriene Modifiers:-
¾ Leukotriene Synthesis Inhibitors
o Zileuton (5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor)
¾ Leukotriene Antagonists
o Zafirlukast
o Montelukast
Chemistry:
Montelukast, the molecule is
shown to the right, is a
quinoline derivative.
It is chemically described as [R-(E)]-1-[[[1-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl]phenyl]-3-[2-
(1-hydroxy-1-ethylethyl)phenyl]propyl]thio]methyl]cyclopropaneacetic acid, monosodium
salt.
Molecular weight : 608.18
Empirical Formula : C35 H35 Cl N Na O3 S
Physical appearance:
Montelukast sodium is a hygroscopic, optically active and white to off-white powder.
Montelukast sodium is freely soluble in ethanol, methanol and water and practically insoluble
in Acetonitrile.
14
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
APPROVED INDICATIONS
Montelukast is approved for use in prophylaxis and chronic treatment of Asthma in
adults and pediatric patients 12 months of age and older. It is also recommended for
relief of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults and pediatric patients 2 years
of age and older.
PHARMACOLOGY:
PHARMACODYNAMICS:
Action:
Montelukast selectively inhibits the action of Leukotriene D4, LTD4 at the
Cysteinyl Leukotriene receptor CysLT1 at the membrane of affected cells,
thereby inhibiting the release of chemical substances that lead to the
symptoms of asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Effects:
After inhibiting the Leukotrienes from binding at their receptors,
Montelukast significantly and successfully reduces the symptoms of asthma
by reducing bronchoconstriction and checking the release of fluid into the
breathing airway. That eventually results in easy and unobstructed passage of
air through the airways, giving patient comfort and relief.
PHARMACOKINETICS:
Onset of action:
After absorption, therapeutic effects of Montelukast are shown with
in 3 to 4 hours.
Absorption:
Montelukast is rapidly absorbed after oral administration and 64% of
the dose taken is absorbed into the systemic circulation. As
mentioned, the therapeutic effects are shown with in 3 to 4 hours.
15
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Distribution:
The time (Tmax) taken to reach maximum therapeutic concentration
(Cmax) changes with the dose of the drug.
Bioavailability
Dose Tmax
(%)
(mg) (hrs)
With meal In Fasting condition
4 2 - -
5 2 – 2.5 63 73
64
10 3–4 64
(not influenced by food)
Montelukast is 99% bound to plasma proteins. The average steady
state volume of distribution is 8 to 11 liters.
Half Life:
2.7 to 5.5 hours in healthy adults. Less chances of drug accumulation.
Metabolism:
Montelukast is extensively metabolized by the liver enzymatic system
CYP 450. However, Montelukast does not inhibit this enzymatic
system.
Excretion:
The plasma clearance of Montelukast averages about 45mL / min in
healthy adults. Montelukast is exclusively excreted through bile into
the feaces.
Interactions:
There are no significant drug interactions of Montelukast with
Theophylline, Warfarin, Digoxin, Terfenadine, Fexofenadine, Oral
contraceptives, Prednisolone and Prednisone.
Drugs that induce hepatic metabolism may alter the AUC of
Montelukast, like Phenobarbital and Rifampin.
16
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Adverse Effects:
They are generally mild and do not cause patients to stop taking their
medicine. The most common adverse effects are stomach pain,
stomach or intestinal upset, heartburn, tiredness, fever, stuffy nose,
cough, flu, URTI (Upper Respiratory Tract Infections), dizziness,
headache and rash. Lesser common side effects include nausea,
diarrhea and palpitation.
Posology:
In brief, Posology is the study of dosing of drugs. It refers to dosage
schedule of a drug.
15 Years and above : one 10mg tablet
6 to 14 yrs : one 5mg tablet
2 to 5 yrs : one 4mg tablet
Asthma in patients 12 months and older
Once daily in the evening. For exercise induced asthma, a single dose should
be taken 2 hours before exercise. The next dose should not be taken with in
24 hours of the last dose.
Allergic Rhinitis (AR)
Seasonal AR in patients 2 yrs and older
Perennial AR in patients 6 months and older
Once daily.
Time should be adjusted to suit patient needs.
Asthma and AR in patients 12 months and older
Patients with both Asthma and AR should take only one tablet daily in the
evening.
17
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
Warnings:
No information available.
Precautions:
Not for reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthmatic attack. Montelukast
should not be abruptly substituted for inhaled or oral corticosteroids.
Doctor should know whether the patient taking Montelukast have had a liver
disease.
Doctor should be consulted if pregnancy appears while taking Montelukast.
Patients with known aspirin sensitivity should continue avoidance of aspirin
or non-steroidal antiinflammatory agents while taking Montelukast. Although
Montelukast is effective in improving airway function in asthmatics with
documented aspirin sensitivity, it has not been shown to truncate
bronchoconstrictor response to aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-
inflammatory drugs in aspirinsensitive asthmatic patients
18
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
AIRFLO PORTFOLIO
Airflo contains Montelukast Sodium that is approved for preventing difficulty in breathing,
chest tightness, wheezing1 and coughing caused by asthma.
Montelukast (Airflo) is also used to prevent bronchospasm2 during exercise. Montelukast
(Airflo) is also used to treat the symptoms of seasonal3 and perennial4 allergic rhinitis5.
Montelukast (Airflo) is in a class of medications called Leukotriene receptor antagonists
(LTRAs).
Montelukast (Airflo) acts by inhibiting the actions of the chemical substances that cause
asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Amson is introducing Airflo in the following dosage form and strengths:
Dosage Form : Tablet
Strengths : 4mg, 5mg and 10mg
1. Wheezing: Whistle like sound during breathing
2. Bronchospasm: Constriction of trachea and bronchi, causing difficulty in breathing
3. Seasonal: Form the allergic rhinitis that happens at certain times of the year, related to season
4. Perennial: That happens to occur throughout the year
5. Allergic rhinitis: A condition associated with sneezing and stuffy, runny or itchy nose.
19
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
CHALLENGE!
Challenge 1.
Allergies are the primary cause of asthma
Challenge 2.
Asthma is not a serious problem.
Challenge 3.
Asthma can be cured
Challenge 4.
Asthma triggers can be emotional and environmental.
Challenge 5.
Asthmatic patients can easily exercise without taking medications.
Challenge 6.
Asthma can be transferred from one patient to another.
Challenge 7.
Asthma can be transferred from parents to children.
Challenge 8.
Anti – asthma medicines causes dependance.
Challenge 9.
Changing environment cures asthma.
Challenge 10.
Asthma does not require medical treatment
Challenge 11.
Asthma can reoccur.
-.-.-.-.-..*^*..-.-.-.-.-
20
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
ANSWERS
Ans1. Right
Approximately 70% of people with asthma have allergies to substances in the environment
that can be inhaled. They include pollen, mold, animal dander (dead skin flakes), house dust
mites, and cockroach droppings. Often the symptoms of asthma are caused by these
allergies.
Ans2. Wrong
Asthma is a serious problem and if not controlled, it may lead to emergency hospitalization
and even death.
Ans3. Wrong
There is no permanent remedy for asthma. It can however be controlled through the
required medical care.
Ans4. Right
Asthma can be caused by environmental factors like pollen, pollution, animal dander etc,
however emotional factors alone cannot exacerbate asthma, they contribute in asthma sign
and symptoms.
Ans5. Wrong
Although there is no restriction for asthmatic patients to exercise, equipped with proper
medications they can exercise.
Ans6. Wrong
Asthma is not transferrable from one patient to another. It is not contagious.
Ans7. Right
Asthma can be transferred from parents to children. 6% chances if neither parent has
asthma, 30% chances if one parent is asthmatic and 70%
chances if both parents are asthmatic.
Ans8. Wrong
Asthma medication do not cause any form of
dependance.
Ans9. Wrong
Changing environment can relieve symptoms
temporarily but it does not cure asthma.
Ans10. Wrong
Asthma is a serious clinical condition that does require
medical attention and proper treatment.
Ans11. Right
Asthma can reoccur at any age.
21
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
GLOSSARY
A
Alveoli (Al – we – o – li)
Plural of alveolus. Alveolus is a sac (pouch) like structure at the end of bronchiole.
Arachidonic Acid (Ara – ki – donik acid)
An unsaturated fatty acid, C20H32O2, found in animal fats, that is essential in human nutrition
and is a precursor in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins and Leukotrienes.
B
Breathing (Bre – thing)
The mechanical process of taking air into lungs (inhalation) and out of lungs (exhalation)
Bronchoconstriction (Bronko – kun – strik – shun)
Narrowing of the bronchi / trachea. Narrowing of air passages of the lungs from smooth
muscle contraction, as in asthma
Bronchospasm (Bronko – spazm)
A contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles, causing
narrowing of the lumen
Bruise (Brooz)
Injury
C
Cataract (kat – a – rakt)
Opacity of lens of the eye, causing impairment of vision or blindness
Congestion (kon – jes – shun)
The presence of an abnormal amount of fluid or blood in a part
Convulsions (kon – vul - shun)
An intense, paroxysmal, involuntary muscular contraction or a series of such contractions
[Paroxysm (par – ok – sizm) = a sharp spasm]
D
Diaphragm (diah – fram)
Skeletal muscles that separates the chest cavity from abdominal cavity and helps in breathing
Eicosanoids (eko – san – oids)
A class of compounds that are derived from poly-unsaturated essential fatty acids containing
20 Carbon atoms. (eico = 20). These include the Leukotrienes, prostaglandins, prostacyclins
22
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
E
Exacerbate (ekza – ser – bat)
Worsen
H
Hoarseness (hors – ness)
Rough quality of the voice
Hygroscopic (hi – gro – sko – pik)
That absorbs moisture from atmosphere
I
Insomnia (In – som – nia)
Inability to sleep, sleeplessness
P
Permeability (per – me – ability)
Property / ability of allowing passage or transfer of material
Prophylaxis (pro – fi – lak – sis)
Preventive treatment
R
Respiration (res – pi – ra – shun)
The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the body cells,
including breathing (inhalation and exhalation); diffusion of oxygen from alveoli to blood
and of carbon dioxide from blood to alveoli; and transport of oxygen to and carbon dioxide
from body cells.
The oxidative process occurring within living cells by which the chemical energy of organic
molecules is released in a series of metabolic steps involving the consumption of oxygen and
the liberation of carbon dioxide and water.
S
Sneezing
Sudden, reflex, noisy expiration through the nasal cavities; prominent sign in cases of rhinitis
W
Wheezing
Whistle like sound during breathing
23
AMSON VACCINES & PHARMA (PVT) LTD.
You might also like
- Montelukast Training ManualDocument24 pagesMontelukast Training ManualFaisal Zaheer100% (1)
- Asthma Management & MontelukastDocument43 pagesAsthma Management & Montelukastامتیاز ہاشم بزنجوNo ratings yet
- Natural AllergenDocument28 pagesNatural Allergengaurav saxenaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1Document55 pagesRespiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1ahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- Asthma 160424141552Document54 pagesAsthma 160424141552almukhtabir100% (1)
- Sams Guide 2nd Edition 2016 10Document361 pagesSams Guide 2nd Edition 2016 109s2ntk5ywpNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectCrazy about Jungles88% (32)
- Bronchial Asthma ManagementDocument55 pagesBronchial Asthma ManagementBirhanu AyenewNo ratings yet
- Agriculture PoisoningDocument30 pagesAgriculture PoisoningBhagabati BhusalNo ratings yet
- O P Poisoning AnithaDocument56 pagesO P Poisoning AnithaAnitha NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesAsthma Cheat SheetervinalisdayaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesDrugs For Disorders of The Respiratory SystemkwennybiangNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological GroupsDocument96 pagesPharmacological GroupsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Asthama VireshDocument34 pagesAsthama VireshVarun MahajaniNo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCOPD Case PresentationNaresh JeengarNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medical Services Agency Lessons Learned: To: AlDocument4 pagesEmergency Medical Services Agency Lessons Learned: To: AlMega MuzdalifahNo ratings yet
- 7 - PesticidesDocument10 pages7 - Pesticidesghada.k.elsamanNo ratings yet
- Kodex LDocument48 pagesKodex Lamitdwivedi11No ratings yet
- 2.3 (Mfa) Toxic Hazards of ChemicalsDocument12 pages2.3 (Mfa) Toxic Hazards of ChemicalsTEY NuwansaraNo ratings yet
- COPD Case PresentationDocument44 pagesCOPD Case PresentationNaresh JeengarNo ratings yet
- Xylene MsdsDocument11 pagesXylene Msdssheqarayzan0% (1)
- Opthalmology DrugDocument52 pagesOpthalmology Drugrayx323No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Therapy Antihistamine Oral On Rhinitis AlergiDocument7 pagesTherapy Antihistamine Oral On Rhinitis AlergiElizabeth Joan SalimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT 2 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 2 UNIT 2 PDFTanay ManeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Document63 pagesDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument107 pagesHypersensitivity ReactionsKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- ALLERGIESDocument13 pagesALLERGIESpravisankar1978No ratings yet
- Flash Cards Common MedicationDocument58 pagesFlash Cards Common MedicationJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorDocument40 pagesDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaNo ratings yet
- Opc PoisoningDocument57 pagesOpc PoisoningJanthonyNo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document21 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Sadam ArigaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Toxicology 2021Document41 pagesClinical Toxicology 2021abc aptNo ratings yet
- National Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidDocument55 pagesNational Core Manual - Chapter 5 Pesticide Hazards and First AidMarvinGarciaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Respiratory DrugsDocument51 pagesPharmacology Respiratory DrugsAngel DamoNo ratings yet
- Rasionalitation in Anti-Asthma Drugs: Nurfatimah I.R. (030100088) Pipi Malindo H. (030100092) Deyvia Daulay (030100094)Document31 pagesRasionalitation in Anti-Asthma Drugs: Nurfatimah I.R. (030100088) Pipi Malindo H. (030100092) Deyvia Daulay (030100094)Vita DesriantiNo ratings yet
- PesticidesDocument30 pagesPesticidesahmedzohair2005No ratings yet
- Usa Safety Data Sheet: LORD Corporation 111 LORD Drive Cary, NC 27511-7923 USADocument7 pagesUsa Safety Data Sheet: LORD Corporation 111 LORD Drive Cary, NC 27511-7923 USAErnesto PadillaNo ratings yet
- Therapy Basics AsthmaDocument82 pagesTherapy Basics AsthmaShrestha BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Adult Nursing - The Final PresentationDocument70 pagesAdult Nursing - The Final Presentationក្មេងប្រុស ល្ងីល្ងើNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity: A Damage To Host Mediated by Immunity To Self or Foreign AntigenDocument54 pagesHypersensitivity: A Damage To Host Mediated by Immunity To Self or Foreign Antigenapi-19916399No ratings yet
- SDS - GP Cleaner C-Y1Document6 pagesSDS - GP Cleaner C-Y1Sophie TranNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument33 pagesPDFIvanes IgorNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Synthesis Lab Report Last OgDocument11 pagesAcetaminophen Synthesis Lab Report Last Ogandrewriberakurora15No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pharmacology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document4 pagesChapter 7 Pharmacology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Akhilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disease 2..for PrintingDocument9 pagesDrug Therapy of Respiratory Disease 2..for Printingstanleyofforbuike54No ratings yet
- Pharmacology 3 Unit 3Document20 pagesPharmacology 3 Unit 3Akshay ShindeNo ratings yet
- 20) Unit V Natural AllergensDocument32 pages20) Unit V Natural AllergensAnuj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaDocument47 pagesDrugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaNavlika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of AsthmaDocument4 pagesSymptoms of AsthmaAthina Maricar CabaseNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On Pathophysiology and Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disorders. byDocument34 pagesAn Assignment On Pathophysiology and Drug Therapy of Respiratory Disorders. byShaik ShoaibNo ratings yet
- OrganophosphatesDocument6 pagesOrganophosphatesDhruboNo ratings yet
- GRP 1 Report 1Document13 pagesGRP 1 Report 1SOFIA YVONNE ZANONo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials and Cytotoxic Drugs: DR Caroline Tetteyfio Koney 37 Military Hospital Accra Feb 2012Document58 pagesAntimicrobials and Cytotoxic Drugs: DR Caroline Tetteyfio Koney 37 Military Hospital Accra Feb 2012Fred OseiNo ratings yet
- JZ Asthma and Copd FinalDocument65 pagesJZ Asthma and Copd Finalapi-745571307No ratings yet
- Shifting Exam (Environmental Peadiatric Poisoning and Toxidromes)Document14 pagesShifting Exam (Environmental Peadiatric Poisoning and Toxidromes)GrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- ToxicDocument16 pagesToxicنوف الحربي.No ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Air and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthFrom EverandAir and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pandey Et Al 2014 The 7th Japan Korea Chemical Biology Symposium Chemical Biology of Natural Bioactive MoleculesDocument5 pagesPandey Et Al 2014 The 7th Japan Korea Chemical Biology Symposium Chemical Biology of Natural Bioactive MoleculesISHIKA GHOSH 20093No ratings yet
- Brochure SoothexDocument2 pagesBrochure SoothexRojas Evert AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Antiallergic AgentsDocument56 pagesAntiallergic AgentsTazrian FarahNo ratings yet
- Leukotriene B4Document6 pagesLeukotriene B4activnetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Clove Oil (Eugenol)Document47 pagesChapter 6-Clove Oil (Eugenol)jimmyboy111No ratings yet
- Lipids: Structure and ClassificationDocument83 pagesLipids: Structure and ClassificationGOT7 ł IGOT7 TRUSTNo ratings yet
- Genetic Factors in Drug MetabolismDocument9 pagesGenetic Factors in Drug MetabolismGloria Adetokunbo OjoNo ratings yet
- RISPDocument149 pagesRISPDessu AshagrieNo ratings yet
- AutacoidDocument28 pagesAutacoidPKay RecordsNo ratings yet
- 2 Bloktiene Actavis Montelukast DR Budhi AntariksaDocument36 pages2 Bloktiene Actavis Montelukast DR Budhi AntariksaAbd UaNo ratings yet
- H-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityDocument72 pagesH-Y Yang: National Yang-Ming UniversityShing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Boswellia Serrata, A Potential Antiinflammatory AgentDocument7 pagesBoswellia Serrata, A Potential Antiinflammatory AgentSunny GuptaNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument124 pagesAutacoidsMuhammad Modu BulamaNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Parasitology 50) - Academic Press (2001)Document275 pages(Advances in Parasitology 50) - Academic Press (2001)Stoian GoranovNo ratings yet
- Article WJPR 1513745964Document12 pagesArticle WJPR 1513745964Sivakumar LakshminarayananNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis (OA) - CM Plex Cream Study by DR KraemerDocument9 pagesOsteoarthritis (OA) - CM Plex Cream Study by DR KraemerHisWellnessNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingDocument10 pagesSynthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- Garcinol - Mini-Review - Liu Et Al - Cancer Letters 362 (2015) 8-14Document7 pagesGarcinol - Mini-Review - Liu Et Al - Cancer Letters 362 (2015) 8-14Phan Do Dang KhoaNo ratings yet
- PLT APRESFLEX Product Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPLT APRESFLEX Product Sheet PDFVic Veeraj GoyaramNo ratings yet
- Advances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchDocument243 pagesAdvances in Prostaglandin, Leukotriene, and Other Bioactive Lipid ResearchCarmen PopaNo ratings yet
- Insight and Control of Infectious Disease in Global Scenario - P. Roy (Intech, 2012) WWDocument454 pagesInsight and Control of Infectious Disease in Global Scenario - P. Roy (Intech, 2012) WWgoutham sivasailamNo ratings yet
- Kamatou, G. P. P., Viljoen, A. M. (2009). A Review of the Application and Pharmacological Properties of α-Bisabolol and α-Bisabolol-Rich Oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 87(1), 1–7Document7 pagesKamatou, G. P. P., Viljoen, A. M. (2009). A Review of the Application and Pharmacological Properties of α-Bisabolol and α-Bisabolol-Rich Oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 87(1), 1–7VIỆT NAM NUHANCIAMNo ratings yet
- 2010 Drug AllergyDocument78 pages2010 Drug AllergyEve Methaw100% (1)
- 411 PDFDocument9 pages411 PDFAmmar Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Bioisosterism A Rational Approach in Drug DesignDocument30 pagesBioisosterism A Rational Approach in Drug DesignFrancy FeltNo ratings yet
- Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine 20th Ed-2544-2694Document151 pagesHarrison's Principle of Internal Medicine 20th Ed-2544-2694EstellaNo ratings yet
- Ginger: A Functional Herb: January 2013Document30 pagesGinger: A Functional Herb: January 2013marutheshNo ratings yet
- EJMC1999Document1,011 pagesEJMC1999Mini MinuteNo ratings yet
- (RSC Drug Discovery Series, 26) Jeremy I Levin - Stefan Laufer - Anti-Inflammatory Drug Discovery (2012, Royal Society of Chemistry)Document545 pages(RSC Drug Discovery Series, 26) Jeremy I Levin - Stefan Laufer - Anti-Inflammatory Drug Discovery (2012, Royal Society of Chemistry)Cosmina GeorgianaNo ratings yet

























































![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1720998242?v=1)





























