Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Uploaded by
Aaquil RaziCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Job Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankDocument1 pageJob Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankRamy100% (6)
- 7 April IG1 AnswerDocument8 pages7 April IG1 AnswerAaquil Razi100% (1)
- Checklist de NFPA 59A PDFDocument2 pagesChecklist de NFPA 59A PDFKurt StanburyNo ratings yet
- TEMA Spec SheetDocument1 pageTEMA Spec SheetvikzefgNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Risk Management 5th EditionDocument505 pagesHealth and Safety Risk Management 5th EditionAaquil Razi100% (3)
- CSE Presentation For Lead Worker Updated Aug 7 2019Document92 pagesCSE Presentation For Lead Worker Updated Aug 7 2019Engr Bilal Ali Rajput100% (3)
- JSA Confined Sapce EntryDocument1 pageJSA Confined Sapce EntryprasongNo ratings yet
- Whole Body VibrationDocument1 pageWhole Body VibrationAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsKUSNONo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsyadhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Hazard IdentificationDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Hazard IdentificationRawsht MuradyNo ratings yet
- MultimediaDocument2 pagesMultimediaarman setyawanNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsDocument2 pagesHousekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsShamel Jen FacundoNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteDocument13 pagesConfined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteWaleed MorsyNo ratings yet
- AB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBDocument19 pagesAB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBsokeara phoungNo ratings yet
- Attachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)Document10 pagesAttachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)mustaffa bakriNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Safety finalDocument16 pagesConfined Space Safety finalmyarlay17No ratings yet
- LCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFDocument10 pagesLCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFhendrawanNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument5 pagesJob Hazard AnalysisShamel Jen FacundoNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Document4 pagesJob Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Kyle Garagara-MogolNo ratings yet
- Confined Space G3Document6 pagesConfined Space G3Vench Benedict LeañoNo ratings yet
- DOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Document1 pageDOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Nuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: A Brief Guide To Working SafelyDocument7 pagesConfined Spaces: A Brief Guide To Working SafelyandidipayadnyaNo ratings yet
- Aviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsDocument20 pagesAviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsSiwaNo ratings yet
- BCFS 8.5x11 SIFpDocument2 pagesBCFS 8.5x11 SIFpiftikhar ahmadNo ratings yet
- JSA Any OprationDocument12 pagesJSA Any Oprationn.aboshhewaNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument2 pagesConfined Space EntrynoniebellNo ratings yet
- Capstan (OSRV) SOPDocument7 pagesCapstan (OSRV) SOPakbar muslimNo ratings yet
- Confined Space SafetyDocument16 pagesConfined Space Safetymyarlay17No ratings yet
- Module 01 Front-End Loader OperationDocument15 pagesModule 01 Front-End Loader Operationreda mesbahNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification PlanDocument9 pagesHazard Identification PlanLijo JohnNo ratings yet
- 02 Risk AssessmentDocument8 pages02 Risk Assessmentيوسف خضر النسورNo ratings yet
- TB TrenchDocument4 pagesTB TrenchNuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Confined Space: Mona Lestari, S.K.M., M.K.K.K. Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja, FKM UnsriDocument20 pagesConfined Space: Mona Lestari, S.K.M., M.K.K.K. Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja, FKM UnsriAprilia Nur HanisaNo ratings yet
- Confined SpaceDocument55 pagesConfined SpaceTayyab Hasnain Saadat JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Demolition 2016 VersionDocument3 pagesDemolition 2016 VersionArun Koshy AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Dangers and Hazards of Entry Into Live Substations Enclosures Barry Gass ActomDocument9 pagesDangers and Hazards of Entry Into Live Substations Enclosures Barry Gass ActomJaco BreylNo ratings yet
- Aviation Safety ReportDocument14 pagesAviation Safety ReportKrl DreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5JRyan Babiera NangkilNo ratings yet
- Confined Space AwarenessDocument49 pagesConfined Space Awarenesstejas gajelli100% (1)
- 3724.2 Anchoring - Risk AssessmentDocument3 pages3724.2 Anchoring - Risk Assessmentsawan raiNo ratings yet
- HE Vietnam Induction - Offshore HSE Induction For Contractors - ENG - April2023Document69 pagesHE Vietnam Induction - Offshore HSE Induction For Contractors - ENG - April2023Bien MLNo ratings yet
- Surgical AttireDocument10 pagesSurgical AttireNana Yaa PomaahNo ratings yet
- EPC-DUQM-Confined Space Entry-S151Document80 pagesEPC-DUQM-Confined Space Entry-S151like saddamNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument2 pagesConfined Space EntryRaymond TuazonNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Document5 pagesJob Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Madhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)Document51 pagesChapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)akhjazrNo ratings yet
- Safety - Mast ClimbingDocument78 pagesSafety - Mast ClimbingparadigmanNo ratings yet
- Clearing RADocument24 pagesClearing RAStansilous Tatenda NyagomoNo ratings yet
- Ha 41px Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesHa 41px Risk AssessmentTrần Văn ViễnNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talk 9: Critical Risks - ExcavationsDocument2 pagesToolbox Talk 9: Critical Risks - ExcavationsPravin GowardunNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis DemolishDocument4 pagesJob Hazard Analysis Demolishyajid bustomiNo ratings yet
- Power Shovel Operation: Surface Metal and Nonmetal MinesDocument16 pagesPower Shovel Operation: Surface Metal and Nonmetal MinesHowk RiosNo ratings yet
- Confined Space SafetyDocument73 pagesConfined Space Safetymagoroland88No ratings yet
- Common Office HazardsDocument2 pagesCommon Office HazardsbosesubrataNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Work and Basic Atmosphere and Gas Testing - LCM WebinarDocument100 pagesConfined Space Work and Basic Atmosphere and Gas Testing - LCM WebinararchtgozarNo ratings yet
- 05 - Hole Watch3Document21 pages05 - Hole Watch3SuadNo ratings yet
- Improvised Explosive Device Awareness - Course of ActionsDocument5 pagesImprovised Explosive Device Awareness - Course of ActionsVishal BhukoryNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Rescue Awareness PDFDocument36 pagesConfined Space Rescue Awareness PDFEr. Shamim AnsariNo ratings yet
- PR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkDocument6 pagesPR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkJuan Nacimba NacimbaNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry BahasaDocument20 pagesConfined Space Entry BahasamukhtarNo ratings yet
- Hydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingDocument1 pageHydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingSKH CultureNo ratings yet
- 8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceDocument16 pages8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 2 How Health and Safety Management Systems Work and What They Look Like2Document13 pagesELEMENT 2 How Health and Safety Management Systems Work and What They Look Like2Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Stretching Exercises: Safety TalksDocument1 pageStretching Exercises: Safety TalksAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) : WeldingDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) : WeldingAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Field Level Risk AssessmentDocument31 pagesField Level Risk AssessmentAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- CAUSATIVEDocument7 pagesCAUSATIVEAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- 2014 04 Machine Guarding All in OneDocument27 pages2014 04 Machine Guarding All in OneAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 10 Fire1Document13 pagesELEMENT 10 Fire1Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- West Nile Quick CardDocument1 pageWest Nile Quick CardAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification Checklist: Issues/Areas To ConsiderDocument3 pagesHazard Identification Checklist: Issues/Areas To ConsiderAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 9 Work Equipment1Document24 pagesELEMENT 9 Work Equipment1Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Hazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesDocument2 pagesHazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Dump Truck Tipovers DriversDocument1 pageDump Truck Tipovers DriversAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Sheet: OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens StandardDocument2 pagesSheet: OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens StandardAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Brazing: Brazing Is A Metal-Joining Process in Which Two or More Metal Items Are JoinedDocument20 pagesBrazing: Brazing Is A Metal-Joining Process in Which Two or More Metal Items Are JoinedAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope: InspectionDocument1 pageWire Rope: InspectionAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Aramco QuestionsDocument31 pagesAramco QuestionsAaquil Razi100% (2)
- Bloodborne PathogensDocument2 pagesBloodborne PathogensAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Amputation FactsheetDocument2 pagesAmputation FactsheetAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Blasting: Abrasive Blasting, More Commonly Known As Sandblasting, Is The Operation of ForciblyDocument8 pagesAbrasive Blasting: Abrasive Blasting, More Commonly Known As Sandblasting, Is The Operation of ForciblyAaquil Razi100% (1)
- Geared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8Document2 pagesGeared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8seetharaman K SNo ratings yet
- (FHWA, 2016) - Highway Performance Monitoring System, Field ManualDocument295 pages(FHWA, 2016) - Highway Performance Monitoring System, Field Manualali faresNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Drought On Pastoralism in Kajiado CountyDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Drought On Pastoralism in Kajiado Countynelson OmenyeNo ratings yet
- animaLS AND THEIR NEEDS PDFDocument4 pagesanimaLS AND THEIR NEEDS PDFsilvia2350No ratings yet
- Development of 1 Phase of Master Plan at Mormugao Port: Final Feasibility ReportDocument173 pagesDevelopment of 1 Phase of Master Plan at Mormugao Port: Final Feasibility ReportMinh TríNo ratings yet
- CellStructureSEDocument7 pagesCellStructureSEkumardarsheel65No ratings yet
- Great Hall OBI Case StudyDocument17 pagesGreat Hall OBI Case StudyChanchal SoniNo ratings yet
- Chim Chim WorkoutDocument5 pagesChim Chim Workoutretro100% (5)
- Coordinate Geometry - by TrockersDocument48 pagesCoordinate Geometry - by TrockersGracious ChiweraNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationRam1zNo ratings yet
- F5 Physics: Chapter 3: ElectricityDocument7 pagesF5 Physics: Chapter 3: ElectricityTEE LI XUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Section A: Answer Sheet: INBO - 2016 Roll NoDocument9 pagesSection A: Answer Sheet: INBO - 2016 Roll NoDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- FM Transmitter by YewlsewDocument50 pagesFM Transmitter by Yewlsewyewlsewmekonen75% (8)
- Excavadora Doosan 225 Ficha TecnicaDocument6 pagesExcavadora Doosan 225 Ficha TecnicaBruno Lionel Barriga NinaNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya Bharati Institute of Technology (A) CED Question Bank-HWRE (18CEC25) Unit-1Document12 pagesChaitanya Bharati Institute of Technology (A) CED Question Bank-HWRE (18CEC25) Unit-1AKHILA UMMANAVENANo ratings yet
- 5.4 Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocument17 pages5.4 Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- Program: Computing Project 4: Truss AnalysisDocument4 pagesProgram: Computing Project 4: Truss AnalysisshagsNo ratings yet
- PPE Risk Assessment DocumentDocument5 pagesPPE Risk Assessment DocumentFarzanaNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4waar lockNo ratings yet
- 3Document14 pages3amk2009No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingIsmael Enrique ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- Soil Spore Banks of Temperate Ferns Dyer 1992Document36 pagesSoil Spore Banks of Temperate Ferns Dyer 1992Luis PedreroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1Document152 pagesChapter 2.1Naoto MikaNo ratings yet
- Chodas Day2 BriefingDocument21 pagesChodas Day2 BriefingScribduseraccountNo ratings yet
- Quectel BC95-GV NB-IoT Specification V1.0.0 Preliminary 20211020Document3 pagesQuectel BC95-GV NB-IoT Specification V1.0.0 Preliminary 20211020Felipe MottaNo ratings yet
- Lighting FixturesDocument18 pagesLighting FixturesJuax DiestoNo ratings yet
- Genie z-60 - 34 ManualDocument34 pagesGenie z-60 - 34 ManualRussell Alan JeanneretNo ratings yet
- Acorales PDFDocument2 pagesAcorales PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Uploaded by
Aaquil RaziOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Uploaded by
Aaquil RaziCopyright:
Available Formats
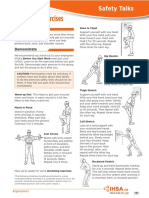
Confined IHSA’S SAFETY TALKS
48
spaces
Physical hazards
List confined spaces on site Identify controls
What can we can do to control some of the
physical hazards?
• Isolate the space by disconnecting supply and
drain lines. Lock out and tag the lines so they
won’t be reopened while you’re working inside.
• Inspect the space for dangerous contents such as
grain or sand that could slide, shift, and bury
you inside.
• Lock out any electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic
equipment that could unexpectedly rotate, drop,
Explain dangers roll, or snap shut in the space.
• Block and secure any equipment that could
In addition to dangerous atmospheres, confined
move because of gravity or stored momentum.
spaces such as tanks, vats, vessels, hoppers, and bins
can present physical hazards: • Wear safety harnesses and lifelines to make
• poor entry and exit rescue more efficient in case of an emergency.
• cramped working conditions • Develop a rescue plan for the space and practice
• temperature extremes to make sure that everyone knows what to do.
• rotating or moving equipment • Use an entry permit system. This helps identify
• reactive or corrosive residues hazards and controls, and keeps track of who is
inside.
• electrical hazards
• uncontrolled movement of liquids or solids.
Some of these hazards involve greater risk inside a
Demonstrate
confined space than outside.
Review procedures for lockout, tagging, and entry.
For example, electrical flashover can be more Discuss some of the controls shown in the diagram.
dangerous in a
cramped maintenance
hole where there’s
limited escape than in
an electrical room
with clear exits. And
fire in a confined
space can be far more
dangerous than fire in
an open work area.
You might also like
- Job Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankDocument1 pageJob Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankRamy100% (6)
- 7 April IG1 AnswerDocument8 pages7 April IG1 AnswerAaquil Razi100% (1)
- Checklist de NFPA 59A PDFDocument2 pagesChecklist de NFPA 59A PDFKurt StanburyNo ratings yet
- TEMA Spec SheetDocument1 pageTEMA Spec SheetvikzefgNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety Risk Management 5th EditionDocument505 pagesHealth and Safety Risk Management 5th EditionAaquil Razi100% (3)
- CSE Presentation For Lead Worker Updated Aug 7 2019Document92 pagesCSE Presentation For Lead Worker Updated Aug 7 2019Engr Bilal Ali Rajput100% (3)
- JSA Confined Sapce EntryDocument1 pageJSA Confined Sapce EntryprasongNo ratings yet
- Whole Body VibrationDocument1 pageWhole Body VibrationAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsKUSNONo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsyadhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Hazard IdentificationDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Hazard IdentificationRawsht MuradyNo ratings yet
- MultimediaDocument2 pagesMultimediaarman setyawanNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsDocument2 pagesHousekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsShamel Jen FacundoNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteDocument13 pagesConfined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteWaleed MorsyNo ratings yet
- AB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBDocument19 pagesAB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBsokeara phoungNo ratings yet
- Attachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)Document10 pagesAttachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)mustaffa bakriNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Safety finalDocument16 pagesConfined Space Safety finalmyarlay17No ratings yet
- LCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFDocument10 pagesLCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFhendrawanNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument5 pagesJob Hazard AnalysisShamel Jen FacundoNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Document4 pagesJob Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Kyle Garagara-MogolNo ratings yet
- Confined Space G3Document6 pagesConfined Space G3Vench Benedict LeañoNo ratings yet
- DOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Document1 pageDOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Nuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: A Brief Guide To Working SafelyDocument7 pagesConfined Spaces: A Brief Guide To Working SafelyandidipayadnyaNo ratings yet
- Aviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsDocument20 pagesAviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsSiwaNo ratings yet
- BCFS 8.5x11 SIFpDocument2 pagesBCFS 8.5x11 SIFpiftikhar ahmadNo ratings yet
- JSA Any OprationDocument12 pagesJSA Any Oprationn.aboshhewaNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument2 pagesConfined Space EntrynoniebellNo ratings yet
- Capstan (OSRV) SOPDocument7 pagesCapstan (OSRV) SOPakbar muslimNo ratings yet
- Confined Space SafetyDocument16 pagesConfined Space Safetymyarlay17No ratings yet
- Module 01 Front-End Loader OperationDocument15 pagesModule 01 Front-End Loader Operationreda mesbahNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification PlanDocument9 pagesHazard Identification PlanLijo JohnNo ratings yet
- 02 Risk AssessmentDocument8 pages02 Risk Assessmentيوسف خضر النسورNo ratings yet
- TB TrenchDocument4 pagesTB TrenchNuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Confined Space: Mona Lestari, S.K.M., M.K.K.K. Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja, FKM UnsriDocument20 pagesConfined Space: Mona Lestari, S.K.M., M.K.K.K. Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja, FKM UnsriAprilia Nur HanisaNo ratings yet
- Confined SpaceDocument55 pagesConfined SpaceTayyab Hasnain Saadat JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Demolition 2016 VersionDocument3 pagesDemolition 2016 VersionArun Koshy AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Dangers and Hazards of Entry Into Live Substations Enclosures Barry Gass ActomDocument9 pagesDangers and Hazards of Entry Into Live Substations Enclosures Barry Gass ActomJaco BreylNo ratings yet
- Aviation Safety ReportDocument14 pagesAviation Safety ReportKrl DreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5JRyan Babiera NangkilNo ratings yet
- Confined Space AwarenessDocument49 pagesConfined Space Awarenesstejas gajelli100% (1)
- 3724.2 Anchoring - Risk AssessmentDocument3 pages3724.2 Anchoring - Risk Assessmentsawan raiNo ratings yet
- HE Vietnam Induction - Offshore HSE Induction For Contractors - ENG - April2023Document69 pagesHE Vietnam Induction - Offshore HSE Induction For Contractors - ENG - April2023Bien MLNo ratings yet
- Surgical AttireDocument10 pagesSurgical AttireNana Yaa PomaahNo ratings yet
- EPC-DUQM-Confined Space Entry-S151Document80 pagesEPC-DUQM-Confined Space Entry-S151like saddamNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument2 pagesConfined Space EntryRaymond TuazonNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Document5 pagesJob Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Madhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)Document51 pagesChapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)akhjazrNo ratings yet
- Safety - Mast ClimbingDocument78 pagesSafety - Mast ClimbingparadigmanNo ratings yet
- Clearing RADocument24 pagesClearing RAStansilous Tatenda NyagomoNo ratings yet
- Ha 41px Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesHa 41px Risk AssessmentTrần Văn ViễnNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talk 9: Critical Risks - ExcavationsDocument2 pagesToolbox Talk 9: Critical Risks - ExcavationsPravin GowardunNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis DemolishDocument4 pagesJob Hazard Analysis Demolishyajid bustomiNo ratings yet
- Power Shovel Operation: Surface Metal and Nonmetal MinesDocument16 pagesPower Shovel Operation: Surface Metal and Nonmetal MinesHowk RiosNo ratings yet
- Confined Space SafetyDocument73 pagesConfined Space Safetymagoroland88No ratings yet
- Common Office HazardsDocument2 pagesCommon Office HazardsbosesubrataNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Work and Basic Atmosphere and Gas Testing - LCM WebinarDocument100 pagesConfined Space Work and Basic Atmosphere and Gas Testing - LCM WebinararchtgozarNo ratings yet
- 05 - Hole Watch3Document21 pages05 - Hole Watch3SuadNo ratings yet
- Improvised Explosive Device Awareness - Course of ActionsDocument5 pagesImprovised Explosive Device Awareness - Course of ActionsVishal BhukoryNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Rescue Awareness PDFDocument36 pagesConfined Space Rescue Awareness PDFEr. Shamim AnsariNo ratings yet
- PR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkDocument6 pagesPR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkJuan Nacimba NacimbaNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry BahasaDocument20 pagesConfined Space Entry BahasamukhtarNo ratings yet
- Hydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingDocument1 pageHydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingSKH CultureNo ratings yet
- 8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceDocument16 pages8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 2 How Health and Safety Management Systems Work and What They Look Like2Document13 pagesELEMENT 2 How Health and Safety Management Systems Work and What They Look Like2Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Stretching Exercises: Safety TalksDocument1 pageStretching Exercises: Safety TalksAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) : WeldingDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) : WeldingAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Field Level Risk AssessmentDocument31 pagesField Level Risk AssessmentAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- CAUSATIVEDocument7 pagesCAUSATIVEAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- 2014 04 Machine Guarding All in OneDocument27 pages2014 04 Machine Guarding All in OneAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 10 Fire1Document13 pagesELEMENT 10 Fire1Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- West Nile Quick CardDocument1 pageWest Nile Quick CardAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification Checklist: Issues/Areas To ConsiderDocument3 pagesHazard Identification Checklist: Issues/Areas To ConsiderAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- ELEMENT 9 Work Equipment1Document24 pagesELEMENT 9 Work Equipment1Aaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Hazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesDocument2 pagesHazard Alert: Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid in Commercial Cleaners For VehiclesAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Dump Truck Tipovers DriversDocument1 pageDump Truck Tipovers DriversAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Sheet: OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens StandardDocument2 pagesSheet: OSHA's Bloodborne Pathogens StandardAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Brazing: Brazing Is A Metal-Joining Process in Which Two or More Metal Items Are JoinedDocument20 pagesBrazing: Brazing Is A Metal-Joining Process in Which Two or More Metal Items Are JoinedAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope: InspectionDocument1 pageWire Rope: InspectionAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Aramco QuestionsDocument31 pagesAramco QuestionsAaquil Razi100% (2)
- Bloodborne PathogensDocument2 pagesBloodborne PathogensAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Amputation FactsheetDocument2 pagesAmputation FactsheetAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Blasting: Abrasive Blasting, More Commonly Known As Sandblasting, Is The Operation of ForciblyDocument8 pagesAbrasive Blasting: Abrasive Blasting, More Commonly Known As Sandblasting, Is The Operation of ForciblyAaquil Razi100% (1)
- Geared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8Document2 pagesGeared Motor Device 100/130V E1/6-T8seetharaman K SNo ratings yet
- (FHWA, 2016) - Highway Performance Monitoring System, Field ManualDocument295 pages(FHWA, 2016) - Highway Performance Monitoring System, Field Manualali faresNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Drought On Pastoralism in Kajiado CountyDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Drought On Pastoralism in Kajiado Countynelson OmenyeNo ratings yet
- animaLS AND THEIR NEEDS PDFDocument4 pagesanimaLS AND THEIR NEEDS PDFsilvia2350No ratings yet
- Development of 1 Phase of Master Plan at Mormugao Port: Final Feasibility ReportDocument173 pagesDevelopment of 1 Phase of Master Plan at Mormugao Port: Final Feasibility ReportMinh TríNo ratings yet
- CellStructureSEDocument7 pagesCellStructureSEkumardarsheel65No ratings yet
- Great Hall OBI Case StudyDocument17 pagesGreat Hall OBI Case StudyChanchal SoniNo ratings yet
- Chim Chim WorkoutDocument5 pagesChim Chim Workoutretro100% (5)
- Coordinate Geometry - by TrockersDocument48 pagesCoordinate Geometry - by TrockersGracious ChiweraNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationRam1zNo ratings yet
- F5 Physics: Chapter 3: ElectricityDocument7 pagesF5 Physics: Chapter 3: ElectricityTEE LI XUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Section A: Answer Sheet: INBO - 2016 Roll NoDocument9 pagesSection A: Answer Sheet: INBO - 2016 Roll NoDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- FM Transmitter by YewlsewDocument50 pagesFM Transmitter by Yewlsewyewlsewmekonen75% (8)
- Excavadora Doosan 225 Ficha TecnicaDocument6 pagesExcavadora Doosan 225 Ficha TecnicaBruno Lionel Barriga NinaNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya Bharati Institute of Technology (A) CED Question Bank-HWRE (18CEC25) Unit-1Document12 pagesChaitanya Bharati Institute of Technology (A) CED Question Bank-HWRE (18CEC25) Unit-1AKHILA UMMANAVENANo ratings yet
- 5.4 Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocument17 pages5.4 Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- Program: Computing Project 4: Truss AnalysisDocument4 pagesProgram: Computing Project 4: Truss AnalysisshagsNo ratings yet
- PPE Risk Assessment DocumentDocument5 pagesPPE Risk Assessment DocumentFarzanaNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4waar lockNo ratings yet
- 3Document14 pages3amk2009No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingIsmael Enrique ArciniegasNo ratings yet
- Soil Spore Banks of Temperate Ferns Dyer 1992Document36 pagesSoil Spore Banks of Temperate Ferns Dyer 1992Luis PedreroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1Document152 pagesChapter 2.1Naoto MikaNo ratings yet
- Chodas Day2 BriefingDocument21 pagesChodas Day2 BriefingScribduseraccountNo ratings yet
- Quectel BC95-GV NB-IoT Specification V1.0.0 Preliminary 20211020Document3 pagesQuectel BC95-GV NB-IoT Specification V1.0.0 Preliminary 20211020Felipe MottaNo ratings yet
- Lighting FixturesDocument18 pagesLighting FixturesJuax DiestoNo ratings yet
- Genie z-60 - 34 ManualDocument34 pagesGenie z-60 - 34 ManualRussell Alan JeanneretNo ratings yet
- Acorales PDFDocument2 pagesAcorales PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet