Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPSEC: Network Layer Security: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL (Continued)
IPSEC: Network Layer Security: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL (Continued)
Uploaded by
maher moon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesSecure Socket Layer (SSL) provides security for TCP-based applications by encrypting data transmission and allowing for authentication. It is commonly used for secure web browsing (HTTPS) and protects any application using TCP. SSL uses public key cryptography for authentication, where the server has a certificate signed by a trusted certificate authority that is validated by the client. It then establishes an encrypted session using a symmetric key to encrypt all further communication. At the network layer, IPsec uses two main protocols - Authentication Header and Encapsulating Security Payload - to provide authentication, integrity and confidentiality to IP packets through security associations and encryption. These techniques are foundational aspects of network security that are applied in various scenarios like secure email, transport layers, and
Original Description:
security leturer
Original Title
5-1-4up
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSecure Socket Layer (SSL) provides security for TCP-based applications by encrypting data transmission and allowing for authentication. It is commonly used for secure web browsing (HTTPS) and protects any application using TCP. SSL uses public key cryptography for authentication, where the server has a certificate signed by a trusted certificate authority that is validated by the client. It then establishes an encrypted session using a symmetric key to encrypt all further communication. At the network layer, IPsec uses two main protocols - Authentication Header and Encapsulating Security Payload - to provide authentication, integrity and confidentiality to IP packets through security associations and encryption. These techniques are foundational aspects of network security that are applied in various scenarios like secure email, transport layers, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesIPSEC: Network Layer Security: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL (Continued)
IPSEC: Network Layer Security: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) SSL (Continued)
Uploaded by
maher moonSecure Socket Layer (SSL) provides security for TCP-based applications by encrypting data transmission and allowing for authentication. It is commonly used for secure web browsing (HTTPS) and protects any application using TCP. SSL uses public key cryptography for authentication, where the server has a certificate signed by a trusted certificate authority that is validated by the client. It then establishes an encrypted session using a symmetric key to encrypt all further communication. At the network layer, IPsec uses two main protocols - Authentication Header and Encapsulating Security Payload - to provide authentication, integrity and confidentiality to IP packets through security associations and encryption. These techniques are foundational aspects of network security that are applied in various scenarios like secure email, transport layers, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SSL (continued)
Secure sockets layer (SSL)
Encrypted SSL session: ❒ SSL: basis of IETF
❒ Server authentication: ❒ Browser generates Transport Layer Security
❒ PGP provides security for a
SSL-enabled browser symmetric session key, (TLS) RFC 2246.
specific network app. ❍
encrypts it with server’s
includes public keys for ❒ SSL can be used for non-
❒ SSL works at transport trusted CAs. public key, sends encrypted
layer. Provides security to key to server. Web applications, e.g.,
❍ Browser requests server
any TCP-based app using IMAP.
certificate, issued by ❒ Using its private key, server
SSL services. trusted CA. decrypts session key. ❒ Client authentication can
❒ SSL: used between WWW
❍ Browser uses CA’s public ❒ Browser, server agree that be done with client
key to extract server’s future msgs will be certificates.
browsers, servers for I- public key from
commerce (shttp). certificate. encrypted.
❒ Visit your browser’s ❒ All data sent into TCP
❒ SSL security services:
security menu to see its socket (by client or server)
❍ server authentication is encrypted with session
trusted CAs.
❍ data encryption key.
❒ www.openssl.org for more
❍ client authentication
info
(optional)
7: Network Security 39 7: Network Security 40
Authentication Header (AH) Protocol
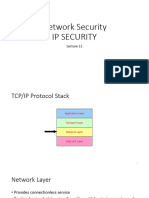
IPSEC: Network Layer Security
AH header includes:
❒ Network-layer secrecy: ❒ Provides source host
❒ RFCs 2401, 2411, 2402, 2406 authentication, data ❒ connection identifier
❍ sending host encrypts the
❒ For both AH and ESP, source, integrity, but not secrecy. ❒ authentication data: signed
data in IP datagram
destination handshake: ❒ AH header inserted message digest, calculated
❍ TCP and UDP segments;
❍ create network-layer between IP header and IP over original IP datagram,
ICMP and SNMP logical channel called a providing source
messages. data field.
(service agreement-no) authentication, data integrity.
(security agreement-no) ❒ Protocol field = 51.
❒ Network-layer authentication
❒ Next header field: specifies
security association (SA) ❒ Intermediate routers
❍ destination host can type of data (TCP, UDP, ICMP,
authenticate source IP ❒ Each SA unidirectional process datagrams as usual.
etc.)
address ❒ Uniquely determined by:
❍ security protocol (AH or
❒ Two principle protocols:
ESP)
❍ authentication header
❍ source IP address
(AH) protocol
❍ 32-bit connection ID
❍ encapsulation security
payload (ESP) protocol
7: Network Security 41 7: Network Security 42
ESP Protocol Network Security (summary)
❒ Provides secrecy, host ❒ ESP authentication Basic techniques…...
authentication, data field is similar to AH
integrity. ❒ cryptography (symmetric and public)
authentication field.
❒ Data, ESP trailer ❒ authentication
❒ Protocol = 50.
encrypted. ❒ message integrity
❒ Next header field is in ❍ message digest
ESP trailer. ❍ digital signatures
…. used in many different security scenarios
❒ secure email
❒ secure transport (SSL)
❒ IP sec
See also: firewalls , in network management
7: Network Security 43 7: Network Security 44
You might also like
- Find Username, Password & CVV Data Using Google DorksDocument5 pagesFind Username, Password & CVV Data Using Google Dorksmuna cliff100% (9)
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- Network Security Protocols: Anisha RaghuDocument53 pagesNetwork Security Protocols: Anisha RaghuMuktesh MukulNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To SSL/TLS: Providing Secure Communication Over The InternetDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To SSL/TLS: Providing Secure Communication Over The InternetVargheseMartinNo ratings yet
- DCN Unit 7Document40 pagesDCN Unit 7RazinNo ratings yet
- Chapt2-Transport Level Security-SSL, TLSDocument28 pagesChapt2-Transport Level Security-SSL, TLSsomethingNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document70 pagesUnit 4Raj PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Ipsec Ike PDFDocument26 pagesIpsec Ike PDFPushpendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec 11Document34 pagesLec 11Areeba NawazNo ratings yet
- 7 VPN Services - VLANDocument21 pages7 VPN Services - VLANNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- VPNDocument109 pagesVPNPitendra GulpadiyaNo ratings yet
- Dcs Lecture 11 - Ssl-Ipsec-WpaDocument81 pagesDcs Lecture 11 - Ssl-Ipsec-WpaRoy LovenutsNo ratings yet
- Ns 6Document35 pagesNs 6Harsha GangwaniNo ratings yet
- VPN Part-1.1Document28 pagesVPN Part-1.1RuRuele RuNo ratings yet
- Tls Wireshark PDFDocument30 pagesTls Wireshark PDFShashank PolasaNo ratings yet
- SSL TLS Decryption Uncovering SecretsDocument30 pagesSSL TLS Decryption Uncovering SecretsfanvantanNo ratings yet
- Ch17 Crypto6eDocument38 pagesCh17 Crypto6emanjunatharaddiNo ratings yet
- Network SecurityDocument49 pagesNetwork Securityhidiyah marthiyaNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer Security: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDocument66 pagesTransport Layer Security: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasPradeep KhaitanNo ratings yet
- 13344422 (1)Document52 pages13344422 (1)Rameshkumar MNo ratings yet
- Network Security 4Document64 pagesNetwork Security 4Sibghat RehmanNo ratings yet
- Transport Layer SecurityDocument49 pagesTransport Layer Securityfivie ni'mahNo ratings yet
- Internet Security: How The Internet Works and Some Basic VulnerabilitiesDocument39 pagesInternet Security: How The Internet Works and Some Basic Vulnerabilitiessalim ucarNo ratings yet
- Comptia Casp Certification: Cram GuideDocument9 pagesComptia Casp Certification: Cram GuideNuria CantosNo ratings yet
- Lec16 VpnsDocument51 pagesLec16 VpnsDr.W.Regis Anne - PSGCTNo ratings yet
- 8 - VPNDocument1 page8 - VPNDarlin DountsNo ratings yet
- An toàn hệ thốngDocument35 pagesAn toàn hệ thốngnhiNo ratings yet
- Maxq1061/Maxq1062 Deepcover Cryptographic Controller For Embedded DevicesDocument4 pagesMaxq1061/Maxq1062 Deepcover Cryptographic Controller For Embedded DevicesCarl ClarkNo ratings yet
- Ssl/TlsDocument76 pagesSsl/Tlswilde.ksnehilNo ratings yet
- MBSS - Huawei WLC - V0.1Document86 pagesMBSS - Huawei WLC - V0.1Rohit MishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ipsec: Charlie KaufmanDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Ipsec: Charlie KaufmanSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu Open VPNDocument11 pagesTài liệu Open VPNhiệu úy mô kimNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document5 pagesCH 16manjunatharaddiNo ratings yet
- CSC 526-Chapter 6-Fall 2023Document45 pagesCSC 526-Chapter 6-Fall 2023Sami Ullah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Security at The Transport Layer - Ver2Document35 pagesLecture 9 - Security at The Transport Layer - Ver2monaabdelaziz963No ratings yet
- Isec311 LCN 07Document38 pagesIsec311 LCN 07Ayan leghariNo ratings yet
- 10 Ssl-Tls PDFDocument24 pages10 Ssl-Tls PDFcnNo ratings yet
- VPN+IPsec 2Document2 pagesVPN+IPsec 2Ham DokNo ratings yet
- 6.858 Lecture 14 Ssl/Tls An D HttpsDocument10 pages6.858 Lecture 14 Ssl/Tls An D HttpsBertrand TardifNo ratings yet
- 05 Quiz-1 TopicsDocument17 pages05 Quiz-1 TopicsRAMADURGARAO PEDDIREDDYNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: CMPE 466Document38 pagesComputer Networks: CMPE 466foofoof123No ratings yet
- Week 14 SVDocument25 pagesWeek 14 SVthanhtin2109No ratings yet
- TandemDocument2 pagesTandemshanthi rajeshNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document94 pagesModule 1shreya n patelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - TLSDocument28 pagesChapter 17 - TLSnsd8681No ratings yet
- VPN Technology TPDocument2 pagesVPN Technology TPBienvenu MessanhNo ratings yet
- CCN Guest Lecture ReportDocument11 pagesCCN Guest Lecture ReportNikhil RautNo ratings yet
- Skype B2B Business ModelDocument6 pagesSkype B2B Business ModelAjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Pki Entities: Certificate Authority (CA)Document15 pagesPki Entities: Certificate Authority (CA)Arifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- T5-Web and Transport-Level SecurityDocument39 pagesT5-Web and Transport-Level SecuritySérgio SantosNo ratings yet
- Transport-Level SecurityDocument24 pagesTransport-Level SecurityRandom SanNo ratings yet
- Crug 2009 11 Digital Certificate QuickstartDocument65 pagesCrug 2009 11 Digital Certificate QuickstartÖzgür HepsağNo ratings yet
- SSL/TLS: Vitaly ShmatikovDocument77 pagesSSL/TLS: Vitaly Shmatikov19nillbarai92No ratings yet
- 7 Tcp-Ip-DnsDocument36 pages7 Tcp-Ip-DnsManaarul HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lab: Configuration of Ipsec VPN: Vpns Are Used Generally ForDocument3 pagesLab: Configuration of Ipsec VPN: Vpns Are Used Generally ForMy ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- Ip Security (Ipsec)Document18 pagesIp Security (Ipsec)gdayanand4uNo ratings yet
- OpenVPN Installation and Configuration TutorialDocument6 pagesOpenVPN Installation and Configuration Tutorialsaulparada0% (1)
- Unit 4 (Part 1)Document64 pagesUnit 4 (Part 1)Akshay UtaneNo ratings yet
- Online Security: Instructor: Prof. T. VijayethaDocument35 pagesOnline Security: Instructor: Prof. T. VijayethaShaheen MondalNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 - CDI 9Document9 pagesActivity 9 - CDI 9Melody SaipenNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security IntroductionDocument44 pagesCyber Security IntroductionShivani100% (1)
- Data Storage Security in Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesData Storage Security in Cloud ComputingZaid Khan SherwaniNo ratings yet
- Encyption From L6 DataDocument12 pagesEncyption From L6 DatahuuihsduidhuiNo ratings yet
- ISRODocument47 pagesISROPramio SarkarNo ratings yet
- Profiles - Final Draft - 2Document68 pagesProfiles - Final Draft - 2varagg24No ratings yet
- User Authentication and Single Sign On PDFDocument119 pagesUser Authentication and Single Sign On PDFravibabu1620No ratings yet
- Merging of Captcha and Graphical PasswordsDocument4 pagesMerging of Captcha and Graphical PasswordsAngel SyedNo ratings yet
- Libopenabe v1.0.0 DesignDocument30 pagesLibopenabe v1.0.0 DesignjasonwNo ratings yet
- Wpa Wpa2Document21 pagesWpa Wpa2G Siva Prakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- My WorksDocument3 pagesMy WorksLubna KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Server Security - AnswerDocument10 pagesAssignment Server Security - AnswerRyan JeeNo ratings yet
- User Manual - eKYC - EmployeesDocument12 pagesUser Manual - eKYC - EmployeesEEID ONGOLENo ratings yet
- How To Register On SIMCC Membership Development Portal For AMO 2021Document21 pagesHow To Register On SIMCC Membership Development Portal For AMO 2021Sushama JhaNo ratings yet
- Security TestingDocument7 pagesSecurity TestingGedi Chandra Mohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- 10k CorpDocument170 pages10k CorptchimbrebralNo ratings yet
- HTTPS - Secure Shell SSHDocument19 pagesHTTPS - Secure Shell SSHAdityaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Research Methods AssignmentDocument16 pagesAdvanced Research Methods AssignmentkeminalepeteryusufNo ratings yet
- 01 CP Security 101 GaiaDocument36 pages01 CP Security 101 Gaiacharlyv3No ratings yet
- EC-Council: Exam Questions 312-50v10Document6 pagesEC-Council: Exam Questions 312-50v10Ephrem AlemuNo ratings yet
- SteganographyDocument30 pagesSteganographykirangkvkit88% (8)
- Vocer HarianDocument3 pagesVocer HarianAhmad FajarNo ratings yet
- Kim Jong Jong-Il and Me. DEFCON 18 Miller CyberwarDocument85 pagesKim Jong Jong-Il and Me. DEFCON 18 Miller CyberwarChristina HorvathNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime..Document15 pagesCyber Crime..Harneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Cryptanalysis and Types of AttacksDocument3 pagesCryptanalysis and Types of AttacksSourav DebnathNo ratings yet
- Tnteu-Icssr Paper List 803Document803 pagesTnteu-Icssr Paper List 803shahidafzalsyedNo ratings yet
- Cross Interface AttackDocument26 pagesCross Interface Attackpiyush.ml20No ratings yet
- SPDH - A Secure Plain Diffie-Hellman AlgorithmDocument18 pagesSPDH - A Secure Plain Diffie-Hellman AlgorithmGábor TóthNo ratings yet
- Duckduck GoDocument7 pagesDuckduck GoDora EdmondsNo ratings yet