Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relation of Bodies of Water: Hydrology
Relation of Bodies of Water: Hydrology
Uploaded by
Andrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Relation of Bodies of Water: Hydrology
Relation of Bodies of Water: Hydrology
Uploaded by
Andrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoCopyright:
Available Formats
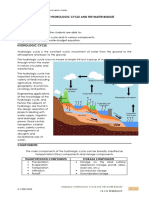
Relation of bodies of water: Hydrology
Hydrology
Surface Hydrology:
Flooding, nutrient runoff, and pollutants are a few of the effects addressed, as well as the destruction of
civil constructions such as dams. Methods of hydraulic and hydrologic design regulation are also
undertaken in this field of study, as researchers simulate the long and short-term effects of
anthropogenically manipulated surface water forms.
Isotope hydrology:
Isotopic dating involves measuring the levels of deviation in the isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen in
water. Researchers are able to determine groundwater dated as far back as the Ice Age by using these
techniques. Isotope hydrology deals with water usage policy, mapping aquifers, conservation of water
resources, and maintaining pollution levels.
Hydromorphology: is the study of the physical characteristics of bodies of water on the Earth's surface,
including river basins, channels, streams, and lakes. Water quality, levels of pollution, and biological
components needed for ecological system maintenance are a few areas assessed when classifying water
systems. Hydromorphology studies the dynamics of groundwater flow into channels, lakes, and streams.
It measures flow patterns and geometry as well as routing flows to avoid flooding or drought.
Hydrogeochemistry: Hydrogeochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to
explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the earth's crust and its oceans. .
Hydrography as it applies to the area of coastlines can be defined as ' (1) the description and study of
seas, lakes, rivers and other waters. (2) The science of locating aids and dangers to navigation. (3) The
description of physical properties of the waters of a region'. The term 'Hydrography' as it applies to the
area of reclamation can be defined as ' Scientific study of physical aspects of all waters on the Earth's
surface. Water features in 7.5-minute quads include lakes, shorelines, and drainage routing'.
Arid zone hydrology:
Arid areas lack vegetation and they are also called deserts. Arid zones are usually areas of scarce
hydrological data. Any study requires an iterative approach to be adopted to develop water resources,
with initial information often derived from other geographical regions which have similar aridity
characteristics. Arid zones present special problems to hydrologists. Describing the hydrological balance
is difficult as very little of the potential evaporation demand is satisfied. Only a small proportion of the
rainfall becomes runoff except in extreme storms. The amount of rainfall tends to be highly variable in
arid regions both in time and space. This leads to very high variability of runoff. Water, especially
groundwater, is the key to life in semi-arid and arid zones
You might also like
- Module 1.1 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument18 pagesModule 1.1 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrea Ann Arabiana Aguinaldo88% (8)
- Groundwater Exploration and Exploitation in The PhilippinesDocument17 pagesGroundwater Exploration and Exploitation in The PhilippinesMaria Gienalin100% (4)
- Technological Institute of The Philippines - Manila: DECEMBER 04, 2020Document7 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines - Manila: DECEMBER 04, 2020Andrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- S4Es-Ivb-2: Chapter 2-Water in The Environment Lesson 59: Uses of Water From The Different SourcesDocument5 pagesS4Es-Ivb-2: Chapter 2-Water in The Environment Lesson 59: Uses of Water From The Different SourcesEmily M100% (2)
- Hydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofDocument8 pagesHydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofkamdemonnNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Hydrology & Hydrologic Cycle & Watershed DefinitionDocument4 pages1-2 Hydrology & Hydrologic Cycle & Watershed Definitioncat buenafeNo ratings yet
- Ce 324 Updated LectureDocument32 pagesCe 324 Updated LectureCharles William ValentonNo ratings yet
- Ground Water HydrologyDocument24 pagesGround Water HydrologyKonda Ramesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Hydrology PDFDocument24 pagesGround Water Hydrology PDFKonda Ramesh Reddy100% (1)
- Hydrology NotesDocument26 pagesHydrology NotesJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Hydrology-2022 Page 1Document22 pagesHydrology-2022 Page 1Rhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityDocument42 pagesCourse Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityAbdisadebele BedaneNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: Outline of Hydrology Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album)Document8 pagesHydrology: Outline of Hydrology Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album)Pete BasNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lec 1Document54 pagesHydrology Lec 1christianNo ratings yet
- Environmental HydrologyDocument88 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyTigist TameneNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album) Outline of HydrologyDocument6 pagesHydrology: Hydrology (Agriculture) Hydrology (Album) Outline of HydrologyBernard PalmerNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project CIVIL ENGG.Document22 pagesFinal Year Project CIVIL ENGG.Anuj Agarwal100% (5)
- 2nd Semester NoteDocument40 pages2nd Semester NoteAbinash Mardi100% (1)
- Water Resource EngineeringDocument29 pagesWater Resource EngineeringRamesh DaundkarNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: For The Study of Agricultural Water Management, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesHydrology: For The Study of Agricultural Water Management, See - For Other Uses, SeeJeanMVillaverdeNo ratings yet
- Unit VI:: Definition of Hydrology, Oceanography and HydrosphereDocument9 pagesUnit VI:: Definition of Hydrology, Oceanography and HydrosphereSAMANTHA L. POLICARPIO100% (1)
- Use of Hydrogen Isotopes in Ground-Water StudiesDocument29 pagesUse of Hydrogen Isotopes in Ground-Water StudiesDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andDocument8 pagesHydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andMonika KshetriNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 1Document11 pagesHydrology 1Asem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hyrodology AboutDocument2 pagesHyrodology AboutHnut hinorNo ratings yet
- Introduction HydrologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction Hydrologyrustam222No ratings yet
- Intro HydrologyDocument30 pagesIntro HydrologyIvanne Fuentes EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction HydrologyDocument31 pagesIntroduction HydrologyRicoyan YanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 PresentationDocument22 pagesGroup 1 PresentationJessen DañoNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Chapter 1Document6 pagesHydrology Chapter 1Aya MusaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 01 Definition of HydrologyDocument8 pagesLESSON 01 Definition of HydrologyRio Kyla Netzy BaclaanNo ratings yet
- Water Yield From A BasinDocument2 pagesWater Yield From A BasinIrene Palawan EmpleoNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument2 pagesHydrologyJerryme FacunlaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 1Document41 pagesHydrology 1hazelanncabinianNo ratings yet
- هندسة مصادر المياهDocument442 pagesهندسة مصادر المياهTarekNo ratings yet
- Introduction HydrologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction HydrologyHaroon AbidNo ratings yet
- River Dynamics Chapter1Document14 pagesRiver Dynamics Chapter1Yuseth GomezNo ratings yet
- LimnologyDocument57 pagesLimnologyShakina TalkahNo ratings yet
- Introduction HydrologyDocument30 pagesIntroduction HydrologyMehmet AyNo ratings yet
- BCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Document29 pagesBCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Philip TibenderanaNo ratings yet
- Es Study Guide - Lesson6-Water ResourcesDocument7 pagesEs Study Guide - Lesson6-Water Resourceskirstenefr23No ratings yet
- Coastal ReservoirDocument5 pagesCoastal Reservoirhram_phdNo ratings yet
- Geochem Geophys Geosyst - 2021 - Munk - Hydrogeologic and Geochemical Distinctions in Freshwater Brine Systems of An AndeanDocument20 pagesGeochem Geophys Geosyst - 2021 - Munk - Hydrogeologic and Geochemical Distinctions in Freshwater Brine Systems of An AndeanjuanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Week 1 Day 2Document22 pagesHydrology - Week 1 Day 2Christian Millan CerezoNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Week 1 Day 3Document33 pagesHydrology - Week 1 Day 3Christian Millan CerezoNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andDocument5 pagesHydrology Is The Scientific Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality of Water On Earth andMonika KshetriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument19 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Insci Reviewer Activity 4Document9 pagesInsci Reviewer Activity 4Czarina AsisNo ratings yet
- Faculty of EngineeringDocument41 pagesFaculty of EngineeringAhmed Abdi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Environmental HydrologyDocument60 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyAbelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-4Document64 pagesLecture 1-4KshitizNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 Assessment of Water QuantityDocument6 pagesTOPIC 3 Assessment of Water QuantityJayson Paul BulosanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Hdrology: Hydrology Created By: Engr. Aline Benneth V. JacoboDocument70 pagesHydrology Hdrology: Hydrology Created By: Engr. Aline Benneth V. JacoboRafael IlaganNo ratings yet
- Hydrology-Module 1-Phase 1Document11 pagesHydrology-Module 1-Phase 1Kristine DizonNo ratings yet
- Ecohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,Document14 pagesEcohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,annisaNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument50 pagesHydrologyMuhammad HanifNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Lesson 2 PDFDocument8 pagesHydrology Lesson 2 PDFhey cuteNo ratings yet
- Hydrology - Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesHydrology - Basic ConceptsEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of HydrologyDocument8 pagesConcepts of HydrologyCamille SantosNo ratings yet
- Solute Variation in Small Watersheds of KeralaDocument11 pagesSolute Variation in Small Watersheds of KeralaDrThrivikramji KythNo ratings yet
- Floodplain Wetland Biota in the Murray-Darling Basin: Water and Habitat RequirementsFrom EverandFloodplain Wetland Biota in the Murray-Darling Basin: Water and Habitat RequirementsKerrylee RogersNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Techniques for Discharge Studies - Part 1From EverandPhysical and Chemical Techniques for Discharge Studies - Part 1RB SalamaNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Cabinet AND Wardrobe ClosetDocument23 pagesKitchen Cabinet AND Wardrobe ClosetAndrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Water ProofingDocument6 pagesWater ProofingAndrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- CE 505 Construction Method and Project ManagementDocument6 pagesCE 505 Construction Method and Project ManagementAndrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Sea: Years)Document5 pagesPhilippine Sea: Years)Andrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Sample Assignment Format SY 2020-2021-1Document4 pagesSample Assignment Format SY 2020-2021-1Andrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- PLATE 1 - AguinaldoDocument7 pagesPLATE 1 - AguinaldoAndrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Technological Institute of The Philippines ManilaDocument1 pageCivil Engineering: Technological Institute of The Philippines ManilaAndrea Ann Arabiana AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Summary of A Protocol For The Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality Guidelines (En) PDFDocument27 pagesSummary of A Protocol For The Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality Guidelines (En) PDFsamfarghNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design of TunnelDocument94 pagesPreliminary Design of TunnelJohn WT'FankNo ratings yet
- 765 65445Document31 pages765 65445Joshi DhvanitNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Managing WaterDocument282 pagesReflections On Managing WaterBalipara FoundationNo ratings yet
- Report On Reuse of Abandoned Quarries and Mine Pits in KeralaDocument90 pagesReport On Reuse of Abandoned Quarries and Mine Pits in KeralaDrThrivikramji Kyth100% (10)
- Water Balance and Water BudgetDocument17 pagesWater Balance and Water BudgetCt Kamariah Md SaatNo ratings yet
- 01Document149 pages01Hakeem DarpsNo ratings yet
- Project Information Document/ Integrated Safeguards Data Sheet (PID/ISDS)Document16 pagesProject Information Document/ Integrated Safeguards Data Sheet (PID/ISDS)Abdisalam Omar NaleyeNo ratings yet
- Construction Activity Pollution Prevention Plan - 1 Oct2023Document18 pagesConstruction Activity Pollution Prevention Plan - 1 Oct2023JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Kaleshwaram ProjectDocument4 pagesCase Study of Kaleshwaram ProjectsujithaNo ratings yet
- Ketner Et All PDFDocument132 pagesKetner Et All PDFHafiz YozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Groundwater Quality For Irrigation UseDocument5 pagesAssessment of Groundwater Quality For Irrigation UseInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nandini FinalDocument42 pagesNandini FinalRajanikanta MahatoNo ratings yet
- Mine Planning PDFDocument68 pagesMine Planning PDFDicky Affandi100% (1)
- Ra 9275Document4 pagesRa 9275Jenesa Marie DuroNo ratings yet
- China Environment Series 13: Special Issue On UrbanizationDocument110 pagesChina Environment Series 13: Special Issue On UrbanizationThe Wilson CenterNo ratings yet
- PDF Irrigation in The Mediterranean Technologies Institutions and Policies Francois Molle Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Irrigation in The Mediterranean Technologies Institutions and Policies Francois Molle Ebook Full Chaptermarielle.goudy268100% (4)
- Mahmoud 2014Document13 pagesMahmoud 2014kashemNo ratings yet
- Eckhard Worch - Drinking Water Treatment - An Introduction-De Gruyter (2019)Document324 pagesEckhard Worch - Drinking Water Treatment - An Introduction-De Gruyter (2019)Ali MohieldinNo ratings yet
- Meech Lake Association Brief 2003Document29 pagesMeech Lake Association Brief 2003Jean-Paul MurrayNo ratings yet
- Sustainable in Situ Remediation of Recalcitrant Organic Pollutants in Groundwater With Controlled Release Materials: A ReviewDocument14 pagesSustainable in Situ Remediation of Recalcitrant Organic Pollutants in Groundwater With Controlled Release Materials: A ReviewEdson MartinsNo ratings yet
- GroudwaterDocument229 pagesGroudwaterEr Jogendra SorenNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation ReportDocument17 pagesSoil Investigation Reportamit_saxena_10No ratings yet
- Water Supply & Distribution System StudyDocument187 pagesWater Supply & Distribution System StudyAang Juni PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Maria 2024 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 1293 012002Document16 pagesMaria 2024 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 1293 012002Fernando SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Epfl TH5869Document250 pagesEpfl TH5869Amandus TalloNo ratings yet
- 2nd Edition Geography Optional Paper II Pyq Topic Wise CompilationDocument55 pages2nd Edition Geography Optional Paper II Pyq Topic Wise CompilationSagar Muley0% (1)
- CEC 207 1-4-Converted (1) - 1Document13 pagesCEC 207 1-4-Converted (1) - 1Joshua OluwadamilareNo ratings yet
- Textbook Groundwater Development and Management Pradip K Sikdar Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Groundwater Development and Management Pradip K Sikdar Ebook All Chapter PDFwilliam.hoy388100% (12)