Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Myasthenia 2 Pathology
Myasthenia 2 Pathology
Uploaded by
Gokul Gopi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pagemyasthenia
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmyasthenia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageMyasthenia 2 Pathology
Myasthenia 2 Pathology
Uploaded by
Gokul Gopimyasthenia
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1
•CJ " Item: 13 of 44
Q. ld: 3809 [
IIPMark <J
Previous
[:>
Next
jf
Lab Values
~·
Notes
~
Calculator
• 3
4
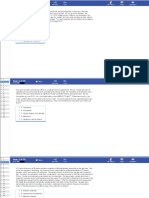
5 A 33-year-old Caucasian female comes to the office and complains of occasional diplopia and ptosis. These
6 symptoms become especially prominent w hen she looks above her head for some time. She also complains
7 of fatigue in her hands and leg muscles after exercising, such as sw imming. W hat is the level of the lesion in
8 the disease that is being described?
9
10 ~ n A. Neuromuscular junction [92%]
11 B. Nerve conduction [3%]
12
C. Muscle contraction [1 %]
14 D. Corticospinal tract [1 %]
15 ~ E . Autonomic nervous system [1 %]
16
17
18 Explanation: User ld:
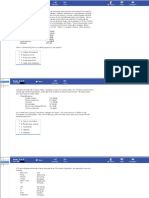
19
20 This patient's clinical presentation is suggestive of m yasthenia gravis (MG). MG is generally seen in females
21 in their second or third decade, or in males older than sixty years. The typical presentation includes fatigability
22 and w eakness of the skeletal muscles. There are no reflex, sensory or coordination abnormalities. A
23 characteristic feature is that the symptoms are typically seen on exertion and resolve w ith rest. W eakness
24 of the eye muscles can lead to diplopia and ptosis, especially on looking over one's head. Abnormal eye
25 muscle movement, w hich cannot be attributed to one nerve or muscle, may be seen on examination;
26 how ever, unlike botulism, the pupils are always spared in MG. Bulbar muscle involvement can lead to
27 "m yasthenic snarl", nasal speech, and difficulty in chew ing or swallow ing.
28
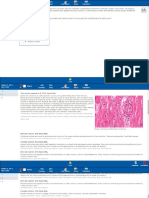
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder. The basic pathology lies at the neuromuscular junction and is
29
mediated by auto-antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor, leading to a decrease in the number of
30
available acetylcholine receptors (AchRs) at the neuromuscular junctions. The histological hallmarks include
31
decreased numbers of acetylcholine receptors, simplification of the postsynaptic clefts, and w idening of the
32
synaptic space w ith a normal presynaptic nerve terminal.
33
34 Educational objective:
35 The basic pathology in m yasthenia gravis lies at the neuromuscular junction (that's w hy it's called
36 m yasthenia) and is mediated by auto-antibodies against the acetylcholine receptor.
37
38
Time Spent: 6 seconds Copyright © UW orld Last updated: [1 2/29/2014]
39
40
You might also like
- Comprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFDocument644 pagesComprehensive Board Exam ENT PDFdrskbarla50% (2)
- Biology Investigatory Parkinson's PDFDocument16 pagesBiology Investigatory Parkinson's PDFaneesh100% (2)
- Traffic Lights Lab Using Mitsubishi PLCDocument9 pagesTraffic Lights Lab Using Mitsubishi PLCmehdi sheamusNo ratings yet
- Cranial Neuralgias: Continuumaudio Interviewavailable OnlineDocument21 pagesCranial Neuralgias: Continuumaudio Interviewavailable OnlineBryanNo ratings yet
- 3 A PDFDocument5 pages3 A PDFArash SamieiNo ratings yet
- 1 A PDFDocument51 pages1 A PDFMysheb SSNo ratings yet
- Poisoning and Environmental ExposureDocument148 pagesPoisoning and Environmental Exposurevishnu palyamNo ratings yet
- Ono Oano: / /min, /min /DL /MM'Document22 pagesOno Oano: / /min, /min /DL /MM'ايات عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- Neurology Neurology 1 PDFDocument327 pagesNeurology Neurology 1 PDFAnonymous amcA7HBENo ratings yet
- Usmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology PhysiologyDocument117 pagesUsmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology PhysiologySreeNo ratings yet
- Q PDFDocument20 pagesQ PDFMhmNo ratings yet
- 1 QDocument45 pages1 QDr.Saleem KhanNo ratings yet
- DermatologyBlock1 PDFDocument242 pagesDermatologyBlock1 PDFTed DoyleNo ratings yet
- R R R R R R: Q.LD: 2781 (Previous Ne T Lab Values Notes CalculatorDocument19 pagesR R R R R R: Q.LD: 2781 (Previous Ne T Lab Values Notes CalculatorMhmNo ratings yet
- Block 1 (17) Miscellaneous (Multisystem) QsDocument21 pagesBlock 1 (17) Miscellaneous (Multisystem) Qstomiso4475No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Patho PDFDocument623 pagesPulmonary Patho PDFNabeel Shahzad100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument479 pagesAnatomyomar aliNo ratings yet
- R R R R R: M Sod M de Bo A E Ea M Ea E G Ase Meq Meq Meq MG MG D MG DDocument5 pagesR R R R R: M Sod M de Bo A E Ea M Ea E G Ase Meq Meq Meq MG MG D MG DMhmNo ratings yet
- 030 Med CytomegalovirusDocument5 pages030 Med CytomegalovirusArun Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Poisoning and Environmental Exposure PDFDocument148 pagesPoisoning and Environmental Exposure PDFAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Johnstone Et Al 1976 LancetDocument3 pagesJohnstone Et Al 1976 LancetvaughanbellNo ratings yet
- Item:: E L E EDocument7 pagesItem:: E L E Eshahbaz HazardousNo ratings yet
- 3 QDocument4 pages3 QMhmNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryBlock 4QDocument13 pagesPsychiatryBlock 4Qboparai.navjantNo ratings yet
- Presentation Bikash PalDocument51 pagesPresentation Bikash PalSetting BhaiNo ratings yet
- Subsequences, ,, 1,1,1,, ,, 1, 1, 1Document7 pagesSubsequences, ,, 1,1,1,, ,, 1, 1, 1SONGS EVERGREEN BUDAKOTINo ratings yet
- Final Revision DGD 2017Document14 pagesFinal Revision DGD 2017farehaNo ratings yet
- Depression in Spinal Cord Injured PatientsDocument5 pagesDepression in Spinal Cord Injured Patientsgstam69No ratings yet
- Usmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology AnatomyDocument54 pagesUsmle RX Qbank 2017 Step 1 Cardiology AnatomySreeNo ratings yet
- 1 A PDFDocument83 pages1 A PDFrofi modiNo ratings yet
- IJ DOE ProjectDocument20 pagesIJ DOE ProjectInderjit JainNo ratings yet
- Aic Lec 23 Ref v01Document40 pagesAic Lec 23 Ref v01Aram ShishmanyanNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Checking SZ2, SZ3, SZ4, and SZ5: (2) Monitoring The Sensor in M-UtilityDocument1 page11.3 Checking SZ2, SZ3, SZ4, and SZ5: (2) Monitoring The Sensor in M-UtilityElvira RodNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Campion College Third FormDocument23 pagesStatistics: Campion College Third FormMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Soton ChEFT SlidesDocument48 pagesSoton ChEFT SlidesPhD LIVENo ratings yet
- Co AeDocument2 pagesCo AeDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes SensingDocument5 pagesDiabetes SensingmovirjonneNo ratings yet
- MP 3VFMAC Dip SWDocument20 pagesMP 3VFMAC Dip SWthanggimme.phanNo ratings yet
- Ith in L Ti I L in I Llitus Is Is Is Ic J in Int L Tid L LlowsDocument6 pagesIth in L Ti I L in I Llitus Is Is Is Ic J in Int L Tid L LlowsAlex ChenNo ratings yet
- 6 Es2c0 Tutorial Worksheet 6 Mosfet BiasingDocument2 pages6 Es2c0 Tutorial Worksheet 6 Mosfet BiasingNamita GeraNo ratings yet
- Project 7Document10 pagesProject 7phamtungduong0308No ratings yet
- Digital SAT Practice Test 1 MathDocument66 pagesDigital SAT Practice Test 1 MathTeerada SuepakdeeNo ratings yet
- Astm D256-10 (2010)Document10 pagesAstm D256-10 (2010)Sergio Fabian ValienteNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document4 pagesPaper 1Sweena MaryNo ratings yet
- This ECG Was Recorded From A Medical Student During A Practical Class. What Does It Show?Document2 pagesThis ECG Was Recorded From A Medical Student During A Practical Class. What Does It Show?Мичидмаа БатбаярNo ratings yet
- 123I Ioflupane Brain SPECT and 123I MIBG Cardiac.35Document8 pages123I Ioflupane Brain SPECT and 123I MIBG Cardiac.35Naif Al ShaibaniNo ratings yet
- 11 Output Analysis For A Single ModelDocument73 pages11 Output Analysis For A Single Modelsaruji_sanNo ratings yet
- PsychaitryDocument421 pagesPsychaitrylaraib emadNo ratings yet
- Dna Computing: Using Dna To Solve Computational ProblemsDocument12 pagesDna Computing: Using Dna To Solve Computational ProblemsJNo ratings yet
- Cardio Histology 3Document12 pagesCardio Histology 3Snehal JayaramNo ratings yet
- Cardio Histology 3Document12 pagesCardio Histology 3arturo quevedoNo ratings yet
- BusDocument18 pagesBusSudip SahaNo ratings yet
- Control ChartsDocument27 pagesControl Chartsreaders123No ratings yet
- Digital SAT Practice Test 1 MathDocument6 pagesDigital SAT Practice Test 1 MathmeiandlyeNo ratings yet
- Unstiffened Cylinders EN 13445-3 - 8.5.2 PDFDocument4 pagesUnstiffened Cylinders EN 13445-3 - 8.5.2 PDFfrlamontNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Objectives of Care Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationDocument8 pagesDate/Time Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis Objectives of Care Nursing Intervention Implementation EvaluationJessel YuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2bitterguardNo ratings yet
- 1 GHZ Frequency Meter Card For PCS: H. KolterDocument4 pages1 GHZ Frequency Meter Card For PCS: H. KolterAg CristianNo ratings yet
- Advanced Epilepsy Research: Multidisciplinary Approach - Sub Project 4. Progress Report 6Document39 pagesAdvanced Epilepsy Research: Multidisciplinary Approach - Sub Project 4. Progress Report 6hosur mvNo ratings yet
- CN Rexroth变量轴向柱塞泵A10VGDocument46 pagesCN Rexroth变量轴向柱塞泵A10VGcunvip163.comNo ratings yet
- Fyodor Dostoevsky and His Falling SicknessDocument7 pagesFyodor Dostoevsky and His Falling SicknessiulianaNo ratings yet
- Benign Neonatal Sleep MyoclonusDocument7 pagesBenign Neonatal Sleep Myoclonusanon_980718648No ratings yet
- Altered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsDocument17 pagesAltered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet
- Martinaud2017 - Visual Agnosia and Focal Brain InjuryDocument10 pagesMartinaud2017 - Visual Agnosia and Focal Brain InjuryErick SolisNo ratings yet
- The Science of Neuropsychiatry: Past, Present, and FutureDocument4 pagesThe Science of Neuropsychiatry: Past, Present, and FutureJuliana VargasNo ratings yet
- Hearing LossDocument4 pagesHearing LossmuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Adverse Neural Tension 2012Document7 pagesAdverse Neural Tension 2012ramesh2007-mptNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nuer1-NDCDocument1 pageTrigeminal Nuer1-NDCckzyshouNo ratings yet
- 2019 Impact Factor Is IDocument267 pages2019 Impact Factor Is IQidiw Qidiw QidiwNo ratings yet
- Subacute Combined Degeneration of Spinal CordDocument4 pagesSubacute Combined Degeneration of Spinal CordPriyanka MathurNo ratings yet
- Seizure Updated ILAE ClassificationDocument12 pagesSeizure Updated ILAE ClassificationNasheei RadjaNo ratings yet
- Animal Nervous System (Earthworm & Fish)Document18 pagesAnimal Nervous System (Earthworm & Fish)Keth LaurelNo ratings yet
- An Essay On Early Onset Alzheimer's Disease As Depicted in The Movie Still AliceDocument5 pagesAn Essay On Early Onset Alzheimer's Disease As Depicted in The Movie Still AliceMahimaNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Finals Assessment of The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNCM116 Finals Assessment of The Nervous SystemRachelle DelantarNo ratings yet
- Meniere's Disease PDFDocument6 pagesMeniere's Disease PDFjdmjdmNo ratings yet
- Essential TremorDocument17 pagesEssential TremorPame100% (1)
- Case Repoport Febriena AmaliaDocument17 pagesCase Repoport Febriena AmaliaAnastasia Widha SylvianiNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumors: Primary BTDocument5 pagesBrain Tumors: Primary BTMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Tapsa THE EARDocument4 pagesTapsa THE EARgalileeNo ratings yet
- Medical E Book TitlesApril 2017Document35 pagesMedical E Book TitlesApril 2017kevin CTNo ratings yet
- Urn - Isbn - 978 952 61 2713 2Document136 pagesUrn - Isbn - 978 952 61 2713 2dewi najiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsVasudha RohatgiNo ratings yet
- SCAT3 PocketDocument2 pagesSCAT3 PocketProfPT44No ratings yet
- MUT17 Booklet 2Document18 pagesMUT17 Booklet 2baang43farhanNo ratings yet
- Craniocerebral TraumaDocument38 pagesCraniocerebral Traumaraissazzima tvNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy For Occupational TherapyDocument10 pagesNeuroanatomy For Occupational TherapymissbxbyNo ratings yet
- دور الدمج المدرسي في تطوير اللغة الشفهية لدى الطفل المعاق سمعيا الخاضع لزراعة القوقعة PDFDocument12 pagesدور الدمج المدرسي في تطوير اللغة الشفهية لدى الطفل المعاق سمعيا الخاضع لزراعة القوقعة PDFLoulouNo ratings yet