Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer
Answer
Uploaded by
Peter AndrewOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer
Answer
Uploaded by
Peter AndrewCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry 311 Physical Chemistry
Homework Assignment # 7
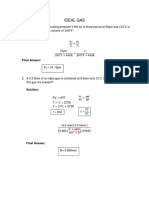
1. Prior to the discovery that Freon-12 (CF2 Cl2 ) was harmful to the Earth’s ozone layer, it was frequently
used as the dispersing agent in spray cans for hair spray, etc.. Its enthalpy of vaporization at its normal
boiling point of −29.2 ◦ C is 20.25 kJ mol−1 . Estimate the minimum pressure a can of hair spray with
Freon-12 had to withstand at 40 ◦ C, the temperature of a can that has been standing in sunlight on a mild
day. Assume that∆vap H ◦ is constant over the temperature range considered.
Answer
The vapor pressure of a liquid at its normal boiling point is equal to the atmospheric pressure (1 atm
or 1.01325 bar). Therefore, we set p1 = 1.00 atm, T1 = (273.15 − 29.2) K, T2 = (273.15 + 40) K, and
solve for p2 using the Claussius-Clapeyron equation:
µ ¶ µ ¶
p2 ∆vap H ◦ 1 1
ln = −
p1 R T1 T2
µ ¶
20250 J mol−1 1 1 1
= −
8.3145 J K mol
−1 −1 243.95 313.15 K
=2.2062
Therefore,
p2 =p1 e2.2062
=9.0811 atm.
In reality, a can has to withstand even higher pressures to provide a safety margin and to account for the
air already present in the can when it is filled with the hairspray and Freon-12.
2. The vapor pressure of pure liquid A at 300 K is 575 torr, and that of pure liquid B is 390 torr. The two
liquids form an ideal mixture in which the mole fraction of A in the liquid phase is 0.350. Calculate (a)
the total pressure of the vapor and (b) the composition of the vapor phase, assuming that no other gases
are present.
Answer
(a) Using Raoult’s Law, we get
pA =xA PA∗ = 0.350 × 575 = 201.25 torr.
pB =(1 − xA )PB∗ = 0.650 × 390 = 253.5 torr.
P =pA + pB = 454.75 torr.
(b) Using Dalton’s Law, we get the vapor composition:
pA 201.25
yA = = = 0.4426,
P 454.75
yB =1 − 0.4426 = 0.5574.
You might also like
- Physics Solutions UNITS 1-4 PDFDocument337 pagesPhysics Solutions UNITS 1-4 PDFAmogh Narvekar67% (6)
- Chem Principles 7e ISM Focus 05 Even FINALDocument62 pagesChem Principles 7e ISM Focus 05 Even FINALSelma MeloNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Separation Process 1Document86 pagesSeparation Process 1hanisshi50% (4)
- Report Phy ChemDocument4 pagesReport Phy ChemReden Jay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EFI Loan Application Form PDFDocument2 pagesEFI Loan Application Form PDFPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Tut 6 Ideal and Nonideal Solutions - SolutionsDocument19 pagesTut 6 Ideal and Nonideal Solutions - SolutionsAsma NasserNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws 1Document18 pagesGas Laws 1Minn SunnNo ratings yet
- Solutions of ExercisesDocument87 pagesSolutions of ExercisesDianiTz MendOzaNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions To Problems: 1. WaterDocument18 pagesWorked Solutions To Problems: 1. WaterGabriel Mendoza Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 1Document8 pagesExample 1jgolloberNo ratings yet
- University of Waterloo Chemistry 254: Thermodynamics Term Test 1 Friday 29 May 2009 12:30-1:20 PMDocument5 pagesUniversity of Waterloo Chemistry 254: Thermodynamics Term Test 1 Friday 29 May 2009 12:30-1:20 PMArvin DalisayNo ratings yet
- NAME: Aguilay, Christopher John C. Section: Bscoe 1-1 Solve The Following ProblemsDocument4 pagesNAME: Aguilay, Christopher John C. Section: Bscoe 1-1 Solve The Following ProblemsEbenezer RayosNo ratings yet
- 12 silberberg8eISMChapter12Document36 pages12 silberberg8eISMChapter12jonggeun0717No ratings yet
- ME2121 Thermodynamics: The Psychrometric ChartDocument4 pagesME2121 Thermodynamics: The Psychrometric ChartDesiree LinNo ratings yet
- Clausius-Clapeyron EquationDocument3 pagesClausius-Clapeyron EquationdivyanshNo ratings yet
- 5 Gases: Practice 5.1 (p.167)Document8 pages5 Gases: Practice 5.1 (p.167)Oscar TSANGNo ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 AA.Document47 pages6 - ch5 AA.mohammed alqNo ratings yet
- Take Home UASDocument10 pagesTake Home UASZariatun Suryani RizkyNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing SkillsDocument41 pagesReading and Writing SkillsFrancynn ManliguezNo ratings yet
- Isentropic ProblemsDocument5 pagesIsentropic ProblemsjecuadranteNo ratings yet
- E Rathakrishnan Gas Dynamics SolutionsDocument216 pagesE Rathakrishnan Gas Dynamics SolutionsVigneshVickey67% (15)
- Bromine Closed System Energy Balance ProblemDocument3 pagesBromine Closed System Energy Balance ProblemImi_dash9No ratings yet
- Air Mixing: (Answer 75 KG) SolutionDocument5 pagesAir Mixing: (Answer 75 KG) SolutionAldrin Lloyd BaalanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Combined Gas LawDocument3 pagesLecture Combined Gas Lawjacobambuan0805No ratings yet
- Exercise 6Document3 pagesExercise 6jay TanshiNo ratings yet
- VLEDocument20 pagesVLEIjal Jamin50% (2)
- Montessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitDocument6 pagesMontessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitAliah Jashel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Free PDF DownloadDocument25 pagesThermodynamics - Free PDF Downloadafranazeer16No ratings yet
- Thermo NotesDocument16 pagesThermo NotesjecuadranteNo ratings yet
- ESE-2018 Mains Test Series: Mechanical Engineering Test No: 12Document41 pagesESE-2018 Mains Test Series: Mechanical Engineering Test No: 12ravi kumar kumawatNo ratings yet
- CH 301 CH5 AnswersDocument4 pagesCH 301 CH5 AnswersArnav ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Example 4Document8 pagesExample 4Nazeer KhanNo ratings yet
- 311 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamicsDocument5 pages311 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamicsmozam haqNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics - Assignemt SolutionsDocument53 pagesGas Dynamics - Assignemt SolutionsSsheshan Pugazhendhi100% (1)
- Chapter 12Document10 pagesChapter 12dervis berk congerNo ratings yet
- 15.docx 1 1Document21 pages15.docx 1 1Nathan EscobalNo ratings yet
- Gas (3 Files Merged)Document76 pagesGas (3 Files Merged)Mashael 7No ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 Aa 0Document49 pages6 - ch5 Aa 0Edlyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- Module 5 L1Document11 pagesModule 5 L1varun shaNo ratings yet
- Cacl Ca: Seigfred John M. Miranda Che121.1 Laboratory 1Document5 pagesCacl Ca: Seigfred John M. Miranda Che121.1 Laboratory 1Kathleen Caryl PiedadNo ratings yet
- Relative PermeabilityDocument9 pagesRelative PermeabilityAamir AwaanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #9Document6 pagesProblem Set #9Jerome MagnoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: ELECTROLYTE: 10.1. Equilibrium Properties of ElectrolyteDocument64 pagesChapter 10: ELECTROLYTE: 10.1. Equilibrium Properties of ElectrolyteNguyễn Hoàng DũngNo ratings yet
- Boris S. Bokstein, Mikhail I. Mendelev, David J. Srolovitz Thermodynamics and Kinetics in Materials Science A Short CourseDocument8 pagesBoris S. Bokstein, Mikhail I. Mendelev, David J. Srolovitz Thermodynamics and Kinetics in Materials Science A Short CourseJuan Angel AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Tut 4 VLE of Pure Fluids - SolutionsDocument13 pagesTut 4 VLE of Pure Fluids - SolutionsAsma NasserNo ratings yet
- CHE 102 Package - Final 2010 PDFDocument29 pagesCHE 102 Package - Final 2010 PDFzain-hiraniNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument14 pagesGas Lawsמתבונן בך אלוהיםNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Theory of Elasticity by Sadhu SinghDocument7 pagesQdoc - Tips Theory of Elasticity by Sadhu Singhking royalNo ratings yet
- Sect 2 Eqns of StateDocument35 pagesSect 2 Eqns of State조기현/초빙교수/스마트소재부품공학No ratings yet
- 05 - Energy BalanceDocument28 pages05 - Energy BalanceNoman AslamNo ratings yet
- AssignmentII With AnswersDocument7 pagesAssignmentII With AnswersChetan SoamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5350 Advanced Physical Chemistry Fall Semester 2013Document2 pagesChemistry 5350 Advanced Physical Chemistry Fall Semester 2013Josef CatiggayNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 Key PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz1 Key PDFJosef CatiggayNo ratings yet
- Resolução Dos Exercícios Atkins Capt 1Document22 pagesResolução Dos Exercícios Atkins Capt 1Matheus BritoNo ratings yet
- Dummy 331Document2 pagesDummy 331MOHAMMA MUSANo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: SolutionDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: SolutionCeren DENİZNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- 03 Handbook PDFDocument1 page03 Handbook PDFPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- HwuwbwyDocument12 pagesHwuwbwyPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Completion: Raaley Memoshero Ogatis SubaldoDocument2 pagesCertificate of Completion: Raaley Memoshero Ogatis SubaldoPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- JsisnsDocument3 pagesJsisnsPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- IgtDocument2 pagesIgtPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - SugarDocument7 pagesLab Report - SugarPeter AndrewNo ratings yet
- Room Checksums: by Gulf Consult 1St-Extra Bedroom Heating Coil Peak CLG Space Peak Cooling Coil Peak TemperaturesDocument50 pagesRoom Checksums: by Gulf Consult 1St-Extra Bedroom Heating Coil Peak CLG Space Peak Cooling Coil Peak TemperaturesSajidNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 7.13: - 1/5 - 1 F, L1 L1 L1 5 - 1/5 5 - 1 - 3Document2 pagesPROBLEM 7.13: - 1/5 - 1 F, L1 L1 L1 5 - 1/5 5 - 1 - 3João Pedro CamargoNo ratings yet
- HW 14 SolutionsDocument8 pagesHW 14 SolutionsSeleneblueNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Digital MultimeterDocument2 pagesInstruction Manual: Digital MultimeterAbdalhakeem AlturkyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Experiment 5: Product Compare To Each Other?Document4 pagesLab Report: Experiment 5: Product Compare To Each Other?Ariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Physical Science: Sixth EditionDocument82 pagesConceptual Physical Science: Sixth EditionExpert TutoraNo ratings yet
- 1PX - Installation Manual Single PhaseDocument2 pages1PX - Installation Manual Single PhaseKD7 ITSolutionNo ratings yet
- Matt Visser - Traversable Wormholes: Some Simple ExamplesDocument7 pagesMatt Visser - Traversable Wormholes: Some Simple ExamplesRtpomNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Circular PipesDocument105 pagesFlow Through Circular PipesArchangel VenantNo ratings yet
- CollisionsDocument35 pagesCollisionsRaz MansorNo ratings yet
- An11001-Rev03 3l NPC TNPC TopologyDocument12 pagesAn11001-Rev03 3l NPC TNPC Topologyrambabu potluriNo ratings yet
- Halo Hook: Ammeter For Overhead Powerlines On Systems Up To 36kVDocument1 pageHalo Hook: Ammeter For Overhead Powerlines On Systems Up To 36kVsivasankarNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Examination ReferenceDocument23 pagesAppendix A: Examination ReferenceRehan hassan janjuaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1. Developing HYSYS Material Stream: 1.1. Component and Fluid List SelectionDocument7 pagesCase Study 1. Developing HYSYS Material Stream: 1.1. Component and Fluid List SelectionChakravarthy BharathNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of Electrolytes Vs Nonelectrolytes and Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument15 pagesColligative Properties of Electrolytes Vs Nonelectrolytes and Introduction To ThermodynamicsEdd VillamorNo ratings yet
- Zinc Washer Coating ExperimentDocument7 pagesZinc Washer Coating Experimentherpaderp1101No ratings yet
- Conversion of Specific Gravity To Salinity For BalDocument25 pagesConversion of Specific Gravity To Salinity For BalNaing Win TunNo ratings yet
- ST330C16Document9 pagesST330C16Bruno NevesNo ratings yet
- 7 Science 3rd Quarter Summative TestDocument2 pages7 Science 3rd Quarter Summative TestVirgen delas flores High School0% (1)
- Test-Practice On EarthingDocument3 pagesTest-Practice On EarthingShobu YarlagadaNo ratings yet
- Lean Season Analysis Report - 4.9.2023Document18 pagesLean Season Analysis Report - 4.9.2023y.wangchuk3373No ratings yet
- Application Note: Extremely Compact, Isolated Gate Driver Power Supply For Sic-Mosfet (6 - 10 W)Document5 pagesApplication Note: Extremely Compact, Isolated Gate Driver Power Supply For Sic-Mosfet (6 - 10 W)Wesley de PaulaNo ratings yet
- The MoleDocument4 pagesThe MolePirated VirusNo ratings yet
- Bifiler and Trifiler SuspensionDocument4 pagesBifiler and Trifiler Suspensionchandan_j4uNo ratings yet
- 03 Solution Assignment CEDocument28 pages03 Solution Assignment CERNo ratings yet
- v4555 PipDocument7 pagesv4555 Pipbdrepublicadominicana2020No ratings yet
- Hydronic Piping SystemsDocument2 pagesHydronic Piping SystemsNestor S. ReEyesNo ratings yet
- P Forces Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesP Forces Knowledge Organiserc.sproatNo ratings yet
- 3 Assignment SolutionDocument3 pages3 Assignment SolutionJohnson JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hw5 SolDocument12 pagesHw5 SolMISKIR TADESSENo ratings yet