Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is The Relationship Between Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
What Is The Relationship Between Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
Uploaded by
Rugen RajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is The Relationship Between Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
What Is The Relationship Between Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
Uploaded by
Rugen RajCopyright:
Available Formats
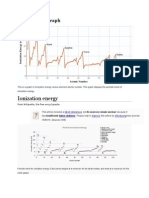
What is the relationship between atomic radius and
ionization energy?
Answer: Inversely proportional
Explanation:
Ionization energy by definition is the energy required to move an electron from a gaseous
atom (or ion)
Atomic radius is the measure of the size of an atom. (An estimate of the radius, or distance,
between the nucleus and the electron on the furthest occupied shell.
As for the atom structure, the positive nucleus is in the center, and the negatively charged
electrons are around, so the only force (relatively) acting on the electron that will affect the
ionization energy is the electrostatic force by the nucleus.
Therefore the closer the electron to the nuclear the higher the attraction force, and thus the
higher the energy required to overcome this attraction and remove the electron.
Therefore the smaller the radius the higher the ionization energy, and the bigger the radius
the lower the energy need.
What is the relationship between atomic radius
and electronegativity ?
ANSWER: Electronegativity is inversely proportional to
atomic radius
Explanation :
As we move down along a column in the periodic table the electronegativity decreases. This
implies that as the size of the atom increases the electronegativity decreases.
As we move from the left to the right across a row, the electronegativity increases. So
elements like fluorine and chlorine which lie at the extreme right, just before the noble
gases are the most electronegative.
You might also like
- Electrostatic Attraction Guided InquiryDocument2 pagesElectrostatic Attraction Guided Inquiryarg0nautNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table IIDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table IIPrinceblesed EdemNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 Lecture Note FiveDocument5 pagesCHM 111 Lecture Note Fivealfreddanladi321No ratings yet
- Atmosphere and Plasma InformationDocument3 pagesAtmosphere and Plasma Informationhashir zamanNo ratings yet
- Atomic RadiusDocument2 pagesAtomic RadiusnapilgabethNo ratings yet
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Document11 pagesAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument19 pagesPeriodic TrendsgehgehkkNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument74 pagesClassification of ElementsJimit Patel BankNo ratings yet
- 5DP Ionisation EnergiesDocument17 pages5DP Ionisation EnergiesVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- L 7-8 Periodic Variations in Atomic PropertiesDocument15 pagesL 7-8 Periodic Variations in Atomic PropertiesアゼロスレイゼルNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry - Trends in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesAP Chemistry - Trends in The Periodic Tableilias1973No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument23 pagesChemistryYehualashet BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 NotesNickNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Klmpok 3 4 Dan 5Document3 pagesTugas 1 Klmpok 3 4 Dan 5Dede DwikaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: R Is A Radius of AtomDocument7 pagesAtomic Radii: R Is A Radius of AtomGHS Chak JhumraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends Cheat Sheetjoe blowNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsDocument5 pagesAtomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartDocument31 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartKeshan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic StructureElmarNo ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument1 pageElectron AffinityPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: Ionisation EnergyDocument3 pagesPeriodicity: Ionisation EnergyFouziaNo ratings yet
- Module - Part 1Document3 pagesModule - Part 1Florence Dela Cruz DolorNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends: ElectronegativityZaara RyeenNo ratings yet
- Ed Lect 3 FinalDocument8 pagesEd Lect 3 FinalAKANKSHA GARGNo ratings yet
- Alevel Chemistry Unit 1 1.4Document2 pagesAlevel Chemistry Unit 1 1.4Ayaz Ahmed AwanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radius and Effective Nuclear ChargeDocument8 pagesAtomic Radius and Effective Nuclear ChargeKisses EldswidthNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends and The Octet RuleDocument5 pagesPeriodic Trends and The Octet Rule10chirag10No ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument3 pagesElectron AffinityAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy By: Jamica Ella D. Dela CruzDocument13 pagesPeriodic Trends: Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy By: Jamica Ella D. Dela CruzSydney HalconNo ratings yet
- What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic RadiiDocument5 pagesWhat Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic RadiiJeanisil CerenoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument11 pagesPeriodic TrendsFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity in Elements NotesDocument7 pagesPeriodicity in Elements NotesjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- Ionazation Energy GraphDocument15 pagesIonazation Energy GraphMaricel Cotanda EginaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges: What Is Atom?Document5 pagesElectric Charges: What Is Atom?Alif Rachmat RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Element and Their Property UsesDocument2 pagesElement and Their Property UsesMa Anna HiyanNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document19 pagesGroup 5KISAAKYE SIMON PETER KASOZINo ratings yet
- Atomic SizeDocument11 pagesAtomic Sizeivannambusiness2020No ratings yet
- Trends in Periodic TableDocument18 pagesTrends in Periodic TableNicole FarquharsonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument9 pagesAtoms and Moleculesalokesh1982No ratings yet
- The Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesThe Structure of MatterFull StudyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 3 Periodic TrendsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 3 Periodic Trendsaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties of The ElementsDocument13 pagesPeriodic Properties of The Elementschideraebenyi96No ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument22 pagesPeriodic TrendsVasudev M SNo ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy ClassDocument13 pagesIonisation Energy ClassKordell McShineNo ratings yet
- PeriodicityDocument6 pagesPeriodicityNetkoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties-Jorge Soriano AguilarDocument1 pagePeriodic Properties-Jorge Soriano AguilarJorge SOAGNo ratings yet
- Ionization EnergyDocument2 pagesIonization EnergynapilgabethNo ratings yet
- Group Trends of Chemical PropertiesDocument12 pagesGroup Trends of Chemical PropertiesZeeshan ul-haqNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument32 pagesAtomic StructureFatima ShahNo ratings yet
- Aether and Structure of ElectronDocument7 pagesAether and Structure of ElectrondllabarreNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 30: Energy Band DiagramDocument10 pagesModule 6: Physics of Semiconductor Devices Lecture 30: Energy Band Diagramvj.krlambaNo ratings yet
- IonizationDocument14 pagesIonizationsvirkomartinkoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryJosh ColeNo ratings yet
- Ionization Energy Trend in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesIonization Energy Trend in The Periodic TableOluwabamire OreoluwaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicityakeemoluwadamilare623No ratings yet
- Periodic Properties ConceptsDocument4 pagesPeriodic Properties ConceptsMuhammad Hafizan GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties Copy 2Document30 pagesPeriodic Properties Copy 2Rodayna HosniNo ratings yet
- The Photoelectric Effect (Notes)Document10 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect (Notes)Chathumi LelwalaNo ratings yet