Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Boiler and Auxiliaries
Boiler and Auxiliaries
Uploaded by
Rc Tuppal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageThe document discusses boiler losses, including flue gas losses, unburned fuel loss, and radiant heat losses. Flue gas losses are one of the major energy losses from the boiler as heat is contained in the flue gas discharged from air heaters up the stack. Too much cooling of flue gas can cause condensation of water and acid in the air heater, leading to corrosion damage. Flue gas losses consist of dry flue gas loss and moisture losses.
Original Description:
Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses boiler losses, including flue gas losses, unburned fuel loss, and radiant heat losses. Flue gas losses are one of the major energy losses from the boiler as heat is contained in the flue gas discharged from air heaters up the stack. Too much cooling of flue gas can cause condensation of water and acid in the air heater, leading to corrosion damage. Flue gas losses consist of dry flue gas loss and moisture losses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageBoiler and Auxiliaries
Boiler and Auxiliaries
Uploaded by
Rc TuppalThe document discusses boiler losses, including flue gas losses, unburned fuel loss, and radiant heat losses. Flue gas losses are one of the major energy losses from the boiler as heat is contained in the flue gas discharged from air heaters up the stack. Too much cooling of flue gas can cause condensation of water and acid in the air heater, leading to corrosion damage. Flue gas losses consist of dry flue gas loss and moisture losses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
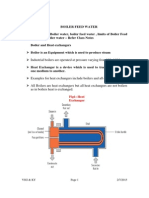
BOILER AND AUXILIARIES
Operational Theory and Limiting Factors
a.) Boiler Losses
Any heat energy not transferred to the water and steam represents a boiler
loss. The major energy losses in a coal-fired boiler are flue gas losses, unburned fuel
loss, and radiant heat losses.
1. Flue Gas Losses
a. One of the major energy losses associated with the operation of the
boiler is the heat contained in the flue gas discharged from the air
heaters and eventually lost up the stack.
b. Too much cooling of flue gas may result to condensation of water
and acid on the flue gas side of the air heater because of the water
vapor and sulfur oxides (H2O + SOx = H2SO4 - Sulfuric Acid). This
leads to corrosion damage of ductwork and downstream
components (i.e., ESPs, ID Fans) and/or plugging of the air heater.
c. Flue Gas Losses, also referred to as Stack Losses, consist of the Dry
Flue Gas Loss and Moister Losses.
d.
You might also like
- 2 Long Term OverheatingDocument17 pages2 Long Term OverheatingWalter RuedaNo ratings yet
- Heat Losses in BoilersDocument5 pagesHeat Losses in Boilersgad480100% (1)
- Sulfur - Sulfuric Acid IndustryDocument18 pagesSulfur - Sulfuric Acid IndustryS S S REDDY50% (2)
- Elements in Power Plant and Industrial Plant EngineeringDocument19 pagesElements in Power Plant and Industrial Plant EngineeringRc Tuppal75% (8)
- Failures in Boiler TubesDocument15 pagesFailures in Boiler Tubesniraj_hwb100% (2)
- Gases in Steam: Material Btu/hr-Ft2 - °f/inDocument5 pagesGases in Steam: Material Btu/hr-Ft2 - °f/inaliNo ratings yet
- Volume Increases 1,600 Times.: Furnace Boiler ProperDocument17 pagesVolume Increases 1,600 Times.: Furnace Boiler ProperAyush DeoreNo ratings yet
- 3 Strategies For Reducing Cement KilnDocument14 pages3 Strategies For Reducing Cement Kilnorientanjali7066100% (1)
- High Temperature Corrosion Problems in Waste Heat BoilersDocument2 pagesHigh Temperature Corrosion Problems in Waste Heat BoilersEdenrafaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Factors Promote Corrosion in Steam PlantDocument16 pages4 - Factors Promote Corrosion in Steam PlantMohammed AlSaleh100% (4)
- Preservation PlantDocument17 pagesPreservation PlantSanjeevi Kumar SpNo ratings yet
- High Pressure BoilersDocument27 pagesHigh Pressure BoilersAaryaveerNo ratings yet
- 5 Steam Boiler FeedwaterDocument16 pages5 Steam Boiler FeedwaterCristhian Garcia Villarroel100% (1)
- Guia para Preservar Una Caldera AcuotubularDocument6 pagesGuia para Preservar Una Caldera Acuotubularjuan joseNo ratings yet
- Takoradi Thermal Power Station: HRSG Boiler Chemistry TrainingDocument75 pagesTakoradi Thermal Power Station: HRSG Boiler Chemistry TrainingAfia Mireku100% (2)
- Preservation of Boiler During Idle PeriodDocument4 pagesPreservation of Boiler During Idle PeriodSachin PatelNo ratings yet
- Scale Formation in Reheating FurnaceDocument7 pagesScale Formation in Reheating FurnaceDeepti ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Water Chemistry: Korba Simulator 339Document12 pagesBoiler Water Chemistry: Korba Simulator 339Rakesh Kiran100% (2)
- The Soot and Scale Problems: IssueDocument12 pagesThe Soot and Scale Problems: IssuebjaabdouNo ratings yet
- Report On Corrosion Resistant of Boiler Tubes by Different CoatingsDocument94 pagesReport On Corrosion Resistant of Boiler Tubes by Different Coatingsshakeel360No ratings yet
- Waterside Scaling Deposition and Corrosion in Steam Generators PDFDocument19 pagesWaterside Scaling Deposition and Corrosion in Steam Generators PDFking1qNo ratings yet
- Reducing Corrosion and Potential Boiler Failure With Superior Iron Transport TechnologyDocument46 pagesReducing Corrosion and Potential Boiler Failure With Superior Iron Transport TechnologymnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Scaling, Corrosion and Water Treatment On Steam Generator Systems 30 BarDocument17 pagesScaling, Corrosion and Water Treatment On Steam Generator Systems 30 BarAvinawNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Aspects of Boiler Tube FailureDocument17 pagesMetallurgical Aspects of Boiler Tube FailureAshwani Dogra100% (1)
- Condensate Corrosion in Steam Generating Systems (51300-98718-Sg)Document40 pagesCondensate Corrosion in Steam Generating Systems (51300-98718-Sg)abdallah.hammodNo ratings yet
- Q A BoilerDocument19 pagesQ A Boilerlavpandey8719No ratings yet
- Deaerating Boiler FeedwaterDocument4 pagesDeaerating Boiler Feedwaterritesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feedwater: A. DeaerationDocument11 pagesBoiler Feedwater: A. DeaerationRaja TNo ratings yet
- Steam-System Water Preparation - Chemical Engineering - Page 1Document6 pagesSteam-System Water Preparation - Chemical Engineering - Page 1Rahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Constraints of Slag FormationDocument4 pagesThermodynamic Constraints of Slag FormationPinNo ratings yet
- Transient Thermal Stress Analysis of BOF Hood Failure: Technicalarticle-Peer-ReviewedDocument9 pagesTransient Thermal Stress Analysis of BOF Hood Failure: Technicalarticle-Peer-ReviewedEzequiel RuggieroNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Boiler: Fireside Fouling and CorrosionDocument5 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Boiler: Fireside Fouling and CorrosionFrancisco 777No ratings yet
- Anselmo Report No.8Document6 pagesAnselmo Report No.8Vince PatricioNo ratings yet
- Drmpfile 1Document10 pagesDrmpfile 1ramadoss_alwar7307No ratings yet
- Crying Up and Down A SmileDocument8 pagesCrying Up and Down A SmileMr SinghNo ratings yet
- Penthouse Spring 1998Document2 pagesPenthouse Spring 1998John M. CavoteNo ratings yet
- Soot & ScaleDocument12 pagesSoot & ScaleLow Shen WeiNo ratings yet
- Failure of Heat Exchanger in Sulphur Recovery Unit PDFDocument8 pagesFailure of Heat Exchanger in Sulphur Recovery Unit PDFticaram rNo ratings yet
- Boiler QuestionsDocument39 pagesBoiler Questionssk3146100% (11)
- Boiler Water TreatmentDocument13 pagesBoiler Water TreatmentAisyah M YahyaNo ratings yet
- Ill Effects of Water in Steam GenerationDocument15 pagesIll Effects of Water in Steam GenerationCHARITHANo ratings yet
- Boiler Corrosion PDFDocument12 pagesBoiler Corrosion PDFWasif MalikNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2Document23 pagesKuliah 2Maritsya Dita Kurnia PutriNo ratings yet
- Acid Dewpoint CorrosionDocument1 pageAcid Dewpoint CorrosionNandaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Boiler and Steam Condensate CorrosionDocument3 pagesMechanism of Boiler and Steam Condensate CorrosionMutasim Hasan MehranNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2Document24 pagesKuliah 2Novia ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tube Leakage: Analysis, Symptoms, CausesDocument33 pagesBoiler Tube Leakage: Analysis, Symptoms, Causeshmaza shakeel100% (1)
- Boiler Water TreatmentDocument4 pagesBoiler Water TreatmentgovimanoNo ratings yet
- Water Technology-2Document16 pagesWater Technology-2Anjan Prasad100% (1)
- Boiler Tube LeakagesDocument33 pagesBoiler Tube LeakagesVIBHAV0% (1)
- Investigation of Repeated Economiser TubDocument9 pagesInvestigation of Repeated Economiser TubAamir malikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Water TreatmentDocument9 pagesChapter 2: Water TreatmentRavi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 76 500cDocument4 pages76 500cImam BukhoriNo ratings yet
- Boiler TroublesDocument9 pagesBoiler TroublesMadhavanIce50% (2)
- Metallurgical Industry 12.5-1 10/86: (Reformatted 1/95)Document3 pagesMetallurgical Industry 12.5-1 10/86: (Reformatted 1/95)rmuhumuzaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Purification of IronDocument8 pagesChemistry Project: Purification of IronShivam JaggiNo ratings yet
- The Steam and Feedwater SystemDocument5 pagesThe Steam and Feedwater SystemROYALNEWSSNo ratings yet
- Root Causes of Boiler FailureDocument5 pagesRoot Causes of Boiler Failuredineshkbunker08No ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Masinloc Power Facility Fire Pump Flow Test: Technical Summary ReportDocument8 pagesMasinloc Power Facility Fire Pump Flow Test: Technical Summary ReportRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- The Script - Cycle IsolationDocument2 pagesThe Script - Cycle IsolationRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Optimization of Coal Blend Proportions For Sustained Improvements in Generation & Efficiency PDFDocument23 pagesPaper 2 Optimization of Coal Blend Proportions For Sustained Improvements in Generation & Efficiency PDFRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- Effect of Coal Moisture On Denitration Efficiency and Boiler EconomyDocument7 pagesEffect of Coal Moisture On Denitration Efficiency and Boiler EconomyRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- What HOW Where (Applications) When Advantages LimitationsDocument4 pagesWhat HOW Where (Applications) When Advantages LimitationsRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Plant Engineering Elements ReviewDocument4 pagesIndustrial Plant Engineering Elements ReviewRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- Machine Design ElementsDocument16 pagesMachine Design ElementsRc TuppalNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Dynamics - SuspensionsDocument18 pagesVehicle Dynamics - SuspensionsRc TuppalNo ratings yet