Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
Uploaded by
Faiyaz AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DeloitteDocument40 pagesDeloittemohamedNo ratings yet
- Web Focus TrainingDocument26 pagesWeb Focus TrainingRajasekhar MudadlaNo ratings yet
- 100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsDocument6 pages100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Data Models Using InfoSetsDocument2 pagesData Models Using InfoSetsMani KandanNo ratings yet
- ConnectivityDocument1 pageConnectivityMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Working Procedure of Sap BW/ Bi Testting: This Paper CoversDocument1 pageWorking Procedure of Sap BW/ Bi Testting: This Paper CoversMani KandanNo ratings yet
- BEx Query ExecutionDocument18 pagesBEx Query ExecutionMani Kandan100% (1)
- ADSO Scenario DescriptionDocument11 pagesADSO Scenario DescriptionMani Kandan0% (1)
- SD & MM TablesDocument5 pagesSD & MM TablesMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Optimization: Administration PerformanceDocument7 pagesOptimization: Administration PerformanceMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Production Support - in My Current Engagement Main TwoDocument2 pagesProduction Support - in My Current Engagement Main TwoMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Lo UpdateDocument4 pagesLo UpdateMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Logistic CockpitDocument6 pagesLogistic CockpitMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalDocument58 pagesOptimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Pps Unit-4 FunctionsDocument47 pagesPps Unit-4 FunctionsVickey MylcatNo ratings yet
- Capacity Building and Change Management Program For The Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (CBCMP)Document12 pagesCapacity Building and Change Management Program For The Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (CBCMP)International Executive Service CorpsNo ratings yet
- Install and Configuration Computer System Session Plan 1Document5 pagesInstall and Configuration Computer System Session Plan 1Reninio100% (3)
- Report PrototypeDocument103 pagesReport PrototypeJaimali PathakNo ratings yet
- Primary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsDocument4 pagesPrimary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsKnjigescribdNo ratings yet
- Detonado Dragon Quest VIII PDF: Mirror Link #1Document4 pagesDetonado Dragon Quest VIII PDF: Mirror Link #1AllysonWaine0% (1)
- Python Jinja TutorialDocument10 pagesPython Jinja TutorialSuraj Kamal ShaikNo ratings yet
- CloudReady Installation InstructionsDocument13 pagesCloudReady Installation Instructionsabhijeet834uNo ratings yet
- MR5.14.10 Release Note Version CDocument86 pagesMR5.14.10 Release Note Version CChristian KranzNo ratings yet
- Creating An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) With AWS Cloud FormationDocument18 pagesCreating An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) With AWS Cloud Formationgoyal_86964227No ratings yet
- CV - Luis TariDocument3 pagesCV - Luis TariHenry Satria PutraNo ratings yet
- Network Security Monitoring ProcedureDocument3 pagesNetwork Security Monitoring ProcedureGhislain MurenziNo ratings yet
- Self Defending NetworksDocument17 pagesSelf Defending Networkssarthak_ganguly100% (1)
- Dynamic Pricing Model For EV Charging-Discharging Service Based On Cloud Computing SchedulingDocument20 pagesDynamic Pricing Model For EV Charging-Discharging Service Based On Cloud Computing Schedulingunmec12No ratings yet
- Aveva PdmsDocument33 pagesAveva PdmsSri Surya LankapalliNo ratings yet
- Addictive Drums ManualDocument28 pagesAddictive Drums Manualspine66No ratings yet
- Electronic Disclosures and Signatures ConsentDocument2 pagesElectronic Disclosures and Signatures Consentjdaniel.hrNo ratings yet
- A Uhf Rfid Measurement and Evaluation Test System2659Document7 pagesA Uhf Rfid Measurement and Evaluation Test System2659mano012No ratings yet
- Linux ForYou - Oct 2008Document116 pagesLinux ForYou - Oct 2008Santhosh Mahankali100% (1)
- MAPPING DRIVES PowerPoint PresentationDocument6 pagesMAPPING DRIVES PowerPoint PresentationDave MilnerNo ratings yet
- Embedded Hardware DesignDocument16 pagesEmbedded Hardware DesignAbhay SharmaNo ratings yet
- SCRUM WikipediaDocument9 pagesSCRUM WikipediaikedrinNo ratings yet
- PytestDocument122 pagesPytestdeepavali123No ratings yet
- SCM ImpDocument88 pagesSCM ImpKiran GandlaNo ratings yet
- We Can Insert or Delete Nodes We Can't Insert or Delete A NodeDocument5 pagesWe Can Insert or Delete Nodes We Can't Insert or Delete A Nodeprakash reddyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A Laboratory Information Management System at LRHDocument7 pagesImplementation of A Laboratory Information Management System at LRHUdara Senarathne100% (1)
- Measurement Reports ExportDocument25 pagesMeasurement Reports ExportKhắc Biên NgôNo ratings yet
- Advanced MMIS Design Characteristics of APR1400: Yeong Cheol SHIN, Hak Young CHUNG, Tae Young SONGDocument9 pagesAdvanced MMIS Design Characteristics of APR1400: Yeong Cheol SHIN, Hak Young CHUNG, Tae Young SONGelsayedNo ratings yet
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
Uploaded by
Faiyaz AhmedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
ABAP Data Dictionary Interview Questions SAP ABAP
Uploaded by
Faiyaz AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
ABAP Data dictionary interview questions @ SAP ABAPSAP ABAP ABAP tutorials,
notes, ebooksHome About Subscribe to Feed ABAP Data dictionary
interview questions Posted in May 17, 2009 ¬ 5:27 pmh.
CINTHIA NAZNEEN
Q. What’s the full form of ECC?
Ans: Enterprice Central Component.
Q. What’s the full form of IDES?
Ans: Internet Demonstration and Evaluation System.
Q. What’s ABAP dictionary and its role in SAP?
Ans: ABAP dictionary is the central information base for the developers.
This manages all definitions(metadata) required for different applications in SAP.
ABAP dictionary is completely integrated into ABAP development workbench.
All other component of ABAP development workbench can access the
data definitions(meta data) stored in the data dictionary.
Role: ABAP data dictionary supports definition of user-defined types
(data elements, structures, table types). structure of database objects
(tables, indexes and views) can also be defined.
These user-defined types/objects are then automatically created in the
underlying relational database using the above data definitions.
The ABAP dictionary also provides tools for editing screen fields
(e.g., for assigning a field an input help i.e. F4 help).
Data dictionary ensures data integrity, consistency and security.
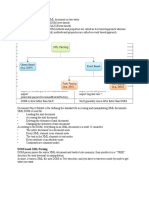
Q. What are the main object types of ABAP dictionary?
Ans: The object types of ABAP dictionary can be of following type:
Tables: Tables are defined in the ABAP Dictionary independently of the database.
A table having the same structure is then created from this table definition
in the underlying database.
Views: are logical views on more than one table.
The structure of the view is defined in the ABAP Dictionary.
A view on the database can then be created from this structure.
Types (elements, structures, table types):
Types are created in ABAP programs.
The structure of a type can be defined globally in ABAP programs.
Changes to a type automatically take effect in all the programs using the type.
Lock objects:are used to synchronize access to the same data by more than
one user.
Function modules that can be used in application programs are
generated from the definition of a lock object in the ABAP Dictionary.
Domains:
Different fields having the same technical type can be combined
in domains.
Domain defines the value range of all table fields and
structure components that refer to this domain.
Data element:
The ABAP Dictionary also contains the information displayed with
the F1 and F4 help for a field in an input template. The
documentation about the field is created for a data element.
Input help: The list of possible input values that appears
for the input help is created by a foreign key or a search help.
Q. Note on SAP tables(defining through ABAP dictionary).
Ans: Tables are defined independently of the database in ABAP dictionary.
The fields of the table are defined with their (Database-independent)
data types and lengths. Using the table definitions stored in the
ABAP dictionary, a table is automatically created in the physical
database(when the table is activated).
Q. What are the components of a table definition.
Ans: Table fields: For table fields, field names and data types are
defined.
Foreign keys: Relationship between the table and the
other tables are defined. Technical settings: Data class and
size category defines that what type of table to be created
and how much space required.
Indexes: Secondary indexes are
created for a table for faster data selection. Again following are defined for a
table fields: Field name can be of maximum 16 characters in a table and must start
with a letter. Key flag determines if a field should be the table key. Field type
depicts the data type of the field in the ABAP dictionary. Field length denotes the
number of valid places in the field. Decimal places Number of places after decimal
point for float type value. Short text describes the business meaning of the field.
Also fields from other structures can be added to the table definition as include.
Q. How data Type, field Length and short Text of any field is assigned? Ans: i.
Data type, field length (and if necessary decimal places) short text can be
directly assigned to a field in the table definition. ii. Data element can be
assigned to a field so that data type, field length (and decimal places) are
automatically determined from the domain of the data element. The short description
of the data element is then assigned to the field as a short text.
Q. What are the assignment options to the field?
Ans:
i. Direct assignment of data types, field length, short text to a field.
ii. Data element assignment to a field.
iii. An input check(check table) for a field can be defined with a foreign key.
iv. A search help can be assigned to a field.
v. Reference field or reference table must be specified for a table
field that holds currency or quantity type value.
Q. What’s reference table and reference field?
Ans: Reference table is specified for fields containing
quantities(data type QUAN) or currency(Data type CURR).
This reference table must contain a field with the format
for the currency key (data type CUKY) or unit of measure
(data type UNIT). This field is called the reference
field of the output field. The reference field can also
reside in the table itself. E.g.: TAB1 contains the
field PRICE which holds price values. Field UNIT
contains currency key for PRICE. So,TAB1 is the reference
table for field PRICE and UNIT is the reference field for
field PRICE.
Q. What’s table include?
Ans: In addition to listing the individual fields in
a table or structure, fields from another structure
can be included as includes.
Q. What’s named include?
Ans: If an include is added to define a database table
or database structure, a name can be assigned to that
included (included substructure). The group of fields
of that include can be addressed as a whole in ABAP
application programs with a group name which is called
as named include. E.g.:We can access field of a table/
structure in the ABAP application program in the
following manner:
<TABLE / STRUCTURE NAME > - < FIELD NAME> <TABLE / STRUCTURE NAME >
- <GROUP NAME>-<FIELD NAME> <TABLE / STRUCTURE NAME > - <GROUP NAME>
Q. Give an example of nested include.
Ans: Structure S1 may include structure S2 and again S2 may include S3.
Q.What’s the maximum depth of nested includes in a table?
Ans: Maximum depth is 9 i.e. maximum 9 structures can be included
in a table/structure.
Q. What’s the number of characters limit for field name?
Ans: A field name may not have more than 16 characters in a table,
but in a structure maximum 30 characters are allowed for a field name.
Q. What are foreign keys?
Ans: Relationships between tables are defined in the ABAP dictionary
by creating foreign keys.
Q. Whare are the uses of foreign keys in SAP?
Ans: Using foreign keys(as main table-field is linked with check table),
input value check for any input field can be done. Foreign keys can also be used to
link several tables. Explaination on foreign keys: Suppose, tab1(Foreign key table
or dependent table) contains the following fields: fld1(primary key), fld2, fld3,
fld4, fld5 and Tab2(Referenced table) contains the following fields: fld6(primary
key), fld7(primary key), fld8, fld9 and tab1-fld2 is connected to tab2-fld5, tab1-
fld4 is connected to tab2-fld6Therefore, fld2 and fld4 fields of the table tab1 are
called as foreign key fields to the table tab2 and tab2 is called as check table or
referenced table. Q. What are foreign key fields? Ans: One field of the foreign key
table corresponds to each key field of the check table. That field of the is called
as foreign key field. Uses: A foreign key permits assigning data records in the
foreign key table and check table. One record of the foreign key table uniquely
identifies a record of the check table (using the value entries in the foreign key
fields of the foreign key table). Q. What’s check table?
Ans: Check table is maintained at field level for data validation.
Q. What’s check field?
Ans: One of the foreign key field is marked as the check field.
This depicts that the foreign key relationship is maintained
for that field. When a value is entered for that check field
in the table, input validation checking is done i.e.
a checking is done that whether the inserted value exists
in the check table or not. If doesn’t exist then system rejects
the entry else input validation check for that field is successful.
Q. What’s generic and constant foreign keys?
Q. What’s cardinality? Q. What are the types of foreign key fields?
Q. What are text table? Q. What is ‘technical settings’ of a table?
What are the important parameters to be mentioned within it?
Q. What’s data class?
Ans: Data class is that which allows the table to get
automatically assigned under specific tablespace/dbspace
during table creation in the SAP database
i.e. dataclass determines that under which table space/dbspace
the table will be stored.
Q. How many types of data classes are there in SAP?
Data classes
are mainly of three types(for application tables):
i.Choose APPL0(master data) for data that is frequently accessed but rarely
updated/changed.
ii.Choose APPL1(transaction data) for data that is frequently changed. iii.Choose
APPL2(organizational data) for customizing data that is defined/entered during
system installation and rarely changed. The other two types of data classes are:USR
and USR1(for customer’s own development purpose). Q. What’s size category? Ans: The
Size category is used to defined the space requirement for the table in the
database. Q. How many types of size category are there in SAP? Ans: There are five
size categories. Size category from 0 to 4 can be choosen for the tables. A certain
fixed memory size is assigned to each category in the SAP database. Q. What’s the
utility of size category? Ans: During table creation, the SAP system reserves an
initial space i.e. an initial extent) in the database.If in any case more space is
needed, then additional memory is added according to the mentioned size category
for that table. correct size category prevents the creation of a large number of
small extents for a table i.e. prevents memory wastage. Q. What’s buffering? Q. How
buffers are filled up? Q. What are the different buffering types? Q. What are the
different buffering permissions? Q. How database tables are buffered? Q. What’s
logging? Q. How many tables are there in SAP? Ans: i. Transparent tables, ii. Pool
tables, iii. Cluster tables. Q. What is transparent table? Ans: The tables which
create 1-to-1 correspondence between the table definition in the ABAP data
dictionary and the table definition in the physical database are called as
transparent tables in SAP. Q. Give examples of transparent table. Ans: VBAK, VBAP,
KNA1 etc. Q. What is table pool? Ans: Table pool is a table in the SAP database in
which many pool tables are assigned. Q. What are pool tables? Ans: Tables assigned
to a table pool are called as pool tables.
Q. What are table clusters?
Ans: Table cluster is a table in the SAP database in which many
cluster tables are stored.
Q. What are clustered tables?
Ans: Tables assigned to a Table cluster are called as clustered tables.
Q. Uses of table pool or table cluster.
Ans: Table pool or table cluster is used to store SAP’s
internal control information (screen sequences, program parameters,
temporary data, continuous texts such as documentation).
Q. Example of table cluster and cluster tables.
Ans: i. The table cluster RFBLG holds data for five
transparent tables i.e. BSEC, BSED, BSEG, BSES and BSET.
ii. Other examples of table clusters are CDCLS, CDHDR,
RFBLG, DOKCLU, DOKTL .
Q. What are the differences between transparent and cluster/pool tables?
Ans: i. A transparent table has 1-to-1 cardinality between the
table definition in the data dictionary and in the table
definition of sap database whereas cluster/pool tables
have many-to-1 cardinality between the table definition
in the data dictionary and in the table definition of sap database.
ii. Transparent tables are accessible both by Open and native
SQL statements
whereas table pool/cluster tables
are accessible only by open SQL but never by native SQL.
iii. Transparent tables can store table relevant data wherea
s table pool or cluster tables can store only system data/
application data based on the transparent tables.
Q. What are tabs under the maintenance screen of the ABAP data dictionary screen?
Ans: There are five tabs under ABAP dictionary.
i.Attributes, ii.Delivery & maintenance,
iii. Fields, iv. Entry help/check, v. Currency/Quantity fields.
Q. What is delivery class?
Ans: We need to insert an delivery class value while creating
customized table in SAP through the transaction code SE11.
Delivery class is that which regulates the transport of the table’s
data records (during SAP installations, SAP software upgrade,
client copies, and data transport to other SAP system).
SAP and its customers have different write types depending
on the variety of delivery class. If Delivery class is A,
it depicts that the application table for master and transaction
data changes only rarely.
Q. How many types of delivery classes are there in SAP?
Ans: There are following delivery classes:
i. A: Application table (master and transaction data) is
maintained by the customers using application transaction.
ii. C: Customer table. Data is maintained only by the customer.
iii. L: Table for storing temporary data.
iv. G: Customer table, new data records can be inserted
but may not overwrite or delete existing ones.
v. E: System table with its own namespaces for customer entries.
vi. S: System table, data changes have the status of program changes
i.e. System table for program’s nature. Maintained only by SAP.
E.g.: Codes for SAP transactions.
vii. W: System table for system operation and maintenance.
Table contents are maintained by maintenance transactions.
E.g.: function module table.
Q. What are the differences between domain and data element?
Ans: i.Domain depicts the technical attributes of a field
(its data type, field length, no. of decimal places, appreance on the sreen)
of a SAP database table. Whereas data element denotes
the semantic attributes(short description, label names) for a field.
ii.Data elements are directly attaced to the fields of SAP database
tables and each data element has an underlying domain within it.
Whereas domains are not directly attached to the fields and
a single domain can be under many data elements.
iii.Within domain value range of a field can be described.
Whereas within the data element parameter id and search
help for a particular field can be assigned.
Q. What’s value table?
Ans: Value table is maintained at domain level in SAP.
During domain creation, value range of the domain is defined by
specifying value table. Suppose for a particular domain,
its value table holds the values ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘Z’. So whenever
the domain will be used, system will allow to use these values only.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DeloitteDocument40 pagesDeloittemohamedNo ratings yet
- Web Focus TrainingDocument26 pagesWeb Focus TrainingRajasekhar MudadlaNo ratings yet
- 100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsDocument6 pages100 Abap Questions: ABAP Development FAQ Types of ReportsMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Data Models Using InfoSetsDocument2 pagesData Models Using InfoSetsMani KandanNo ratings yet
- ConnectivityDocument1 pageConnectivityMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Working Procedure of Sap BW/ Bi Testting: This Paper CoversDocument1 pageWorking Procedure of Sap BW/ Bi Testting: This Paper CoversMani KandanNo ratings yet
- BEx Query ExecutionDocument18 pagesBEx Query ExecutionMani Kandan100% (1)
- ADSO Scenario DescriptionDocument11 pagesADSO Scenario DescriptionMani Kandan0% (1)
- SD & MM TablesDocument5 pagesSD & MM TablesMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Optimization: Administration PerformanceDocument7 pagesOptimization: Administration PerformanceMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Production Support - in My Current Engagement Main TwoDocument2 pagesProduction Support - in My Current Engagement Main TwoMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Lo UpdateDocument4 pagesLo UpdateMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Logistic CockpitDocument6 pagesLogistic CockpitMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalDocument58 pagesOptimizing Bex Query Performance For Sap Hana: Pravin Gupta Teklink InternationalMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Pps Unit-4 FunctionsDocument47 pagesPps Unit-4 FunctionsVickey MylcatNo ratings yet
- Capacity Building and Change Management Program For The Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (CBCMP)Document12 pagesCapacity Building and Change Management Program For The Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation and Livestock (CBCMP)International Executive Service CorpsNo ratings yet
- Install and Configuration Computer System Session Plan 1Document5 pagesInstall and Configuration Computer System Session Plan 1Reninio100% (3)
- Report PrototypeDocument103 pagesReport PrototypeJaimali PathakNo ratings yet
- Primary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsDocument4 pagesPrimary Distribution Circuit-Breakers With Integrated Protection, Control and SensorsKnjigescribdNo ratings yet
- Detonado Dragon Quest VIII PDF: Mirror Link #1Document4 pagesDetonado Dragon Quest VIII PDF: Mirror Link #1AllysonWaine0% (1)
- Python Jinja TutorialDocument10 pagesPython Jinja TutorialSuraj Kamal ShaikNo ratings yet
- CloudReady Installation InstructionsDocument13 pagesCloudReady Installation Instructionsabhijeet834uNo ratings yet
- MR5.14.10 Release Note Version CDocument86 pagesMR5.14.10 Release Note Version CChristian KranzNo ratings yet
- Creating An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) With AWS Cloud FormationDocument18 pagesCreating An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) With AWS Cloud Formationgoyal_86964227No ratings yet
- CV - Luis TariDocument3 pagesCV - Luis TariHenry Satria PutraNo ratings yet
- Network Security Monitoring ProcedureDocument3 pagesNetwork Security Monitoring ProcedureGhislain MurenziNo ratings yet
- Self Defending NetworksDocument17 pagesSelf Defending Networkssarthak_ganguly100% (1)
- Dynamic Pricing Model For EV Charging-Discharging Service Based On Cloud Computing SchedulingDocument20 pagesDynamic Pricing Model For EV Charging-Discharging Service Based On Cloud Computing Schedulingunmec12No ratings yet
- Aveva PdmsDocument33 pagesAveva PdmsSri Surya LankapalliNo ratings yet
- Addictive Drums ManualDocument28 pagesAddictive Drums Manualspine66No ratings yet
- Electronic Disclosures and Signatures ConsentDocument2 pagesElectronic Disclosures and Signatures Consentjdaniel.hrNo ratings yet
- A Uhf Rfid Measurement and Evaluation Test System2659Document7 pagesA Uhf Rfid Measurement and Evaluation Test System2659mano012No ratings yet
- Linux ForYou - Oct 2008Document116 pagesLinux ForYou - Oct 2008Santhosh Mahankali100% (1)
- MAPPING DRIVES PowerPoint PresentationDocument6 pagesMAPPING DRIVES PowerPoint PresentationDave MilnerNo ratings yet
- Embedded Hardware DesignDocument16 pagesEmbedded Hardware DesignAbhay SharmaNo ratings yet
- SCRUM WikipediaDocument9 pagesSCRUM WikipediaikedrinNo ratings yet
- PytestDocument122 pagesPytestdeepavali123No ratings yet
- SCM ImpDocument88 pagesSCM ImpKiran GandlaNo ratings yet
- We Can Insert or Delete Nodes We Can't Insert or Delete A NodeDocument5 pagesWe Can Insert or Delete Nodes We Can't Insert or Delete A Nodeprakash reddyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A Laboratory Information Management System at LRHDocument7 pagesImplementation of A Laboratory Information Management System at LRHUdara Senarathne100% (1)
- Measurement Reports ExportDocument25 pagesMeasurement Reports ExportKhắc Biên NgôNo ratings yet
- Advanced MMIS Design Characteristics of APR1400: Yeong Cheol SHIN, Hak Young CHUNG, Tae Young SONGDocument9 pagesAdvanced MMIS Design Characteristics of APR1400: Yeong Cheol SHIN, Hak Young CHUNG, Tae Young SONGelsayedNo ratings yet