Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter - 1 Accidents in India: Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (2005-2015)
Chapter - 1 Accidents in India: Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (2005-2015)
Uploaded by
Ranjith RajOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter - 1 Accidents in India: Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (2005-2015)
Chapter - 1 Accidents in India: Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (2005-2015)
Uploaded by
Ranjith RajCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER – 1
ACCIDENTS IN INDIA
Introduction
Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths
An accident is an unplanned event that during the Decade (2005-2015)
results in injury, deaths, damage to property
or some other losses. For statistical purpose, The accidental deaths is having an
Accidental Deaths have been classified as increasing trend during the period from 2005 -
deaths that could be due to forces/factors of 2014 with a slight decline in the year 2015.
the nature which have been termed as However, an overall increase of 40.5% in
‘Natural Accidental Deaths’ or could be due to accidental deaths was reported during 2015 in
deliberate or negligent conduct of human comparison with 2005. The population growth
beings, which is termed as ‘Un-natural during the period from 2005 - 2015 was
Accidental Deaths’ or due to causes not 14.2% whereas the increase in the rate of
covered in the above two categories and with accidental deaths during the same period was
no initial apparent cause of deaths which have 22.8%. The percentage change of accidental
been categorised as ‘Other Causes of Deaths’ deaths is presented in Table-1.1.
like poisoning, sudden death etc.
A total of 4,13,457 accidental deaths were
This is the second edition of the report reported in the country during 2015 showing a
after the completion of comprehensive decrease of 8.5% in comparison to 2014 and
revision of the proformae for data collection of 9.6% decrease in the rate of ‘Accidental
‘Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India’ Deaths’ in 2015 in comparison to the year
completed in 2014 in consultation with 2014 [Table-1(A)].
Ministry of Home Affairs, States/UTs Police
and others stakeholders.
Table – 1 (A)
Percentage Change in Population, Number and Rate of Accidental
Deaths over the Corresponding Previous Year during 2011 to 2015
Percentage Change in Percentage Change in Percentage Change in Rate
Year Population over the Accidental Deaths over of Accidental Deaths over
Previous Year the Previous Year the Previous Year
(1) (2) (3) (4)
2011 2.1 1.6 -0.3
2012 0.3 1.0 0.9
2013 1.3 1.4 0.0
2014 1.2 12.8 11.3
2015 1.2 -8.5 -9.6
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [1]
Figure 1.1
Percentage Change in Population, Number and Rate of Accidental Deaths
during 2011 – 2015 (Over Corresponding Previous Year)
15.0 12.8
11.3
10.0
5.0
2.1
1.6 1.2 1.2
1.0 1.0 1.3 1.4
0.9 0.0
0.0
2011-0.3 2012 2013 2014 2015
-5.0
-10.0 -8.5
-9.6
-15.0
Population Number Rate
Out of 4,13,457 accidental deaths, There was a decline of 48.0% (from 20,201
3,36,051(81.3%) deaths were due to un-natural deaths in 2014 to 10,510 deaths in 2015) in
causes and 66,896(16.2%) deaths were due to deaths due to causes attributable to forces of
other causes and the remaining 10,510(2.5%) nature and a decrease of 6.6%(from 4,31,556
deaths were due to causes attributable to deaths in 2014 to 4,02,947 deaths in 2015) in
forces of nature. deaths due to un-natural causes during 2015
as compared to 2014 [Table-1(B)].
Table — 1 (B)
Number of Accidental Deaths by Natural & Un-natural Causes (2011 to 2015)
Causes Attributable to Nature Un-natural Causes# Total Accidental Deaths
Year % Change % Change % Change
Number Over Previous Number Over Previous Number Over Previous
Year Year Year
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7)
2011 23,690 –5.5 3,67,194 2.1 3,90,884 1.6
2012 22,960 –3.1 3,72,022 1.3 3,94,982 1.0
2013 22,759 –0.9 3,77,758 1.5 4,00,517 1.4
2014 20,201 -11.2 4,31,556 14.2 4,51,757 12.8
2015 10,510 -48.0 4,02,947 -6.6 4,13,457 -8.5
Note: ‘#’ also includes 1,14,728 and 66, 896 deaths due to Other Causes of Accidents for the year 2014 and 2015 respectively.
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [2]
STATE/UT - WISE ACCIDENTAL DEATHS DURING 2015
Accidental Deaths
upto 200
201 to 1000
1001 to 5000
5001 to 15000
Above 15000
Map Powered by DevInfo, UNICEF
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [3]
Figure 1.2
Number of Accidental Deaths by Natural, Un-natural and Other Causes during 2011-2015
,
Note: ‘*’ ‘Causes Not Known’ and ‘Other Causes’ have been excluded and now made as part of ‘Un-natural Accidents’.
Number & Rate of Accidental Deaths in 17.1% has accounted for 8.9% of accidental
States, UTs and Cities deaths in the country. The other States having
higher percentage share in total accidental
Out of 4,13,457 accidental deaths, like deaths were Madhya Pradesh (9.8%), Tamil
previous year in 2015 also, Maharashtra has Nadu (8.1%), Gujarat (6.9%), Rajasthan
reported highest number of accidental (6.8%), Karnataka (6.4%), Chhattisgarh (4.7%),
deaths(64,566), contributing nearly one-sixth Andhra Pradesh (4.2%), and West Bengal
(15.6%) of total accidental deaths reported in (3.7%) during 2015 [Table-1.2]. These States
the country. Uttar Pradesh, the most populous had nearly similar percentage share in 2014
State in the country with population share of also.
Figure 1.3
Percentage Share of Major States in Accidental Deaths during 2015
ANDHRA PRADESH WEST BENGAL
[4.2%] [3.7%]
CHHATTISGARH
[4.7%]
KARNATAKA OTHERS
[6.4%] [24.7%]
RAJASTHAN
[6.8%]
GUJARAT
[6.9%]
MAHARASHTRA
[15.6%]
TAMIL NADU
[8.1%]
UTTAR PRADESH MADHYA PRADESH
[8.9%] [9.8%]
Other States include Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, Assam, Chandigarh, Goa, Haryana, Jammu & Kashmir, Jharkhand, Kerala, Manipur, Mizoram, Meghalaya,
Nagaland, Odisha, Punjab, Sikkim, Telangana, Tripura, Uttarakhand, A & N Island, D&N Haveli, Daman & Diu, Delhi, Lakshadweep and Puducherry
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [4]
The highest rate of accidental deaths was rate of 32.8. 17 out of 36 States/UTs have
reported from Chhattisgarh (75.1) followed by reported higher rates of ‘Accidental Deaths’
Puducherry (73.4), Maharashtra (54.2), as compared to All India Average of 32.8
Madhya Pradesh (52.7), Haryana (48.8) and deaths per one lakh of population [Figure–
Tamil Nadu (48.7) against the national average 1.4].
Figure 1.4
Rate of Accidental Deaths in Various States/UTs during 2015
CHHATTISGARH 75.1
PUDUCHERRY 73.4
MAHARASHTRA 54.2
MADHYA PRADESH 52.7
HARYANA 48.8
TAMIL NADU 48.7
HIMACHAL PRADESH 47.8
GUJARAT 45.7
DAMAN & DIU 45.2
KARNATAKA 42.6
GOA 32.4
TELANGANA 40.0
States / UTs
RAJASTHAN 39.2
PUNJAB 36.0
A & NISLANDS 34.2
ANDHRA PRADESH 33.9
DELHI (UT) 33.1
SIKKIM 32.7
KERALA 32.3
ODISHA 29.8
D & N HAVELI 29.7
ARUNACHAL PRADESH 28.3
UTTARAKHAND 26.1
MIZORAM 17.3
JHARKHAND 17.2
UTTAR PRADESH 17.1
WEST BENGAL 16.3
JAMMU & KASHMIR 15.5
MEGHALAYA 15.3
CHANDIGARH 15.3
TRIPURA 14.5
ASSAM 13.5
MANIPUR 11.1
BIHAR 10.1
LAKSHADWEEP 8.8
NAGALAND 3.7
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0 120.0 140.0 160.0 180.0 200.0
National Average 32.8
Rate
The number of accidental deaths has in total accidental deaths in the year 2015 as
decreased by 8.5% at national level during compared to 2014 followed by Chandigarh
2015 as compared to 2014. The number of (41.2%), Mizoram (40.2%) and Manipur (36%)
‘Accidental Deaths’ due to causes attributable [Table-1.3].
to forces of nature have decreased by 48.0%
and deaths by un-natural causes (including Gender-wise analysis reveals that female
other causes) have decreased by 6.6% during and male constitute 20.6% and 79.4% of total
2015 over the year 2014 [Table-1.3]. victims respectively. 1/9th victims of accidental
deaths were children (below 18 years of age).
Uttarakhand has reported the highest
Age group of most of the victims was
percentage increase (121.1%) in total
between 18 to 45 years. This group of people
accidental deaths in the year 2015 as
has accounted for 59.7% of all persons killed in
compared to 2014 (from 1,243 in 2014 to 2,748
accidents in the country during the year 2015.
in 2015), followed by Nagaland (49.2%),
A total of 37,081 senior citizens (60 years &
Lakshadweep (16.7%), Uttar Pradesh(11.7%),
above of age) have also got killed in various
Daman and Diu (6.6%) and Andhra Pradesh
accidents during 2015 [Table-1.4].
(6.5%). Tripura has reported a decline of 44.7%
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [5]
STATE/UT - WISE RATE OF ACCIDENTAL DEATHS DURING 2015
Accidental Rate
All India Average 32.8
upto 10
11 to 20
Note: 21 to 30
Rate of Accidental Deaths means Number of Accidental
Deaths per 1,00,000 population. 31 to 50
Above 50
Map Powered by DevInfo, UNICEF
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [6]
Causes of Accidental Deaths
The share of causes of deaths not
attributable to forces of nature has increased
Accidental deaths have been grouped into
such as ‘Air-Crash’, ‘Collapse of Structure‘,
three broad categories i.e. ‘Accidents due to
‘Electrocution’, ’Falls’, ‘Fire-arm’, ‘Traffic
Forces of Nature (Natural Accidents), ‘Un-
Accidents’, ‘Stampede’ ‘Sudden Deaths’,
natural Accidents’ and ‘Deaths due to Other
‘Deaths of Women during Pregnancy’, ‘Killed by
Causes’. Classification of types and causes of
Animals’, ‘Poisoning’ and ‘Suffocation’ whereas
accidental deaths has been done for statistical
the share of causes of deaths due to ‘Ship
purpose only.
Accident’, ‘Drowning’, ‘Accidental Explosion’,
‘Factory/ Machine Accidents’, ‘Accidental Fire’,
Under ‘Causes Attributable to Forces of
‘Mines and Quarry Disaster’, ‘Deaths due to
Nature’, the share of deaths due to ‘Avalanche’,
Consumption of Illicit/Spurious Liquor’ and
‘Exposure to Cold’, ‘Earthquake’, ‘Epidemic’,
‘Drug Overdose’ in accidental deaths have
‘Flood’, ‘Lightning’, ‘Torrential Rain’, ‘Forest
decreased in 2015 as compared to the previous
Fire’ and Heat/Sun Stroke’ have increased
year 2014.
during the year over the previous year 2014
whereas the share of causes of deaths due to
Cause-wise details of accidental deaths,
‘Cyclone’, ‘Tornado’, ‘Starvation due to Natural
rate and its percentage variation during 2015
Calamity’, and ‘Landslide’ have decreased in
over 2014 are presented in Table-1(C).
2015 over 2014.
Figure 1.5
Percentage Share of Various Major Causes of Accidental Deaths during 2015
(Natural, Un-natural and Other Causes)
Natural Causes
[2.5%] Electrocution
Accidental Fire [2.4%]
[4.2%]
Other Causes
[21.7%]
Falls Traffic Accidents
[4%] [42.9%]
Sudden Deaths
Poisoning [8.4%] Drowning
[6.3%] [7.2%]
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [7]
Table-1(C)
Number, Share and Rate of Accidental Deaths by Causes Attributable to Nature, Un-natural and Other
Causes of Accidents during 2014 & 2015
2014 2015
% Variation
Sl.
Cause % Share % Share during 2015
No.
No. (w.r.t. Rate No. (w.r.t. Rate over 2014
All India) All India)
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9)
A. CAUSES ATTRIBUTABLE TO NATURE
1 Avalanche 23 0.1 0.0 38 0.4 0.0 65.2
2 Exposure to Cold 913 4.5 0.1 1149 10.9 0.1 25.8
3 Cyclone 62 0.3 0.0 15 0.1 0.0 -75.8
4 Tornado 42 0.2 0.0 13 0.1 0.0 -69.0
5 Tsunami 0 0.0 0.0 0 0.0 0.0 -
6 Starvation Due to Natural Calamity 50 0.2 0.0 30 0.3 0.0 -40.0
7 Earthquake 2 0.0 0.0 92 0.9 0.0 4500.0
8 Epidemic 48 0.2 0.0 218 2.1 0.0 354.2
9 Flood 541 2.7 0.0 846 8.0 0.1 56.4
10 Heat/Sun Stroke 1248 6.2 0.1 1908 18.2 0.2 52.9
11 Landslide 499 2.5 0.0 232 2.2 0.0 -53.5
12 Lightning 2582 12.8 0.2 2641 25.1 0.2 2.3
13 Torrential Rain 156 0.8 0.0 195 1.9 0.0 25.0
14 Forest Fire 11 0.1 0.0 19 0.2 0.0 72.7
15 Other Natural Causes 14024 69.4 1.1 3114 29.6 0.2 -77.8
16 Total (A) 20201 100.0 1.6 10510 100.0 0.8 -48.0
B. UN-NATURAL CAUSES
1 Air-Crash 15 0.0 0.0 23 0.0 0.0 53.3
2 Ship Accidents 7 0.0 0.0 1 0.0 0.0 -85.7
3 Collapse of Structure 1821 0.6 0.1 1885 0.6 0.1 3.5
4 Drowning 29903 9.4 2.4 29822 8.9 2.4 -0.3
5 Electrocution 9606 3.0 0.8 9986 3.0 0.8 4.0
6 Accidental Explosion 1194 0.4 0.1 831 0.2 0.1 -30.4
7 Falls 15399 4.9 1.2 16759 5.0 1.2 8.8
8 Factory/Machine Accidents 797 0.3 0.1 695 0.2 0.1 -12.8
9 Accidental Fire 19513 6.2 1.6 17700 5.3 1.5 -9.3
10 Firearm 633 0.2 0.1 736 0.2 0.1 16.3
11 Mines or Quarry Disaster 210 0.1 0.0 118 0.0 0.0 -43.8
12 Traffic Accidents 169107 53.4 13.6 177423 52.8 13.4 4.9
13 Stampede 178 0.1 0.0 480 0.1 0.0 169.7
14 Other Un-natural Causes 55482 17.5 4.5 64427 19.2 4.4 16.1
15 Causes Not Known 12963 4.1 1.0 15165 4.5 1.0 17.0
Total(B) 316828 100.0 25.5 336051 100.0 25.2 6.1
C. OTHER CAUSES
1 Sudden Deaths 26526 23.1 2.1 35023 52.4 2.8 32.0
2 Deaths of Women during Pregnancy 1017 0.9 0.1 1040 1.6 0.1 2.3
Deaths due to Consumption of
3 1699 1.5 0.1 1522 2.3 0.1 -10.4
Illicit/Poisonous Liquor
4 Killed by Animals 886 0.8 0.1 951 1.4 0.1 7.3
5 Poisoning 20587 17.9 1.7 26173 39.1 2.1 27.1
6 Suffocation 1255 1.1 0.1 1437 2.1 0.1 14.5
7 Drug Overdose 874 0.8 0.1 750 1.1 0.1 -14.2
8 Causes Not Known 8588 7.5 0.7 @ @ @ @
9 Other Than Above Mentioned Causes 53296 46.5 4.3 @ @ @ @
8 Total (C) 114728 100 25.4 66896 100.0 5.3 -
Grand Total (A+B+C) 451757 100.0 36.3 413457 100.0 32.8 -8.5
@ discontinued in the year 2015 and made as part of Sl. 15 and 14 of Part-B respectively.
‘Rate’ – Refers to No. of deaths per 1,00,000 population
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [8]
STATE/UT - WISE DEATHS DUE TO CAUSES ATTRIBUTABLE TO FORCES OF
NATURE (NATURAL CAUSES) DURING 2015
Accidental Deaths
upto 10
11 to 200
201 to 500
501 to 1000
Above 1000
Map Powered by DevInfo, UNICEF
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [9]
Natural Causes of Accidental Deaths 55.3%(636 out of 1,149 deaths), 60.5%(23 out
of 38 deaths), 46.2%(6 out of 13 deaths),
Cause - wise accidental deaths due to
92.2%(201 out of 218 deaths), 64.6%(126 out
forces of nature are presented in Table-1.5.
of 195 deaths), 89.5%(17 out of 19 deaths) and
Out of 10,510 accidental deaths due to causes
40%(12 out of 30 deaths) of total such deaths
attributable to forces of nature, 25.1% deaths
reported in the country respectively during
were due to ‘Lightning’(2,641 deaths), 18.2%
2015. Majority of deaths due to ‘Earthquake’
deaths due to ‘Heat/Sun Stroke’(1,908 deaths)
were reported in Bihar which accounted for
and 10.9% deaths due to ‘Exposure to
78.3%(41 out of 55 deaths) of total such deaths
Cold’(1,149 deaths) during the year 2015.
during 2015.
‘Flood’ and ‘Landslide’ caused 8%(846 deaths)
and 2.2%(232 deaths) of total deaths Un-natural Causes of Accidental Deaths
attributable to forces of nature respectively
It is generally accepted that accidents due
during 2015.
to ‘Un-natural Causes’ are preventive and can
The age group-wise distribution of be reduced by effective safety measures and
accidental deaths by causes attributable to safety consciousness. The accidents which
forces of nature is given in Table-1.5. As per occur due to deliberate or negligent actions of
age-wise classification of victims, 4.3% of such human have been classified as un-natural
victims were below 14 years of age (453 out of accidents.
10,510 deaths), 20.0% in the age-group of 18
A total of 6,63,483 cases of ‘Un-natural
years to below 30 years(2,098 deaths), 29.0%
Accidents’ were reported in the country which
in the age-group of 30 years to below 45
resulted in 3,36,051 deaths and left 4,98,195
years(3,043 deaths) and 26.5% victims were in
persons injured during 2015[Table-1.6].
age group 45 years to below 60 years(1,201
deaths) during 2015. Senior citizens (60 yrs. The cause-wise analysis of un-natural
and above) constituted 15.1% (1,590 deaths) of deaths revealed that majority of deaths were
the total such victims. due to traffic accidents which accounted for
52.8% (1,77,423 out of 3,36,051 deaths) of
State/UT - wise and gender - wise
total un-natural deaths during the year 2015.
distribution of accidental deaths in the country
Besides, ‘Drowning’, 'Accidental Fire’, 'Fall' and
by forces of nature along with their share in
'Electrocution' caused 8.9%(29,822 deaths),
total deaths is presented Table-1.8. ‘Landslide’
5.3%(17,700 deaths), 5.0%(16,759 deaths) and
caused 73.7%, 30.0%,10.0% and 7.4% of total
3.0%(9,986 deaths) of total deaths due to un-
deaths in Meghalaya(14 out of 19 deaths),
natural accidents respectively [Table-1(C)].
Sikkim(3 out of 10 deaths), West Bengal(29 out
of 291 deaths) and Himachal Pradesh(21 out of The age-group-wise distribution of
283 deaths) respectively. Similarly, ‘Lightning’ accidental deaths in the country by various Un-
caused 95.8%, 87.7%, 73.3%, 67.5%, 64.7% natural causes along with their share in total
and 58.1% of total such deaths in Karnataka deaths is presented in Table-1.7. Majority of
(137 out of 143 deaths), Chhattisgarh(229 out victims were in age groups 30 above - below 45
of 261 deaths), Madhya Pradesh(475 out of years and 18 above - below 30 years which
648 deaths), Kerala(27 out of 40 deaths), accounted for 31.4%(1,05,639 deaths) and
Maharashtra(291 out of 450 deaths) and West 30.2%(1,01,502 deaths) of total such deaths
Bengal(169 out of 291 deaths) respectively. respectively.
83.0%(196 out of 236 deaths) of deaths in
Assam were due to ‘Flood’. ‘Heat/Sun Stroke’ State/UT-wise and gender-wise distribution
caused 84.8%(654 out of 771 deaths) of total of accidental deaths in the country by various
accidental deaths attributable to natural causes un-natural causes is presented in Table-1.9.
in Andhra Pradesh. 53.3%(127 out of 238 Maharashtra with 9.5% (one-eleventh) of
deaths) of deaths in Punjab were due to country’s population has reported
‘Exposure to Cold’ during 2015. 15.6%(51,435 out of 3,36,051 deaths) of
accidental deaths due to un-natural causes.
Majority of accidental deaths due to Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu,
‘Cyclone’, ‘Exposure to Cold’, ‘Avalanche’, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Karnataka accounted
‘Tornado’, ‘Epidemic’, ‘Torrential Rain’, ‘Forest for 9.7%, 9.1%, 8.5%, 6.9% 6.6% and 6.0% of
Fire’ and ‘Starvation Due to Natural Calamity’ total such deaths respectively during the year
were reported in Uttar Pradesh which 2015.
accounted for 86.7%(13 out of 15 deaths),
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [10]
STATE/UT - WISE ACCIDENTAL DEATHS DUE TO UN-NATURAL CAUSES
DURING 2015
Accidental Deaths
upto 200
201 to 1000
1001 to 5000
5001 to 15000
Above 15000
Map Powered by DevInfo, UNICEF
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [11]
Other Causes of Accidental Deaths followed by Puducherry(149 deaths), Madhya
Pradesh (246 deaths), Chhattisgarh (140
Under this category of classification of
deaths), Uttar Pradesh(125 deaths) and
accidents, the Bureau has included accidental
Haryana(115 deaths) during 2015.
deaths which occurred due to factors other than
deliberate or negligent act of human beings. In
earlier publication, these accidental deaths
were part of ‘Un-natural Accidental Deaths’. Fire Accidents
Now the Bureau has presented these accidents Considering the number of fire accidents in
separately. the country and potential of the damage that
A total of 69,282 cases of ‘Other Causes of could be caused by such accidents, the Bureau
Accidents’ were reported in the country which has also collected data on fire accidents
caused 66,896 deaths during 2015. The cause- according to places of occurrence for
wise analysis of deaths revealed that 52.4%, appropriate preventive strategies.
39.1%, 2.3% and 2.1% of total deaths(66,896) A total of 18,450 cases of fire accidents
under ‘Other Cause of Accidents’ were reported were reported in the country during 2015,
under ‘Sudden Deaths’ (35,023), 'Poisoning' showing a decrease of 9.5% during 2015 over
(26,173), ‘Deaths due to Consumption of 2014 (20,377 cases). 18,450 incidents of fire
Illicit/Spurious Liquor’ (1,522) and 'Suffocation' accidents caused injuries to 1,193 persons and
(1,437) respectively during 2015. ‘Food 17,700 deaths during 2015. The cause-wise
Poisoning’ and ‘Snake Bites’ caused 1,624 and analysis of fire accidents revealed that 42.1%of
8,554 deaths respectively during 2015 [Table- total deaths(7,445 out of 17,700) due to fire
1.10]. accidents were reported in residential/dwelling
The State/UT-wise analysis of other causes buildings during 2015 [Table 1.12].
of accidental deaths revealed that 62.7% (42 Large number of cases of fire accidents
out of 67) of total deaths in Chandigarh and were reported in Maharashtra (4,087 out of
61.0% (7,735 out of 12,681) of total deaths in 18,450), accounting for 22.1% of total such
Maharashtra under ‘Other Cause of Accidents’ cases during 2015 [Table-1.13].
were due to heart attacks during 2015.
State/UT wise and Cause-wise details on The State/UT-wise analysis of place of fire
‘Other Cause of Accidents’ is presented in accidents revealed that 19 States & UTs have
Table 1.11. State/UT – wise analysis reveals reported 50.0% or more deaths due to ‘Fire in
that a total of 7,735 out of 18,820 deaths due to residential or dwelling building’ during 2015.
heart attacks were reported in Maharashtra These States/UTs were A & N Island,
alone accounting for 41.1% of total such deaths Lakshadweep, Tripura (100% each)
in the country during 2015. Similarly, 60.9% Uttarakhand (87.7%), Meghalaya (86.7%),
(633 out of 1,040) of deaths of women during Jharkhand (85.1%), Chandigarh (83.3%),
pregnancy were reported in Maharashtra alone. Telangana (83%), Punjab (76.7%), Gujarat
74.9%, 70.3%, 66.8%, 66.7% and 63.6% (73.4%) and Kerala (70.4%). Uttar Pradesh
deaths in Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, alone, accounted for 64.3% of total deaths
Madhya Pradesh, D & N Haveli and Meghalaya under ‘Fire in government building’ in the
under ‘Other Cause of Accidents’ were due to country during 2015. Out of the total deaths
poisoning respectively during 2015. reported under ‘Fire in commercial building’
49.8% were reported in Karnataka. A total of 58
A total of 1,624 incidents of consumption of cases of accidental fire in trains were also
illicit/spurious liquor caused 1,522 deaths in the reported during 2015 which caused 59 deaths
country during 2015. Majority of such deaths in the country during 2015 [Table-1.13].
were reported in Maharashtra (278 deaths)
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [12]
STATE/UT - WISE ACCIDENTAL DEATHS DUE TO OTHER CAUSES
DURING 2015
Accidental Deaths
upto 100
101 to 500
501 to 1000
1001 to 5000
Above 5000
Map Powered by DevInfo, UNICEF
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [13]
Accidents in Cities Accidental Deaths due to Natural Causes in
Cities
The term ‘Mega City’ refers to cities which
have a population of over 10 lakh or more. As A total of 1,688 deaths due to causes
per the Population Census 2011, the status of attributable to forces of nature were reported in
mega city has been accorded to 53 cities. these 53 mega cities during 2015. Among
specified causes of accidents due to forces of
A total of 69,372 accidental deaths were
nature in 53 cities, maximum deaths were
reported in 53 mega cities during 2015. Maximum
reported due to ‘Heat/Sun Stroke’ followed by
numbers of accidental deaths (8,286 deaths)
‘Exposure to Cold’, accounting for 12.8% and
were reported in Mumbai accounting for 11.9% of
12.1% of total such accidental deaths during
total deaths, followed by Delhi (5,930), Pune
2015. All deaths in Jabalpur were due to
(4,665), Chennai (3,952), Bengaluru (3,733) and
‘Exposure to Cold’ during 2015. All deaths in
Jaipur (3,138).
Hyderabad, 88.5% deaths in Vijayawada and
Evidently, average rate of accidental deaths 58.8% deaths in Ahmadabad were due to
in these 53 mega cities were higher (43.2) than ‘Heat/Sun Stroke’.
all India rate of accidental deaths (32.8). The rate
Accidental Deaths due to Un-natural Causes
of accidental deaths was highest in Bhopal
in Cities
(157.1) followed by Allahabad (116.3), Jaipur
(102.2), Pune (92.4), Raipur (92.1) and Nasik A total of 1,17,112 cases of un-natural
(88.2) as compared to average rate for the cities accidents were reported in 53 mega cities
(43.2) [Table-1.2]. which caused injuries to 73,870 persons and
53,104 deaths during 2015. The cause-wise
Out of 69,372 accidental deaths in 53 mega
analysis of un-natural deaths revealed that
cities; 1,688, 53,104 and 14,580 deaths were
36.1%, 8.2%, 5.5% and 5.4% deaths in 53
due to causes attributable to forces of nature,
cities were due to 'Traffic Accidents', 'Falls',
un-natural and other causes of accidents
‘Drowning’ and 'Fire Accidents' respectively.
respectively during 2015. A declining trend has
been observed in nearly all causes of Among 53 cities, Mumbai city accounted for
accidental deaths in these 53 mega cities; 12.7% of total deaths reported under un-natural
deaths due to natural calamities and un-natural accidents followed by Delhi which accounted for
accidents (including other causes of accidents) 9.2% during 2015.
have shown a decrease of 62.5% and 4.7%
Accidental Deaths due to Other Causes in
during 2015 over 2014 respectively [Table-1.3]
Cities
Kolkata, the third largest city in terms of
A total of 16,091 cases of ‘Other Causes of
population (8.8% of the total population of all
Accidents’ in 53 mega cities caused 14,580
mega cities) among 53 cities after Mumbai
deaths during 2015, among ‘Other Causes of
(11.4%), reported the lowest share of deaths in
Accidents’, maximum deaths were due to
cities accounting for 1.1% of total accidental
‘Hearth Attacks’ followed by ‘Poisoning’,
deaths in 53 mega cities during 2015. The
accounted for 39.0% and 22.4% of total such
comparative reporting of ‘Accidental Deaths’
deaths.
during 2015 in the top four-mega cities is
presented in Table-1(D). “Data on City-wise information is available on
our website under ‘Additional Tables for ADSI”
Table – 1 (D)
Rate of Accidental Deaths in Metropolitan Cities during 2015
Share of Rate (No. of
Sl. Population Share of Deaths In
City Population In Deaths Per One
No. (In Lakhs) Cities (Percent)
Cities (Percent) Lakh Population)
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
1. Chennai 87.0 5.4 5.7 45.4
2. Delhi 163.2 10.1 8.5 36.3
3. Kolkata 141.1 8.8 1.1 5.6
4. Mumbai 184.1 11.4 11.9 45
************
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2015 [14]
You might also like
- Hse Interview Questions - Various Project SitesDocument5 pagesHse Interview Questions - Various Project SitesNadeem100% (5)
- Are Nurses Ready - Disaster Preparedness in - 2008 - Australasian Emergency Nur PDFDocument10 pagesAre Nurses Ready - Disaster Preparedness in - 2008 - Australasian Emergency Nur PDFHikmat PramajatiNo ratings yet
- Dirr-112 Week 11-19 by KuyajovertDocument10 pagesDirr-112 Week 11-19 by KuyajovertRobert Macalanao100% (4)
- Chapter-1 AccidentsDocument13 pagesChapter-1 AccidentsDhanesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Adsi2021 Chapter 1 AccidentsDocument12 pagesAdsi2021 Chapter 1 AccidentsTEI- Aadarsh Pandey.No ratings yet
- Accidental Deaths 11 - 0Document17 pagesAccidental Deaths 11 - 0Justin MatthewsNo ratings yet
- JUNE 2014 Higher Growth, Lower Unemployment Predicted For Second Half of 2014Document10 pagesJUNE 2014 Higher Growth, Lower Unemployment Predicted For Second Half of 2014nm2007kNo ratings yet
- InflationKSA en Q4-2020 EnglishDocument8 pagesInflationKSA en Q4-2020 Englishindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
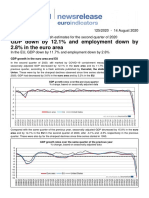
- GDP Down by 12.1% and Employment Down by 2.8% in The Euro AreaDocument4 pagesGDP Down by 12.1% and Employment Down by 2.8% in The Euro AreaOrestis VelmachosNo ratings yet
- Indonesia PDFDocument54 pagesIndonesia PDFDista Fildzah AmalinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Economic Development AEP 2014 RevisedDocument41 pagesChapter 4 Economic Development AEP 2014 RevisedХењае Чувај СеNo ratings yet
- Early Estimate of Motor Vehicle Traffic Fatalities in 2023Document6 pagesEarly Estimate of Motor Vehicle Traffic Fatalities in 2023Sravan kumar KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Air Freight in India - Macroeconomic IndicatorsDocument5 pagesAir Freight in India - Macroeconomic IndicatorsnitinNo ratings yet
- InflationKSAEn Q4-2019Document9 pagesInflationKSAEn Q4-2019indraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- InflationKSA en Q1-2021 EnglishDocument8 pagesInflationKSA en Q1-2021 Englishindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- Inflation en Q3-2021ksaDocument8 pagesInflation en Q3-2021ksaindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- The Construction Sector of Indonesia: 21 Asia Construct ConferenceDocument37 pagesThe Construction Sector of Indonesia: 21 Asia Construct Conferencewidyastuty utamiNo ratings yet
- Demographic Profile of Region 1: IndicatorsDocument2 pagesDemographic Profile of Region 1: IndicatorsC MarquezNo ratings yet
- Human Development For Everyone: IsraelDocument8 pagesHuman Development For Everyone: IsraelFiona AurelieNo ratings yet
- Pd303 Research AssignmentDocument10 pagesPd303 Research AssignmentPayal prasadNo ratings yet
- Inflation in IndonesiaDocument9 pagesInflation in IndonesiaNaurah Atika DinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Accidental Deaths in India: Incidence and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (1994-2004)Document17 pagesChapter - 1 Accidental Deaths in India: Incidence and Rate of Accidental Deaths During The Decade (1994-2004)Sameer KumarNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Alfalasi - Quiz 2Document3 pagesMohammed Alfalasi - Quiz 2mahamshoaib1No ratings yet
- NevadaOpioidSurveillance10 17 (4 2018)Document11 pagesNevadaOpioidSurveillance10 17 (4 2018)Zac SlotemakerNo ratings yet
- Rate of Inflation and Rate of Unemployment in That CountryDocument7 pagesRate of Inflation and Rate of Unemployment in That CountryumairahNo ratings yet
- GDP and Unemplyoment RateDocument6 pagesGDP and Unemplyoment RateWassay KhanNo ratings yet
- InflationKSAEn Q3-2019 EnglishDocument9 pagesInflationKSAEn Q3-2019 Englishindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- Census State QuickfactsDocument13 pagesCensus State QuickfactsVictor UzowuruNo ratings yet
- Inflation en Q2-2021 EnglishKSADocument8 pagesInflation en Q2-2021 EnglishKSAindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- Gender Stats Yr20 190721Document29 pagesGender Stats Yr20 190721Milazar NigelNo ratings yet
- Jayaram An 2015Document14 pagesJayaram An 2015divi kayaNo ratings yet
- InflationKSA en Q4 2021Document8 pagesInflationKSA en Q4 2021indraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- U.S Inflation Rate (2010-2020)Document4 pagesU.S Inflation Rate (2010-2020)Hiếu Nguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Group Chapter 24 - Inflation ExercisesDocument27 pagesGroup Chapter 24 - Inflation ExercisesTú AnhNo ratings yet
- Take-Home Assignment - MBA 1133 Statistics For BusinessDocument4 pagesTake-Home Assignment - MBA 1133 Statistics For BusinessIsuru KasthurirathneNo ratings yet
- KSAInflation en Q1 2022Document8 pagesKSAInflation en Q1 2022indraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- Country - India & Saudi ArabiaDocument48 pagesCountry - India & Saudi ArabiaRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Infrastructure Development For Thailand's Future GrowthDocument36 pagesEnhancing Infrastructure Development For Thailand's Future GrowthirinasiregarNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Data Analysis SG G15 Team 02 Northern Europe and South AsiaDocument25 pagesMacroeconomic Data Analysis SG G15 Team 02 Northern Europe and South AsiaHùng DuyNo ratings yet
- Бүрэлдэхүүн 2010-I 2010-II 2010-III 2010-IV 2011-I 2011-II 2011-IIIDocument7 pagesБүрэлдэхүүн 2010-I 2010-II 2010-III 2010-IV 2011-I 2011-II 2011-IIITergel NyamlkhagvaNo ratings yet
- Crime Stats Auckland City 20141231Document26 pagesCrime Stats Auckland City 20141231Amit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Inflation Data mr110128Document4 pagesInflation Data mr110128Rohn J JacksonNo ratings yet
- Crime Stats Wellington 20141231Document26 pagesCrime Stats Wellington 20141231Amit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Human Development For Everyone: CanadaDocument8 pagesHuman Development For Everyone: CanadaNacho GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Inequalities in Human Development in The 21 Century: Viet NamDocument10 pagesInequalities in Human Development in The 21 Century: Viet NamvalkriyeNo ratings yet
- SAARC in Figures 2016Document16 pagesSAARC in Figures 2016Anish BhusalNo ratings yet
- Economic AssignmentDocument13 pagesEconomic AssignmentZhomeNo ratings yet
- INS-Indonesia - Country Explanatory Note - HDR2016Document8 pagesINS-Indonesia - Country Explanatory Note - HDR2016Agung Arga LabuanNo ratings yet
- LIAM Mortality Investigation Summary Report 2011 2015Document23 pagesLIAM Mortality Investigation Summary Report 2011 2015Hafiz IqbalNo ratings yet
- NevadaOpioidSurveillance Through2018Document12 pagesNevadaOpioidSurveillance Through2018Zac SlotemakerNo ratings yet
- Human Development For Everyone: BangladeshDocument8 pagesHuman Development For Everyone: Bangladeshrash4344No ratings yet
- Union Membership Byte 2019Document14 pagesUnion Membership Byte 2019Center for Economic and Policy ResearchNo ratings yet
- InflationKSAEn Q3-2020 EnglishDocument10 pagesInflationKSAEn Q3-2020 Englishindraseenayya chilakalaNo ratings yet
- Economic Instability in PakistanDocument35 pagesEconomic Instability in PakistanJunaid NaseemNo ratings yet
- Employment RateDocument3 pagesEmployment RateVesnaMMNo ratings yet
- LAC CFS 2017 Ecuador ENDocument4 pagesLAC CFS 2017 Ecuador ENMichaelNo ratings yet
- The Rise of The South:: Human Progress in A Diverse WorldDocument4 pagesThe Rise of The South:: Human Progress in A Diverse WorldHackmeNo ratings yet
- Monthly Review On Price Indices: January, 2013Document12 pagesMonthly Review On Price Indices: January, 2013junaid112No ratings yet
- Inequalities in Human Development in The 21 Century: NigerDocument10 pagesInequalities in Human Development in The 21 Century: NigerJesus AntonioNo ratings yet
- 10.services SectorDocument19 pages10.services SectorAlviro CossemeNo ratings yet
- Survey2018 Hong KongDocument12 pagesSurvey2018 Hong KongBarlici MihaitaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of FSIBL & ICBILDocument12 pagesRatio Analysis of FSIBL & ICBILAmitNo ratings yet
- Middle East and North Africa Quarterly Economic Brief, January 2014: Growth Slowdown Heightens the Need for ReformsFrom EverandMiddle East and North Africa Quarterly Economic Brief, January 2014: Growth Slowdown Heightens the Need for ReformsNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere MapsDocument5 pagesHydrosphere Mapsapi-242748507No ratings yet
- Pittsfield Police Log 9-10-2014Document6 pagesPittsfield Police Log 9-10-2014iBerkshires.comNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument8 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk ReductionJunelle LaguaNo ratings yet
- Spot Report 30 MARCH 2024 Purok 6, San Ignacio, City of IlaganDocument3 pagesSpot Report 30 MARCH 2024 Purok 6, San Ignacio, City of IlaganGelo LibanNo ratings yet
- Zombie Apocalypse Draft FinishedDocument5 pagesZombie Apocalypse Draft Finishedapi-272724747No ratings yet
- Physics Laboratory Safety HandoutDocument2 pagesPhysics Laboratory Safety Handoutnanio_7No ratings yet
- Tot Pt. 1.1-3Document1 pageTot Pt. 1.1-3Cip GrecuNo ratings yet
- Monsoon AlertDocument1 pageMonsoon AlertsarfarazNo ratings yet
- MOA SchoolDocument6 pagesMOA SchoolJoylene SembranoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake DrillDocument68 pagesEarthquake DrillFieNo ratings yet
- Civil Air Patrol News - Mar 2006Document59 pagesCivil Air Patrol News - Mar 2006CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- EOH 3206 Assigment 2 - Highland Tower TragedyDocument8 pagesEOH 3206 Assigment 2 - Highland Tower TragedyHemaNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Action Plans-FormatsDocument12 pagesEmergency and Action Plans-Formatsanoushia alviNo ratings yet
- NY B19 Misc FDR - NYC OEM Situation Report 16Document19 pagesNY B19 Misc FDR - NYC OEM Situation Report 169/11 Document Archive100% (2)
- DITCHINGDocument26 pagesDITCHINGSyyed HasnainNo ratings yet
- Explosives Act & RulesDocument38 pagesExplosives Act & RulesYogesh DhekaleNo ratings yet
- Electrical Shock First AidDocument17 pagesElectrical Shock First Aiddpc876No ratings yet
- GPPB NPM 3-2020 Res Nos 3 and 5-2020Document26 pagesGPPB NPM 3-2020 Res Nos 3 and 5-2020JulPadayaoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response Plan: in Case of Emergency CallDocument11 pagesEmergency Response Plan: in Case of Emergency Callapi-282590709No ratings yet
- Bydrrmp TemplateDocument42 pagesBydrrmp Templatesklinaolibon26No ratings yet
- Lacanaria Et AlDocument142 pagesLacanaria Et AlTlf SlcNo ratings yet
- Research 10Document14 pagesResearch 10Bench Nool BermudoNo ratings yet
- The Harsh Truth About Bugging Out of Cities, by Patrice LewisDocument7 pagesThe Harsh Truth About Bugging Out of Cities, by Patrice LewisEd klussNo ratings yet
- NDRRMC - 201Document11 pagesNDRRMC - 201Mdrrmo Agoo100% (1)
- Deck Ref LibraryDocument25 pagesDeck Ref LibrarycptmehmetkaptanNo ratings yet
- Confined Space: Hole Watch TrainingDocument36 pagesConfined Space: Hole Watch TrainingMalik JunaidNo ratings yet
- Pendulum As Earthquake IndicatorDocument13 pagesPendulum As Earthquake IndicatorSheng ShengNo ratings yet