Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Scan in A Ut
A Scan in A Ut
Uploaded by
Bandaluppi Venkatesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesA SCAN PRESENTATION IN A UT
Original Title
A SCAN IN A UT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA SCAN PRESENTATION IN A UT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesA Scan in A Ut
A Scan in A Ut
Uploaded by
Bandaluppi VenkateshA SCAN PRESENTATION IN A UT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
A-Scan Presentation
• The A-scan presentation displays the amount
of received ultrasonic energy as a function of
time.
• The relative amount of received energy is
plotted along the vertical axis and the elapsed
time
• which may be related to the sound energy
travel time within the material is displayed
along the horizontal axis.
• A-scan presentation to the right, the initial
pulse generated by the transducer is
represented by the signal IP, which is near
time zero.
• As the transducer is scanned along the surface
of the part, four other signals are likely to
appear at different times on the screen.
• When the transducer is in its far left position,
only the IP signal and signal A, the sound
energy reflecting from surface A, will be seen
on the trace.
• As the transducer is scanned to the right, a signal from
the backwall BW will appear later in time, showing that
the sound has traveled farther to reach this surface.
• When the transducer is over flaw B, signal B will
appear at a point on the time scale that is
approximately halfway between the IP signal and
the BW signal.
• Since the IP signal corresponds to the front surface of
the material, this indicates that flaw B is about halfway
between the front and back surfaces of the sample.
• When the transducer is moved over flaw C, signal C will
appear earlier in time since the sound travel path is
shorter and signal B will disappear since sound will no
longer be reflecting from it.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 01 Hardening, Tempering, and Heat TreatmentDocument64 pages01 Hardening, Tempering, and Heat TreatmentBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Radiography Testing (RT)Document5 pagesRadiography Testing (RT)Bandaluppi Venkatesh100% (1)
- Visual TestDocument6 pagesVisual TestBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Pid of A Piping SystemDocument4 pagesPid of A Piping SystemBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- 3D Isometric 5mm A4 Graph Paper PDFDocument1 page3D Isometric 5mm A4 Graph Paper PDFBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Details of Spiral Staircase of HFO TankDocument1 pageFabrication Details of Spiral Staircase of HFO TankBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet
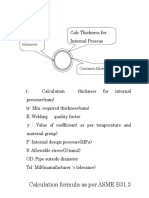
- Calculation Formula As Per ASME B31.3: Mill ToleranceDocument1 pageCalculation Formula As Per ASME B31.3: Mill ToleranceBandaluppi VenkateshNo ratings yet