Professional Documents
Culture Documents
D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in Breathing
D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in Breathing
Uploaded by
Reinette LastrillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in Breathing
D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in Breathing
Uploaded by
Reinette LastrillaCopyright:
Available Formats
D.
Nursing Care Plan
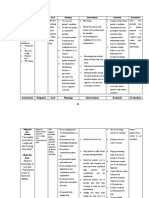
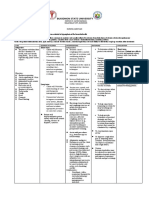
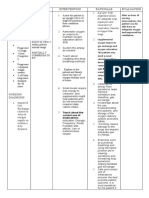
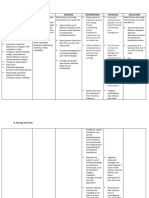
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE DATA Impaired gas exchange After 8 hours of nursing Place patient with A sitting position After 8 hours of nursing
“Nahihirapan talaga siya related to altered oxygen interventions, the client proper body alignment permits interventions, the client
huminga” as verbalized by supply as evidenced by will: for maximum breathing maximum lung was able to:
patient’s daughter difficulty in breathing pattern. excursion and
Demonstrate improved chest expansion. Demonstrate
ventilation and improved
adequate oxygenation Note respiratory rate, Respirations may ventilation and
of tissues by increased depth and ease. observe be increased as a adequate
O2 saturation for use of accessory result of pain oxygenation of
OBJECTIVE DATA
muscles, pursed- lip tissues by increased
Patient indicates, breathing, changes in O2 saturation
Difficulty of breathing
either verbally or skin or mucous
Restlessness through behavior, membrane, pallor, Patient indicates,
Hypoxemia feeling of less cyanosis either verbally or
Dependence on O2 respiratory distress through behavior,
supplementation of 3 Encourage sustained deep These feeling of less
lpm breaths by: techniques respiratory distress
Using demonstration: promotes deep
highlighting slow inspiration,
inhalation, holding end which increases
inspiration for a few oxygenation and
seconds, and passive prevents
exhalation atelectasis.
Utilizing incentive Controlled
spirometer breathing
Requiring the patient to methods may
yawn also aid slow
respirations in
patients who are
tachypneic.
Prolonged
expiration
prevents air
D. Nursing Care Plan
trapping.
This prevents
Encourage small crowding of the
frequent meals. diaphragm
These measures
Teach patient about: allow patient to
pursed-lip breathing participate in
abdominal breathing maintaining
performing relaxation te health status and
chniques improve
performing relaxation ventilation.
techniques
taking prescribed
medications (ensuring
accuracy of dose and
frequency and
monitoring adverse
effects)
scheduling activities to
avoid fatigue and
provide for rest periods
You might also like
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Acute Respiratory DistressDocument2 pagesAcute Respiratory Distressminaanne100% (3)
- Ards Concept MapDocument1 pageArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardo100% (1)
- Biol 1700 - Assignment 2Document16 pagesBiol 1700 - Assignment 2api-456450673100% (1)
- NCP For Scenario BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP For Scenario Breathingmy moznNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Dela Peña NCP 3Document2 pagesDela Peña NCP 3Mark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- OSMUN Case Study 1 Part 2Document8 pagesOSMUN Case Study 1 Part 2Jay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 9/29/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. ZoletaSofiaLopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Paln of Mrs Richard (Clinical Scenario-3)Document20 pagesNursing Care Paln of Mrs Richard (Clinical Scenario-3)Axsa AlexNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPie CanapiNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Nursi NG Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument2 pagesNursi NG Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluations Subjective Data: "I HaveDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluations Subjective Data: "I HaveRicha AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis PneumoniaDocument1 pageNursing Diagnosis PneumoniaPasa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- RusheDocument1 pageRusheCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- Kel 7 - Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesKel 7 - Nursing Care PlanWahda PrameswariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPAnne Nicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care Planalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoDocument19 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoKen BaxNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan: Lipa City CollegesVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- NCP For CAP TB.Document5 pagesNCP For CAP TB.Cherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- CopdDocument6 pagesCopdapi-3717941100% (2)
- Innefective Airway Clearance NCPDocument4 pagesInnefective Airway Clearance NCPAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- Careplan 1Document11 pagesCareplan 1ligaba1559No ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective AirwayRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute BronchitisDocument9 pagesNCP Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP Copdjcgarcia06192002No ratings yet
- Subjective: IndependentDocument2 pagesSubjective: IndependentRea LynNo ratings yet
- Problem: DOB ASSESSMENT S: "Hindi Siya MakahingaDocument13 pagesProblem: DOB ASSESSMENT S: "Hindi Siya MakahingauzumakiruleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNo ratings yet
- NCP of PnuemoniaDocument13 pagesNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Valeriano, NCPDocument4 pagesValeriano, NCPVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- Bukidnon State University: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument1 pageBukidnon State University: Subjective: Short Term: Short TermSimbo Ralph JulesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIrish Jane GalloNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Task NCPDocument12 pagesTask NCPferdy ilhamNo ratings yet
- Iudmc ActivityDocument10 pagesIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.RDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.Rcen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- NCP Room 303 TelarmaDocument2 pagesNCP Room 303 TelarmaasdasdNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Document6 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Princess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Fuel Minds: Phase 5: Breathing Exercises for Mental ClarityFrom EverandFuel Minds: Phase 5: Breathing Exercises for Mental ClarityNo ratings yet
- THE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeFrom EverandTHE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeNo ratings yet
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Chronic Pain Related ToDocument2 pagesD. Nursing Care Plan: Chronic Pain Related ToReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- MAHMOUD, Mohamed Z. Bs MDT - 2ADocument1 pageMAHMOUD, Mohamed Z. Bs MDT - 2AReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Reinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- General Education Professional Education Major (Pre-School) : Breto, Angelica Mae CDocument49 pagesGeneral Education Professional Education Major (Pre-School) : Breto, Angelica Mae CReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Reinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- Project in CwtsDocument23 pagesProject in CwtsReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- Alabang-Zapote Road, Pamplona 3, Las Piñas City, Metro Manila 1740, PHILIPPINES WWW - Perpetualdalta.edu - PH - +63 (02) 871-06-39 Loc 113Document1 pageAlabang-Zapote Road, Pamplona 3, Las Piñas City, Metro Manila 1740, PHILIPPINES WWW - Perpetualdalta.edu - PH - +63 (02) 871-06-39 Loc 113Reinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- Lungs Ibstyle QnsDocument2 pagesLungs Ibstyle QnsGeorge KoukouvesNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 - Chapter 11 - Blood - Chapter Notes: Here Is A Micrographs Showing Formed Elements in Human BloodDocument7 pagesBiology 12 - Chapter 11 - Blood - Chapter Notes: Here Is A Micrographs Showing Formed Elements in Human BloodChan KarlokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Structure and Function of The Pulmonary System - Nursing Test BanksDocument25 pagesChapter 25 - Structure and Function of The Pulmonary System - Nursing Test BanksNeLNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank List HariyanaDocument22 pagesBlood Bank List HariyanadaniNo ratings yet
- HSB QA What Is DigestionDocument37 pagesHSB QA What Is DigestionVivienne WrightNo ratings yet
- Activity Journal Mobile Blood Donation Advocacy 1Document3 pagesActivity Journal Mobile Blood Donation Advocacy 1Cherrymae BenzonNo ratings yet
- Speed Dating CardsDocument15 pagesSpeed Dating Cardsapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Breathing With Your DiaphragmDocument6 pagesBreathing With Your DiaphragmSarasvati SháktiNo ratings yet
- Kerry GomesDocument23 pagesKerry GomesAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of MicturictionDocument19 pagesAnatomy of MicturictionsalomonmarinaNo ratings yet
- TH E RE SP IRA TO RY SY ST EM: Learning ObjectivesDocument36 pagesTH E RE SP IRA TO RY SY ST EM: Learning Objectivesmaria tafaNo ratings yet
- 27 Acvtivity SheetDocument6 pages27 Acvtivity SheetHart OlpendaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentUjjwal MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument15 pagesHuman Brainanjalirajendran100% (1)
- Psychiatric Clerking Sheet 3 NovDocument5 pagesPsychiatric Clerking Sheet 3 Novsiti nur aishah jalilNo ratings yet
- Animals Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesAnimals Circulatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- SCI Bladder SurgeryDocument4 pagesSCI Bladder SurgeryKrish NevageNo ratings yet
- Power Nap: The Three R'S: Rest, Relaxation, and RecoveryDocument4 pagesPower Nap: The Three R'S: Rest, Relaxation, and Recoveryalimirza18No ratings yet
- Human Body PuzzleDocument1 pageHuman Body Puzzleshara_inznNo ratings yet
- Morning WoodDocument3 pagesMorning WoodSaurav VaruasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Bundle Breathing Foundations 1.5 G1aqan PDFDocument57 pagesLesson Bundle Breathing Foundations 1.5 G1aqan PDFTrevor RashadNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument55 pagesBlood Transfusionanand7504100% (2)
- Birth Partners' Affirmations Script..Document6 pagesBirth Partners' Affirmations Script..nadyaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument66 pagesUrinary SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Week 1 BIO Learn - ExcretionDocument22 pagesWeek 1 BIO Learn - ExcretionEseel AlsammarraieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: ObjectivesChaden Al TawilNo ratings yet
- Breathing ExercisesDocument22 pagesBreathing ExercisesRachanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3 - Digestive Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Assignment On: Oxygen Administrration (Nasal Catheter, Mask, Oxygen Hood& Cpap)Document10 pagesAssignment On: Oxygen Administrration (Nasal Catheter, Mask, Oxygen Hood& Cpap)Suganthi ParthibanNo ratings yet