Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Uploaded by
Princess Ting TingCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Garam Bab 8Document29 pagesGaram Bab 8ctohNo ratings yet
- Salt 2020 PDFDocument42 pagesSalt 2020 PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- PH Indicator Acid Neutral BaseDocument6 pagesPH Indicator Acid Neutral BaseYasser ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- SAlt Preperation - 1Document14 pagesSAlt Preperation - 1youssefelassal2009No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableAlliyah vidanesNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry - SaltDocument6 pagesForm 4 Chemistry - SaltSze NingNo ratings yet
- Must Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Document4 pagesMust Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Chaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Wan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffDocument33 pagesWan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffThilagavathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SALTSDocument75 pagesChapter 8 SALTSSiti Hajar Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Types of OxideDocument1 pageTypes of OxideTamoya ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Document29 pagesChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Heat Cao S Ho Ca Oh Aq: Hol H G OgDocument12 pagesHeat Cao S Ho Ca Oh Aq: Hol H G OgValyanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Name: Nur Farahanna BT SuidDocument7 pagesChemistry: Name: Nur Farahanna BT SuidNur AinnajwaNo ratings yet
- 8b Qualitative Analysis of SaltsDocument8 pages8b Qualitative Analysis of SaltsIshen PerumalNo ratings yet
- STD 7 Question Bank With Answers-Acids Bases and SaltsDocument14 pagesSTD 7 Question Bank With Answers-Acids Bases and Saltssmritijha1502No ratings yet
- 8 SaltsDocument22 pages8 SaltsHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Properties of Silver (I), Mercury (I) and Lead (II) SaltsDocument7 pagesProperties of Silver (I), Mercury (I) and Lead (II) SaltsnothaboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument16 pagesChapter 8 - Acids, Bases and Saltsjannat amgadNo ratings yet
- 02 AcidsSalts&SolubilityDocument2 pages02 AcidsSalts&SolubilityDiamondNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Some IonsDocument42 pagesQualitative Analysis of Some IonsShaina Mae ContilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SaltsDocument14 pagesChapter 8: SaltsLynn HengNo ratings yet
- PHCH112LDocument3 pagesPHCH112LRhaine Nicole CodezarNo ratings yet
- Cha 11Document11 pagesCha 11Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- SCCH 211 BACE Part For Exam 2023Document29 pagesSCCH 211 BACE Part For Exam 2023rooni202061No ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision NotesDocument12 pagesJee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision Noteslakshyajeetbhati05No ratings yet
- Chemistry F4 SaltsDocument13 pagesChemistry F4 Saltscivichitam18No ratings yet
- Chemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Document26 pagesChemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Notes Updates SaltsDocument32 pagesNotes Updates SaltsLim Jing YeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week 2 4Document6 pagesChemistry Week 2 4nkweguedward1No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 EquationsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11No ratings yet
- Part IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesPart IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisCharmine HolmesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDocument32 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDocument3 pagesReactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDarshanaK 728714No ratings yet
- SALTDocument22 pagesSALTparitoshNo ratings yet
- G12 Viva Chem Prac Part 3Document8 pagesG12 Viva Chem Prac Part 3Its meNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases SummaryDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases SummaryTan Yong KhaiNo ratings yet
- Booklet On Acid and Base and Redox MSDocument43 pagesBooklet On Acid and Base and Redox MShalahossam8899No ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesAcid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisKronix GamingNo ratings yet
- Cations I-V, Anions I-VDocument6 pagesCations I-V, Anions I-VMarecarNo ratings yet
- Write The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Document2 pagesWrite The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- WS 1 Mole - FormulaDocument6 pagesWS 1 Mole - FormulaSEAW FUI MINGNo ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SALT / GARAM 8.1 Salt / Garam: Salts UsesDocument40 pagesChapter 8: SALT / GARAM 8.1 Salt / Garam: Salts UsesFion0% (1)
- Chemistry Info SheetDocument3 pagesChemistry Info SheetClara GreenNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument3 pagesQualitative AnalysisYukeling TayNo ratings yet
- Stuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListDocument2 pagesStuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListedeceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupJan MezoNo ratings yet
- Basic Inorganic Chemistry PHR 125: Prof. Dr. Mona BedairDocument33 pagesBasic Inorganic Chemistry PHR 125: Prof. Dr. Mona BedairAvvari AnnamaniNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 NotesDocument19 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Metal ReactivityDocument30 pagesMetal ReactivityMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- OXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)Document4 pagesOXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)gauri guptaNo ratings yet
- Notes On SaltsDocument4 pagesNotes On SaltsFelix S100% (1)
- 8A Salts - AnswerDocument14 pages8A Salts - AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- 10th OswaalDocument24 pages10th OswaalAbhishek DwivediNo ratings yet
- T.Y.B.sc Inorganic Practical 2017 Sem IIDocument29 pagesT.Y.B.sc Inorganic Practical 2017 Sem IIshriyansh opNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 - Daesan - General - EN - 201201Document1 pageISO 9001 - Daesan - General - EN - 201201QcNo ratings yet
- Safer Tattoing enDocument105 pagesSafer Tattoing enCharleneNo ratings yet
- Duraslurry: Cementitious Waterproofing SlurryDocument2 pagesDuraslurry: Cementitious Waterproofing Slurryengramir070% (1)
- Kinetices IB QuestionsDocument5 pagesKinetices IB QuestionsAhmed AbdelgawadNo ratings yet
- TABU Spa Pre Dyed CatalogueDocument97 pagesTABU Spa Pre Dyed CataloguePratik SavlaNo ratings yet
- 5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersDocument2 pages5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersAlan MartínNo ratings yet
- WaterproofingDocument23 pagesWaterproofingKenneth Ituralde BesmonteNo ratings yet
- Complexation and Protein BindingDocument15 pagesComplexation and Protein BindingShivraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- Clout and Simonson-Precambrian Iron Formations and Iron Formation-Hosted Iron Ore DepositsDocument38 pagesClout and Simonson-Precambrian Iron Formations and Iron Formation-Hosted Iron Ore Deposits作者月No ratings yet
- Lindsay Et Al, 1959 IIIDocument4 pagesLindsay Et Al, 1959 IIIexportar2299No ratings yet
- A Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and PunarnarishtaDocument5 pagesA Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and Punarnarishtaalnrmamckoppa19No ratings yet
- Chemistry SheetDocument10 pagesChemistry Sheetbakr ferasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 CarbohydratesDocument44 pagesLesson 2 CarbohydratesEloisa Canlas - QuizonNo ratings yet
- Homework Questions For Writing PracticeDocument8 pagesHomework Questions For Writing Practicenirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- Grade 9 2nd Quarter Module 4 Carbon A Special Element FinalizedDocument26 pagesGrade 9 2nd Quarter Module 4 Carbon A Special Element FinalizedAkisha Jen CalicdanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Pure and Stable Chitosan Nanofibers by Electrospinning in The Presence of Poly (Ethylene Oxide)Document16 pagesPreparation of Pure and Stable Chitosan Nanofibers by Electrospinning in The Presence of Poly (Ethylene Oxide)يحيى بورغدةNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial FinishesDocument32 pagesAntimicrobial Finisheschahat anejaNo ratings yet
- AcridineDocument7 pagesAcridineDr. Sulochana BhalekarNo ratings yet
- السلائف والكيمياوياتDocument21 pagesالسلائف والكيمياوياتZaoui Abd El HafidNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortarDocument10 pagesFactors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortaraikalessNo ratings yet
- Chemistry July 2019 STD 12th Science HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperDocument3 pagesChemistry July 2019 STD 12th Science HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperGoneNo ratings yet
- Chloride Corrosion Threshold of Reinforcing Steel in Alkaline Solutions-Open-Circuit Immersion TestsDocument10 pagesChloride Corrosion Threshold of Reinforcing Steel in Alkaline Solutions-Open-Circuit Immersion TestsshameekaNo ratings yet
- Biorad Control - 89730 L2Document2 pagesBiorad Control - 89730 L2mohammad.khanNo ratings yet
- CHM 477 Experiment 3 4 5 PDFDocument10 pagesCHM 477 Experiment 3 4 5 PDFAhmad ZakwanNo ratings yet
- How To Make PhosphorusDocument1 pageHow To Make Phosphorusmythtek100% (1)
- 13 Hydrogen Production TechnologiesDocument8 pages13 Hydrogen Production Technologiesthisisanonymous6254No ratings yet
- National Competition Theoretical Tasks Solutions 2019Document23 pagesNational Competition Theoretical Tasks Solutions 2019Thái Khắc MạnhNo ratings yet
- Bull'S Eye Content: C H E M I S T R YDocument3 pagesBull'S Eye Content: C H E M I S T R YHitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and HalogenoalkanesDocument67 pagesAlkanes and HalogenoalkanesRAFIDNo ratings yet
- Parofluor PTD3026 enDocument16 pagesParofluor PTD3026 enVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Uploaded by
Princess Ting TingOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Chapter 8: Salts: Flow Chart of Preparation of Salts
Uploaded by
Princess Ting TingCopyright:
Available Formats
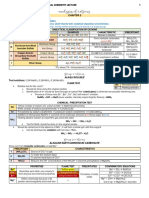
Chapter 8 : Salts
Flow chart of preparation of salts
Precipitation of salt by double Example :
Soluble in water decomposition reaction PbI2, PbCl2, PbSO4,
No
BaSO4, AgCl, CaSO4
Yes
Salts of K+, Na+, NH4+?
No
Yes
Neutralisation Acid + metal oxide salt + water
Acid + alkali salt + water Acid + metal salt + hydrogen gas
Acid + metal carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide
Example : KNO3, NaCl, (NH4)2SO4
Example : ZnCl2, CuSO4, Pb(NO3)2, Mg(NO3)2
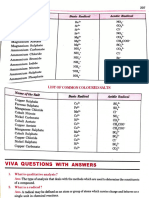
Colour of some cation/ anion/ substance in solid and aqueous solution
Salt/metal oxide Colour
Solid Aqueous solution
Potassium salts, sodium salts, calcium salts,
magnesium salts, aluminium salts, zinc salts, White Colourless
lead(II) salts, ammonium salts, barium salts,
silver salts (If the anion is colourless)
Nitrate salts (NO3-), chloride salts (Cl-),
carbonate salts (CO32-),sulphate salts (SO42-) White Colourless
(If the cation is colourless)
Copper(II) salts :
Copper(II) carbonate Green Insoluble
Copper(II) sulphate, Copper(II) nitrate, Blue Blue
Copper(II) chloride
Copper(II) oxide Black Insoluble
Iron(II) salts :
Iron(II) sulphate, Iron(II) nitrate, Iron(II) Green Pale green
chloride
Iron(III) salts : Yellow, yellowish-
Iron(III) sulphate, Iron(III) nitrate, Iron(III) Brown brown, brown
chloride (depends on the
concentration )
Zinc oxide Yellow when hot ; Insoluble
White when cold
Lead(II) oxide Brown when hot ; Insoluble
Yellow when cold
Solubility in water
Salts Solubility in water
Sodium salts
Potassium salts All soluble
Ammonium salts
Nitrate salts All soluble
Chloride salts All soluble except :
Lead(II) chloride, PbCl2 (soluble in hot
water but insoluble in cold water)
Silver chloride, AgCl
Sulphate salts All soluble except :
Lead(II) sulphate, PbSO4
Barium sulphate, BaSO4
Calcium sulphate, CaSO4
Carbonate salts All insoluble except :
Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3
Potassium carbonate, K2CO3
Ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3
Metal oxides All insoluble except :
Sodium oxide, Na2O
Potassium oxide, K2O
Calcium oxide, CaO (slightly soluble)
Metal hydroxides All insoluble except :
Sodium hydroxide, NaOH
Potassium hydroxide, KOH
Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2 and
barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 (slightly
soluble)
Action of heat on carbonate salts
1. All carbonate salts decompose when heated except sodium carbonate and
potassium carbonate.
2. Decomposition of carbonate salts on heating produce carbon dioxide gas.
Carbonate salts Action of heat
Sodium carbonate Not decompose by heat
Potassium carbonate
Decompose on heating to produce carbon dioxide gas and
metal oxide. Example :
Calcium carbonate CaCO3 (S) CaO (S) + CO2 (g)
Magnesium carbonate MgCO3 (S) MgO (S) + CO2 (g)
Aluminium carbonate Al2(CO3)3 (S) Al2O3 (S) + 3CO2 (g)
Zinc carbonate ZnCO3 (S) ZnO (S) + CO2 (g)
Lead(II) carbonate PbCO3 (S) PbO (S) + CO2 (g)
Copper(II) carbonate CuCO3 (S) CuO (S) + CO2 (g)
Action of heat on nitrate salts
1. All nitrate salts decompose when heated.
Nitrate salts Action of heat
Decompose on heating to produce oxygen gas and metal nitrite.
Example :
Sodium nitrate 2NaNO3 (S) 2NaNO2 (S) + O2 (g)
Potassium nitrate 2KNO3 (S) 2KNO2 (S) + O2 (g)
Decompose on heating to produce oxygen gas, nitrogen dioxide
gas and metal oxide. Example :
Calcium nitrate 2Ca(NO3)2 (S) 2CaO (S) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Magnesium nitrate 2Mg(NO3)2 (S) 2MgO (S) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Aluminium nitrate 4Al(NO3)3 (S) 2Al2O3 (S) + 12NO2 (g) + 3O2 (g)
Zinc nitrate 2Zn(NO3)2 (S) 2ZnO (S) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Lead(II) nitrate 2Pb(NO3)2 (S) 2PbO (S) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Copper(II) nitrate 2Cu(NO3)2 (S) 2CuO (S) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Action of heat on sulphate salts
1. Usually sulphate salts are not decomposed by heat.
2. Only a few sulphate salts decompose when heated strongly.
Carbonate salts Action of heat
Decompose on heating to produce water vapour, sulphur
dioxide, sulphur trioxide and iron(III) oxide.
Iron(II) sulphate 2FeSO4 . 7H2O Fe2O3 (S) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g) + 3H2O (l)
Decompose on heating to produce sulphur trioxide gas and
metal oxide. Example :
Zinc sulphate 2ZnSO4 (S) ZnO (S) + SO3 (g)
Copper(II) sulphate 2CuSO4 (S) CuO (S) + SO3 (g)
Iron(III) sulphate Fe2(SO4)3 (S) Fe2O3 (S) + SO3 (g)
Sublimes and decomposes to produce ammonia gas and fumes
of sulphuric acid.
Ammonium sulphate (NH4)2 SO4 (S) 2NH3 (g) + H2SO4 (g)
Action of heat on chloride salts
1. All chloride salts are not decomposed by heat except ammonium chloride.
2. Sublimes and decomposes to produce white fumes containing ammonia gas and
hydrogen chloride gas.
NH4Cl (S) NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
Physical and chemical properties of gas and test for various gases.
Gas Physical properties Chemical Test
properties
Colour Smell
Oxygen gas - - Neutral Rekindles a glowing splinter.
Hydrogen - - Neutral Gives ‘pop’ sound when
gas burning splinter is introduced.
Carbon - - Acidic Turn limewater milky.
dioxide gas
Ammonia - Pungent Alkali White fumes with glass rod
gas dipped in concentrated
hydrochloric acid, HCl.
Gas Physical properties Chemical Test
properties
Colour Smell
Nitrogen Brown Pungent Acidic Turn damp litmus paper from
dioxide gas blue to red.
Chlorine gas Greenish Pungent Acidic Turn damp litmus paper from
yellow blue to red, then bleached.
Hydrogen Colourless Pungent Acidic Fumes with glass rod dipped in
chloride gas concentrated ammonia, NH3
solution.
Sulphur Colourless Pungent Acidic Turn acidified Potassium
dioxide gas manganate(VII) solution,
KMnO4 from purple to
colourless.
Turn acidified potassium
dichromate (VI), K2Cr2O7
solution from orange to
green.
Hydrogen Colourless Pungent Acidic Damp lead(II) ethanoate paper
sulphide gas (rotten egg) turns black.
Water vapour Colourless Odourless Neutral White anhydrous copper(II)
sulphate turns blue.
To identify cations by using aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Cation + Aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH
No change Form precipitate
NH4+
White Coloured
precipitate precipitate
Pb2+,Zn2+,Al3+, Fe2+,Fe3+,Cu2+
Ca2+,Mg2+
Dissolves in excess Insoluble in excess Green Brown Blue
precipitate precipitate precipitate
Pb2+,Zn2+,Al3+ Ca2+,Mg2+
Fe2+ Fe3+ Cu2+
To identify cations by using aqueous ammonia.
Cation + Ammonia aqueous, NH4OH
No change Form precipitate
NH4+, Ca2+
White Coloured
precipitate precipitate
Pb2+,Zn2+,Al3+, Fe2+,Fe3+,Cu2+
Mg2+
Dissolves in excess Insoluble in excess Green Brown Blue
precipitate precipitate precipitate,
Zn2+ Pb2+,Mg2+,Al3+ dissolves in
Fe2+ Fe3+
excess
Cu2+
Confirmatory tests for iron(II) ion and iron(III) ion
Cation Potassium Potassium Potassium Potassium
hexacyanoferrate(II) hexacyanoferrate(III thiocyanate manganate(VII)
solution,K4Fe(CN)6 ) solution,K3Fe(CN)6 solution,KSCN solution,
KMNO4
Fe2+ Pale blue precipitate Dark blue precipitate Pale red Decolourises
colouration the purple
solution
Fe3+ Dark blue precipitate Greenish-brown Blood red
solution colouration
Identification of cations by reaction with Nessler’s reagent, solution of chloride ions, solution of sulphate ions, solution of carbonate ions and
potassium iodide solution.
Cation Nessler’s Dilute HCl or NaCl solution Dilute H2SO4 or Na2SO4 Na2CO3 solution Potassium iodide solution
reagent solution
Na+ - - - -
Ca2+ - - White precipitate formed. White precipitate formed. -
Ca2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) CaSO4(s) Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) CaCO3(s)
Mg2+ - - - White precipitate formed. -
Mg2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) MgCO3(s)
Al3+ - - - White precipitate formed. -
Al3+(aq) + CO32-(aq) Al2(CO3)3(s)
Zn2+ - - - White precipitate formed. -
Zn (aq) + CO32-(aq) ZnCO3(s)
2+
Pb2+ - White precipitate formed. White precipitate formed. White precipitate formed. Yellow precipitate formed.
Pb2+(aq) + Cl-(aq) PbCl2(s) Pb2+(aq) + SO42 (aq) PbSO4(s) Pb2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) PbCO3(s) Pb2+(aq) + I-(aq) PbI2(s)
Soluble in hot water Soluble in hot water
Fe2+ - - - Green precipitate formed. -
Fe (aq) + CO32-(aq) FeCO3(s)
2+
Fe3+ - - - Brown precipitate formed. Reddish-brown solution.
Fe3+(aq) + CO32-(aq) Fe2(CO3)3(s) 2Fe3+(aq) + 2I-(aq) 2Fe2+(aq)
+ I2(aq)
Cu2+ - - - Blue precipitate formed. White precipitation in brown
Cu (aq) + CO32-(aq) CuCO3(s)
2+
solution.
2Cu2+(aq) + 4I-(aq) 2CuI(s)
+ I2(aq)
NH4+ Brown - - - -
precipitate
Tests for anions
Anion Dilute acid Dilute HCl followed by BaCl2 Dilute HNO3 + AgNO3 solution, Dilute H2SO4 + FeSO4 solution +
solution (or dilute HNO3 then add NH3 solution concentrated H2SO4
followed by Ba(NO3)2 solution)
CO32- Effervescence.
Colourless gas turns lime water - - -
milky.
CO32-(aq) + 2H+ CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Cl- - - White precipitate is formed. -
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl(s)
SO42- - White precipitate is formed. - -
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) BaSO4(s)
NO3- - - - Brown ring is formed.
You might also like
- Garam Bab 8Document29 pagesGaram Bab 8ctohNo ratings yet
- Salt 2020 PDFDocument42 pagesSalt 2020 PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- PH Indicator Acid Neutral BaseDocument6 pagesPH Indicator Acid Neutral BaseYasser ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- SAlt Preperation - 1Document14 pagesSAlt Preperation - 1youssefelassal2009No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableAlliyah vidanesNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry - SaltDocument6 pagesForm 4 Chemistry - SaltSze NingNo ratings yet
- Must Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Document4 pagesMust Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Chaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- 3 Experiment ChemistryDocument30 pages3 Experiment ChemistryThangavel SarujanNo ratings yet
- Wan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffDocument33 pagesWan Noor Afifah BT Wan YusoffThilagavathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SALTSDocument75 pagesChapter 8 SALTSSiti Hajar Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Types of OxideDocument1 pageTypes of OxideTamoya ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Document29 pagesChemistry F4: Theme 3: Interaction Between Matters Chapter 6: Acid, Base & Salt (6.8 - 6.11)Novah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Heat Cao S Ho Ca Oh Aq: Hol H G OgDocument12 pagesHeat Cao S Ho Ca Oh Aq: Hol H G OgValyanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Name: Nur Farahanna BT SuidDocument7 pagesChemistry: Name: Nur Farahanna BT SuidNur AinnajwaNo ratings yet
- 8b Qualitative Analysis of SaltsDocument8 pages8b Qualitative Analysis of SaltsIshen PerumalNo ratings yet
- STD 7 Question Bank With Answers-Acids Bases and SaltsDocument14 pagesSTD 7 Question Bank With Answers-Acids Bases and Saltssmritijha1502No ratings yet
- 8 SaltsDocument22 pages8 SaltsHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Properties of Silver (I), Mercury (I) and Lead (II) SaltsDocument7 pagesProperties of Silver (I), Mercury (I) and Lead (II) SaltsnothaboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument16 pagesChapter 8 - Acids, Bases and Saltsjannat amgadNo ratings yet
- 02 AcidsSalts&SolubilityDocument2 pages02 AcidsSalts&SolubilityDiamondNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Some IonsDocument42 pagesQualitative Analysis of Some IonsShaina Mae ContilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SaltsDocument14 pagesChapter 8: SaltsLynn HengNo ratings yet
- PHCH112LDocument3 pagesPHCH112LRhaine Nicole CodezarNo ratings yet
- Cha 11Document11 pagesCha 11Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- SCCH 211 BACE Part For Exam 2023Document29 pagesSCCH 211 BACE Part For Exam 2023rooni202061No ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision NotesDocument12 pagesJee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision Noteslakshyajeetbhati05No ratings yet
- Chemistry F4 SaltsDocument13 pagesChemistry F4 Saltscivichitam18No ratings yet
- Chemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Document26 pagesChemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Notes Updates SaltsDocument32 pagesNotes Updates SaltsLim Jing YeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week 2 4Document6 pagesChemistry Week 2 4nkweguedward1No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 EquationsDocument11 pagesLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11No ratings yet
- Part IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesPart IV Acids and Alkalis: LQ 01 (Answer) Properties of Acids and AlkalisCharmine HolmesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDocument32 pagesChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDocument3 pagesReactions of Metals With Dilute AcidsDarshanaK 728714No ratings yet
- SALTDocument22 pagesSALTparitoshNo ratings yet
- G12 Viva Chem Prac Part 3Document8 pagesG12 Viva Chem Prac Part 3Its meNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases SummaryDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases SummaryTan Yong KhaiNo ratings yet
- Booklet On Acid and Base and Redox MSDocument43 pagesBooklet On Acid and Base and Redox MShalahossam8899No ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesAcid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisKronix GamingNo ratings yet
- Cations I-V, Anions I-VDocument6 pagesCations I-V, Anions I-VMarecarNo ratings yet
- Write The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Document2 pagesWrite The Formulas For The Following Ionic Compounds:: Bonding and Naming WS 4Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- WS 1 Mole - FormulaDocument6 pagesWS 1 Mole - FormulaSEAW FUI MINGNo ratings yet
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesXGC Ahssn YtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SALT / GARAM 8.1 Salt / Garam: Salts UsesDocument40 pagesChapter 8: SALT / GARAM 8.1 Salt / Garam: Salts UsesFion0% (1)
- Chemistry Info SheetDocument3 pagesChemistry Info SheetClara GreenNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument3 pagesQualitative AnalysisYukeling TayNo ratings yet
- Stuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListDocument2 pagesStuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListedeceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Cations: - Ions, Which Form Compounds, Having Similar Properties Are Placed in A Single GroupJan MezoNo ratings yet
- Basic Inorganic Chemistry PHR 125: Prof. Dr. Mona BedairDocument33 pagesBasic Inorganic Chemistry PHR 125: Prof. Dr. Mona BedairAvvari AnnamaniNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 NotesDocument19 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 2 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Metal ReactivityDocument30 pagesMetal ReactivityMin Nyo SinNo ratings yet
- OXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)Document4 pagesOXIDES (Metals & Non-Metals)gauri guptaNo ratings yet
- Notes On SaltsDocument4 pagesNotes On SaltsFelix S100% (1)
- 8A Salts - AnswerDocument14 pages8A Salts - AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- 10th OswaalDocument24 pages10th OswaalAbhishek DwivediNo ratings yet
- T.Y.B.sc Inorganic Practical 2017 Sem IIDocument29 pagesT.Y.B.sc Inorganic Practical 2017 Sem IIshriyansh opNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 - Daesan - General - EN - 201201Document1 pageISO 9001 - Daesan - General - EN - 201201QcNo ratings yet
- Safer Tattoing enDocument105 pagesSafer Tattoing enCharleneNo ratings yet
- Duraslurry: Cementitious Waterproofing SlurryDocument2 pagesDuraslurry: Cementitious Waterproofing Slurryengramir070% (1)
- Kinetices IB QuestionsDocument5 pagesKinetices IB QuestionsAhmed AbdelgawadNo ratings yet
- TABU Spa Pre Dyed CatalogueDocument97 pagesTABU Spa Pre Dyed CataloguePratik SavlaNo ratings yet
- 5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersDocument2 pages5.7-5.10 Naming Mixed Ionic and Covalent Compounds AnswersAlan MartínNo ratings yet
- WaterproofingDocument23 pagesWaterproofingKenneth Ituralde BesmonteNo ratings yet
- Complexation and Protein BindingDocument15 pagesComplexation and Protein BindingShivraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- Clout and Simonson-Precambrian Iron Formations and Iron Formation-Hosted Iron Ore DepositsDocument38 pagesClout and Simonson-Precambrian Iron Formations and Iron Formation-Hosted Iron Ore Deposits作者月No ratings yet
- Lindsay Et Al, 1959 IIIDocument4 pagesLindsay Et Al, 1959 IIIexportar2299No ratings yet
- A Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and PunarnarishtaDocument5 pagesA Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and Punarnarishtaalnrmamckoppa19No ratings yet
- Chemistry SheetDocument10 pagesChemistry Sheetbakr ferasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 CarbohydratesDocument44 pagesLesson 2 CarbohydratesEloisa Canlas - QuizonNo ratings yet
- Homework Questions For Writing PracticeDocument8 pagesHomework Questions For Writing Practicenirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- Grade 9 2nd Quarter Module 4 Carbon A Special Element FinalizedDocument26 pagesGrade 9 2nd Quarter Module 4 Carbon A Special Element FinalizedAkisha Jen CalicdanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Pure and Stable Chitosan Nanofibers by Electrospinning in The Presence of Poly (Ethylene Oxide)Document16 pagesPreparation of Pure and Stable Chitosan Nanofibers by Electrospinning in The Presence of Poly (Ethylene Oxide)يحيى بورغدةNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial FinishesDocument32 pagesAntimicrobial Finisheschahat anejaNo ratings yet
- AcridineDocument7 pagesAcridineDr. Sulochana BhalekarNo ratings yet
- السلائف والكيمياوياتDocument21 pagesالسلائف والكيمياوياتZaoui Abd El HafidNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortarDocument10 pagesFactors Influencing The Sulphate Resistance of Cement Concrete and MortaraikalessNo ratings yet
- Chemistry July 2019 STD 12th Science HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperDocument3 pagesChemistry July 2019 STD 12th Science HSC Maharashtra Board Question PaperGoneNo ratings yet
- Chloride Corrosion Threshold of Reinforcing Steel in Alkaline Solutions-Open-Circuit Immersion TestsDocument10 pagesChloride Corrosion Threshold of Reinforcing Steel in Alkaline Solutions-Open-Circuit Immersion TestsshameekaNo ratings yet
- Biorad Control - 89730 L2Document2 pagesBiorad Control - 89730 L2mohammad.khanNo ratings yet
- CHM 477 Experiment 3 4 5 PDFDocument10 pagesCHM 477 Experiment 3 4 5 PDFAhmad ZakwanNo ratings yet
- How To Make PhosphorusDocument1 pageHow To Make Phosphorusmythtek100% (1)
- 13 Hydrogen Production TechnologiesDocument8 pages13 Hydrogen Production Technologiesthisisanonymous6254No ratings yet
- National Competition Theoretical Tasks Solutions 2019Document23 pagesNational Competition Theoretical Tasks Solutions 2019Thái Khắc MạnhNo ratings yet
- Bull'S Eye Content: C H E M I S T R YDocument3 pagesBull'S Eye Content: C H E M I S T R YHitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and HalogenoalkanesDocument67 pagesAlkanes and HalogenoalkanesRAFIDNo ratings yet
- Parofluor PTD3026 enDocument16 pagesParofluor PTD3026 enVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet