Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algoritmo Peritoneal Effusion
Algoritmo Peritoneal Effusion
Uploaded by
Juliana Torres GarciaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algoritmo Peritoneal Effusion
Algoritmo Peritoneal Effusion
Uploaded by
Juliana Torres GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Tree Diagnostics / Emergency Medicine Peer reviewed
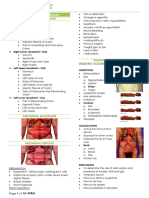
Peritoneal Effusion
abdominocentesis &
Peritoneal Effusion characterization of fluid
Pure transudate Modified transudate Chylous effusion (very rare)
• Clear, colorless • Clear, straw colored • White/opaque
• TP <2.5 g/dL • TP >2.5 g/dL • TP >2 g/dL
• <1000 cells/µL • 1000–7000 cells/µL • variable cell count
• Mononuclear cells • Mononuclear cells, increasing • Predominantly small
predominate numbers of neutrophils, lymphocytes
lymphocytes • Effusion triglycerides > serum
triglycerides
Low albumin (<1.5–
1.8 g/dL)?
Portal hypertension FasT, chest radiographs
• Liver disease
• right-sided heart failure
Yes No (auscultation, echocardiogram,
chest radiographs) Trauma or thoracic duct rupture?
• Liver failure/disease
• addison’s disease
No Yes
• Protein-losing
nephropathy
• Protein-losing
enteropathy • Treat as necessary
• surgery if indicated
• Monitor
• abdominal Us abdominal Us normal?
• Bile acids
• resting cortisol levels
• Urinalysis (UP:C if
• Effusion creatinine >2¥ serum
indicated) No Yes creatinine
• vitamin B12/folate
• Effusion potassium >1.4¥ serum
potassium
• vasculitis (rare)
• rickettsial disease
• Immune-mediated
disease
Uroabdomen (transudate/modified
transudate)
Pancreatitis Hepatic splenic/ neoplasia
disease intestinal surgery may be indicated
torsion
FAST = focused assessment with sonography for trauma,
supportive Biopsy + FIP = feline infectious peritonitis, PT = prothrombin time,
surgery Chemotherapy
treatment bile acids PTT = partial thromboplastin time, TP = total protein,
UP:C = urine protein:creatinine, US = ultrasound
18 cliniciansbrief.com • October 2013
Gretchen Statz, DVM, DACVECC
Internal Medicine Consultant
Antech Diagnostics
Exudate Hemorrhagic effusion Malignant effusion
• Turbid, hemorrhagic to purulent • PCv >10% • Light yellow, clear to cloudy
• TP >2.5 g/dL (often >3 g/dL) • TP >2.5 g/dL • TP >2.5 g/dL
• >5000 cells/µL • variable cell count • variable cell count
• neutrophils predominate • similar to peripheral blood, • neoplastic cells identified
does not clot
neoplasia
• Intracellular bacteria present? FasT, chest radiographs
• Peripheral blood glucose
>20 mg/dL higher than glucose abdominal Us, chest
in abdominal fluid (also seen in radiographs, CT
neoplastic effusions)?
Trauma?
• Positive culture (needs
treatment before results)?
surgery ± chemotherapy
• Treat as necessary
No Yes No Yes • abdominal pressure wrap
• surgery if indicated
• Monitor
severely elevated PT/PTT?
nonseptic FIP PCr- septic
effusion positive effusion
effusion
No Yes
Effusion Emergency Coagulopathy Ingestion of
bilirubin > surgery ± anticoagulant
FIP ruptured/damaged rodenticide
serum abdominal
bilirubin vascular neoplasia/
Us
organ Plasma +
vitamin K Decontamination
Treat as ± emesis ±
Bile necessary vitamin K
peritonitis Cats: Dogs:
• neoplasia • neoplasia
Diagnosis
• Hepatic diseases (hemangio-
• Hemorrhagic sarcoma) Differential
surgery cyst • splenic Diagnosis
• ruptured hematoma
Investigation See Aids &
bladder • splenic torsion
Resources, back
Treatment page, for refer-
Treat as necessary (eg, surgery ± imaging)
ences & suggested
results
reading.
October 2013 • clinician’s brief 19
You might also like
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument5 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosisampogison08No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition by MahonDocument16 pagesTest Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition by MahonShirley Young100% (33)
- NBPME Practice Tests 2005Document39 pagesNBPME Practice Tests 2005Pat TNo ratings yet
- Approach To JaundiceDocument55 pagesApproach To JaundicePankaj IngleNo ratings yet
- NCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDDocument14 pagesNCM116j Reviewer Endocrine UPDATEDAliza Abn bklNo ratings yet
- Làm Gì Khi SDMA TăngDocument1 pageLàm Gì Khi SDMA TăngNguyễn Tấn TàiNo ratings yet
- Enzymology TableDocument2 pagesEnzymology TablePepper MintNo ratings yet
- Home Care RN Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesHome Care RN Skills ChecklistGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis - IanDocument21 pagesAcute Pancreatitis - Ianhandrian rahmanNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesLiver CirrhosisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Surgical Diseases of Liver1Document54 pagesSurgical Diseases of Liver1DR MOHAMED HEALTH CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: DR Monika PathaniaDocument27 pagesJaundice: DR Monika PathaniaMuhammed al-jumailyNo ratings yet
- UGIBDocument34 pagesUGIBChe Ainil ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument1 pageCirrhosis of LiverShaini ChristianNo ratings yet
- Specific Diseases: Special PathologyDocument19 pagesSpecific Diseases: Special Pathologyhumag143No ratings yet
- Vasculitis: Allison Eunice B. ServandoDocument116 pagesVasculitis: Allison Eunice B. ServandoAllison Eunice ServandoNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole (FSW)Document3 pagesOmeprazole (FSW)khelxoNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument45 pagesAcute Kidney Injuryajusdabo95No ratings yet
- Terapi Sirosis HatiDocument40 pagesTerapi Sirosis HatiRisydaMKhNo ratings yet
- Slides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Document47 pagesSlides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Maryam OmarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case: Parameter Test Value Normal Range Bilirubin AST (IU/L) ALT (IU/L) Alkp (IU/L)Document12 pagesClinical Case: Parameter Test Value Normal Range Bilirubin AST (IU/L) ALT (IU/L) Alkp (IU/L)wonderwall_867133No ratings yet
- GI Liver PerceptionDocument9 pagesGI Liver PerceptionJUDE ARIZALANo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument86 pagesAbdominal PainThitanun TungchutworakulNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Exam Body Parts Included Common Indications Exam PreparationsDocument2 pagesUltrasound Exam Body Parts Included Common Indications Exam Preparationstimvrghs123No ratings yet
- Emergenze Addome RXDocument9 pagesEmergenze Addome RXBrovazzo PieroNo ratings yet
- Acute Lower Extremity Ischaemia (ALEXI) : Nadraj G NaidooDocument25 pagesAcute Lower Extremity Ischaemia (ALEXI) : Nadraj G NaidooVishad NaidooNo ratings yet
- DCLDDocument36 pagesDCLDAnonymous uoxEU3mkNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument33 pagesObstructive JaundiceEvediciNo ratings yet
- 3 Antitubercular Therapy Hepatitis 18032022Document1 page3 Antitubercular Therapy Hepatitis 18032022Nido MalghaniNo ratings yet
- Sirosis Hepatis Dan KomplikasiDocument36 pagesSirosis Hepatis Dan KomplikasiMuhammad HafizdNo ratings yet
- Ascites New and ManagementDocument29 pagesAscites New and ManagementANENA RHODANo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document26 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)DR-Somalaraju Sateesh Kumar RajuNo ratings yet
- Liver Tests SlidesDocument65 pagesLiver Tests SlidesDokter MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Surgery PancreasDocument11 pagesSurgery PancreasMATTHEW EARL MALUMAYNo ratings yet
- 2.10 (IM) Liver FailureDocument12 pages2.10 (IM) Liver FailureMohammad Amoran SampalNo ratings yet
- S1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency CasesDocument70 pagesS1M3 Update Fluid Resuscitation Management in Emergency Casesgriya medicaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Oxygenation Handouts 2007 Nclex 1232010737844931 1Document23 pagesMicrosoft Word Oxygenation Handouts 2007 Nclex 1232010737844931 1api-19824701100% (1)
- Sirosis Hepatis Dan KomplikasiDocument26 pagesSirosis Hepatis Dan KomplikasiTiyas UtamiNo ratings yet
- Paediatric CardiologyDocument15 pagesPaediatric CardiologyAaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Jaundice MasterDocument76 pagesJaundice MasterSuresh Kubavat100% (3)
- Hepatobiliary Notes 2.0Document18 pagesHepatobiliary Notes 2.0Sri VathanahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- PUD KeymessageDocument13 pagesPUD Keymessagenando baehaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cardinal Manifestations of Renal Disease DR MoraDocument36 pages1.2 Cardinal Manifestations of Renal Disease DR MoraJewelNo ratings yet
- CirrhosisDocument39 pagesCirrhosisC ONo ratings yet
- Hepatology NoteDocument3 pagesHepatology Notenistobdhoraat3No ratings yet
- 1 Acute Renal FailureDocument65 pages1 Acute Renal FailureDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaNo ratings yet
- GI Quiz 1 NotesDocument8 pagesGI Quiz 1 NotesSara JosephNo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument11 pagesRenal and Urinary DisordersChristian Espanilla100% (4)
- Emergency Case Report December 14 - 15 2021Document17 pagesEmergency Case Report December 14 - 15 2021harisNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Urinalysis Children-Tadulako2015Document33 pagesAbnormal Urinalysis Children-Tadulako2015Yeyen Hastriam AkramNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Urinalysis Children-Tadulako2015Document33 pagesAbnormal Urinalysis Children-Tadulako2015ani bandasoNo ratings yet
- Cirhosis HepatisDocument44 pagesCirhosis HepatisDhea NisaNo ratings yet
- NON Malig HaemDocument49 pagesNON Malig HaemNisini ImanyaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Acute PeritonitisDocument6 pagesCauses of Acute PeritonitisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis & Pseudocyst in ChildrenDocument56 pagesPancreatitis & Pseudocyst in ChildrendrkiranmNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Ankit Kumawat Roll No. 8Document13 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Ankit Kumawat Roll No. 8Raksha G GowdaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests PPT Monette PDFDocument14 pagesLiver Function Tests PPT Monette PDFSam VeraNo ratings yet
- HARLE FinalsDocument15 pagesHARLE Finalsangelapadilla0893No ratings yet
- Mispa I200 BrochureDocument2 pagesMispa I200 Brochurep11.sethiaNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesMicrobiologyKeishaAaliyahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reviews - March 2010Document596 pagesChemical Reviews - March 2010Khurram MallNo ratings yet
- ACG Clinical Guideline: Hereditary HemochromatosisDocument17 pagesACG Clinical Guideline: Hereditary HemochromatosisSimona JuncuNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDDocument38 pagesSpecimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDRica Rebadomia100% (2)
- Professor C. B. Bunker: Curriculum VitaeDocument97 pagesProfessor C. B. Bunker: Curriculum Vitaejosiah masukaNo ratings yet
- Mikroba Saluran PencernaanDocument70 pagesMikroba Saluran PencernaanAde Yurga TonaraNo ratings yet
- Protozoa: Department of Parasitology Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityDocument21 pagesProtozoa: Department of Parasitology Medical Faculty, Hasanuddin UniversityNurul fatimahNo ratings yet
- Immunology Worksheet1Document4 pagesImmunology Worksheet1Caviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- AEB Practical GuideDocument79 pagesAEB Practical GuideMihir DesaiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Courses Affiliated To The Kerala University of Health SciencesDocument124 pagesSyllabus For Courses Affiliated To The Kerala University of Health SciencesgoldaNo ratings yet
- KK5701 PDFDocument4 pagesKK5701 PDFcommgmailNo ratings yet
- Malaria SlidesDocument60 pagesMalaria Slidescana geel 2018No ratings yet
- Retiform Purpura Associated With Levamisole-Adulterated Cocaine. Do Procoagulant Genetic Alterations May Influence?Document3 pagesRetiform Purpura Associated With Levamisole-Adulterated Cocaine. Do Procoagulant Genetic Alterations May Influence?asclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Practical Obstetric Hematology PDFDocument208 pagesPractical Obstetric Hematology PDFSteve CullenNo ratings yet
- Seeds: Rajasthan State Corporation LTD.Document7 pagesSeeds: Rajasthan State Corporation LTD.Swatantra SinghNo ratings yet
- Anti-HCV Reagent Kit: B8P060 G71272R05Document8 pagesAnti-HCV Reagent Kit: B8P060 G71272R05LoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3, 4 5 HopmeworkDocument5 pagesChapter 3, 4 5 HopmeworkDanNo ratings yet
- Cetrimide Agar Base (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1102Document2 pagesCetrimide Agar Base (European Pharmacopoeia) : CAT Nº: 1102Tatjana MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document4 pagesClass 12royNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis MalariaDocument18 pagesDiagnosis MalariaCiciNo ratings yet
- A Simple Method For DNA Isolation From Clotted Blo PDFDocument4 pagesA Simple Method For DNA Isolation From Clotted Blo PDFWinnie van den BoogaardNo ratings yet
- 6.paleogenesis and Paleo-Epidemiology of Primate MalariaDocument25 pages6.paleogenesis and Paleo-Epidemiology of Primate Malarialaura isabellaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Biological Molecules - Proteins QPDocument24 pages2.2 Biological Molecules - Proteins QPsuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- +2 Bio Zoo em 7 12 LessonsDocument30 pages+2 Bio Zoo em 7 12 LessonsInnovative IndustryNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Noteslaurette danzine0% (1)
- Chapter 10Document7 pagesChapter 10HERRERA, ANGELANo ratings yet
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesRamsay Hunt Syndrome: Infectious DiseasesAldy BimaNo ratings yet