Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Brochure Rex
Physics Brochure Rex
Uploaded by
Lovely Ro-Ann SositoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Brochure Rex
Physics Brochure Rex
Uploaded by
Lovely Ro-Ann SositoCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY SUMMARY
1. John is on top of the building and jack is Projectile Motion is the free fall motion of any
down. If john throws a ball at an angle of 60° body in a horizontal path with constant
and with initial velocity 20 m/s. At what velocity.
height will the ball reach after 2 s?
The object is called a projectile, and its path is
2. An object is launched at a velocity of 20 called its trajectory.
m/s in a direction making an angle of 25°
upward with the horizontal. What is the
maximum height reached by the object?
3. A projectile starting from ground hits a
target on the ground located at a distance of REFERENCES
1000 meters after 40 seconds. At what initial
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/physics/ch
velocity was the projectile launched?
apter/3-4-projectile-motion/
https://formulas.tutorvista.com/physics/projecti
le-motion-formula.html
ESTIMATING
PROJECTION
A PRESENTATION ABOUT
PROJECTILE MOTION IN PHYSICS
REX O. ESON JR.
Grade 12-STEM-Heisenberg
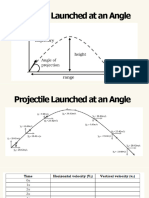
PROJECTILE MOTION FORMULAS
Projectile motion is the motion of an Below is the diagram showing 2-D projectile
object thrown or projected into the air, motion with the formulas needed in solving
subject to only the acceleration of gravity. projectile-related problems.
The object is called a projectile, and its path
is called its trajectory. The motion of falling
objects is a simple one-dimensional type of
projectile motion in which there is no SAMPLE PROLBLEM
horizontal movement. In this section, we 1. A body is projected with a velocity of 20
consider two-dimensional projectile motion, m/s at 50° to the horizontal. Find a)
such as that of a football or other object for Maximum height reached b) Time of flight
which air resistance is negligible. and c) Range of the projectile.
Projectile Motion is the free fall motion Solution:
of any body in a horizontal path with Vi = 20 m/s θ = 50°
constant velocity.
a. H = Vo2sin2θ/2g
= (20m/s)2 sin(50°)2/(2×9.8m/s2)
= 11.97 m
b. t = 2V0 sin θ / g
= 2 × 20m/s × sin(50°) / 9.8 m/s2
= 3.126 s
c. R = v02sin2θ/g
= 20m/s2 sin(100°) / 9.8 m/s2
= 40.196 m
You might also like
- Journal 6 2 FinalDocument392 pagesJournal 6 2 FinalFranz ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument74 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesArah Louise Apostol100% (1)
- 2019 5G Plugins Commercial Presentation - 20.Q1 Recording Slides - 2019-12-02Document53 pages2019 5G Plugins Commercial Presentation - 20.Q1 Recording Slides - 2019-12-02Tamasree Dhar100% (1)
- Andy McKee - (2007) The Gates of GnomeriaDocument2 pagesAndy McKee - (2007) The Gates of GnomeriarealizadorNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Grp2Document21 pagesProjectile Motion Grp2Maria Sunshine ToledoNo ratings yet
- L12 ProjectilesDocument7 pagesL12 ProjectilesGhazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics Unit 1 Lesson 5 Motion in 2 and 3 DimensionsDocument9 pagesGen. Physics Unit 1 Lesson 5 Motion in 2 and 3 DimensionsMary Love JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Projectile-MotionDocument46 pagesProjectile-MotionSidnee MadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: A Two - Dimensional MotionDocument34 pagesProjectile Motion: A Two - Dimensional MotionNovie Jane HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Particular's Page NoDocument41 pagesProjectile Motion: Particular's Page NoRafsanjaniNo ratings yet
- Q4-Solving UamDocument22 pagesQ4-Solving UamStefhanie AgotillaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: AP Physics CDocument26 pagesProjectile Motion: AP Physics CCedric VargasNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Motion in Two DimensionsDocument35 pagesProjectile Motion: Motion in Two DimensionsJennifer Magango100% (5)
- Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesProjectile MotionGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Analysis Experiment 103: Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion Is Defined As ADocument15 pagesAnalysis Experiment 103: Projectile Motion. Projectile Motion Is Defined As ARicardo LunaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion NotesDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion NotesJoseph MawonikeNo ratings yet
- LC 4 Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesLC 4 Projectile MotionSarah GanganNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionDocument34 pagesMotion in Two DimensionMarArizalaNo ratings yet
- Free FallDocument34 pagesFree Fallcrossline093No ratings yet
- 2 9 LAS Q4 Week 2 Projectlie Motion Part 2 Hosana FinalDocument5 pages2 9 LAS Q4 Week 2 Projectlie Motion Part 2 Hosana FinalAllyssa BuenaNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two DimensionDocument34 pagesMotion in Two DimensionMarArizala100% (1)
- 1 Projectile Motion Case I and IIDocument40 pages1 Projectile Motion Case I and IIMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson-5-Two-Dimensional MotionDocument34 pagesLesson-5-Two-Dimensional MotionJazelle DignoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4 Sci204 MechanicsDocument44 pagesChapter 1-4 Sci204 MechanicsNoreen Fae T. AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - CH 3 Projectile Motion-FinalDocument21 pagesAP Physics 1 - CH 3 Projectile Motion-Finalchankatrina011No ratings yet
- Gen Phy 1 W4Document4 pagesGen Phy 1 W4Leo LinNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2dDocument27 pagesMotion in 2dMark Alexis AtesorNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - 101Document27 pagesProjectile Motion - 101Gerlie Velasco100% (2)
- 01 KinematicsDocument33 pages01 Kinematicscath deluxeNo ratings yet
- Assignment From ModuleDocument3 pagesAssignment From ModulehimanshuNo ratings yet
- 08AP Physics C - Projectile MotionDocument21 pages08AP Physics C - Projectile MotionRyan Ata100% (1)
- ACT. SHEETS SCIENCE 9 4TH QTR W1 3Document5 pagesACT. SHEETS SCIENCE 9 4TH QTR W1 3mareng aryanNo ratings yet
- Acceleration and Free Fall LabDocument5 pagesAcceleration and Free Fall LabMariam ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 From NetDocument19 pagesChapter 3 From NetWaffleNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and Uniform AccelerationDocument17 pagesKinematics and Uniform AccelerationunknownNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion at An AngleDocument24 pagesProjectile Motion at An AngleRHEAMAE GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Motion of A Projectile (Section 12.6) Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesMotion of A Projectile (Section 12.6) Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesbigbangmelvanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in Two Dimension: What Is This Module About?Document11 pagesKinematics in Two Dimension: What Is This Module About?Eugene Clark EridaoNo ratings yet
- Projectile at AngleDocument24 pagesProjectile at AngleappleNo ratings yet
- UNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument16 pagesUNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated Motionflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- UNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument16 pagesUNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionSahat Rein Jeremay PardedeNo ratings yet
- Motion (Freely Falling Bodies and Projectile Motion) : Course Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesMotion (Freely Falling Bodies and Projectile Motion) : Course Learning OutcomesYoo JungNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesModule 4 - Projectile MotionAllen Simon BaulaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Mid G9 Phy Rev AK 2024Document3 pages3rd Mid G9 Phy Rev AK 2024mnasir1976No ratings yet
- Science LAS 4.1Document15 pagesScience LAS 4.1Paul AceroNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Intro To Dynamics & Kinematic MotionDocument42 pagesLecture - Intro To Dynamics & Kinematic MotionSamuel Corvera100% (5)
- 9 2D Motion - ProjectileDocument42 pages9 2D Motion - ProjectileBebe rhexaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: When An Object Is Thrown HorizontallyDocument8 pagesProjectile Motion: When An Object Is Thrown Horizontallyjannah hinayNo ratings yet
- Projectile at AngleDocument24 pagesProjectile at AngleappleNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument35 pagesProjectile Motionjamespatrickvolante218No ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument2 pagesKinema TicsAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- MET Dynamics 06.30.2017 4-7pmDocument49 pagesMET Dynamics 06.30.2017 4-7pmRovick TarifeNo ratings yet
- Motion - Free Failing Bodies and Projectile MotionDocument31 pagesMotion - Free Failing Bodies and Projectile MotionYoo JungNo ratings yet
- 2022+Projectile+Motion+2022+Edited Converted Converted CompressedDocument89 pages2022+Projectile+Motion+2022+Edited Converted Converted CompressedAlthea Joy Castor SobretodoNo ratings yet
- Physics LectDocument4 pagesPhysics LectJanine PalizaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: AP Physics BDocument18 pagesProjectile Motion: AP Physics B菲合彩Hannah Althea PanerioNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 4 Projectile MotionDocument14 pagesPhysics Lab Report 4 Projectile MotionJustin PedrozaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument40 pagesProjectile MotionJoshua VicenteNo ratings yet
- GENPHY1FPT1SEMDocument11 pagesGENPHY1FPT1SEMNoimar DayocNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Motion AssignmentDocument3 pagesPhysics Projectile Motion Assignmentpatelsp9098No ratings yet
- Kindin Lec5 PDFDocument27 pagesKindin Lec5 PDFAndi SeftyandiNo ratings yet
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesFrom Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNo ratings yet
- Textile Mathematics J.E. BOOTH Vol 3 PDFDocument30 pagesTextile Mathematics J.E. BOOTH Vol 3 PDFdipo67% (3)
- Calcinosis Involving Multiple Paws in A Cat With Chronic Renal Failure and in A Cat With Hyperthyroidism (Pages 74-78)Document5 pagesCalcinosis Involving Multiple Paws in A Cat With Chronic Renal Failure and in A Cat With Hyperthyroidism (Pages 74-78)jenNo ratings yet
- Biology EducationDocument10 pagesBiology EducationAzah BalQisNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)Document19 pagesDoctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)kirti gargNo ratings yet
- Study of Fully Homomorphic Encryption Over IntegersDocument4 pagesStudy of Fully Homomorphic Encryption Over IntegersAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument134 pagesChapter 2 Solutionsapi-209868636No ratings yet
- La Tolérance Et Ses Limites: Un Problème Pour L'ÉducateurDocument7 pagesLa Tolérance Et Ses Limites: Un Problème Pour L'ÉducateurFatima EL FasihiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Parables of JesusDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Parables of JesusRaul PostranoNo ratings yet
- Lymphoproliferative DiseasesDocument8 pagesLymphoproliferative DiseasesRegla Mailyn Perez PerezNo ratings yet
- تأثير الغش على أحكام المسؤولية العقديةDocument24 pagesتأثير الغش على أحكام المسؤولية العقديةsirineghozzinefaaNo ratings yet
- Flow English Lyrics All .LREDocument21 pagesFlow English Lyrics All .LREGustavo KstNo ratings yet
- Ielts Task 2 Writing Band DescriptorsDocument2 pagesIelts Task 2 Writing Band DescriptorsmaikoNo ratings yet
- DIGEST - Marcelo v. CADocument2 pagesDIGEST - Marcelo v. CADanielle AbuelNo ratings yet
- Botany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872Document9 pagesBotany Assignment MUHSIN K P - 872muhsinNo ratings yet
- Punjab CuisineDocument6 pagesPunjab CuisineIbrahim FaRizzNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Colonialism and Its Impact in Africa Ocheni and Nwankwo CSCanada 2012 PDFDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Colonialism and Its Impact in Africa Ocheni and Nwankwo CSCanada 2012 PDFkelil Gena komichaNo ratings yet
- Field Trip/ Lakbay-Aral: By: Christian A. GalletaDocument2 pagesField Trip/ Lakbay-Aral: By: Christian A. GalletaHajime HikariNo ratings yet
- De Agbayani v. PNB, 38 SCRA 429Document4 pagesDe Agbayani v. PNB, 38 SCRA 429Rhei BarbaNo ratings yet
- International Trade LawDocument30 pagesInternational Trade LawVeer Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Prayer Book 2nd Week (Thursday)Document26 pagesPrayer Book 2nd Week (Thursday)Aly SyntaxNo ratings yet
- My Teaching ExperienceDocument3 pagesMy Teaching Experienceapi-325313138No ratings yet
- (J. A Short) Drilling A Source Book On Oil and Ga PDFDocument588 pages(J. A Short) Drilling A Source Book On Oil and Ga PDFZana Qadir100% (1)
- Quectel GSM FTP at Commands Manual V1.4Document34 pagesQuectel GSM FTP at Commands Manual V1.4Thanh nhaNo ratings yet
- Otable Ews: Mennonite Children's ChoirDocument14 pagesOtable Ews: Mennonite Children's ChoirMaria BowmanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologi, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis DM, BPJS 2015Document35 pagesEpidemiologi, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis DM, BPJS 2015Samuel Albert Andrian SiagianNo ratings yet
- 2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaDocument5 pages2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaJating JamkhandiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsDocument27 pagesCongenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsVikram Simha NagendlaNo ratings yet