Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
Uploaded by
Jelminda AlfaroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 11 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 11 PDFTiago CardosoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Part27Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Part27nikhil modgil100% (1)
- Engineering ScienceDocument22 pagesEngineering SciencePinto PintoNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL Moment Distribution Method - Beam With and Without SettlementDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL Moment Distribution Method - Beam With and Without SettlementAhmad Farhan Hamzah100% (1)
- Structural Analysis: Lecture SeriesDocument15 pagesStructural Analysis: Lecture SeriesAjit GargNo ratings yet
- SA61Document9 pagesSA61Eng AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Stranalysis SD METHODDocument78 pagesStranalysis SD METHODNaveen RevannaNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Method 3rd DamDocument19 pagesSlope Deflection Method 3rd DamAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection ExamplesDocument20 pagesSlope Deflection ExamplesSammish83No ratings yet
- Kuliah Anstruk - 04 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method BeamDocument14 pagesKuliah Anstruk - 04 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method BeamRizky Sunarya Adam AviannurNo ratings yet
- Unit2-HPS Structural Analysis IIDocument89 pagesUnit2-HPS Structural Analysis IISmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument6 pagesSlope Deflection MethodRaja RajanNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument32 pagesSlope Deflection MethodXenon Asuncion100% (1)
- Slope Deflection Examples:: Fixed End MomentsDocument18 pagesSlope Deflection Examples:: Fixed End MomentsfransvladNo ratings yet
- Assignment MechanicsDocument12 pagesAssignment MechanicsRishav GogoiNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection ExamplesDocument20 pagesSlope Deflection ExamplesMlg JoséNo ratings yet
- Slope-Deflection EquationsDocument33 pagesSlope-Deflection Equationstosha_flNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 SolutionsDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 Solutionsutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayDocument11 pagesTheory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayBone SnowNo ratings yet
- SLOPE DEFLECTION METHOD Examples With SolutionsDocument23 pagesSLOPE DEFLECTION METHOD Examples With SolutionsErwin EleserioNo ratings yet
- m3l15 Lesson 15 The Slope-Deflection Method: Beams (Continued)Document15 pagesm3l15 Lesson 15 The Slope-Deflection Method: Beams (Continued)Vitor Vale100% (1)
- Moment DistributionDocument14 pagesMoment DistributionStephanie HaynesNo ratings yet
- Displacement MethodDocument16 pagesDisplacement MethodnunpluggedNo ratings yet
- Deflection Continuous Beams - 08Document21 pagesDeflection Continuous Beams - 08LuisNo ratings yet
- Moment Equation Using Singularity FunctionDocument42 pagesMoment Equation Using Singularity FunctionJay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit4-Kani's Method PDFDocument34 pagesUnit4-Kani's Method PDFnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Anstruk - 05 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method FramesDocument23 pagesKuliah Anstruk - 05 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method FramesRizky Sunarya Adam AviannurNo ratings yet
- Displacement Method of AnalysisDocument52 pagesDisplacement Method of Analysisahmad nabilNo ratings yet
- Module 4.2 Slope Deflection MethodDocument6 pagesModule 4.2 Slope Deflection MethodJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Slope ND DeflectionDocument19 pagesSlope ND DeflectionprashantbaraskarNo ratings yet
- El Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enDocument5 pagesEl Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enFrack Starsky Coronel LeonNo ratings yet
- El Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enDocument5 pagesEl Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enAlbert PizarroNo ratings yet
- Problem A 42Document5 pagesProblem A 42tupac2930No ratings yet
- CE3503 Lecture5Document53 pagesCE3503 Lecture5Ali AratNo ratings yet
- By Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodDocument34 pagesBy Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodmahakNo ratings yet
- Example 21.2 Stiffness Method Beam 3 NodesDocument25 pagesExample 21.2 Stiffness Method Beam 3 NodesSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Continuous BeamDocument12 pagesContinuous BeamMadhavManikanth100% (1)
- Conquer HexagonsDocument10 pagesConquer HexagonsJulio Armando RiveraNo ratings yet
- 3 Moments EquationDocument15 pages3 Moments EquationJuan Carlos Urueña CruzNo ratings yet
- PDF 4 Mechanics of DBDocument16 pagesPDF 4 Mechanics of DBRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- Shear and MomentDocument70 pagesShear and MomentDhyz Quinquilleria100% (4)
- The Euler Line of A Triangle: William M. Faucette May 2007Document9 pagesThe Euler Line of A Triangle: William M. Faucette May 2007Chanthana ChongchareonNo ratings yet
- Contoh 2 Slope DeflectionghjgkjDocument9 pagesContoh 2 Slope DeflectionghjgkjHarisal PutraNo ratings yet
- 404 To 410Document22 pages404 To 410Muhammad Jhangeer KhanNo ratings yet
- E3Document300 pagesE3JuinNo ratings yet
- 9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment DistributionDocument11 pages9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment Distributionvincent.siswajiNo ratings yet
- Moment DistributionDocument153 pagesMoment DistributionHerbert P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Werwerewqrqwrewqerwqerwqrwr - Shear and Moment of Beams Definition of A BeamDocument15 pagesWerwerewqrqwrewqerwqerwqrwr - Shear and Moment of Beams Definition of A BeamLC LeeNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Hyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaDocument27 pagesFoundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaJelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Chapter 7Document39 pagesFDN Engg Chapter 7Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument88 pagesMechanics of Deformable BodiesJelminda Alfaro100% (3)
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Statute Civil Law: Judge Made LawsDocument2 pagesStatute Civil Law: Judge Made LawsJelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
Uploaded by
Jelminda AlfaroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
SA60 Exercise1 PDF
Uploaded by
Jelminda AlfaroCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Analysis– SA60 (Solution for Exercise Problem 1)
Three-Moment Equation
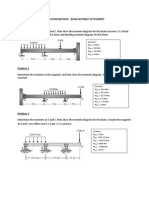
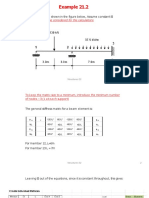
Analyze the following beam using the three-moment equation.
Solution
The general form of the three-moment equation is:
L AB L L L L L
M A + 2M B ( AB + BC ) + BC M C =
− AB (FEM AB + 2FEM BA ) − BC (2FEM BC + FEM CB )
I AB I AB I BC I BC I AB I BC
Let I denote I AB . Therefore, I BC = 2I . Then the above equation can be written as:
L AB L L L L L
M A + 2M B ( AB + BC ) + BC M C =
− AB (FEM AB + 2FEM BA ) − BC (2FEM BC + FEM CB )
I I 2I 2I I 2I
Multiplying both sides of the equation by I, we get:
L AB M A + 2M B (L AB + 0.5L BC ) + 0.5L BC M C =
−L AB (FEM AB + 2FEM BA ) − 0.5L BC (2FEM BC + FEM CB )
And since, L=
AB L=
BC 8 the above equation becomes:
8M A + 2M B (8 + 4) + 4M C =
−8(FEM AB + 2FEM BA ) − 4(2FEM BC + FEM CB )
Furthermore, we know that M=
A C 0 . Hence:
M=
24M B =
−8(FEM AB + 2FEM BA ) − 4(2FEM BC + FEM CB )
Now we need to calculate the fixed-end moments. Segment AB is subjected to a uniformly
distributed load, therefore it fixed-end moments are as shown below.
For segment BC, the fixed-end moments are:
Lab101.Space EDUCATIVE TECHNOLOGIES, LLC P a g e |1
Substituting the fixed-end moment values in the three-moment equation, we get:
24M B =
−8(16 + 32) − 4(160 + 80)
Or, M B = −56 kN.m .
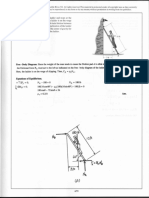
Knowing the moment at B, we can draw the free-body diagram for each beam segment as shown
below.
For segment AB, we can write and solve two equilibrium equations for the member-end shear
forces as follows:
8VBA − 56 − 3(8)(4)
= 0 = V 19 kN
⇒ BA
VAB + VBA= − 3(8) 0 = VAB 5 kN
For segment BC, we can write:
8VCB + 56 − (80)(4)
= 0 = V 33 kN
⇒ CB
VBC +=VCB −80 0 = VBC 47 kN
Knowigng the shear forces, we can determine the support reactions, as shown below.
Lab101.Space EDUCATIVE TECHNOLOGIES, LLC P a g e |2
You might also like
- Chapter 11 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 11 PDFTiago CardosoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Part27Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Part27nikhil modgil100% (1)
- Engineering ScienceDocument22 pagesEngineering SciencePinto PintoNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL Moment Distribution Method - Beam With and Without SettlementDocument2 pagesTUTORIAL Moment Distribution Method - Beam With and Without SettlementAhmad Farhan Hamzah100% (1)
- Structural Analysis: Lecture SeriesDocument15 pagesStructural Analysis: Lecture SeriesAjit GargNo ratings yet
- SA61Document9 pagesSA61Eng AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Stranalysis SD METHODDocument78 pagesStranalysis SD METHODNaveen RevannaNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Method 3rd DamDocument19 pagesSlope Deflection Method 3rd DamAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection ExamplesDocument20 pagesSlope Deflection ExamplesSammish83No ratings yet
- Kuliah Anstruk - 04 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method BeamDocument14 pagesKuliah Anstruk - 04 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method BeamRizky Sunarya Adam AviannurNo ratings yet
- Unit2-HPS Structural Analysis IIDocument89 pagesUnit2-HPS Structural Analysis IISmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument6 pagesSlope Deflection MethodRaja RajanNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument32 pagesSlope Deflection MethodXenon Asuncion100% (1)
- Slope Deflection Examples:: Fixed End MomentsDocument18 pagesSlope Deflection Examples:: Fixed End MomentsfransvladNo ratings yet
- Assignment MechanicsDocument12 pagesAssignment MechanicsRishav GogoiNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection ExamplesDocument20 pagesSlope Deflection ExamplesMlg JoséNo ratings yet
- Slope-Deflection EquationsDocument33 pagesSlope-Deflection Equationstosha_flNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 SolutionsDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 Solutionsutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayDocument11 pagesTheory of Structures 2 Chapter 4.1 - Analysis of Frames: No SideswayBone SnowNo ratings yet
- SLOPE DEFLECTION METHOD Examples With SolutionsDocument23 pagesSLOPE DEFLECTION METHOD Examples With SolutionsErwin EleserioNo ratings yet
- m3l15 Lesson 15 The Slope-Deflection Method: Beams (Continued)Document15 pagesm3l15 Lesson 15 The Slope-Deflection Method: Beams (Continued)Vitor Vale100% (1)
- Moment DistributionDocument14 pagesMoment DistributionStephanie HaynesNo ratings yet
- Displacement MethodDocument16 pagesDisplacement MethodnunpluggedNo ratings yet
- Deflection Continuous Beams - 08Document21 pagesDeflection Continuous Beams - 08LuisNo ratings yet
- Moment Equation Using Singularity FunctionDocument42 pagesMoment Equation Using Singularity FunctionJay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit4-Kani's Method PDFDocument34 pagesUnit4-Kani's Method PDFnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Anstruk - 05 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method FramesDocument23 pagesKuliah Anstruk - 05 Displacement Methods The Slope Deflection Method FramesRizky Sunarya Adam AviannurNo ratings yet
- Displacement Method of AnalysisDocument52 pagesDisplacement Method of Analysisahmad nabilNo ratings yet
- Module 4.2 Slope Deflection MethodDocument6 pagesModule 4.2 Slope Deflection MethodJayLord Mico PacisNo ratings yet
- Slope ND DeflectionDocument19 pagesSlope ND DeflectionprashantbaraskarNo ratings yet
- El Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enDocument5 pagesEl Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enFrack Starsky Coronel LeonNo ratings yet
- El Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enDocument5 pagesEl Sistema de La Figura Se Puede Descomponer enAlbert PizarroNo ratings yet
- Problem A 42Document5 pagesProblem A 42tupac2930No ratings yet
- CE3503 Lecture5Document53 pagesCE3503 Lecture5Ali AratNo ratings yet
- By Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodDocument34 pagesBy Prof. A.B.Harwalkar PDA College of Engineering, Gulbarga: Chapter-4: Kani's MethodmahakNo ratings yet
- Example 21.2 Stiffness Method Beam 3 NodesDocument25 pagesExample 21.2 Stiffness Method Beam 3 NodesSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Continuous BeamDocument12 pagesContinuous BeamMadhavManikanth100% (1)
- Conquer HexagonsDocument10 pagesConquer HexagonsJulio Armando RiveraNo ratings yet
- 3 Moments EquationDocument15 pages3 Moments EquationJuan Carlos Urueña CruzNo ratings yet
- PDF 4 Mechanics of DBDocument16 pagesPDF 4 Mechanics of DBRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- Shear and MomentDocument70 pagesShear and MomentDhyz Quinquilleria100% (4)
- The Euler Line of A Triangle: William M. Faucette May 2007Document9 pagesThe Euler Line of A Triangle: William M. Faucette May 2007Chanthana ChongchareonNo ratings yet
- Contoh 2 Slope DeflectionghjgkjDocument9 pagesContoh 2 Slope DeflectionghjgkjHarisal PutraNo ratings yet
- 404 To 410Document22 pages404 To 410Muhammad Jhangeer KhanNo ratings yet
- E3Document300 pagesE3JuinNo ratings yet
- 9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment DistributionDocument11 pages9e. Re - Tambahan Contoh Soal - Slopde Deflection Dan Moment Distributionvincent.siswajiNo ratings yet
- Moment DistributionDocument153 pagesMoment DistributionHerbert P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Werwerewqrqwrewqerwqerwqrwr - Shear and Moment of Beams Definition of A BeamDocument15 pagesWerwerewqrqwrewqerwqerwqrwr - Shear and Moment of Beams Definition of A BeamLC LeeNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Hyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaDocument27 pagesFoundation Engineering: Engr. Gabriel GamanaJelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- FDN Engg Chapter 7Document39 pagesFDN Engg Chapter 7Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument88 pagesMechanics of Deformable BodiesJelminda Alfaro100% (3)
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8Jelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Statute Civil Law: Judge Made LawsDocument2 pagesStatute Civil Law: Judge Made LawsJelminda AlfaroNo ratings yet