Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design and Development of Fault Detection and Location System For Electrical Distribution Network
Design and Development of Fault Detection and Location System For Electrical Distribution Network
Uploaded by
atif jabbarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design and Development of Fault Detection and Location System For Electrical Distribution Network
Design and Development of Fault Detection and Location System For Electrical Distribution Network
Uploaded by
atif jabbarCopyright:
Available Formats
Design and Development of Fault Detection and
Location System for Electrical Distribution Network
Syed Sheraz-ul-Hasan Mohani Muhammad Shoaib Ameer Atif Jabbar
Faculty of Engineering Sciences and Faculty of Engineering Sciences and Faculty of Engineering Sciences and
Technology Technology Technology
Iqra University Iqra University Iqra University
Karachi, Pakistan Karachi, Pakistan Karachi, Pakistan
smohani@iqra.edu.pk shoaibameer33@gmail.com atifjabbar@outlook.com
Abstract— this low cost fault detection and locating system
is especially valuable in rural environments where crews have
long drive times or in a building with complex distribution
network. These devices can make a huge financial impact by
removing operational costs and allowing utilities to deliver
safe, affordable and reliable energy.
Keywords—Fault location, Fault detection, SIM908
(GSM/GPS/GPRS), Arduino, Lab VIEW
Fig. 1. Simplified model of impedance based locators
I. INTRODUCTION
Since the establishment of electrical distribution B. Travelling wave based locators
networks, fault location and detection has been a primary Traveling wave-based fault location methods can be
aspect of power systems. To prevent any major damage to divided into two-terminal and one-terminal. With traveling
the equipment, fault detection helps to save them by wave analysis, however, one-terminal methods rely on the
disconnecting faulted lines. Faults can be easily eliminated timing between reflections of voltage or current at
by accurately locating fault occurring areas which also helps impedance discontinuities – in this case, the fault – to find
in lowering power outage frequency. This system is designed the distance between the sensor and the fault while two-
to effectively and more accurately perform this task. terminal methods work based on the time delay between
Fault Detection and Location system will provide arrivals of information at the ends of the transmission line.
distribution monitoring in real - time. It will be an affordable
solution that will be deployable in minutes. The FDL system
consists of microcontroller, current and potential
transformers, electrically controlled breakers, liquid crystal
display (LCD), 24V battery, GSM/GPS modem and antenna,
personal computer (PC), some small logic and inverter
circuits (Hardware equipment) and lab view, Arduino IDE
(Software tools).
II. TECHNOLOGY HISTORY
The safe operation of electrical power systems
(distribution and transmission networks) is guaranteed by the
accurate fault detection. Programmed fault elimination from
distribution or transmission lines would be impossible Fig. 2. Traveling wave based locators
without fault detection. As a result, crucial electrical
equipment could be destroyed or damaged. It is not C. Knowledge based locators
necessary to have fault detection and location system for Knowledge based methods are used to reduce the time
power system safety, but it can help to detect areas where taken by impedance based locators by pre-calculating the set
faults have occurred on distribution or transmission of data and matching it the current impedance. The area of
networks. knowledge based approaches falls under soft computing.
Many artificial intelligence methods are used to compute the
Many fault location techniques have been designed in fault location which includes but not limited to Artificial
past years. Systems which are used commonly include Neural network (ANN), Fuzzy Logic (FL), Expert System
(ES) and Genetic Algorithm (GA), etc. In soft computing the
A. Impedance based locators restrictions are looser and the possibilities to find complex
Impedance based locators are used to locate the distance correlations higher but the accuracy and certainty comes with
of fault from primary supply to the fault location by a cost, which result in a trade of between precision and
measuring current and voltages using one-end or two-end uncertainty
locators. These values are then fed to the mathematical
equations for estimation of fault location.
978-1-5386-8249-4/18/$31.00 ©2018 IEEE
The Following tables show the requirements and Hardware Description
advantages and disadvantages of locators mentioned above.
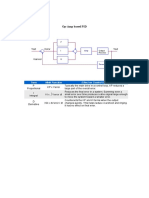
D. System Model
Fig. 3. System Model
Figure 3 shows the working block diagram of the project.
Table 1. Requirements of different locators FDL master device present in a control room of grid station
with a Lab view GUI interface and FDL slave device were
installed on the pole for fault detection working. FDL
master and slave devices communicate using
GSM/GPS/GPRS communication link through short message
service (SMS).
E. FDL Master Device
Table 2. Accuracy and cost comparison of locators Fig. 4. Block diagram of FDL Master Device
Master device comprises of a PC/laptop with a modem to
communicate with slave devices. The modem is connected
with PC through USB port . The modem consists of
GPS/GSM/GPRS and a passive antenna for GSM and an
active antenna for GPS. We used lab view program as hyper
terminal to communicate with modem. The DTE (Data
Terminal Equipment) which in our case is a PC is set on a
baud rate of 9600 to communicate with DCE (Data
Communication Equipment) and in DCE auto bauding is set.
F. FDL Slave Device
Fig. 5 Block diagram of FDL Slave Device
Table 3. Detailed comparison of locators
The slave devices have all the circuits need to detect
fault and locate it. We used Arduino UNO as platform for
this device to measure the parameters and to control the
device and a modem is used to communicate with master
device. It also consists of three potential transformers to step
down the line voltage up to 1.5 VAC which after measure
through A/D converter which is built-in with Arduino.
Fig. 6. FDL Slave Device Circuits
Other circuits in slave device include an AC
measurement circuit, LCD circuit, Battery cut off and battery
charging circuit, Circuit Breaker control circuit, logic
converter circuit which converts 3.3 volts to 5 or vice versa,
24 VDC testing circuit (Receive and transmit), 5 VDC (4
Amps) high current power supply, two 12 V batteries
connected in series and other miscellaneous things like
LCD, GSM antenna (passive), GPS antenna (active),
Electrically controlled Circuit Breakers, Exhaust fan and a
power button.
III. SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION
A basic algorithm to implement fault location and
detection method on microcontroller is as follows:
Lab View (Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation
Engineering Workbench) is software from National
Instruments, which is used for visual programming language.
In this project we used lab view as GUI (Graphical User
Interface) to monitor the status of fault and to control the
FDL devices from remote.
IV. RESULTS V. CONCLUSION
Lab view environment was tested by sending and Overall conclusion of this paper is to give a brief idea of
receiving messages from a mobile to GSM module ac voltage fault detection and to find fault location. This
connected to pc paper gives an idea of measuring ac voltages and taking a
decision on its condition as well as to integrate sim908
gsm/gprs/gps modem by using microcontroller and easily
available components. There are number of uses of sim908
modems in industries for transmitting location and sensor
data from remote location an intelligent system. This system
is designed especially for the power distribution companies
but this can also applicable in industries which have a length
of cables running in the field. Few major component and
ideas used in this project are as follow;
a) A C voltage measurement
b) Using GS M t o communicate
c) Using GPS to find location
d) Using Google maps to display location.
Fig. 7. LABView GUI in normal mode Advantages of project as compared to other approaches
include:
a) Easy installation
b) Plug and play support
c) Portability
d) No significant hardware changes required in existing
setup
e) Low cost maintenance
f) Parts availibility
g) Modular device, can add more functionalities in
future
Demerits of project includes:
a) Security issue due to hacking but GSM is very much
hack proof
Fig. 8. LABView GUI when fault occured b) Signal jamming issue but can be mitigated by using
redundant frequency and protocols
REFERENCES
[1] Kurt Josef Ferreira, Fault Location for Power Transmission Systems
Using Magnetic Field Sensing Coils, April 2007.
[2] Alsafasfeh, Qais H., Ikhlas Abdel-Qader, and Ahmad M. Harb. "Fault
[3] Classification and Localization in Power Systems Using Fault
Signatures and Principal Components Analysis." Energy and Power
Engineering 4.06 (2012): 506.
[4] Rucha V.Deshmukh, Combine Study of Transmission Line Fault
Detection Techniques, IJARCET, February 2014, vol. 3.
[5] Hartebrodt, Martin, and Klaus Kabitzsch. "Fault detection in
fieldbuses
[6] with time domain reflectometry." AFRICON, 2004. 7th AFRICON
Conference in Africa. Vol. 1. IEEE, 2004.
Fig. 9. LABView GUI after fault location has been identified
[7] http://www.tequipment.net/megger/tdr-and-cable-length-meters
[8] Gilany, Mahmoud, Doaa Khalil Ibrahim, and ES Tag Eldin.
"Traveling-wave-based fault-location scheme for multiend-aged
underground cable system." Power Delivery, IEEE Transactions on
22.1 (2007): 82-89.
[9] Mirzaei, M., et al. "Review of fault location methods for distribution
power system." Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 3.3
(2009): 2670-2676.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- AI For Everyone Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesAI For Everyone Quiz Answersatif jabbar79% (58)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 5 Year Idp Cse - 2013Document146 pages5 Year Idp Cse - 2013JDeekshithReddyNo ratings yet
- Pads and Attenuators Lab 3Document6 pagesPads and Attenuators Lab 3Michael K GooneratneNo ratings yet
- Turkey Visa Requirement: Levhasi" in Turkish) of The Inviter (For Business Visa)Document1 pageTurkey Visa Requirement: Levhasi" in Turkish) of The Inviter (For Business Visa)atif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Atif Jabbar: BE (Electronics), ME (Mechatronics)Document2 pagesAtif Jabbar: BE (Electronics), ME (Mechatronics)atif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Apt Aerox III 3.2kw - Manual 20181224Document41 pagesApt Aerox III 3.2kw - Manual 20181224atif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Based PID: Term Math Function Effect On Control SystemDocument3 pagesOp-Amp Based PID: Term Math Function Effect On Control Systematif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Single Loop ControlDocument4 pagesNtroduction: Single Loop Controlatif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Victor Brochure VturnII-16 - 20 - 23 - 26 (20091230)Document16 pagesVictor Brochure VturnII-16 - 20 - 23 - 26 (20091230)atif jabbarNo ratings yet
- Hearing Aid PDFDocument43 pagesHearing Aid PDFBILAL DIFNo ratings yet
- Chopper: Class-C or Type-CDocument42 pagesChopper: Class-C or Type-CDr.K.Krishna VeniNo ratings yet
- High and Medium Voltage Circuit Breaker TestingDocument10 pagesHigh and Medium Voltage Circuit Breaker TestingFaridahmad AziziNo ratings yet
- JVC GV Chassis Av30w475 TV D PDFDocument24 pagesJVC GV Chassis Av30w475 TV D PDFRoosevelt Vega SanchezNo ratings yet
- An-42036 PCB Grounding System and FAN2001 FAN2011Document3 pagesAn-42036 PCB Grounding System and FAN2001 FAN2011Spiinn PhattrakulNo ratings yet
- 900 ADA - Rev13Document306 pages900 ADA - Rev13Miguel Ignacio Roman BarreraNo ratings yet
- Lecture15 Laplace Transform in CCT AnalysisDocument11 pagesLecture15 Laplace Transform in CCT AnalysisTahreem AkmalNo ratings yet
- SKF Static Motor Analyzer Baker DX: DX Capabilities and Added FlexibilityDocument4 pagesSKF Static Motor Analyzer Baker DX: DX Capabilities and Added FlexibilityPablo Marcelo Garnica TejerinaNo ratings yet
- Mugtextiletechnology PDFDocument96 pagesMugtextiletechnology PDFDr. Gollapalli NareshNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Inductors Capacitors and Alternating Current CircuitsDocument42 pagesBab 2 Inductors Capacitors and Alternating Current CircuitsVimal SaravananNo ratings yet
- Cusat Civil Engg SyllabusDocument81 pagesCusat Civil Engg SyllabusAkhil Madhusoodanan100% (1)
- Chapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC ChoppersDocument55 pagesChapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC Choppersfor life100% (1)
- Schem of WorkDocument60 pagesSchem of Workeugene100% (1)
- Cmos Ota ThesisDocument5 pagesCmos Ota Thesislisabrownolathe100% (2)
- 3rd Sem Electric CircuitDocument57 pages3rd Sem Electric CircuitRajkumarJhapteNo ratings yet
- L-1/T-2/IPE Date: 07/09/2021Document17 pagesL-1/T-2/IPE Date: 07/09/2021Indrajit KarmakerNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mass Flow ControllerDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Mass Flow ControllerHERDI SUTANTONo ratings yet
- Description of Schematic DiagramDocument18 pagesDescription of Schematic Diagramtest2k3No ratings yet
- Introduction To Logic Circuit & Digital Electronics: Romel B. Cristobal, Ed.D., PH.DDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Logic Circuit & Digital Electronics: Romel B. Cristobal, Ed.D., PH.DRichard Pascual ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Sverker 750Document80 pagesSverker 750Yosua A.E. Sitorus100% (2)
- Analog Methodology Perry HeedleyDocument38 pagesAnalog Methodology Perry HeedleyHend FaresNo ratings yet
- Tda16888 150winfineon PDFDocument20 pagesTda16888 150winfineon PDFhiep leNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Control of A DC - DC Multilevel Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesModelling and Control of A DC - DC Multilevel Boost ConverterAnonymous jxm0WNS7QaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Plant Watering System Using Arduino UNO: A Project Report OnDocument23 pagesAutomatic Plant Watering System Using Arduino UNO: A Project Report OnCHAUDHARY HASSANNo ratings yet
- Application Bulletin: Operational Amplifier Macromodels: A ComparisonDocument5 pagesApplication Bulletin: Operational Amplifier Macromodels: A ComparisonAgfagf212No ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - 06Document27 pagesLecture 05 - 06nerd memesNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical ComponentsDocument8 pagesSymmetrical Componentssrikanth velpulaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document9 pagesLab Report 1Hajer JejeNo ratings yet