Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
Uploaded by
nykeba smithCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CIE Resources: Educ - ICTDocument7 pagesCIE Resources: Educ - ICTflowerkm44% (9)
- Opening and Closing Speech For English CampDocument2 pagesOpening and Closing Speech For English CampVivien Na Rungsri100% (6)
- Automobile Cooling System Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesAutomobile Cooling System Lesson PlanAyobami olaNo ratings yet
- 7.1. Emission Control SystemDocument18 pages7.1. Emission Control SystemChristian Icaza SamaniegoNo ratings yet
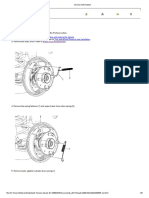
- Brake Shoe Replacement PDFDocument8 pagesBrake Shoe Replacement PDFY. VásquezNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesDocument42 pagesOutcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear PotentiometerDocument3 pagesLinear PotentiometerProdip KhanikarNo ratings yet
- 2020-MC-274 System 2Document17 pages2020-MC-274 System 2David James100% (1)
- Cooliing System TTLM PR - by S-DDocument142 pagesCooliing System TTLM PR - by S-DElias WeldeyohansNo ratings yet
- TVET ManagementDocument134 pagesTVET Managementdesubie bireNo ratings yet
- Assessment Plan TemplateDocument1 pageAssessment Plan TemplateUmesh Banga100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of Alaoji Thermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Alaoji Thermal Power PlantIjaems JournalNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Lab Activities For A Course On Fluid PowerDocument35 pagesDesign and Development of Pneumatic Lab Activities For A Course On Fluid PowerKhaled MahranNo ratings yet
- (Jurutera Dalam Masyarakat) : EUP222 - Engineers in SocietyDocument13 pages(Jurutera Dalam Masyarakat) : EUP222 - Engineers in SocietySaiful MunirNo ratings yet
- 204-00 Ride Height MeasurementDocument4 pages204-00 Ride Height MeasurementAngy SalasNo ratings yet
- How To Install Your Boost ControllerDocument4 pagesHow To Install Your Boost ControllerRonNo ratings yet
- This Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesThis Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionspransuNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIALDocument4 pagesDIFFERENTIALsaffrin100% (1)
- Manual Steering System: SectionDocument21 pagesManual Steering System: SectionEduardo ColinNo ratings yet
- Pascal's LawDocument5 pagesPascal's LawRushilNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2Document47 pagesUNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2dhavalNo ratings yet
- Cad Notes Lesson 1Document7 pagesCad Notes Lesson 1AmuomNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Automatic Car Washing SystemDocument3 pagesArduino Based Automatic Car Washing SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Engine Tune Up ppt.1Document23 pagesEngine Tune Up ppt.1Kifu YeNo ratings yet
- Solid Modeling Final - Manual-06!05!19 New by MailDocument276 pagesSolid Modeling Final - Manual-06!05!19 New by MailRajat ShrirameNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3 Maintenance PrinciplesDocument50 pagesUnit 2.3 Maintenance Principlesyared Belete100% (1)
- Groundnut ThrusterDocument39 pagesGroundnut ThrusterBoopathi KalaiNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Writing of Industrial Training Report-JPTDocument5 pagesGuideline On Writing of Industrial Training Report-JPTRahmad SudirmanNo ratings yet
- The QCE of The NBC No.461 Instrument For Instruction/Teaching Effectiveness Rating Period: - ToDocument1 pageThe QCE of The NBC No.461 Instrument For Instruction/Teaching Effectiveness Rating Period: - ToTiffany Ruth Rebolledo-quinitipNo ratings yet
- Competency Based Curriculum NC3 AutomotiveDocument10 pagesCompetency Based Curriculum NC3 AutomotiveGilbert MendozaNo ratings yet
- Apply Quality ControlDocument24 pagesApply Quality Controlrame100% (1)
- Trainer Guide: Automotive Service TechnicianDocument30 pagesTrainer Guide: Automotive Service Technicianjameel babooramNo ratings yet
- Automotive Handbook: 7Th EditionDocument9 pagesAutomotive Handbook: 7Th EditionGeorgiana Busuioc0% (1)
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsDocument47 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsnuncafalhaNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head & Valve Mechanism Inspection & ServiceDocument19 pagesCylinder Head & Valve Mechanism Inspection & ServiceGetachew Tikue100% (1)
- City and Gulds SyllabusDocument240 pagesCity and Gulds SyllabusKishan Rock StormsNo ratings yet
- 60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding RevisedDocument60 pages60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding Reviseddmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Automotive Components Lab Manual - NewDocument92 pagesAutomotive Components Lab Manual - NewAnonymous 3x3Wuew0DHNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Reference: Engineeringmanagement by RobertomedinaDocument15 pagesEngineering Management: Reference: Engineeringmanagement by RobertomedinaZchary SkyNo ratings yet
- Clutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitDocument60 pagesClutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitPete MoonNo ratings yet
- Parallel ParkingDocument5 pagesParallel Parkingbra9tee9tiniNo ratings yet
- FDP Brochure HeatDocument2 pagesFDP Brochure HeatKesavan DhuraiNo ratings yet
- Mechathon Problem Statement-2 PDFDocument3 pagesMechathon Problem Statement-2 PDFFarhan Ahamed HameedNo ratings yet
- Northern Railway, Diesel Shed, LudhianaDocument18 pagesNorthern Railway, Diesel Shed, LudhianaGarry SagguNo ratings yet
- Motivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementDocument30 pagesMotivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementJaspher Jan PasolNo ratings yet
- Assessor Moderator, Mentor CoachDocument24 pagesAssessor Moderator, Mentor Coachgeraldine franzsenNo ratings yet
- AURAEA002 KnowledgeAssessmentDocument20 pagesAURAEA002 KnowledgeAssessmentMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Suspension System Service: Chapter ObjectivesDocument21 pagesSuspension System Service: Chapter ObjectivesMujeres Virglius PabliusNo ratings yet
- Akpk (Problem Ratio)Document5 pagesAkpk (Problem Ratio)Nur AishahNo ratings yet
- Toyota Vehicle Security System (TVSS) Owners Manual: VIOS - DEC - 2020 - 001Document12 pagesToyota Vehicle Security System (TVSS) Owners Manual: VIOS - DEC - 2020 - 001Pafuncio AlecrimNo ratings yet
- Inspecting The Ignition System PDFDocument3 pagesInspecting The Ignition System PDFJayson CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Quality Engineering and ManufacturingDocument1 pageJntuworld: Quality Engineering and ManufacturingcomputerstudentNo ratings yet
- Pre-Delivery InspectionDocument17 pagesPre-Delivery InspectionSyron L. CarijutanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of Flywheel: Batchelor of Technology IN Mechanical EngineeringDocument45 pagesModeling and Analysis of Flywheel: Batchelor of Technology IN Mechanical EngineeringMohammed Ghazi Mubarriz AbbadNo ratings yet
- ME8512 Thermal Lab ManualDocument186 pagesME8512 Thermal Lab ManualManikandanNo ratings yet
- Automotive Applications of Thermoelectric MaterialsDocument7 pagesAutomotive Applications of Thermoelectric Materialsgljr32941181011No ratings yet
- DGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDocument13 pagesDGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDharmendra SahaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 NotesPankaj Gaurav100% (1)
- Advancement in AutomobileDocument14 pagesAdvancement in AutomobileVardhan ChipperNo ratings yet
- PTS Reviewer For INTERVIEW of TraineesDocument7 pagesPTS Reviewer For INTERVIEW of TraineesMARJORIE BIBON100% (1)
- Module in Ed 107-Assessment in Learning Ii (Chapter 2)Document7 pagesModule in Ed 107-Assessment in Learning Ii (Chapter 2)Alliah Jane Delfin100% (5)
- PTS Info IdeasDocument7 pagesPTS Info IdeasJay De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten LP-Q3-Week 5 Day 3Document3 pagesKindergarten LP-Q3-Week 5 Day 3Sharicka Anne Veronica Tambor100% (1)
- City of Malabon University: College of Teacher EducationDocument60 pagesCity of Malabon University: College of Teacher EducationJan Quincy FormanezNo ratings yet
- Character Education at Eton FinalDocument35 pagesCharacter Education at Eton FinalAlber SánchezNo ratings yet
- SUMSEM-2021-22 HUM1022 ETH VL2021220701716 DA-1 QP KEY F1 F2 Digital Assignment I HUM1022Document4 pagesSUMSEM-2021-22 HUM1022 ETH VL2021220701716 DA-1 QP KEY F1 F2 Digital Assignment I HUM1022Nathan ShankarNo ratings yet
- My OBE Music Overview IDocument2 pagesMy OBE Music Overview IChad BallonNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Class Program 2022-2023Document1 pageGrade 4 Class Program 2022-2023Geoff Rey100% (3)
- Organizational Change: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EDocument20 pagesOrganizational Change: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EMuraliNo ratings yet
- Esp 351 - Pre Class Questions Emily PureDocument2 pagesEsp 351 - Pre Class Questions Emily Pureapi-528999972No ratings yet
- Myth of ComputerDocument3 pagesMyth of ComputerscribdomminiNo ratings yet
- Final Project Rubric 2021-2Document1 pageFinal Project Rubric 2021-2rodriguezchaconNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Skills and PTE Young LearnersDocument51 pages21st Century Skills and PTE Young LearnersSan Htiet OoNo ratings yet
- Ref M Schraw y MoshmanDocument23 pagesRef M Schraw y MoshmanNicolás ParraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍADocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍAJacky García Solano100% (1)
- Shakespeare Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesShakespeare Lesson Planapi-490377001No ratings yet
- Assessment Method-Based Instructions and Guidelines: Knowledge TestDocument13 pagesAssessment Method-Based Instructions and Guidelines: Knowledge TestAlessandro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 SPCM Research - Chapter 1 - ProposalDocument23 pagesGROUP 3 SPCM Research - Chapter 1 - ProposalHershey DulinNo ratings yet
- Listening StrategiesDocument2 pagesListening StrategiesGEHNo ratings yet
- MATERI BCLnD-Success in BINUS Online LearningDocument60 pagesMATERI BCLnD-Success in BINUS Online Learninghafidz_gantengNo ratings yet
- Parental Monitoring and Academic Performance and Behavior of The Students in Bohol Wisdom School by MR GutangDocument73 pagesParental Monitoring and Academic Performance and Behavior of The Students in Bohol Wisdom School by MR GutangJumar Gabrinao Gutang100% (1)
- Valiandes 2017Document17 pagesValiandes 2017Banu a/p Ramanan IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- BDNHS Homeroom Guidance AssessmentDocument3 pagesBDNHS Homeroom Guidance AssessmentElenor May Chantal MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- Competency GuideDocument20 pagesCompetency GuidekapsicumNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - PronunciationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - PronunciationBia MQ100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan - Day 1 To Day 5 - CL and HCLDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan - Day 1 To Day 5 - CL and HCLkcppsp5No ratings yet
- Nagar Yuwak Shikshan Sanstha: Name of The Institution: Shri Datta Meghe Polytechnic, Nagpur Annual Progress ReportDocument6 pagesNagar Yuwak Shikshan Sanstha: Name of The Institution: Shri Datta Meghe Polytechnic, Nagpur Annual Progress ReportRamdas pawankarNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Cognitive and MetacognitiveDocument1 pageIndicators of Cognitive and MetacognitiveMiguel Angelo AnggamNo ratings yet
- Investigating Student Engagement in Blended Learning Settings Usingexperience Sampling and Structural Equation ModelingDocument13 pagesInvestigating Student Engagement in Blended Learning Settings Usingexperience Sampling and Structural Equation ModelingkulaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Poetry PresentationsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Poetry Presentationstanuja viswanathNo ratings yet
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
Uploaded by
nykeba smithOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
CBET characteristicsCOMPETENCY
Uploaded by
nykeba smithCopyright:
Available Formats
KEY FEATURES OF COMPETENCY-BASED TRAINING
1. Industry Involvement
Description- CBET is based on industry standards develop by industry experts to the
guide the attainment of competencies.
Combines technical vocational education and training with work practice and
work-based assessment of performance
Training is based on nationally and internationally agreed standards directly
related to the needs of occupations
It recognizes that learning takes place in many settings including the work
setting
Industry experts are involved in the development of standards where
competencies are carefully identified, verified and placed in the public
domain.
2. Programme Design & Development
Description
- Programmes that are designed and developed using a competency-based approach are
guaranteed to be current, relevant and most suited to prepare an individual for new and
emerging job opportunities.
There must be a clearly defined approach and methodology for staff development and
facilitator training
Competency-based philosophy must be used as a guide for TVET practitioners
preparation and training
o Training needs analysis
o Innovative approaches in instructional delivery
o Flexible training strategies
o Resources
3. Programme Implementation - Delivery/Instructional Strategies
Description
Competencies are predictors of professional effectiveness
Focused on what learners know/do/show
Based on competencies/skills/attitude acquisition
Driven by and measured against standards
Individualized self-paced learning strategy
Attainments indicated by levels of “mastery”.
Ideally skills are identified by industry,
Includes simulation of workplace performance
Performance criteria must be established
Dynamic/creative instructional delivery modes.
4. Assessment
Description - A system of capturing and measuring the trainee’s/learner’s knowledge, skills
and attitudes in relation to a stated outcome.
Identification of assessment tasks – aligned with competencies
Formative and Summative Assessment
Competency-based philosophy must be used as a guide for instructor/facilitator
preparation/training
Training begins with use of standards
Innovative approaches in instructional delivery
Flexible training strategies
Validity and Reliability of Assessment - Moderation and verification of assessment results
and tasks
Using assessment results
Certification
5. Quality Assurance
Description- A well-documented and administered system of internal and external
verification of processes is essential in establishing and maintaining credibility.
Internal – within the organization
o Verification/monitoring system, processes and procedures
External – accreditation
o Standards, process, and procedures
CBET IS characterised by:
1. An emphasis on performance-based activities rather than the content of the
course;
2. Theoretical knowledge that underpins performance requirements
3. Learning experiences that are relevant to real-world practices.
4. Facilitation of the relationships among knowledge, skills, attitude and job
functions.
Commented [NS1]: Repetition of 3
5. Generating applicable lessons to various situations;
6. Encouraging self-direction of individuals;
7. Transforming the role of the teachers towards facilitating and problem solving.
8. Competencies are carefully identified, verified and in the public domain (of
public knowledge).
9. Instruction is aimed at the development of each competency.
10. The assessment and evaluation take into account knowledge, skills, attitudes
and performance, as the main sources of evidence.
11. Combines technical vocational education and training with work practice and
work based assessment of performance
12. Training is based on nationally and internationally agreed standards directly
related to the needs of occupations
13. It recognizes that learning takes place in many settings including the work
setting
14. The progress of the trainees during the training goes at the pace of each
individual.
15. Instruction is individualised as much as possible.
16. Emphasis is placed on the results – outcomes based.
17. The participation of workers in the development and implementation of learning
strategies is required.
18. The learning experiences are guided by continuous feedback.
19. Combines technical vocational education and training with work practice and work based
assessment of performance
20. Training is based on nationally and internationally agreed standards dir ectly related to the
needs of occupations
21. It recognizes that learning takes place in many settings including the work setting
You might also like
- CIE Resources: Educ - ICTDocument7 pagesCIE Resources: Educ - ICTflowerkm44% (9)
- Opening and Closing Speech For English CampDocument2 pagesOpening and Closing Speech For English CampVivien Na Rungsri100% (6)
- Automobile Cooling System Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesAutomobile Cooling System Lesson PlanAyobami olaNo ratings yet
- 7.1. Emission Control SystemDocument18 pages7.1. Emission Control SystemChristian Icaza SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Brake Shoe Replacement PDFDocument8 pagesBrake Shoe Replacement PDFY. VásquezNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesDocument42 pagesOutcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Linear PotentiometerDocument3 pagesLinear PotentiometerProdip KhanikarNo ratings yet
- 2020-MC-274 System 2Document17 pages2020-MC-274 System 2David James100% (1)
- Cooliing System TTLM PR - by S-DDocument142 pagesCooliing System TTLM PR - by S-DElias WeldeyohansNo ratings yet
- TVET ManagementDocument134 pagesTVET Managementdesubie bireNo ratings yet
- Assessment Plan TemplateDocument1 pageAssessment Plan TemplateUmesh Banga100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of Alaoji Thermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Alaoji Thermal Power PlantIjaems JournalNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Pneumatic Lab Activities For A Course On Fluid PowerDocument35 pagesDesign and Development of Pneumatic Lab Activities For A Course On Fluid PowerKhaled MahranNo ratings yet
- (Jurutera Dalam Masyarakat) : EUP222 - Engineers in SocietyDocument13 pages(Jurutera Dalam Masyarakat) : EUP222 - Engineers in SocietySaiful MunirNo ratings yet
- 204-00 Ride Height MeasurementDocument4 pages204-00 Ride Height MeasurementAngy SalasNo ratings yet
- How To Install Your Boost ControllerDocument4 pagesHow To Install Your Boost ControllerRonNo ratings yet
- This Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesThis Set of Building Construction Multiple Choice QuestionspransuNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIALDocument4 pagesDIFFERENTIALsaffrin100% (1)
- Manual Steering System: SectionDocument21 pagesManual Steering System: SectionEduardo ColinNo ratings yet
- Pascal's LawDocument5 pagesPascal's LawRushilNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2Document47 pagesUNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2dhavalNo ratings yet
- Cad Notes Lesson 1Document7 pagesCad Notes Lesson 1AmuomNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Automatic Car Washing SystemDocument3 pagesArduino Based Automatic Car Washing SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Engine Tune Up ppt.1Document23 pagesEngine Tune Up ppt.1Kifu YeNo ratings yet
- Solid Modeling Final - Manual-06!05!19 New by MailDocument276 pagesSolid Modeling Final - Manual-06!05!19 New by MailRajat ShrirameNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3 Maintenance PrinciplesDocument50 pagesUnit 2.3 Maintenance Principlesyared Belete100% (1)
- Groundnut ThrusterDocument39 pagesGroundnut ThrusterBoopathi KalaiNo ratings yet
- Guideline On Writing of Industrial Training Report-JPTDocument5 pagesGuideline On Writing of Industrial Training Report-JPTRahmad SudirmanNo ratings yet
- The QCE of The NBC No.461 Instrument For Instruction/Teaching Effectiveness Rating Period: - ToDocument1 pageThe QCE of The NBC No.461 Instrument For Instruction/Teaching Effectiveness Rating Period: - ToTiffany Ruth Rebolledo-quinitipNo ratings yet
- Competency Based Curriculum NC3 AutomotiveDocument10 pagesCompetency Based Curriculum NC3 AutomotiveGilbert MendozaNo ratings yet
- Apply Quality ControlDocument24 pagesApply Quality Controlrame100% (1)
- Trainer Guide: Automotive Service TechnicianDocument30 pagesTrainer Guide: Automotive Service Technicianjameel babooramNo ratings yet
- Automotive Handbook: 7Th EditionDocument9 pagesAutomotive Handbook: 7Th EditionGeorgiana Busuioc0% (1)
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsDocument47 pagesHydraulic and Pneumatic SystemsnuncafalhaNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head & Valve Mechanism Inspection & ServiceDocument19 pagesCylinder Head & Valve Mechanism Inspection & ServiceGetachew Tikue100% (1)
- City and Gulds SyllabusDocument240 pagesCity and Gulds SyllabusKishan Rock StormsNo ratings yet
- 60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding RevisedDocument60 pages60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding Reviseddmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Automotive Components Lab Manual - NewDocument92 pagesAutomotive Components Lab Manual - NewAnonymous 3x3Wuew0DHNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Reference: Engineeringmanagement by RobertomedinaDocument15 pagesEngineering Management: Reference: Engineeringmanagement by RobertomedinaZchary SkyNo ratings yet
- Clutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitDocument60 pagesClutches, Transmissions, and Drives: Study UnitPete MoonNo ratings yet
- Parallel ParkingDocument5 pagesParallel Parkingbra9tee9tiniNo ratings yet
- FDP Brochure HeatDocument2 pagesFDP Brochure HeatKesavan DhuraiNo ratings yet
- Mechathon Problem Statement-2 PDFDocument3 pagesMechathon Problem Statement-2 PDFFarhan Ahamed HameedNo ratings yet
- Northern Railway, Diesel Shed, LudhianaDocument18 pagesNorthern Railway, Diesel Shed, LudhianaGarry SagguNo ratings yet
- Motivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementDocument30 pagesMotivating: EMN511: Engineering ManagementJaspher Jan PasolNo ratings yet
- Assessor Moderator, Mentor CoachDocument24 pagesAssessor Moderator, Mentor Coachgeraldine franzsenNo ratings yet
- AURAEA002 KnowledgeAssessmentDocument20 pagesAURAEA002 KnowledgeAssessmentMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Suspension System Service: Chapter ObjectivesDocument21 pagesSuspension System Service: Chapter ObjectivesMujeres Virglius PabliusNo ratings yet
- Akpk (Problem Ratio)Document5 pagesAkpk (Problem Ratio)Nur AishahNo ratings yet
- Toyota Vehicle Security System (TVSS) Owners Manual: VIOS - DEC - 2020 - 001Document12 pagesToyota Vehicle Security System (TVSS) Owners Manual: VIOS - DEC - 2020 - 001Pafuncio AlecrimNo ratings yet
- Inspecting The Ignition System PDFDocument3 pagesInspecting The Ignition System PDFJayson CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Quality Engineering and ManufacturingDocument1 pageJntuworld: Quality Engineering and ManufacturingcomputerstudentNo ratings yet
- Pre-Delivery InspectionDocument17 pagesPre-Delivery InspectionSyron L. CarijutanNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of Flywheel: Batchelor of Technology IN Mechanical EngineeringDocument45 pagesModeling and Analysis of Flywheel: Batchelor of Technology IN Mechanical EngineeringMohammed Ghazi Mubarriz AbbadNo ratings yet
- ME8512 Thermal Lab ManualDocument186 pagesME8512 Thermal Lab ManualManikandanNo ratings yet
- Automotive Applications of Thermoelectric MaterialsDocument7 pagesAutomotive Applications of Thermoelectric Materialsgljr32941181011No ratings yet
- DGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDocument13 pagesDGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDharmendra SahaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 NotesPankaj Gaurav100% (1)
- Advancement in AutomobileDocument14 pagesAdvancement in AutomobileVardhan ChipperNo ratings yet
- PTS Reviewer For INTERVIEW of TraineesDocument7 pagesPTS Reviewer For INTERVIEW of TraineesMARJORIE BIBON100% (1)
- Module in Ed 107-Assessment in Learning Ii (Chapter 2)Document7 pagesModule in Ed 107-Assessment in Learning Ii (Chapter 2)Alliah Jane Delfin100% (5)
- PTS Info IdeasDocument7 pagesPTS Info IdeasJay De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten LP-Q3-Week 5 Day 3Document3 pagesKindergarten LP-Q3-Week 5 Day 3Sharicka Anne Veronica Tambor100% (1)
- City of Malabon University: College of Teacher EducationDocument60 pagesCity of Malabon University: College of Teacher EducationJan Quincy FormanezNo ratings yet
- Character Education at Eton FinalDocument35 pagesCharacter Education at Eton FinalAlber SánchezNo ratings yet
- SUMSEM-2021-22 HUM1022 ETH VL2021220701716 DA-1 QP KEY F1 F2 Digital Assignment I HUM1022Document4 pagesSUMSEM-2021-22 HUM1022 ETH VL2021220701716 DA-1 QP KEY F1 F2 Digital Assignment I HUM1022Nathan ShankarNo ratings yet
- My OBE Music Overview IDocument2 pagesMy OBE Music Overview IChad BallonNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Class Program 2022-2023Document1 pageGrade 4 Class Program 2022-2023Geoff Rey100% (3)
- Organizational Change: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EDocument20 pagesOrganizational Change: Mcshane/Von Glinow M:Ob 3EMuraliNo ratings yet
- Esp 351 - Pre Class Questions Emily PureDocument2 pagesEsp 351 - Pre Class Questions Emily Pureapi-528999972No ratings yet
- Myth of ComputerDocument3 pagesMyth of ComputerscribdomminiNo ratings yet
- Final Project Rubric 2021-2Document1 pageFinal Project Rubric 2021-2rodriguezchaconNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Skills and PTE Young LearnersDocument51 pages21st Century Skills and PTE Young LearnersSan Htiet OoNo ratings yet
- Ref M Schraw y MoshmanDocument23 pagesRef M Schraw y MoshmanNicolás ParraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍADocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍAJacky García Solano100% (1)
- Shakespeare Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesShakespeare Lesson Planapi-490377001No ratings yet
- Assessment Method-Based Instructions and Guidelines: Knowledge TestDocument13 pagesAssessment Method-Based Instructions and Guidelines: Knowledge TestAlessandro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 SPCM Research - Chapter 1 - ProposalDocument23 pagesGROUP 3 SPCM Research - Chapter 1 - ProposalHershey DulinNo ratings yet
- Listening StrategiesDocument2 pagesListening StrategiesGEHNo ratings yet
- MATERI BCLnD-Success in BINUS Online LearningDocument60 pagesMATERI BCLnD-Success in BINUS Online Learninghafidz_gantengNo ratings yet
- Parental Monitoring and Academic Performance and Behavior of The Students in Bohol Wisdom School by MR GutangDocument73 pagesParental Monitoring and Academic Performance and Behavior of The Students in Bohol Wisdom School by MR GutangJumar Gabrinao Gutang100% (1)
- Valiandes 2017Document17 pagesValiandes 2017Banu a/p Ramanan IPGKKBNo ratings yet
- BDNHS Homeroom Guidance AssessmentDocument3 pagesBDNHS Homeroom Guidance AssessmentElenor May Chantal MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- Competency GuideDocument20 pagesCompetency GuidekapsicumNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - PronunciationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - PronunciationBia MQ100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan - Day 1 To Day 5 - CL and HCLDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan - Day 1 To Day 5 - CL and HCLkcppsp5No ratings yet
- Nagar Yuwak Shikshan Sanstha: Name of The Institution: Shri Datta Meghe Polytechnic, Nagpur Annual Progress ReportDocument6 pagesNagar Yuwak Shikshan Sanstha: Name of The Institution: Shri Datta Meghe Polytechnic, Nagpur Annual Progress ReportRamdas pawankarNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Cognitive and MetacognitiveDocument1 pageIndicators of Cognitive and MetacognitiveMiguel Angelo AnggamNo ratings yet
- Investigating Student Engagement in Blended Learning Settings Usingexperience Sampling and Structural Equation ModelingDocument13 pagesInvestigating Student Engagement in Blended Learning Settings Usingexperience Sampling and Structural Equation ModelingkulaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Poetry PresentationsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Poetry Presentationstanuja viswanathNo ratings yet