Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1
Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1
Uploaded by
Charrie RagadiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1
Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Case 1
Uploaded by
Charrie RagadiCopyright:
Available Formats
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
1 2
CASE 1
Benign and Malignant
OVARIAN TUMORS
ANA VICTORIA V. DY ECHO, MD
Clinical Associate Professor
Department of OB-GYN
UP-Manila, Philippine General Hospital
3 4
CASE 1 CASE 1
35 years old G0
CC: intermittent abdominal pain
(-) constitutional signs, symptoms What is the most likely diagnosis?
PE:
Abdomen flat, (-) fluid wave
IE: NEG, nulliparous vagina, cervix 3 x 2 cm,
smooth, corpus small, (+) right adnexal mass, 8
x 8 cm, cystic, movable
RVE: bilateral parametria smooth and pliable
5 6
Benign vs. Malignant CASE 1
BENIGN MALIGNANT
Young Older What is the most likely diagnosis?
Unilateral Bilateral
Cystic Solid OVARIAN NEW GROWTH,
Mobile Fixed
PROBABLY BENIGN
Smooth Irregular
No ascites Ascites
Slow growth Rapid growth
McMeekin DS, et al. The adnexal mass. In: Di Saia, et al (Ed).
Clinical Gynecologic Oncology, 5 th Ed. 2012
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 1
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
7 8
CASE 1 Benign Tumors of the Ovary
• FUNCTIONAL • BENIGN NEOPLASMS
What are your differentials?
• Follicular • Germ cell tumor
• Corpus luteum Benign cystic teratoma
• Theca lutein (dermoid cyst)
• Endometrioma
• INFLAMMATORY • Fibroma
• Tubo-ovarian abscess or • Epithelial tumors
complex Adenofibroma and
cystadenofibroma
Transitional cell tumors –
Brenner tumors
Katz VL, et al. Comprehensive Gynecology 6 th Ed, 2012
9 10
Other Differentials CASE 1
• UTERUS • NON-GYNECOLOGIC
What diagnostic tests should be requested?
• Subserous myoma • Diverticular abscess
• Appendiceal abscess or
• FALLOPIAN TUBE mucocele
Transvaginal ultrasound
• Nerve sheath tumors
• Hydrosalpinx
• Ureteral/bladder diverticulum
• Paratubal cyst
• Pelvic kidneys CBC
Blood typing
Castro, et al. Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Masses.
In: POGS CPG on Myoma Uteri and Adnexal Masses, 2010
11 12
CASE 1 Imaging Studies
ULTRASOUND
1. Is the finding a simple (unilocular) or complex
(multicystic/multilocular with solid components)
cyst?
2. Are there papillary projections?
3. Are the cystic walls and/or septa regular and
smooth?
4. What is the echogenicity (tissue characterization)?
Katz VL, et al. Comprehensive Gynecology 6 th Ed, 2012
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 2
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
13 14
Imaging Studies CASE 1
ULTRASOUND
B rules M rules
(Benign tumors) (Malignant tumors)
Unilocular Irregular solid tumor
Presence of acoustic Presence of ascites
shadowing At least 4 papillary structures
Smooth multilocular tumor Irregular multilocular solid
No blood flow tumor
Very strong blood flow
Castro, et al. Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Masses.
In: POGS CPG on Myoma Uteri and Adnexal Masses, 2010
15 16
CASE 1 CASE 1
What is the diagnosis? What is the appropriate management for this
case?
OVARIAN NEW GROWTH,
PROBABLY BENIGN
17 18
Management of Benign Tumors Management of Benign Tumors
• Management depends on diagnosis, patient’s FUNCTIONAL CYSTS
age, patient’s desire for fertility. • Observation
• Cystectomy is the procedure of choice where EPITHELIAL OVARIAN TUMORS
normal ovarian tissue is still appreciated. • Oophorectomy, occasionally cystectomy
• Oophorectomy is indicated when ovarian tissue
cannot be preserved. DERMOID CYSTS, ENDOMETRIOMA
• Cystectomy
• Laparoscopy vs. laparotomy
Gonzales, et al. Management of Adnexal Masses.
In: POGS CPG on Myoma Uteri and Adnexal Masses, 2010 Katz VL, et al. Comprehensive Gynecology 6 th Ed, 2012
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 3
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
19 20
CASE 1 Benign Tumors of the Ovary
DERMOID CYST ENDOMETRIOMA
What is the appropriate management for this
case?
CYSTECTOMY
21 22
Benign Tumors of the Ovary CASE 1
FIBROMA BENIGN BRENNER TUMOR
23 24
CASE 1 CASE 1
What is the final diagnosis?
MATURE CYSTIC TERATOMA, RIGHT OVARY
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 4
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
25 26
CASE 2
CASE 2 55 years old G0
CC: 5 months history of enlarging abdominal mass,
associated with intermittent pain
(-) constitutional signs, symptoms
PE:
(+) 22 x 19 cm abdominopelvic mass, cystic with
solid areas, slight mobility, nontender, (-) fluid wave
IE: NEG, nulliparous vagina, cervix 3 x 2 cm,
smooth, corpus small, inferior pole of mass palpated
at cul-de-sac
RVE: bilateral parametria smooth and pliable
27 28
CASE 2 Benign vs. Malignant
BENIGN MALIGNANT
What is the most likely diagnosis? Young Older
Unilateral Bilateral
Cystic Solid
Mobile Fixed
Smooth Irregular
No ascites Ascites
Slow growth Rapid growth
McMeekin DS, et al. The adnexal mass. In: Di Saia, et al (Ed).
Clinical Gynecologic Oncology, 5 th Ed. 2012
29 30
CASE 2 CASE 2
What is the most likely diagnosis? What are your differentials?
OVARIAN NEW GROWTH,
PROBABLY MALIGNANT
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 5
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
31 32
Malignant Tumors of the Ovary Nongynecologic Malignant Tumors
• EPITHELIAL • SEX CORD STROMAL • GASTRO-INTESTINAL
• Serous carcinoma • Granulosa cell tumors TUMORS
• Mucinous carcinoma • Sertoli cell tumors
• Endometrioid carcinoma
• RETROPERITONEAL
• Clear cell carcinoma
• Malignant Brenner tumor
• MESENCHYMAL SARCOMAS
• GERM CELL TUMORS • METASTATIC
• Dysgerminoma
• Yolk sac tumors
• Immature teratoma
Castro, et al. Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Masses.
Katz VL, et al. Comprehensive Gynecology 6 th Ed, 2012 In: POGS CPG on Myoma Uteri and Adnexal Masses, 2010
33 34
CASE 2 Imaging Studies
DOPPLER STUDIES
What diagnostic tests should be requested?
• Allows assessment of tumor vascularity
Transvaginal ultrasound • Malignant tumors display increased vascularity,
Doppler studies decreased peripheral flow resistance, increased blood
CA-125 + HE4 velocity1
CBC
Blood typing • Resistance index – measures resistance to flow
FBS, BUN, creatinine, AST, ALT, Mg, K, Ca, Cl, alb in the vessels; low in neovascularization
Chest x-ray • RI 0.4-0.62
Whole abdomen ultrasound
1Myer ER, et al. Management of adnexal mass. Evidence report/Technology
12-lead ECG assessment No 130, 2006; 2Katz VL, et al. Comprehensive Gynecology 6 th Ed
35 36
Tumor Markers Tumor Markers
CA-125 CA-125
ADVANTAGE DISADVANTAGE
• Elevated in 80% of • Not expressed in 20% of
nonmucinous EOC (i.e. ovarian cancers MENOPAUSE PREMENOPAUSE
endometrioid, serous CA) • Elevated only in 50% of early 35 U/ml 65 U/ml 200 U/ml
• Elevated even before clinical stage ovarian cancers Sensitivity 78% 77% 69%
onset of ovarian cancer • Elevated in benign conditions Specificity 78% 73% 84%
(i.e. endometriosis, myoma,
PID, liver disease, CHF)
• Exhibit fluctuations in
1ACOG Committee Opinion No 477. The role of the obstetrician-gynecologist in the early detection
premenopause (i.e. menstrual of EOC. 2011 2Dearking AC, et al. How relevant are ACOG and SGO guidelines for referral of
cycle, pregnancy) adnexal mass? Obstet Gynecol 2007 3Uelend FR, et al. Effectiveness of a multivariate index
assay in the preoperative assessment of ovarian tumors. Obstet Gynecol 2011 4Myer ER, et al.
Management of adnexal mass. Evidence report/Technology assessment No. 130 2006
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 6
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
37 38
Tumor Markers CASE 2
HE4
• Complementary to CA-125
• Decreases the contribution of an erroneously elevated
CA 125 (Less false positive findings)
• Serum HE4 is elevated in > 50% of tumors that do not
express CA 125 (increases sensitivity)
• Less susceptible to peritoneal irritation
Moore RG, et al. Comparison of a novel multiple marker assay vs. the risk of malignancy
index for the prediction of epithelial ovarian cancer in patients with a pelvic mass.
Am J Obstet Gynecol 2010
39 40
CASE 2 CASE 2
41 42
CASE 2 CASE 2
CA-125 1,072 mIU/ml
What is the diagnosis?
OVARIAN NEW GROWTH,
PROBABLY MALIGNANT
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 7
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
43 44
CASE 2 Surgery for Ovarian Cancers
1. Systematic abdominal exploration via midline incision
2. Sampling of peritoneal washings (PFC) on four areas:
diaphragm, right and left hemi-abdomen, pelvis EVEN if
What is the plan of management? there is tumor rupture/present of tumor on capsule
3. Careful inspection and palpation of all peritoneal
EL, PFC, THBSO, surfaces
IO, BLND, PALS, RPB, 4. Removal of primary ovarian/fallopian tube tumor with
intact capsule
+ appendectomy 5. Total abdominal hysterectomy + bilateral salpingo-
oophorectomy (THBSO)
6. Infracolic omentectomy (IO): infragastric omentectomy,
for gross omental involvement
SGOP 2015 Clinical Practice Guideline
45 46
Surgery for Ovarian Cancers CASE 2
7. Random biopsies of normal peritoneal surfaces (RPB),
2 from each: undersurface of right hemidiaphragm,
Right ovary was converted into a multiloculated,
bladder reflection, cul-de-sac, right and left paracolic multiseptated complex mass measuring 20 x 15 x
recesses, pelvic sidewalls 7 cm., adherent laterally to the pelvic side wall and
8. Systematic lymphadenectomy (pelvic and para-aortic anteriorly to the posterior bladder surface. It
lymph node) (BLND, PALS) inadvertently ruptured during adhesiolysis.
9. For mucinous tumor, or when appendix is grossly
involved, appendectomy.
The rest of the abdominopelvic organs were
grossly normal.
SGOP 2015 Clinical Practice Guideline
47 48
CASE 2 CASE 2
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 8
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
49 50
CASE 2 Benign vs. Malignant Tumors
What is the final diagnosis?
SEROUS TUMORS
51 52
Benign vs. Malignant Tumors Malignant Tumors
MUCINOUS TUMORS ENDOMETRIOID CLEAR CELL
53 54
Malignant Tumors CASE 2
IMMATURE TERATOMA DYSGERMINOMA
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 9
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
55 56
CASE 2 Ovarian Cancer Staging
STAGE DESCRIPTION
Tumor confined to ovaries or fallopian
I
tubes
What is the final diagnosis? 1 ovary or fallopian tube, no ascites,
IA
intact capsule
2 ovaries or fallopian tubes, no ascites,
IB
SEROUS CARCINOMA, RIGHT OVARY, intact capsule
1 or 2 ovaries or fallopian tubes, with
IC
STAGE ____ any of the following:
IC1 Surgical spill
Capsule ruptured before surgery,
IC2
tumor on surface
Malignant cells on ascites or
IC3 peritoneal washings
57 58
Ovarian Cancer Staging Ovarian Cancer Staging
STAGE DESCRIPTION STAGE DESCRIPTION
II With pelvic extension (below the pelvic III With spread to the peritoneum outside
rim) or primary peritoneal cancer pelvis / (+) retroperitoneal LN
IIA Uterus / fallopian tubes / ovaries IIIA1 Positive retroperitoneal LN
IIB Other pelvic intraperitoneal tissues IIIA1i Metastasis up to 10 mm in diameter
IIIA1ii Metastasis > 10 mm in diameter
IIIA2 Microscopic extrapelvic (above the
brim) peritoneal involvement
IIIB Macroscopic peritoneal metastasis
beyond the pelvis up to 2 cm in
diameter
IIIC Macroscopic peritoneal metastasis
beyond the pelvis > 2 cm in diameter
59 60
Ovarian Cancer Staging CASE 2
STAGE DESCRIPTION
IV Distant metastasis
IVA Pleural effusion with positive cytology Will she require additional treatment?
IVB Parenchymal metastasis and
metastasis to extra-abdominal organs
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 10
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
61 62
Management of EOC CASE 2.1
STAGE STATUS PRIMARY TREATMENT
ADJUVANT
TREATMENT
27 years old G0
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical
IA-IB pregnancy staging
(G1,G2) Reproductive THSBO, complete surgical
None 5 months enlarging abdominopelvic mass
function complete staging ONG, malignant
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical
IC (G1/2, pregnancy staging Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
good Chemotherapy
Reproductive THBSO, complete surgical
histology)
function complete staging
Intraop stage IC2
IA-IC (G3,
CCC, THBSO, complete surgical
Chemotherapy
HGSC), staging
II-III
IV THBSO, tumor debulking Chemotherapy
SGOP 2015 Clinical Practice Guideline
63 64
CASE 2.1 Management of EOC
ADJUVANT
STAGE STATUS PRIMARY TREATMENT
TREATMENT
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical
Will there be a difference in the management of IA-IB pregnancy staging
None
(G1,G2) Reproductive THSBO, complete surgical
this patient? function complete staging
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical
IC (G1/2, pregnancy staging
good Chemotherapy
histology) Reproductive THBSO, complete surgical
function complete staging
IA-IC (G3,
CCC, THBSO, complete surgical
Chemotherapy
HGSC), staging
II-III
IV THBSO, tumor debulking Chemotherapy
SGOP 2015 Clinical Practice Guideline
65 66
CASE 2.1
CASE 3
Will there be a difference in the management of
this patient?
YES, may perform
EL, USO, IO, BLND, PALS, RPB, appendectomy
followed by chemotherapy
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 11
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
67 68
CASE 3 CASE 3
18 years old G0
CC: 3 months history of abdominal enlargement
PE:
(+) 15 x 10 cm abdominopelvic mass, predominantly
solid mass, nontender, (-) fluid wave
DRE: intact rectal vault, (-) intraluminal masses, cervix
small, smooth, corpus difficult to assess due to
abdominopelvic mass which is seems to be anterior to
the uterus
69 70
CASE 3 CASE 3
What diagnostic tests should be requested?
What is the diagnosis?
Transvaginal ultrasound
Doppler studies
OVARIAN NEW GROWTH, CA-125, AFP, LDH, HCG
PROBABLY MALIGNANT
CBC
Blood typing
FBS, BUN, creatinine, AST, ALT, Mg, K, Ca, Cl, alb
Chest x-ray
Whole abdomen ultrasound
12-lead ECG
71 72
CASE 3 CASE 3
What is the plan of management?
EL, PFC, USO + FS, IO, BLND, PALS, RPB
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 12
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
73 74
CASE 3 CASE 3
There is a 3 x 5 cm solid necrotic mass at the right
pelvic sidewall.
There is another 3 x 3 cm solid necrotic mass on
the omentum.
75 76
CASE 3 Management of GCT
ADJUVANT
STAGE STATUS PRIMARY TREATMENT
TREATMENT
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical Chemotherapy
How should this patient be managed pregnancy staging (except pure
IA (G1) dysgeminoma and
intraoperatively? Reproductive THSBO, complete surgical G1 immature
function complete staging teratoma)
Young/desirous of USO/BSO, complete surgical
pregnancy staging Chemotherapy
IA (G2,
EBRT for
G3), II-III Reproductive THBSO, complete surgical dysgerminoma
function complete staging OR tumor debulking
Young/desirous of
USO/BSO, tumor debulking
pregnancy
IV Chemotherapy
Reproductive
THBSO, tumor debulking
function complete
SGOP 2015 Clinical Practice Guideline
77 78
CASE 3 SUMMARY
BENIGN MALIGNANT, MALIGNANT,
YOUNG/DESIROUS, COMPLETED FAMILY,
GERM CELL TUMORS ADVANCED STAGE,
AGGRESSIVE
How should this patient be managed TUMORS
Ultrasound Ultrasound Ultrasound
intraoperatively? CA-125 + HE4 CA-125 + HE4
+ AFP, LDH, HCG + AFP, LDH, HCG
Metastatic work-up Metastatic work-up
EL, PFC, USO, tumor debulking, infragastric USO EL, USO, FS EL, THBSO
omentectomy Cystectomy IO, BLND, PALS, RPB IO, BLND, PALS, PRB
+ appendectomy + appendectomy
For IC above, For IC above,
Carboplatin + Paclitaxel Carboplatin + Paclitaxel
Bleomycin + Etoposide + Bleomycin + Etoposide +
Cisplatin Cisplatin
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 13
UP-PGH OBGYN ORAL EXAM REVIEW July 19, 2016
79
Benign and Malignant
OVARIAN TUMORS
ANA VICTORIA V. DY ECHO, MD
Clinical Associate Professor
Department of OB-GYN
UP-Manila, Philippine General Hospital
OVARIAN TUMORS: DyEcho 14
You might also like
- Unit 9: Lesson 1 Grammar - Verb + - IngDocument15 pagesUnit 9: Lesson 1 Grammar - Verb + - IngGiustinne Lliguin AmbatoNo ratings yet
- Adir SampleDocument4 pagesAdir SampleTerapie Aba67% (3)
- Ieta 2010 Resumen. General ElectricDocument1 pageIeta 2010 Resumen. General ElectricYordan JuncoNo ratings yet
- Sumita Mehta, Poonam Sachdeva (Eds.) - Colposcopy of Female Genital Tract-Springer Singapore (2017)Document243 pagesSumita Mehta, Poonam Sachdeva (Eds.) - Colposcopy of Female Genital Tract-Springer Singapore (2017)Rosu George100% (2)
- Ruptur OASISDocument41 pagesRuptur OASISHen DriNo ratings yet
- Supports of The UterusDocument20 pagesSupports of The UterusAshwin Prem Solomon100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy 2Document9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 2Kristine VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Modul Task: Tanisha Biaspal 0910714016Document5 pagesModul Task: Tanisha Biaspal 0910714016Bali PalNo ratings yet
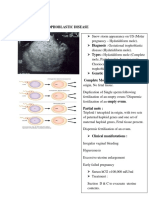
- Adnexal Masses - Ovarian Cysts (2008)Document23 pagesAdnexal Masses - Ovarian Cysts (2008)Michelle Fynes100% (1)
- Module 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsRenz Francis SasaNo ratings yet
- Benign Gyecologic LesionDocument158 pagesBenign Gyecologic LesionArianne Joy C. TamarayNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Management of Endometrial CarcinomaDocument41 pagesGuidelines For Management of Endometrial CarcinomaVeenaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2Document75 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease Pt2yurie_ameliaNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy PDFDocument38 pagesEctopic Pregnancy PDFByron Ruiz Lapuerta100% (1)
- ObGyn Concise Notes NEET-PGDocument57 pagesObGyn Concise Notes NEET-PGMohamed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Benign Disease of The UterusDocument27 pagesBenign Disease of The UterusnyangaraNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics, Gynaecology-Textbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology For Medical Students, 2nd Edition-Akin Agboola-2006Document559 pagesObstetrics, Gynaecology-Textbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology For Medical Students, 2nd Edition-Akin Agboola-2006fagiy51113No ratings yet
- DystociaDocument6 pagesDystociasarguss14100% (2)
- Postpartum CollapseDocument54 pagesPostpartum Collapsemedical chroniclesNo ratings yet
- 62 Colposcopy StandardsDocument73 pages62 Colposcopy Standardsrijal mahdiy pNo ratings yet
- Printable - Thesis On Bishop ScoreDocument103 pagesPrintable - Thesis On Bishop Scoreanuaurv100% (3)
- Abnormal Labor and Dystocia: Dept. of Ob&Gyn, The First Affiliated Hospital He KeDocument63 pagesAbnormal Labor and Dystocia: Dept. of Ob&Gyn, The First Affiliated Hospital He KeJoan LuisNo ratings yet
- Green Top Guidelines 7Document34 pagesGreen Top Guidelines 7garfield1No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument42 pagesTuberculosis in Obstetrics and GynecologyameenNo ratings yet
- Ob Revalida Samplex ZapDocument24 pagesOb Revalida Samplex ZapMariana B.No ratings yet
- Malignant Tumors of Uterus: DR Tahira RizwanDocument52 pagesMalignant Tumors of Uterus: DR Tahira RizwanSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- Dopplerinpregnancy 130823082426 Phpapp02Document64 pagesDopplerinpregnancy 130823082426 Phpapp02Herry SasukeNo ratings yet
- Obs&Gyn MDC Q and ADocument36 pagesObs&Gyn MDC Q and ARufai Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- OB - CPG HTN in Pregnancy BEADocument138 pagesOB - CPG HTN in Pregnancy BEAEllieAdlerNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Detected Ovarian Cysts For Nuh Gynaecology TeamsDocument11 pagesUltrasound Detected Ovarian Cysts For Nuh Gynaecology TeamsDirga Rasyidin LNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Invasive Procedures in ObstetricsDocument18 pagesUltrasound-Guided Invasive Procedures in ObstetricsariNo ratings yet
- C SectionDocument50 pagesC SectionAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Infertile Couple - Role of Ultrasound FinalDocument31 pagesInfertile Couple - Role of Ultrasound FinalBharti Pant Gahtori100% (1)
- The Role Ultrasound in Early PregnancyDocument167 pagesThe Role Ultrasound in Early PregnancyCordova ArridhoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sharda Jain: Director: Secretary GeneralDocument91 pagesDr. Sharda Jain: Director: Secretary GeneraljijaniNo ratings yet
- OSCE Revision OBG DocumentDocument60 pagesOSCE Revision OBG DocumentshreyaNo ratings yet
- Gyn & ObsDocument68 pagesGyn & ObsEsraa Almassri100% (1)
- OSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSDocument24 pagesOSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSMohammad Saifullah100% (1)
- Hypertension in pregnancy-ACOG 2013-1 PDFDocument100 pagesHypertension in pregnancy-ACOG 2013-1 PDFrabinreaganNo ratings yet
- Uterinefibroids 130120064643 Phpapp02Document73 pagesUterinefibroids 130120064643 Phpapp02Tharun Kumar0% (1)
- Instruments in Obstetrics and Gynecology.Document60 pagesInstruments in Obstetrics and Gynecology.Saurabh Gautam100% (2)
- O&G Counselling - TSPDocument6 pagesO&G Counselling - TSPTarran PhagooNo ratings yet
- Endoscopy - Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy Indications, Contraindications and ComplicationsDocument16 pagesEndoscopy - Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy Indications, Contraindications and Complicationsselatur100% (1)
- Mullarian AnomoliesDocument85 pagesMullarian AnomoliesPrathibha GuruguriNo ratings yet
- Secondary AmenorrheaDocument18 pagesSecondary AmenorrheaMaria Gill100% (1)
- OB OSCE ReviewerDocument5 pagesOB OSCE ReviewerPao Ali100% (1)
- 8surgical Management of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding - KabilanDocument14 pages8surgical Management of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding - KabilanNavani TharanNo ratings yet
- Common Gynaecological Conditions Leading To Referral - 071118Document20 pagesCommon Gynaecological Conditions Leading To Referral - 071118zehra khowaja100% (1)
- OB 1.01 DystociaDocument9 pagesOB 1.01 DystociaRaquel Reyes100% (1)
- Review Adnexal Masses Pregnancy Rcog PDFDocument6 pagesReview Adnexal Masses Pregnancy Rcog PDFRosália Coutada100% (1)
- Ob CPCDocument80 pagesOb CPCDonna Meryll Eduave-EsguerraNo ratings yet
- FIGO Accreta Prenantal DiagnosisDocument7 pagesFIGO Accreta Prenantal DiagnosisYosef Dwi Cahyadi Salan100% (1)
- Infertility IDocument36 pagesInfertility Idr_asaleh100% (1)
- Operative Vaginal Delivery PDFDocument56 pagesOperative Vaginal Delivery PDFFarehan Md Isa100% (1)
- Pulmonary Disorders in PregnancyDocument49 pagesPulmonary Disorders in PregnancyMara Medina - BorleoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-13 Transeverse LieDocument15 pagesLecture-13 Transeverse LieMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Disorder and Abnormal BleedingDocument9 pagesMenstrual Disorder and Abnormal Bleedingdr_asalehNo ratings yet
- Nabothian CystsDocument24 pagesNabothian CystsVirna SeptianaNo ratings yet
- Presented by DR - Shahbaz Ahmad Professor of Community MedicineDocument76 pagesPresented by DR - Shahbaz Ahmad Professor of Community MedicinePriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical CancerDocument28 pagesCervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cervical CancerNatnael100% (1)
- Placenta Iugr PDFDocument298 pagesPlacenta Iugr PDFM Iqbal EffendiNo ratings yet
- Hildegard E. Peplau Nursing Nurse: - Client Relationship inDocument4 pagesHildegard E. Peplau Nursing Nurse: - Client Relationship inNicolette LeeNo ratings yet
- Dox Dosage Calculations v4Document4 pagesDox Dosage Calculations v4Mehboob AlamNo ratings yet
- An Unforeseen Adverse Effect of Ivermectin Is It A.8Document1 pageAn Unforeseen Adverse Effect of Ivermectin Is It A.8Kanchi PatelNo ratings yet
- Pediatric GuidlinesDocument124 pagesPediatric GuidlinesAnca Croitoru100% (8)
- Poster AbstractsDocument273 pagesPoster AbstractsCernei Eduard Radu0% (1)
- Bad Choice at MemorialDocument17 pagesBad Choice at Memorialapi-310375757No ratings yet
- New India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusDocument15 pagesNew India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusAazam AdtechiesNo ratings yet
- Megneto TherapyDocument15 pagesMegneto TherapyedcanalNo ratings yet
- Antihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermDocument55 pagesAntihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermN. IndupriyaNo ratings yet
- Platelet Rich Plasma (Hassett, Sheryl A, R.N.)Document2 pagesPlatelet Rich Plasma (Hassett, Sheryl A, R.N.)DariusNo ratings yet
- Brochure SoothexDocument2 pagesBrochure SoothexRojas Evert AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study JoycieeDocument9 pagesDrug Study JoycieeSamira MusaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - English For Academic and Professional Purposes - LAS 1Document17 pagesWeek 1 - English For Academic and Professional Purposes - LAS 1do san namNo ratings yet
- Entitlement To Hazard PayDocument16 pagesEntitlement To Hazard PayJanette SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Behavioural Observation AudiometryDocument4 pagesBehavioural Observation AudiometrydarsunaddictedNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For PharmacistsDocument3 pagesCode of Ethics For PharmacistsAmina Abba HaliruNo ratings yet
- Phenoxymethyl Penicillin Potassium: PaciphenDocument2 pagesPhenoxymethyl Penicillin Potassium: PaciphenKath CorralesNo ratings yet
- Synod Hospital Duty Roster March 2019Document1 pageSynod Hospital Duty Roster March 2019Lasky ChhakchhuakNo ratings yet
- Dean Ornish Mostly PlantsDocument2 pagesDean Ornish Mostly Plantsipman0100% (2)
- Raji Tribe11Document12 pagesRaji Tribe11Keya PandeyNo ratings yet
- 001 Canadian Pharmacy Review Q&A Content Ver1Document6 pages001 Canadian Pharmacy Review Q&A Content Ver1Safvan Mansuri0% (1)
- 2 Worksheets Hygiene and SafetyDocument6 pages2 Worksheets Hygiene and Safetyapi-19768570No ratings yet
- HEEADSSS Assessment Guide USUDocument11 pagesHEEADSSS Assessment Guide USUChris-Goldie LorezoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro Current Concepts and Clinical Decision Making in Electrotherapy PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Intro Current Concepts and Clinical Decision Making in Electrotherapy PDFTracy Magpoc0% (1)
- Do Cells Phones Cause Cancer?Document3 pagesDo Cells Phones Cause Cancer?Jed DiamondNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sherry Rogers On HB-PC Phosphatidyl CholineDocument6 pagesDr. Sherry Rogers On HB-PC Phosphatidyl CholineVergae100% (2)
- Modified Bluegrass Appliance PDFDocument4 pagesModified Bluegrass Appliance PDFRenieKumalaNo ratings yet