Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
Uploaded by
NoamiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug SyudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiNo ratings yet
- HRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayDocument4 pagesHRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayiloveanneNo ratings yet
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDocument1 pageDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- ABC (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence) Chart FormDocument1 pageABC (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence) Chart FormGrowingoptions100% (2)
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageFerrous SulfateZhyrraRamirezGarcia100% (1)
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- CiticolineDocument1 pageCiticolineHarvey BanagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- OXACILLINDocument1 pageOXACILLINJust nowNo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMethergine Drug StudyjoshNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Document2 pagesName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazoleitsmeaya50% (2)
- Drug Study Folic AcidDocument14 pagesDrug Study Folic AcidBianca Marithè Rejano0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRae Marie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudyJj Delacruz0% (1)
- Name of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionJulia Shane Barrios100% (1)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyPrisHee YhaRz SalvadorNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Magnesium SulfateSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateJoesineNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - OxytocinDocument3 pagesOB Drug Study - OxytocinJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocument2 pagesArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument1 pageMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyaagNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirrosisRosebud RoseNo ratings yet
- Biliary Ascariasis 2Document17 pagesBiliary Ascariasis 2Joanna Marie Panganiban100% (1)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocument3 pagesTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument3 pagesDrug NameJeeve DaetNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate and Enervon-DRUG-STUDYDocument4 pagesFerrous Sulfate and Enervon-DRUG-STUDYNil GyiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate6fq2cmfgn4No ratings yet
- Drug Study, Gonzaga.Document3 pagesDrug Study, Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro Module1 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBarecuatro Module1 Drug StudyANGELICA CLAIRE BARECUATRONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageDrug Study: Ferrous SulfateLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyJoshua Dumanjug SyNo ratings yet
- Classification Dosage Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesClassification Dosage Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkamahl252002No ratings yet
- Hepatitis DDocument24 pagesHepatitis DAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Gumilan, Ma - Cristina S. BSN - 3Document16 pagesPrepared By:: Gumilan, Ma - Cristina S. BSN - 3Ageededin HartNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Document17 pagesAtopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Ageededin HartNo ratings yet
- BursitisDocument8 pagesBursitisAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Inflammatory MyopathyDocument24 pagesIdiopathic Inflammatory MyopathyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Art TherapyDocument6 pagesArt TherapyAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- 10.-CLOZAPINE Drug StudyDocument1 page10.-CLOZAPINE Drug StudyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- Anabolic Fat Loss ReBootDocument16 pagesAnabolic Fat Loss ReBootleon100% (2)
- Thesis Klupenger MDocument243 pagesThesis Klupenger MGiorgioNo ratings yet
- Girls-2 To 20 Yrs - BMI For Age PDFDocument1 pageGirls-2 To 20 Yrs - BMI For Age PDFDwi A R MolantikaNo ratings yet
- Siemens Has Your AnswersDocument10 pagesSiemens Has Your AnswersEduardo Saul MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pomr Dewi 190919Document6 pagesPomr Dewi 190919emjehNo ratings yet
- Answering Exam Questions On The HeartDocument5 pagesAnswering Exam Questions On The HeartNahiyan Islam ApuNo ratings yet
- Negative Effects On Excessive Use of GadgetsDocument17 pagesNegative Effects On Excessive Use of GadgetsAriel V. AbanesNo ratings yet
- TSH Conversion PDFDocument1 pageTSH Conversion PDFMarianNo ratings yet
- (2nd File) Health - Declaration - Form - COVID-19 - MCODocument3 pages(2nd File) Health - Declaration - Form - COVID-19 - MCOLinda AliNo ratings yet
- NCCN - Cancer ProstataDocument130 pagesNCCN - Cancer ProstataAndrés VegaNo ratings yet
- Notch DependenceDocument29 pagesNotch DependencepnavasterNo ratings yet
- Cases of Scientific MisconductsDocument11 pagesCases of Scientific MisconductsPau BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Psych Chap 4+5Document26 pagesPsych Chap 4+5lmaoheartsNo ratings yet
- Notes On Medical AstrologyDocument14 pagesNotes On Medical AstrologySachin Makhija50% (2)
- Blast InjuryDocument9 pagesBlast InjuryMayshiaNo ratings yet
- Health PsychologyDocument10 pagesHealth PsychologyDragana ModestyNo ratings yet
- Kevin Biology Project XII - EDocument26 pagesKevin Biology Project XII - EKevin Joseph78% (9)
- Impactul Disfunctiei Articulatiei Sacroiliace in Durerea LombaraDocument6 pagesImpactul Disfunctiei Articulatiei Sacroiliace in Durerea LombaraLarisa OlaruNo ratings yet
- (Colageno) Chattopadhyay - Et - Al-2014-Biopolymers PDFDocument13 pages(Colageno) Chattopadhyay - Et - Al-2014-Biopolymers PDFAndré Zamith SelvaggioNo ratings yet
- ExtractsDocument49 pagesExtractsbhuller21No ratings yet
- MicrobeDocument32 pagesMicrobeFiqa SuccessNo ratings yet
- Calcium Hypochlorite MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument6 pagesCalcium Hypochlorite MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationMohamed MaghawryNo ratings yet
- Aloka Prosound Alpha6 User PDFDocument346 pagesAloka Prosound Alpha6 User PDFJuan Carlos Goyzueta100% (1)
- Microbial EcologyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Ecologyakifuji913No ratings yet
- Murphy MadisonDocument1 pageMurphy Madisonapi-315700369No ratings yet
- Medicare Fee SchuduleDocument50 pagesMedicare Fee SchuduleMusadiq AbbasNo ratings yet
- Text CDocument1,100 pagesText CAli NofalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Healthcare 2012Document100 pagesConsumer Healthcare 2012mimranbhattiNo ratings yet
- Clasificacion de Lesion MunichDocument10 pagesClasificacion de Lesion MunichAlejandra VasquezNo ratings yet
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
Uploaded by
NoamiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
13.-Ferrous-Sulfate Case Press
Uploaded by
NoamiCopyright:
Available Formats
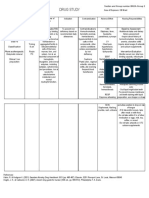
DRUG MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE EFFECTS NSG RESPONSILITIES
ACTION
FERROUS SULFATE Essential component in Prevention, treatment of iron Contraindications: Large doses may aggravate BASELINE ASSESSMENT
formation of Hgb, myoglobin, deficiency anemia due to Hemochromatosis, hemolytic existing GI tract disease Assess nutritional status, dietary
PHARMACOTHERAPEUTIC: enzymes. Promotes effective inadequate diet, anemias. Cautions: Peptic (peptic ulcer, regional history.
Enzymatic mineral. erythropoiesis and transport, malabsorption, pregnancy, ulcer, regional enteritis, enteritis, ulcerative colitis). To prevent mucous membrane and
CLINICAL:Iron preparation. utilization of oxygen. blood loss. ulcerative colitis, pts Severe iron poisoning occurs teeth
Therapeutic Effect: Prevents receiving frequent blood most often in children, staining with liquid preparation,
1 Tab OD iron deficiency. transfusions manifested as vomiting, use
severe abdominal pain, dropper or straw and allow
diarrhea, dehydration, solution to
followed by hyperventilation, drop on back of tongue.
pallor, cyanosis, INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
cardiovascular collapse. Monitor serum iron, total iron-
binding
capacity, reticulocyte count, Hgb,
ferritin.
Monitor daily pattern of bowel
activity,
stool consistency. Assess for
clinical improvement,
record relief of iron deficiency
symptoms (fatigue, irritability,
pallor, paresthesia
of extremities, headache).
PATIENT/FAMILY
TEACHING
•Expect stool color to darken.
Oral liquid may stain teeth. If GI
discomfort occurs, take after meals
or with food. Do not take within 2
hrs of other medication or eggs,
milk, tea, coffee, cereal.
You might also like
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug SyudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiNo ratings yet
- HRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayDocument4 pagesHRZE (Kid's Kit), Toradol, CiprobayiloveanneNo ratings yet
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDocument1 pageDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- ABC (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence) Chart FormDocument1 pageABC (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence) Chart FormGrowingoptions100% (2)
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageFerrous SulfateZhyrraRamirezGarcia100% (1)
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- CiticolineDocument1 pageCiticolineHarvey BanagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- OXACILLINDocument1 pageOXACILLINJust nowNo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMethergine Drug StudyjoshNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Document2 pagesName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazoleitsmeaya50% (2)
- Drug Study Folic AcidDocument14 pagesDrug Study Folic AcidBianca Marithè Rejano0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRae Marie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudyJj Delacruz0% (1)
- Name of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic (Brand) Classification Dose/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing PrecautionJulia Shane Barrios100% (1)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyPrisHee YhaRz SalvadorNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDocument2 pagesSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Magnesium SulfateSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesFerrous SulfateJoesineNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - OxytocinDocument3 pagesOB Drug Study - OxytocinJustin AncogNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocument2 pagesArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument1 pageMetoprololjchowking100% (1)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyaagNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver CirrosisRosebud RoseNo ratings yet
- Biliary Ascariasis 2Document17 pagesBiliary Ascariasis 2Joanna Marie Panganiban100% (1)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Tapazole and Calcium GluconateDocument3 pagesTapazole and Calcium Gluconatekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument3 pagesDrug NameJeeve DaetNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate and Enervon-DRUG-STUDYDocument4 pagesFerrous Sulfate and Enervon-DRUG-STUDYNil GyiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLeah Reese VersonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate6fq2cmfgn4No ratings yet
- Drug Study, Gonzaga.Document3 pagesDrug Study, Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro Module1 Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBarecuatro Module1 Drug StudyANGELICA CLAIRE BARECUATRONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Ferrous SulfateDocument1 pageDrug Study: Ferrous SulfateLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyJoshua Dumanjug SyNo ratings yet
- Classification Dosage Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesClassification Dosage Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkamahl252002No ratings yet
- Hepatitis DDocument24 pagesHepatitis DAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Gumilan, Ma - Cristina S. BSN - 3Document16 pagesPrepared By:: Gumilan, Ma - Cristina S. BSN - 3Ageededin HartNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Document17 pagesAtopic Dermatitis: (Infantile and Childhood Eczema)Ageededin HartNo ratings yet
- BursitisDocument8 pagesBursitisAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Inflammatory MyopathyDocument24 pagesIdiopathic Inflammatory MyopathyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Art TherapyDocument6 pagesArt TherapyAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- 10.-CLOZAPINE Drug StudyDocument1 page10.-CLOZAPINE Drug StudyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology On Schizoaffective Disorder: EchopraxiaAgeededin Hart100% (1)
- Anabolic Fat Loss ReBootDocument16 pagesAnabolic Fat Loss ReBootleon100% (2)
- Thesis Klupenger MDocument243 pagesThesis Klupenger MGiorgioNo ratings yet
- Girls-2 To 20 Yrs - BMI For Age PDFDocument1 pageGirls-2 To 20 Yrs - BMI For Age PDFDwi A R MolantikaNo ratings yet
- Siemens Has Your AnswersDocument10 pagesSiemens Has Your AnswersEduardo Saul MendozaNo ratings yet
- Pomr Dewi 190919Document6 pagesPomr Dewi 190919emjehNo ratings yet
- Answering Exam Questions On The HeartDocument5 pagesAnswering Exam Questions On The HeartNahiyan Islam ApuNo ratings yet
- Negative Effects On Excessive Use of GadgetsDocument17 pagesNegative Effects On Excessive Use of GadgetsAriel V. AbanesNo ratings yet
- TSH Conversion PDFDocument1 pageTSH Conversion PDFMarianNo ratings yet
- (2nd File) Health - Declaration - Form - COVID-19 - MCODocument3 pages(2nd File) Health - Declaration - Form - COVID-19 - MCOLinda AliNo ratings yet
- NCCN - Cancer ProstataDocument130 pagesNCCN - Cancer ProstataAndrés VegaNo ratings yet
- Notch DependenceDocument29 pagesNotch DependencepnavasterNo ratings yet
- Cases of Scientific MisconductsDocument11 pagesCases of Scientific MisconductsPau BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Psych Chap 4+5Document26 pagesPsych Chap 4+5lmaoheartsNo ratings yet
- Notes On Medical AstrologyDocument14 pagesNotes On Medical AstrologySachin Makhija50% (2)
- Blast InjuryDocument9 pagesBlast InjuryMayshiaNo ratings yet
- Health PsychologyDocument10 pagesHealth PsychologyDragana ModestyNo ratings yet
- Kevin Biology Project XII - EDocument26 pagesKevin Biology Project XII - EKevin Joseph78% (9)
- Impactul Disfunctiei Articulatiei Sacroiliace in Durerea LombaraDocument6 pagesImpactul Disfunctiei Articulatiei Sacroiliace in Durerea LombaraLarisa OlaruNo ratings yet
- (Colageno) Chattopadhyay - Et - Al-2014-Biopolymers PDFDocument13 pages(Colageno) Chattopadhyay - Et - Al-2014-Biopolymers PDFAndré Zamith SelvaggioNo ratings yet
- ExtractsDocument49 pagesExtractsbhuller21No ratings yet
- MicrobeDocument32 pagesMicrobeFiqa SuccessNo ratings yet
- Calcium Hypochlorite MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument6 pagesCalcium Hypochlorite MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationMohamed MaghawryNo ratings yet
- Aloka Prosound Alpha6 User PDFDocument346 pagesAloka Prosound Alpha6 User PDFJuan Carlos Goyzueta100% (1)
- Microbial EcologyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Ecologyakifuji913No ratings yet
- Murphy MadisonDocument1 pageMurphy Madisonapi-315700369No ratings yet
- Medicare Fee SchuduleDocument50 pagesMedicare Fee SchuduleMusadiq AbbasNo ratings yet
- Text CDocument1,100 pagesText CAli NofalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Healthcare 2012Document100 pagesConsumer Healthcare 2012mimranbhattiNo ratings yet
- Clasificacion de Lesion MunichDocument10 pagesClasificacion de Lesion MunichAlejandra VasquezNo ratings yet