Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion of
Benghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion of
Uploaded by
Ani Oo SamaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion of
Benghalensis) (B) Still Roots - Delicate Steam Develops Shot and Thick Supporting Roots From The Basal Portion of
Uploaded by
Ani Oo SamaCopyright:
Available Formats
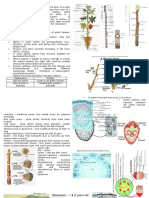
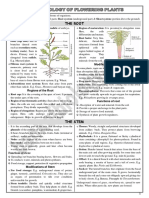
Morphology of root
Non-green underground, descendent part of underground plant axis
Characteristics of root: -(1) colour less exp. Tinospora dordifolia, no nodes internodes and buds, endogenous origin,
root hair exogeneous, growing apex protected - terrestrial root cap and aquatic root pockets
Root regions – Root cap (parenchyma-tous multicellular structure, secrete mucilage)root pockets(Lemna, Pistia
Stratiote), meristematic growth region (1mm) (mitotic cell division), zone of elongation(absorb water & vacuolated &
starts differentiation), Root hair zone(elongation of epidermal cell 1-6cm),Zone of mature cells(outermost layer
covered by periderm or thick cell wall by cuticle
Function of root system: - Primary function (Anchorage, Absorption, Conduction of water and minerals,
Translocation of organic nutrients) Secondary function (food storage, assimilation, aeration, nitrogen fixation,
hydroscopic root, reproduction)
Types of root: - (a)Tap root system (acropetal succession, deep feeders) (b) Adventitious root system (seminal roots
and is also called fibrous root system exp foliar roots bryophyllum, begonia)
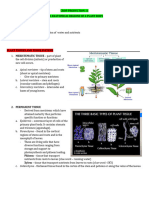
Modification of root: - Normal (1) storage of food (a)Conical (border at base and tapper gradually towards apex
example cone carrot) (B) Fusiform (swollen in middle, narrow towards base & apex example shape spindle radish)(c)
Napiform (nearly globular and spherical in shape, Basel is swollen and apex is tapper, shape top-shaped e.g. Turnip,
beet root)(d)Tuberous (no definite shape e.g. Marcibilis jalapa (2) Nodulated roots (nodule like welling called root
nodules contains nitrogen fixation bacteria[ rizobious leguminiosarium]{nitrogen into ammonia} mutualistic
symbiosis ) (3) Respiratory roots or pneumatophores(pores lenticels)e.g. sonneratia, heritiera, Rhizophora
Modification of adventitious root: - (i) Mechanical root (a) Prop roots - stem branches [ banyan tree ficus
benghalensis] (b) Still roots – delicate steam develops shot and thick supporting roots from the basal portion of
steam e.g. zea maya, pandanus, Sugar cane (c) climbing roots – arise from nodes & twin round the support or
produce a viscous substance which on drying sticks to the plant e.g. Piper betel, Pothos (d) Clinging roots - Vanda (e)
Root thorn – Acanthoriza (f) root buttresses – Bombax ceiba (ii) Storage of food – (a) Root tubers or Tuberous root
e.g. sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) (b) Fasciculate root e.g. Dahlia (c) Palmate tuberous - orchid (d) Moniliform Commented [dp1]:
roots – alternatively swollen & constricted giving a beaded appearance e.g. Dioscorea alata, Momordica charantia
(e) Annulated roots – disk like structure placed one above another e.g. cephaelis
Physiological function (a) Epiphytic root – orchid (Vanda) tissue – velamen (b) Assimilatory root - develop chlorophyll
synthesis carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in presence of sunlight (photosynthesis) e.g. Tinospora
cordifolia (c) Haustorial roots – absorb nutrition e.g. cascuta (d) Reproductive roots – Dahlia, sweet potato
You might also like
- Beech 1900 ManualDocument2 pagesBeech 1900 ManualAlmir Rodrigues0% (2)
- Botany Plant MorphologyDocument42 pagesBotany Plant MorphologyNigel Nicholls100% (7)
- SIP5 7KE85 V07.80 Manual C018-6 en PDFDocument502 pagesSIP5 7KE85 V07.80 Manual C018-6 en PDFDoan Anh TuanNo ratings yet
- ZamZam Water by Dr. EmotoDocument3 pagesZamZam Water by Dr. Emotohadjeas83% (6)
- AM Morphology FamiliesDocument11 pagesAM Morphology Familiestechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Morphology of Flowering Plants - AdvancedDocument79 pagesAnatomy and Morphology of Flowering Plants - AdvancedDheer Bhanushali100% (1)
- PLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesDocument78 pagesPLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesAsam100% (1)
- BotanyDocument5 pagesBotanyRain OmliNo ratings yet
- Morphology.BKK SirDocument20 pagesMorphology.BKK Sirkrishnabaniya17125No ratings yet
- RootsDocument5 pagesRootsShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- GradeDocument3 pagesGradeAntonette McnairNo ratings yet
- RootsDocument32 pagesRootsReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4Document26 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Root Morphology: Major Functions of RootDocument4 pagesRoot Morphology: Major Functions of RootJithinvas MJNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesMorphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAyako HayashidaNo ratings yet
- Tissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionDocument4 pagesTissue-Group of Cells With A Common Function, Structure or Both. Organ - Consists of Several Types of Tissues That Have A Particular FunctionMohammad Raffi GampongNo ratings yet
- PLANTSDocument3 pagesPLANTSAbuhanif SaikNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Experiment No.-1: Lab ManualsDocument2 pagesExperiment No.-1: Lab ManualsAnmol SinghNo ratings yet
- External Morphology of RootsDocument6 pagesExternal Morphology of RootsLian Marie Viñas100% (1)
- Transport Water and SolutesDocument4 pagesTransport Water and SolutesAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants by Rakshita SinghDocument9 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants by Rakshita SinghFarzana ShaikNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology: Roots and Shoots: Peter ShawDocument28 pagesPlant Biology: Roots and Shoots: Peter Shawashishnarayanmishra2541No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument44 pagesPlantsSanjeev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsTamal NayakNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument24 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsDocument9 pagesReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelNo ratings yet
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedDocument52 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: 1. Root 2. Stem 3. Leaf 4. Flower 5. Fruit 6. SeedPrasanth Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Morphology of PlantsDocument58 pagesMorphology of PlantsRishikesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany Rootsartadiel28No ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantDocument51 pagesThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronNo ratings yet
- NR 215 Plant Biology: RootsDocument34 pagesNR 215 Plant Biology: RootsJohn Zephyr TyskaNo ratings yet
- Morphology 12Document513 pagesMorphology 12Vaibhav PanchalNo ratings yet
- 5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleDocument2 pages5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Vegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsDocument5 pagesVegetative Structures and Their Functions: RootsJohn Francis FernandezNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument4 pagesMorphologytarunNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Getting To Know Plants: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument3 pagesChapter - 7 Getting To Know Plants: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksTHIRUMENI SAMYNo ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- BASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Document7 pagesBASIC BIOLOGY NOTES Sem 1 Part 2Polee SheaNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant Function and StructureDocument5 pagesNotes Plant Function and StructureellenialrafeneNo ratings yet
- Development and MorphologyDocument52 pagesDevelopment and Morphologyjag perlasNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Chapters2Document60 pagesPlant Physiology Chapters2Mahad Ahmed HilowleNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Document79 pagesGen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Samantha AcostaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and LeavesDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and Leaveskarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Higher Plants - 2020Document109 pagesChapter 9 Higher Plants - 2020SARA LIM YEN ZI MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Evolution and Diversity of Vascular Plants: Lluvia Flores-RenteriaDocument71 pagesChapter 4: Evolution and Diversity of Vascular Plants: Lluvia Flores-RenteriaHannah GordonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Document180 pagesChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNo ratings yet
- Main Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsDocument4 pagesMain Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- PL MorphDocument9 pagesPL Morphel vnNo ratings yet
- RootDocument40 pagesRootAstha MishraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyDocument7 pagesLesson 2.the Anatomical Regions of A Plant BodyMark Allen L. VicenteNo ratings yet
- MorfhologyDocument60 pagesMorfhologyMohd. FarhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and WhiteDocument96 pages1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi) (2) Black and Whiterivera hutchNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure FunctionDocument58 pagesPlant Structure Functionno siNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Mosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaFrom EverandMosses and Liverworts of Rainforest in Tasmania and South-eastern AustraliaNo ratings yet
- Evertz MVP Manual PDFDocument2 pagesEvertz MVP Manual PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- Compostable BagsDocument17 pagesCompostable Bagslucky jainNo ratings yet
- Silver Schmidt Concrete Test Hammer User Manual PDFDocument28 pagesSilver Schmidt Concrete Test Hammer User Manual PDFICIC CALICUT CENTERNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transmission and DistributionDocument31 pagesElectrical Transmission and DistributionPutri Hanifah SNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument100 pagesFungibhanklhonkNo ratings yet
- Payable Salary Paid SalaryDocument2 pagesPayable Salary Paid SalaryAhmed AmmanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsJhanin BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Tensile Strength of Rock: Concepts and TestingDocument22 pagesA Review of The Tensile Strength of Rock: Concepts and TestingHooman_RostamiNo ratings yet
- Jaisalmer - Secular ArchitectureDocument12 pagesJaisalmer - Secular Architecturearpriyasankar12No ratings yet
- 10 Robotic Filament WindingDocument9 pages10 Robotic Filament WindingYohannes RegassaNo ratings yet
- Benign Ovarian TumorsDocument16 pagesBenign Ovarian TumorsPatNo ratings yet
- MCO 3 (30/3-3/4/2020) Reinforcement Chapter 2 Part A: Objective QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCO 3 (30/3-3/4/2020) Reinforcement Chapter 2 Part A: Objective QuestionsZalini AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Initial Newborn AssessmentDocument14 pagesInitial Newborn Assessmentaclark831No ratings yet
- IE 411 Lecture6 90ABDocument15 pagesIE 411 Lecture6 90ABZain Ul AbidinNo ratings yet
- Daftar Singkatan SMF JAntungDocument5 pagesDaftar Singkatan SMF JAntungBobby RahmantoNo ratings yet
- Edubba A Composite Text Ver3Document7 pagesEdubba A Composite Text Ver3RicardoNo ratings yet
- BFB2 PDFDocument4 pagesBFB2 PDFQuang HuyNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - Nitoproof 600PFDocument2 pagesCatalogue - Nitoproof 600PFkenneth0129aaNo ratings yet
- Expo Class Methods DetailedDocument7 pagesExpo Class Methods DetailedAlison2360No ratings yet
- 16AIC - BIM For Renovation & Retrofitting by Sonny Andalis Part2of3Document3 pages16AIC - BIM For Renovation & Retrofitting by Sonny Andalis Part2of3Ray RamiloNo ratings yet
- Chicken Eggshell Powder As Dietary Calcium Source in Chocolate CakesDocument4 pagesChicken Eggshell Powder As Dietary Calcium Source in Chocolate CakesEM HA EFNo ratings yet
- 415V CALCULATING SHEET AND SETTING LIST FOR EQUIPMENT PROTECTION OF CHP WAGON TIPPER AND ESP (Supplement For Zero Sequence Current Relay)Document25 pages415V CALCULATING SHEET AND SETTING LIST FOR EQUIPMENT PROTECTION OF CHP WAGON TIPPER AND ESP (Supplement For Zero Sequence Current Relay)Amaresh NayakNo ratings yet
- Uses of RefractoryDocument20 pagesUses of RefractoryRicha Tripathi100% (2)
- 1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeDocument14 pages1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeVirendra Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- HESCO Sample PaperDocument3 pagesHESCO Sample PaperzakirNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Matchemphys 2019 05 033Document13 pages10 1016@j Matchemphys 2019 05 033Deghboudj SamirNo ratings yet
- Testing and CommissioningDocument18 pagesTesting and CommissioningAbdullah Afif100% (2)