Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Semisolid Products, Part 2
Semisolid Products, Part 2
Uploaded by
suciCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Semisolid Products, Part 2
Semisolid Products, Part 2
Uploaded by
suciCopyright:
Available Formats
Postapproval Changes
2 to Semisolid Drugs
To ensure continuing product quality and performance dating period, according to the approved proto-
characteristics of the semisolid topical formulations, reg- col, on either the first or first three (see below
ulatory approvals are required for changes to for details) production batches and to report the
results in subsequent annual reports.
1. Components or composition
2. Manufacturing (process and equipment) Definition of level 1 changes are those that are unlikely
3. Scale up/scale down of manufacture to have any detectable effect on formulation quality and
4. Site of manufacture of a semisolid formulation performance. Examples:
during the postapproval period
A. Deletion or partial deletion of an ingredient
It is important to define intended to affect the color, fragrance, or flavor
of the drug product.
1. The levels of change B. Any change in an excipient up to 5% of
2. Recommended chemistry, manufacturing, and approved amount of that excipient. The total
controls tests to support each level of change additive effect of all excipient changes should
3. Recommended in vitro release tests or in vivo not be more than 5%. Changes in the compo-
bioequivalence tests to support each level of sition should be based on the approved target
change composition and not on previous level 1
4. Documentation to support the change changes in the composition. A change in diluent
(q.s. excipient) caused by component and com-
The effect that scale-up and postapproval changes may position changes in excipient may be made and
have on the stability of the drug product should be eval- is excluded from the 5% change limit.
uated. For general guidance on conducting stability stud- C. Change in a supplier of a structure forming
ies, see the FDA Guideline for Submitting Documentation excipient that is primarily a single chemical
for the Stability of Human Drugs and Biologics. For scale- entity (purity 95%) or change in a supplier or
up and postapproval changes submissions, the following technical grade of any other excipient.
points should also be considered:
Definition of level 2 changes are those that could have a
A. In most cases, except those involving scale up, significant effect on formulation quality and performance.
stability data from pilot scale batches will be Examples:
acceptable to support the proposed change.
B. Where stability data show a trend toward A. Changes of >5% and <10% of approved
potency loss or degradant increase under amount of an individual excipient; the total
accelerated conditions, it is recommended that additive effect of all excipient changes should
historical accelerated stability data from a rep- not be more than 10%
resentative prechange batch be submitted for B. Changes in the composition should be based
comparison. It is also recommended that under on the approved target composition and not on
these circumstances, all available long-term previous level 1 or level 2 changes in the com-
data on test batches from ongoing studies be position
provided in the supplement. Submission of C. Changes in diluent (q.s. excipient) caused by
historical accelerated and available long-term component and composition changes in excip-
data would facilitate review and approval of ients are acceptable and are excluded from the
the supplement. 10% change limit
C. A commitment should be included to conduct D. Change in supplier of a structure forming
long-term stability studies through the expiration excipient not covered under level 1
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC
18 Handbook of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Formulations: Semisolid Products
E. Change in the technical grade of structure- changes should be properly validated and may be inspected
forming excipient by appropriate agency personnel. Level 1 changes in batch
F. Change in particle size distribution of the drug size are those up to and including a factor of 10 times the
substance if the drug is in suspension size of the pivotal clinical trial or biobatch, where the
equipment used to produce the test batch or batches is of
Definition of level 3 changes are those that are likely to the same design and operating principles, the batch or
have a significant effect on formulation quality and per- batches are manufactured in full compliance with current
formance. Examples: good manufacturing practice (CGMPs), and the same stan-
dard operating procedures (SOPs) and controls, as well as
A. Any qualitative and quantitative changes in an the same formulation and manufacturing procedures, are
excipient beyond the ranges noted in level 2 used on the test batch or batches and on the full-scale
change. production batch or batches. Level 2 changes in batch size
B. Change in crystalline form of the drug sub- are those from beyond a factor of 10 times the size of the
stance, if the drug is in suspension pivotal clinical trial or biobatch, where the equipment used
to produce the test batch or batches is of the same design
I. PRESERVATIVE and operating principles, the batch or batches is manufac-
tured in full compliance with CGMPs, and the same SOPs
For semisolid products, any change in the preservative and controls, as well as the same formulation and manu-
may affect the quality of the product. If any quantitative facturing procedures, are used on the test batch or batches
or qualitative changes are made in the formulation, addi- and on the full-scale production batch or batches. No level
tional testing should be performed. No in vitro release 3 changes are anticipated in this category.
documentation or in vivo bioequivalence documentation
is needed for preservative changes.
IV. MANUFACTURING SITE
II. MANUFACTURING CHANGES Manufacturing site changes consist of changes in location
Manufacturing changes may affect both equipment used in the site of manufacture, packaging and filling opera-
in the manufacturing process and the process itself. A level tions, or testing for both company-owned and contract
1 change is a change from nonautomated or nonmechan- manufacturing facilities, and they do not include any other
ical equipment to automated or mechanical equipment to level 2 or 3 changes; for example, changes in scale, man-
transfer ingredients or a change to alternative equipment ufacturing (including process or equipment), and compo-
of the same design and operating principles. A level 2 nents or composition. New manufacturing locations
change is a change in equipment to a different design or should have had a satisfactory CGMP inspection within
different operating principles or a change in type of mixing the past 2 years. A stand-alone analytical testing labora-
equipment, such as high shear to low shear and vice versa. tory site change may be submitted as a Changes Being
No level 3 changes are anticipated in this category. Effected Supplement if the new facility has a current and
satisfactory CGMP compliance profile with the FDA for
the type of testing operation in question. The supplement
III. PROCESS should contain a commitment to use the same test methods
Level 1 changes include changes such as rate of mixing, employed in the approved application, written certification
mixing times, operating speeds, and holding times within from the testing laboratory stating that they are in con-
approved application ranges, in addition to the order of formance with CGMPs, and a full description of the test-
addition of components (excluding actives) to either the ing to be performed by the testing lab. If the facility has
oil or water phase. Level 2 changes include changes such not received a satisfactory CGMP inspection for the type
as rate of mixing, mixing times, rate of cooling, operating of testing involved, a prior approval supplement is recom-
speeds, and holding times outside approved application mended. No stability data are needed for a change in a
ranges for all dosage forms in addition to any changes in stand-alone analytical facility. Level 1 changes consist of
the process of combining the phases. No level 3 changes site changes within a single facility where the same equip-
are anticipated in this category. ment, SOPs, environmental conditions (e.g., temperature
and humidity) and controls, and personnel common to
both manufacturing sites are used, and where no changes
Batch Size (Scale Up or Down) are made to the manufacturing batch records, except for
The minimum batch size for the NDA pivotal clinical trial administrative information and the location of the facility.
batch or the ANDA/AADA biobatch is at least 100 kg or “Common” is defined as employees already working on the
10% of a production batch, whichever is larger. All scale campus who have suitable experience with the manufacturing
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC
Postapproval Changes to Semisolid Drugs 19
process. Level 2 changes consist of site changes within a same original contiguous site or where the facilities are
contiguous campus, or between facilities in adjacent city not in adjacent city blocks. To qualify as a level 3 change,
blocks, where similar equipment, SOPs, environmental similar equipment, SOPs, environmental conditions, and
conditions (e.g., temperature and humidity) and controls, controls should be used in the manufacturing process at
and personnel common to both manufacturing sites are the new site. Changes should not be made to the manu-
used, and where no changes are made to the manufacturing facturing batch records except when consistent with other
batch records, except for administrative information and level 1 changes. Administrative information, location, and
the location of the facility. Level 3 changes consist of a language translation may be revised as needed. Any
site change in manufacturing site to a different campus. change to a new contract manufacturer also constitutes a
A different campus is defined as one that is not on the level 3 change.
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC
You might also like
- Change Control Management SOPDocument7 pagesChange Control Management SOPcarbou100% (7)
- Change Control Management SOP PDFDocument7 pagesChange Control Management SOP PDFnetelsrt12980% (1)
- Bangladesh National Formulary (BDNF) 5th Version 2019 PDFDocument924 pagesBangladesh National Formulary (BDNF) 5th Version 2019 PDFMSKC78% (9)
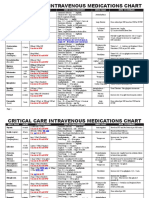
- Critical Care Intravenous Medications ChartDocument2 pagesCritical Care Intravenous Medications ChartMichelle Danielle MolinaNo ratings yet
- Bacpac & SupacDocument60 pagesBacpac & Supacsaurabh100% (1)
- Change Management Systems in The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument6 pagesChange Management Systems in The Pharmaceutical IndustryanagazoliNo ratings yet
- Change Control Management SOP PDFDocument7 pagesChange Control Management SOP PDFPrashansa ShresthaNo ratings yet
- GMP in Pharmaceutical Industry: Global cGMP & Regulatory ExpectationsFrom EverandGMP in Pharmaceutical Industry: Global cGMP & Regulatory ExpectationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Submittedto: DR Harish DurejaDocument38 pagesSubmittedto: DR Harish DurejaHaaMid RaSheedNo ratings yet
- Scale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteDocument9 pagesScale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteAKKAD PHARMANo ratings yet
- Changes To An Approved ProductDocument5 pagesChanges To An Approved Productexicial87No ratings yet
- A Review On Supac Guidance For Modified Release Solid Oraldosage FormsDocument9 pagesA Review On Supac Guidance For Modified Release Solid Oraldosage FormsAhmad Al-RusasiNo ratings yet
- Scale Up Process Approval Changes (Supac)Document21 pagesScale Up Process Approval Changes (Supac)Shibbu Gangwar100% (1)
- Cder Guidance QaletterDocument13 pagesCder Guidance QaletterAna SalvNo ratings yet
- 5.MounicaReviewArticle BE SUPACDocument8 pages5.MounicaReviewArticle BE SUPACrenitadewiNo ratings yet
- Post Approval Changes-Scale Up & Post Approval ChangesDocument37 pagesPost Approval Changes-Scale Up & Post Approval Changesgravity2726No ratings yet
- Scale Up and Post Approval Changes: Tatyasaheb Kore College of Pharmacy, WarnanagarDocument20 pagesScale Up and Post Approval Changes: Tatyasaheb Kore College of Pharmacy, Warnanagarvarsha khadakeNo ratings yet
- BACPACDocument50 pagesBACPACkavya nainitaNo ratings yet
- Scale Up, Post Approval Changes (SUPAC) & Post Marketing SurveillanceDocument39 pagesScale Up, Post Approval Changes (SUPAC) & Post Marketing SurveillanceVenkatesh MadhugiriNo ratings yet
- Scale Up & Post Approval Changes: (Supac)Document15 pagesScale Up & Post Approval Changes: (Supac)NidhiNo ratings yet
- Scale Up & Post Approval Changes (Supac)Document24 pagesScale Up & Post Approval Changes (Supac)Govind AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Re ValidationDocument13 pagesRe ValidationHardik PandyaNo ratings yet
- 2 6b Post Approval ChangesVariationsDocument20 pages2 6b Post Approval ChangesVariationsNitin KashyapNo ratings yet
- Scale Up and Post Approval Changes in ADocument29 pagesScale Up and Post Approval Changes in ADaruvuri Vaidehi Chowdary100% (2)
- Overview of Scale-Up and Post-Approval Changes (SUPAC)Document3 pagesOverview of Scale-Up and Post-Approval Changes (SUPAC)Ashwini DoleNo ratings yet
- Immediate Release Solid Oral SUPACDocument37 pagesImmediate Release Solid Oral SUPACnadanasabapathiNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Stability TestingDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Stability Testingloxfox100% (2)
- Supac GuidelineDocument30 pagesSupac GuidelineSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Gidance SprayDocument1 pageGidance Spraydede DwiNo ratings yet
- Annual Product Quality Review (APQR) SOP - PharmaBDocument14 pagesAnnual Product Quality Review (APQR) SOP - PharmaBrehmat ali100% (1)
- SUPAC-IR Questions and Answers About SUPAC-IR Guidance - FDADocument13 pagesSUPAC-IR Questions and Answers About SUPAC-IR Guidance - FDAmodava-2No ratings yet
- SOP of Change ControlDocument24 pagesSOP of Change ControlPaolo PiccoliniNo ratings yet
- Fda Variation Guidance PDFDocument75 pagesFda Variation Guidance PDFdineshpharmacistNo ratings yet
- Pharma Change Control Peither ExecSeriesDocument55 pagesPharma Change Control Peither ExecSeriesLuc12No ratings yet
- Theoretical YieldDocument8 pagesTheoretical YieldIzzatul HidayahNo ratings yet
- IVT SDCC pgs6Document42 pagesIVT SDCC pgs6sabrinaNo ratings yet
- Change ControlDocument7 pagesChange ControlPrince MoniNo ratings yet
- Change Management: Common Failures and A Checklist For ImprovementDocument5 pagesChange Management: Common Failures and A Checklist For ImprovementPerry BurtonNo ratings yet
- Nbog BPG 2014 3Document19 pagesNbog BPG 2014 3marcelo.lacknerNo ratings yet
- Amendment Guidelines July 2016Document83 pagesAmendment Guidelines July 2016Anand JoshiNo ratings yet
- 2.07 Dissolution Mar11 v4Document11 pages2.07 Dissolution Mar11 v4Harrcanaa RajahNo ratings yet
- Method Devlpoment N Validation Final ProjectDocument51 pagesMethod Devlpoment N Validation Final ProjectPankaj GajareNo ratings yet
- Change Management in Automated QMS SoftwareDocument31 pagesChange Management in Automated QMS SoftwareS SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Change Control - Continuous Quality Improvement in Fda and Iso EnvironmentsDocument6 pagesChange Control - Continuous Quality Improvement in Fda and Iso EnvironmentsNgoc Sang HuynhNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide Change ControlDocument42 pagesTechnical Guide Change Controltito1628No ratings yet
- Sterility Testing Sterisart Second Supplier Validation Guide 1 DataDocument4 pagesSterility Testing Sterisart Second Supplier Validation Guide 1 Datadinesh singhNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Bioequivalence Studies For Different Strengths of Oral Solid Dosage FormsDocument13 pagesGuideline For Bioequivalence Studies For Different Strengths of Oral Solid Dosage Formskayes_abuNo ratings yet
- Change Control Related PharmaDocument3 pagesChange Control Related PharmaSaurabh Raja0% (1)
- Different Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDocument10 pagesDifferent Mesh Sizes and Mesh To Micron ConversionDevanandDongreNo ratings yet
- QA Version 3 - Aseptic Manip UpdatesDocument36 pagesQA Version 3 - Aseptic Manip UpdatesAhmed NabilNo ratings yet
- GMP Standard Operating ProceduresDocument13 pagesGMP Standard Operating Proceduresfagbemi.maNo ratings yet
- Official Journal of The EU C 223 2013Document2 pagesOfficial Journal of The EU C 223 2013Abdelkarim BelkebirNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Process Validation in Solid Dosage Form (Tablet)Document9 pagesBasic Concept of Process Validation in Solid Dosage Form (Tablet)edgar palominoNo ratings yet
- Types of Process ValidationDocument5 pagesTypes of Process ValidationLuanne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- WHO General Guidance On Variations To MultisourceDocument12 pagesWHO General Guidance On Variations To MultisourceDr. Kazy Habibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Official: Á1001Ñ in Vitro Release Test Methods For Parenteral Drug PreparationsDocument6 pagesOfficial: Á1001Ñ in Vitro Release Test Methods For Parenteral Drug PreparationsDilawar BakhtNo ratings yet
- Official: Á1001Ñ in Vitro Release Test Methods For Parenteral Drug PreparationsDocument6 pagesOfficial: Á1001Ñ in Vitro Release Test Methods For Parenteral Drug PreparationsDilawar BakhtNo ratings yet
- What Is Retrospective ValidationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Retrospective ValidationMarvel tumainiNo ratings yet
- Guidance Document For Preparation of GMP Inspections On Traditional Medicines Health Supplements and Cosmetics ManufacturersDocument15 pagesGuidance Document For Preparation of GMP Inspections On Traditional Medicines Health Supplements and Cosmetics ManufacturersBelle BellaNo ratings yet
- 2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFDocument4 pages2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFVishal SomaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry Documents: 90 Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Interview Questions & AnswersFrom EverandPharmaceutical Industry Documents: 90 Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Interview Questions & AnswersNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Quality Management System (QMS) Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPharmaceutical Quality Management System (QMS) Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDocument1 pageAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Gen Profile January 2014 Batch 02Document4 pagesGen Profile January 2014 Batch 02CYRELL PATERNONo ratings yet
- Cagayan Valley Medical Center: 2017 List of Procured and Consigned MedicinesDocument64 pagesCagayan Valley Medical Center: 2017 List of Procured and Consigned MedicinesAlex SibalNo ratings yet
- Protocoale - Iunie 2018Document14 pagesProtocoale - Iunie 2018Botezatu VilusaNo ratings yet
- Components of Poultry Medicine & Their Relation ToDocument13 pagesComponents of Poultry Medicine & Their Relation ToAHAD HASANNo ratings yet
- Ijpsr Vol I Issue I Article 8Document6 pagesIjpsr Vol I Issue I Article 8Okto 'Andri' SaputraNo ratings yet
- Vetipedia - Drugs (Trade Names)Document11 pagesVetipedia - Drugs (Trade Names)Dr-Sadaqat Ali RaoNo ratings yet
- Rubber Particles in InjectionsDocument2 pagesRubber Particles in InjectionsDustin EstesNo ratings yet
- Antihistamines (Hayfever) and BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesAntihistamines (Hayfever) and BreastfeedingEzraGoenadiNo ratings yet
- Kesimira Qonita (18930066)Document12 pagesKesimira Qonita (18930066)Kesimira QonitaNo ratings yet
- Whats New in Minimally Invasive SurgeryDocument38 pagesWhats New in Minimally Invasive SurgerySadashivayya SoppimathNo ratings yet
- Benadryl N Tagamet Dose and Frequency ChartDocument1 pageBenadryl N Tagamet Dose and Frequency Chartrjkl6No ratings yet
- LTHT Paediatric Administration Guide Intravenous Sodium BicarbonateDocument2 pagesLTHT Paediatric Administration Guide Intravenous Sodium BicarbonateAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ'S: ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesMCQ'S: ItraconazolefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- Layout of Pharmacy in HospitalDocument8 pagesLayout of Pharmacy in HospitalUmar JadoonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guidelines For NarcoticsDocument4 pagesClinical Guidelines For NarcoticsClara VerlinaNo ratings yet
- Terbutalin SulfatDocument2 pagesTerbutalin SulfatZainab WowoussNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaFerry FerdiansyahNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Audit of Pain Profiles Following General and Urological Surgery in ChildrenDocument10 pagesA Prospective Audit of Pain Profiles Following General and Urological Surgery in ChildrenLakhwinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga OGB Per April 2022Document2 pagesDaftar Harga OGB Per April 2022arief suryoNo ratings yet
- Tyramine: Drug Class: Indirectly Acting Sympathomimetic (A Byproduct of Tyrosine Metabolism) Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesTyramine: Drug Class: Indirectly Acting Sympathomimetic (A Byproduct of Tyrosine Metabolism) Mechanism of ActionZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Resolor 1mg Film-Coated Tablets (SPC) - DrugsDocument8 pagesResolor 1mg Film-Coated Tablets (SPC) - DrugsDhiren PranamiNo ratings yet
- Harga ObatDocument46 pagesHarga ObatIGDNo ratings yet
- Proton Pump Inhibitors - AMBOSSDocument3 pagesProton Pump Inhibitors - AMBOSSRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Intravenous InfusionDocument9 pagesIntravenous InfusionMarina MuradNo ratings yet
- British Journal of Surgery - 2020 - Small - Acute Postoperative Pain ManagementDocument11 pagesBritish Journal of Surgery - 2020 - Small - Acute Postoperative Pain ManagementkyleNo ratings yet
- ZolpidemDocument27 pagesZolpidemAntonio SanchezNo ratings yet
- Carisoprodol: Carisoprodol, Marketed Under The Brand Name Soma Among Others, IsDocument7 pagesCarisoprodol: Carisoprodol, Marketed Under The Brand Name Soma Among Others, IsSaufa SyarramaNo ratings yet