Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Excitation System
Excitation System
Uploaded by
Yugandhara Rao Nooka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views31 pagesThe document discusses excitation systems for synchronous generators. It describes the basic functions and requirements of excitation systems, including controlling field voltage to regulate voltage and reactive power. The main components of excitation control systems are described, including the exciter, regulator, voltage transducer, and protective circuits. Different types of excitation systems are also summarized, such as DC, AC, and static excitation systems.
Original Description:
Excitation System.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses excitation systems for synchronous generators. It describes the basic functions and requirements of excitation systems, including controlling field voltage to regulate voltage and reactive power. The main components of excitation control systems are described, including the exciter, regulator, voltage transducer, and protective circuits. Different types of excitation systems are also summarized, such as DC, AC, and static excitation systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views31 pages Excitation System
Excitation System
Uploaded by
Yugandhara Rao NookaThe document discusses excitation systems for synchronous generators. It describes the basic functions and requirements of excitation systems, including controlling field voltage to regulate voltage and reactive power. The main components of excitation control systems are described, including the exciter, regulator, voltage transducer, and protective circuits. Different types of excitation systems are also summarized, such as DC, AC, and static excitation systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 31
EXCITATION CONTROL SYSTEM
ELEMENT OF EXCITATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
EXCITATION CONTROL SYSTEM
REQUIREMENT
TYPES OF EXCITATION SYSTEM
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The basic function of an excitation system is to
provide direct current to the synchronous
machine field winding.
The excitation system performs control and
protective functions essential to the satisfactory
performance of the power system by
controlling the field voltage and there by field
current.
The control functions include the control of
voltage and reactive power flow, and
enhancement of system stability
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The performance requirements of the excitation
system are determined by consideration of the
synchronous generator as well as power
system.
The basic requirement is that the excitation
system supply and automatically adjust the
field current of the synchronous generator to
maintain to maintain the terminal voltage as
the output varies within the continuous
capability of the generator.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The excitation system should contribute to
effective control of voltage and enhancement of
system stability, and of modulating the
generator field so as to enhance small signal
stability.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
To fulfill the above roles satisfactory, the excitation
system must satisfy the following requirements:
1.Meet specified response criteria.
2.Meet the desired reliability and availability, by
incorporating the necessary level of redundancy
and internal fault detection and isolation
capability.
3.Provide limiting and protective function as required
to prevent damage to itself, the generator and
other equipment.
4.Meet specified requirements for operating
flexibility.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
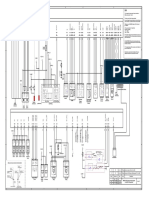
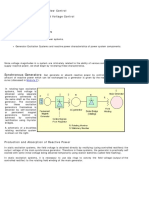
Figure shows the functional block diagram of a
typical excitation control system for a large
synchronous generator.
The following is a brief description of the
various subsystem identified in fig.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
EXCITER:- Provide dc power to the
synchronous machine field winding,
constituting the power stage of the excitation
system.
REGULATOR:- Processes and amplifies input
control signal to a level and form appropriate
for control of the exciter.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
TERMINAL VOLTAGE TRANSDUCER &
LOAD COMPENSATOR:- Senses generator
voltage, rectifies &filter it to dc , and compare it
with reference which represent desire voltage.
POWER SYSTEM STABILIZER:- Provides an
additional input signal to regulator to regulate
damp power system oscillations.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
LIMITERS AND PROTECTIVE CIRCUITS:-
These include a wide array of control and
protective functions which ensure that the
capacity limit of the exciter and synchronous
generator are not exceeded.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Excitation system may be classified into the
following three categories:
1. DC excitation system
2. AC excitation system
3. Static excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
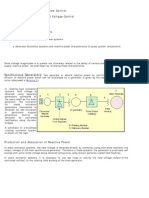
Figure shows a simplified schematic
representation of a typical dc excitation system
with a amplidyne voltage regulator.
It consists of a dc commutator exciter which
supply direct current to the main generator
field through slip rings.
The exciter field is controlled by an amplidyne.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
AC excitation system is used for alternator as
sources of the main excitation power.
The ac output of the exciter is rectified by
rectifiers to produce the direct current needed
for the generator field.
The rectified may be classified in to
a. Stationary rectifier system
b. Rotating rectifier system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
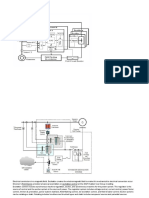
With stationary rectifiers the dc output is fed to
the field winding of the main generator
through slip rings.
As shown in figures two independent modes of
regulation are provided
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
1. AC regulator to automatically maintain the
main generator stator terminal voltage at a
desire value corresponding to the ac reference
2. DC regulator to maintain constant generator
filed voltage as determined by the ac reference.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
With rotating rectifiers the need for slip rings
and is eliminated, and the dc output is directly
fed to the main generator field.
As shown in figures, the armature of the ac
exciter and the diode rectifiers rotate with the
main generator field.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
A small ac pilot exciter, with a permanent
magnet rotor , rotates with the exciter armature
and the diode rectifiers.
The voltage regulator controls the ac exciter
field, which in turn controls the field of the
main generator.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
All components in these systems are static or
stationary.
Static rectifiers, controlled or uncontrolled,
supply the excitation current to the field of the
main synchronous generator through slip
rings.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
This systems are classified in to:
A. Potential-source controlled-rectifier systems
B. Compound-source rectifier system
C. Compound-control rectifier excitation
system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
In this system, the excitation power is supplied
through a transformer from the generator
terminals or the station auxiliary bus, and is
regulated by a controlled rectifier
This type of excitation system is also
commonly known as a bus-fed or transformer-
fed static system.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The power of excitation system is formed by
utilizing the current as well as the voltage of
the main generator.
This may be achieved by means of a power
potential transformer (PPT) and saturable-
current transformer (SCT) as shown in figure.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
This system utilizes controlled rectifier in the
exciter output circuit and the compounding of
voltage and current-derived sources within the
generator stator to provide excitation power.
Figure shows a single line diagram of the
system.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The voltage source is formed by a set of three
phase winding placed in three slots in the
generator stator.
The current source is obtained from a the CT
mounted on stator winding.
These source are combined through
transformer action and ac output is rectified by
power semiconductor.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
The means of control is provided by a
combination of diodes and thyristors connected
to form a shunt bridge’
A static ac voltage regulator controls the firing
circuits of the thyristors and thus regulates the
excitation to the generator field.
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
Sub: Advance power system Topic: Excitation system
You might also like
- Acroba SerManual FA15-30Document190 pagesAcroba SerManual FA15-30Vasile Vrabie100% (4)
- Sim2k-34vr Saipa x100 Wiring Diagram 20101112Document1 pageSim2k-34vr Saipa x100 Wiring Diagram 20101112MAHDI100% (5)
- Excitation SystemDocument31 pagesExcitation SystemAjay Talajiya100% (1)
- Comparison of Various Excitation Systems For Diesel GeneratorDocument8 pagesComparison of Various Excitation Systems For Diesel GeneratorbehroozNo ratings yet
- General Excitation SystemDocument58 pagesGeneral Excitation SystemReza Ghasemi100% (1)
- Excitation System ModelsDocument4 pagesExcitation System ModelsmujahidfadelNo ratings yet
- Excitation SystemDocument4 pagesExcitation SystemMadhan raj VenkatachalamNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentSudar WadiNo ratings yet
- Excitation System Models of Synchronous GeneratorDocument11 pagesExcitation System Models of Synchronous Generatoryasynaslam186No ratings yet
- Tribhuvan UniversityDocument14 pagesTribhuvan UniversitySudhakar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Excitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyDocument12 pagesExcitation System: Neelum Jehlum Hydro Power CompanyAmeer Hamza100% (1)
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02-2 Excitation CourseFulki Kautsar S100% (1)
- Excitation CourseDocument31 pagesExcitation CourseFarhanBaqiNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power ControlDocument25 pagesReactive Power ControlDeepti Gupta100% (1)
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02-2 Excitation CoursejaikolangaraparambilNo ratings yet
- MATLAB-Simulink Based Analysis ofDocument4 pagesMATLAB-Simulink Based Analysis ofAmare KassawNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation of An Alternator - Electrical MachinesDocument4 pagesStatic Excitation of An Alternator - Electrical Machineslim wyNo ratings yet
- Excitation SystemDocument31 pagesExcitation SystemRakesh Kumar100% (2)
- What Is Excitation System - Definition & Types of Excitation System - Circuit GlobeDocument11 pagesWhat Is Excitation System - Definition & Types of Excitation System - Circuit GlobeSabaMannan123No ratings yet
- Static Excitation System - Stage-2Document38 pagesStatic Excitation System - Stage-2raghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3.2 - Excitation SystemsDocument18 pages3.2 - Excitation SystemsEliyanto E BudiartoNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument19 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentRudraraju ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: Raman JainDocument15 pagesExcitation Systems: Raman JainrohitctppNo ratings yet
- Excitation CourseDocument31 pagesExcitation Coursevenkat8eNo ratings yet
- 02 2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02 2 Excitation CourseDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02-2 Excitation CourseShamendu Roy RohitNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02-2 Excitation CourseShamendu Roy RohitNo ratings yet
- Power Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMDocument11 pagesPower Quality Improvement of Distribution System Using D-STATCOMShashankNo ratings yet
- 02-2 Excitation CourseDocument31 pages02-2 Excitation CourseAlirezaNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems of Synchronous MachinesDocument15 pagesExcitation Systems of Synchronous Machinesspark_star100% (1)
- 02 2 Excitation Course PDFDocument31 pages02 2 Excitation Course PDFDjebali Mourad100% (1)
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentshiranughieNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's Consentmabmanik100% (1)
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentmoosuhaibNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDIPAK KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's Consentshivam1001No ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentjawadazamNo ratings yet
- Excitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentDocument31 pagesExcitation Systems: This Material Should Not Be Used Without The Author's ConsentGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (1)
- Avr LFC GB BDDocument53 pagesAvr LFC GB BDBetelhem DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lecxzs PDFDocument3 pagesLecxzs PDFEngr Aman Ullah SialNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power and Voltage Control PDFDocument3 pagesReactive Power and Voltage Control PDFSandeep JoshiNo ratings yet
- Excitation System Models of Synchronous Generator: September 2018Document5 pagesExcitation System Models of Synchronous Generator: September 2018Evan KanigaraNo ratings yet
- Lec 17Document3 pagesLec 17Karthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Generator Excitation SystemDocument34 pagesGenerator Excitation Systemwas00266100% (2)
- Unit 5 Excitation Control: Unit 5.1 Basic Informations of Systems Unit 5.2 Electronic Excitation SystemDocument19 pagesUnit 5 Excitation Control: Unit 5.1 Basic Informations of Systems Unit 5.2 Electronic Excitation SystemBala RajuNo ratings yet
- Excitation SystemsDocument21 pagesExcitation SystemsPfunzo MammbaNo ratings yet
- ExcitationDocument12 pagesExcitationDdumbaNo ratings yet
- Applications-Light Dimmer, Excitation System and Solar PV System in Phase Controlled ConvertersDocument7 pagesApplications-Light Dimmer, Excitation System and Solar PV System in Phase Controlled ConvertersSRAVAN KUMAR.M EEE100% (1)
- Cummins Power Command IWatch100Document31 pagesCummins Power Command IWatch100Leo BurnsNo ratings yet
- Electrical MachinesDocument22 pagesElectrical MachinesJoshtyler 21No ratings yet
- Generation and Absorption of Reactive Power by Various ComponentsDocument2 pagesGeneration and Absorption of Reactive Power by Various ComponentsSrinivas Yelisetti100% (5)
- Electrics of LocomotivesDocument9 pagesElectrics of LocomotivesmajjisatNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation SystemsDocument7 pagesModeling and Analysis of The Synchronous Generators Excitation Systemsni60No ratings yet
- Excitation SystemsDocument15 pagesExcitation SystemsSahiti DarikaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Separatoare Izolate in SF6Document28 pagesSeparatoare Izolate in SF6Dumitru TănaseNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument15 pagesEarthing Systemnavdeepsankhala100% (2)
- LC1D1201 Telemecanique LC1-D12-01 Contactor ReplacementDocument1 pageLC1D1201 Telemecanique LC1-D12-01 Contactor Replacementhippong niswantoroNo ratings yet
- Vs-Vsk.230..Pbf Series: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument9 pagesVs-Vsk.230..Pbf Series: Vishay SemiconductorsrenidwilNo ratings yet
- Problems With Commutation - Suaiso BSEE - 3BDocument4 pagesProblems With Commutation - Suaiso BSEE - 3BRolly Jr. SuaisoNo ratings yet
- ARN ESS TES T: Cable Harness TestDocument8 pagesARN ESS TES T: Cable Harness TestjmartinezmoNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions: Analogue Instruments - Sealed and Ruggedised Meters 08X SeriesDocument2 pagesInstallation Instructions: Analogue Instruments - Sealed and Ruggedised Meters 08X SeriesMauricio GuanellaNo ratings yet
- Minitek PWR CEM-5 12VHPWR Wire To Board Connectors: Application SpecificationDocument13 pagesMinitek PWR CEM-5 12VHPWR Wire To Board Connectors: Application SpecificationŁukasz SrogaNo ratings yet
- HT-TM2200-75: BenefitsDocument5 pagesHT-TM2200-75: BenefitsJan Antonius DjunaediNo ratings yet
- MJD340 (NPN) MJD350 (PNP) High Voltage Power Transistors: DPAK For Surface Mount ApplicationsDocument5 pagesMJD340 (NPN) MJD350 (PNP) High Voltage Power Transistors: DPAK For Surface Mount ApplicationsBertrand Soppo YokiNo ratings yet
- 157 Pum-Si: Vishay BccomponentsDocument10 pages157 Pum-Si: Vishay Bccomponentssamasca_serban0% (1)
- Rele EspecialDocument1 pageRele EspecialAnonymous UxrPsIVNo ratings yet
- Standard Ac PwsDocument17 pagesStandard Ac PwstheXSNo ratings yet
- Smartwire: Installation ManualDocument46 pagesSmartwire: Installation ManualDikdik BudimanNo ratings yet
- DCMT - Set 3 P GR14 Nov 2016Document2 pagesDCMT - Set 3 P GR14 Nov 2016P Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Cat AbbDocument4 pagesCat AbbcxrxixsxNo ratings yet
- Engineering Systems LTD.: PROJECT: 90KLPD Distillery Plant Section: Fermentation ClientDocument7 pagesEngineering Systems LTD.: PROJECT: 90KLPD Distillery Plant Section: Fermentation ClientS B DubalNo ratings yet
- Solucion de Problemas Sigma Solon LD 1Document9 pagesSolucion de Problemas Sigma Solon LD 1Jms QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Modulo de Una Entrada KIDDE GSA-CT1 PDFDocument2 pagesManual Del Modulo de Una Entrada KIDDE GSA-CT1 PDFAnderson CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Three Phase Motor Rev For 10102023 014430pmDocument7 pagesLab 3 Three Phase Motor Rev For 10102023 014430pmSYED ALIYYAN IMRAN ALINo ratings yet
- EE-422-Final-Examination PETE 2207Document6 pagesEE-422-Final-Examination PETE 2207Christian Rogel De TorresNo ratings yet
- TC4451/TC4452: 12A High-Speed MOSFET DriversDocument24 pagesTC4451/TC4452: 12A High-Speed MOSFET DriversVolodiyaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Development of Microcontroller Based Triggering Circuit Using Proteus SoftwareDocument4 pagesSimulation Development of Microcontroller Based Triggering Circuit Using Proteus SoftwareVincent RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Omega Etb 058Document1 pageOmega Etb 058INSIF ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- DVP32SM SN Instruction enDocument2 pagesDVP32SM SN Instruction enخطاب الشاميNo ratings yet
- Amalgam Uv Specs and User ManualDocument3 pagesAmalgam Uv Specs and User ManualNaldre PhamhinthuanNo ratings yet
- Codificare Rezistente SMD 60A Are 412 Ohmi CF TabelDocument6 pagesCodificare Rezistente SMD 60A Are 412 Ohmi CF Tabelromeo1966No ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution SystemDocument3 pagesElectrical Power Distribution SystemmshahidshaukatNo ratings yet