Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Request A Lending and Leasing As A Service Brochure
Request A Lending and Leasing As A Service Brochure
Uploaded by
Fahim ChougleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Request A Lending and Leasing As A Service Brochure
Request A Lending and Leasing As A Service Brochure
Uploaded by
Fahim ChougleCopyright:
Available Formats
Request a lending and leasing as a service brochure
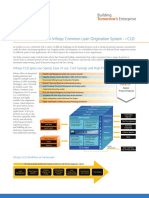
Below are seven stages I feel are the critical components of loan origination
process.
7 Stages:
1. Pre-qualification – The first step in the loan origination process is pre-
qualification. During this stage the potential borrower will receive a list of items
they need to pull together to submit to the lender. This may include:
Current employment information including hourly wage or salary
Total household income
Payment history
Bank statements
Tax returns
Once this information is submitted to the lender, it is typically processed and a
loan pre-approval is made, allowing the borrower to continue in the process to
obtain a loan.
2. Loan Application – In this stage of the loan origination process, the borrower
completes the loan application. Sometimes a paper application is completed, but
more often today, an electronic version is completed and submitted by the
prospective borrower. New technologies allow completing the application online
or through a mobile app, and collected information can be tailored to specific
loan products.
3. Application Processing – When the application is received by the credit
department, the first step is to review it for accuracy and completeness. All
required fields must be filled in, otherwise the application will be returned to the
borrower or the credit analyst will have to reach out to the borrower to procure
the required missing information. Depending on the technology employed by the
lender, a sophisticated Loan Origination System (LOS) can automatically flag files
with missing required fields and return it to the borrowers to re-work.
Depending on the organization, exception processing might be part of this
process, or manual loan processors can review each application for
completeness.
4. Underwriting Process – When an application is deemed complete, the
underwriting process begins. The company runs the application through a
process of taking a variety of components into account: credit score, risk scores,
and many lenders will generate their own additional unique scoring criteria that
are unique to their business or industry. Sometimes this process is fully
automated; other times it is manual or a combination of both. Underwriting
guidelines can be loaded into the LOS.
5. Credit Decision – Depending on the underwriting process, the file can be
approved, denied or sent back to the originator for additional information. A
denial may be revisited if certain parameters are changed, such as a reduced loan
amount or different interest rates to lower payments.
6. Quality Control – Since consumer lending is highly regulated, the quality
control stage of the loan origination process is critical to lenders. Typically the
application would be sent to a quality control queue where the final decision and
other critical variables can be analyzed against internal and external rules and
regulations. This is essentially a last look at the application before it goes to
funding.
7. Loan Funding – Most consumer loans fund shortly after the loan documents
are
signed. Second mortgage loans and lines of credit may require additional time for
legal and compliance reasons. LOS programs can track funding and ensure that
all
necessary documents are executed before or together with funding.
I have had the pleasure of meeting lenders that are strategic, analytical,
aggressive, quality focused, care about the customer, and embrace technology
upgrades such as new loan origination software (LOS) solutions. These are the
lenders that excel in their industry vertical. Here’s a quick list of features and
benefits that should be part of your LOS:
Receipt of applications through multiple channels such as the web or fax
Submit and receive credit bureau information online
Calculation of user-defined credit scores with an internal scorecard, using a
weighted average on criteria from both the application and the credit bureau
data
Make credit decisions automatically or manually
Capability to re-score each applicant separately
Interface with multiple collateral asset valuation guides and VIN checks, plus
VIN check digit
Allow promotions, such as reduced rate or no interest for a period of time
Provide completion checklists to user enhance processing and reduce
training
Automatically transmit decisions back to the dealer, originator or applicant
Link the origination data to funding processes and the servicing module in
real time
Process checks through an external Accounts Payable system or send
Automated Clearing House (ACH) payment(s) directly from the system
Build a customized underwriting workflow based on user-configurable
parameters for a paperless flow of information
Upload scanned documents to an application
Generate reports on applications based on status, dealer, user or
underwriter
You might also like
- Vault QuestionsDocument34 pagesVault QuestionsUni Qlo50% (2)
- Vault Fundamentals BrochureDocument15 pagesVault Fundamentals BrochureUni Qlo50% (2)
- IMPS Process FlowDocument12 pagesIMPS Process FlowThamil Inian100% (1)
- Loan Processing SystemDocument366 pagesLoan Processing SystemAhsan ZamanNo ratings yet
- Core Banking Union Bank of IndiaDocument36 pagesCore Banking Union Bank of IndiaRakesh Prabhakar Shrivastava100% (2)
- Finacle Core Banking SolutionDocument8 pagesFinacle Core Banking SolutionInfosysNo ratings yet
- Core Banking PDFDocument3 pagesCore Banking PDFJanani RaniNo ratings yet
- Core Banking SolutionsDocument13 pagesCore Banking Solutionssharmil_jainNo ratings yet
- Core Banking System in SBIDocument4 pagesCore Banking System in SBINilesh Chandra Sinha92% (12)
- Ezbob SME Digital Lending Product DescriptionDocument34 pagesEzbob SME Digital Lending Product DescriptionMinhminh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Online Bill Payment Design..Document10 pagesOnline Bill Payment Design..Mmoloki KaisaraNo ratings yet
- Corporate Loan OriginationDocument37 pagesCorporate Loan Originationk_adhikary67% (3)
- R14 - UG - Retail Service IjaraDocument57 pagesR14 - UG - Retail Service IjaraSathya Kumar100% (1)
- Core Banking System Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandCore Banking System Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- A Case For A Single Loan Origination System For Core Banking ProductsDocument5 pagesA Case For A Single Loan Origination System For Core Banking ProductsCognizant100% (1)
- Prepaid Payment Systems A Discussion PaperDocument18 pagesPrepaid Payment Systems A Discussion PaperBlessing MukomeNo ratings yet
- Core Banking Solutions FinalDocument6 pagesCore Banking Solutions FinalShashank VarmaNo ratings yet
- LendingDocument96 pagesLendingHimmat SinghNo ratings yet
- Core BankingDocument16 pagesCore Bankingaparnasudha136No ratings yet
- A Case For A Single Loan Origination System For Core Banking Products PDFDocument5 pagesA Case For A Single Loan Origination System For Core Banking Products PDFansh_hcetNo ratings yet
- Temenos Products Infinity BrochureDocument12 pagesTemenos Products Infinity Brochureelswidi100% (1)
- Core Banking Partner GuideDocument19 pagesCore Banking Partner GuideClint JacobNo ratings yet
- Requirement Document Smart Acc - Existing Customer FlowDocument7 pagesRequirement Document Smart Acc - Existing Customer FlowRishu SinhaNo ratings yet
- Core BankingDocument15 pagesCore BankingAnkushnegiNo ratings yet
- TLC Online Learning Pack ContentDocument15 pagesTLC Online Learning Pack ContentjennoNo ratings yet
- Customer Information File User Manual PDFDocument314 pagesCustomer Information File User Manual PDFFahim KaziNo ratings yet
- T24 ARC Internet BankingDocument206 pagesT24 ARC Internet BankingTrần Tiến Trung100% (2)
- Islamic Banking User Manual-MUSHARAKADocument13 pagesIslamic Banking User Manual-MUSHARAKAPranay Kumar Sahu100% (1)
- Core Banking SystemsDocument25 pagesCore Banking SystemsSaravananSrvnNo ratings yet
- Finacle OriginationDocument6 pagesFinacle OriginationAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- NEFT Vs RTGS PaymentsDocument4 pagesNEFT Vs RTGS PaymentsrajeevjprNo ratings yet
- Banking Products & Services IDocument34 pagesBanking Products & Services IAinnur HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Online Paymet SystemsDocument23 pagesOnline Paymet SystemsPrabhjeet Sumit GoklaneyNo ratings yet
- Loan Rebate ProcessingDocument20 pagesLoan Rebate ProcessingYu ShiyuanNo ratings yet
- Content Project 3Document46 pagesContent Project 3ram73110No ratings yet
- Product ArchitectureDocument26 pagesProduct ArchitectureTrần Hữu LượngNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bank Loan SystemDocument16 pagesProject Report On Bank Loan Systempranit bandkarNo ratings yet
- Asian Banker - Core Banking ReplacementDocument173 pagesAsian Banker - Core Banking ReplacementHaris ANo ratings yet
- Liability Products of HDFC BankDocument1 pageLiability Products of HDFC BankNikhil SinghalNo ratings yet
- R11 User GuideDocument39 pagesR11 User Guidemukeshdograji100% (1)
- Core Banking Solution For US Community Banks, Credit Unioins - BankingDocument15 pagesCore Banking Solution For US Community Banks, Credit Unioins - BankingAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Union Bank PDFDocument154 pagesUnion Bank PDFRakesh Prabhakar ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- RFP RTGSDocument14 pagesRFP RTGSShakil Chowdhury0% (1)
- Temenos Integration With Union Pay and VISADocument5 pagesTemenos Integration With Union Pay and VISAPaxy SENGOUDONENo ratings yet
- BASE24 DR With AutoTMF and RDF WhitepaperDocument38 pagesBASE24 DR With AutoTMF and RDF WhitepaperMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Accenture Collateral Management Offering BrochureDocument16 pagesAccenture Collateral Management Offering BrochureinvHnS ok100% (1)
- SBI Core BankingDocument48 pagesSBI Core BankingshahsuhailNo ratings yet
- Payment Gateway Integration and Credit Card Processing v1.0Document57 pagesPayment Gateway Integration and Credit Card Processing v1.0ArunDhamDNo ratings yet
- 4 A Guide To Payment Gateways PDFDocument3 pages4 A Guide To Payment Gateways PDFMishel Carrion lopezNo ratings yet
- Fs Revolutionizing Corp Lending Digital World WPDocument10 pagesFs Revolutionizing Corp Lending Digital World WPRishi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PaymentRoadmap 2021 PDFDocument60 pagesPaymentRoadmap 2021 PDFviolet suNo ratings yet
- Common Loan Origination (InfoSys)Document2 pagesCommon Loan Origination (InfoSys)Baatar SukhbaatarNo ratings yet
- RFP For Core Banking Solution of WBSCB Ltd.Document203 pagesRFP For Core Banking Solution of WBSCB Ltd.santosh5953100% (1)
- Cloud Lending Solutions Overview - Lending Innovation Starts Here™Document16 pagesCloud Lending Solutions Overview - Lending Innovation Starts Here™Cloud Lending SolutionsNo ratings yet
- ADBs Request For Proposal RFP Core Banking SolutionDocument49 pagesADBs Request For Proposal RFP Core Banking Solutionindia nesan100% (2)
- What Is An Account Aggregator?Document7 pagesWhat Is An Account Aggregator?Francis NeyyanNo ratings yet
- Use Case Diagrams (SDLab)Document15 pagesUse Case Diagrams (SDLab)Aravindha Kumar100% (1)
- T24 Islamic Banking - Islamic WorkflowDocument57 pagesT24 Islamic Banking - Islamic WorkflowSaif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Bai-Salam - User Guide: Release R15.000Document22 pagesBai-Salam - User Guide: Release R15.000Yousra HafidNo ratings yet
- Cyclone U and PDocument2 pagesCyclone U and PtomaszNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica de Ups Smart - Pro 3p-3p ModularDocument4 pagesFicha Tecnica de Ups Smart - Pro 3p-3p ModularChristian TrvrNo ratings yet
- MISDocument12 pagesMISPrajakta Sanjay JadhavNo ratings yet
- Dacor Wall OvenDocument77 pagesDacor Wall OvenJim Harmke100% (2)
- Sentinel EMS Product BriefDocument3 pagesSentinel EMS Product BriefajayazadNo ratings yet
- ExportDocument3 pagesExportYogidearNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document121 pagesTest 1JeejuNo ratings yet
- 2 ParamDocument7 pages2 ParamCHAITUCANo ratings yet
- Lom LogDocument4 pagesLom Logjoyssurya123No ratings yet
- 45 - HP Roam For Business BrochureDocument2 pages45 - HP Roam For Business BrochureBAONo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanAubrey DacerNo ratings yet
- DLBCSICS01 Sample Solution 2Document5 pagesDLBCSICS01 Sample Solution 2manjunath.aNo ratings yet
- The Internet of ThingsDocument4 pagesThe Internet of Thingssuljo atlagicNo ratings yet
- NET Memory ProfilerDocument229 pagesNET Memory ProfilerNatalia PeraltaNo ratings yet
- G6TXC08GKPH9 InfoDocument2 pagesG6TXC08GKPH9 InfoBikash LamaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Week3 NotesDocument45 pagesLinear Algebra Week3 NotesWeasley WavesNo ratings yet
- Tsinghua UG English-Taught Courses Syllabi (Fall 2010)Document80 pagesTsinghua UG English-Taught Courses Syllabi (Fall 2010)An WoNo ratings yet
- DNSDocument18 pagesDNSraghavsarikaNo ratings yet
- Nihal's Resume - FrontendDocument1 pageNihal's Resume - FrontendNihal BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Excel Shortcuts CompilationDocument1 pageExcel Shortcuts CompilationAbhimanyu LatherNo ratings yet
- Enigma 1.x - 3.x VM Unpacker 1.0 EditedDocument124 pagesEnigma 1.x - 3.x VM Unpacker 1.0 Editedaril devNo ratings yet
- Creating Libraries in HITECHDocument2 pagesCreating Libraries in HITECHAlgebra92No ratings yet
- Hexagon PPM - Concurrent Engineering Rev0Document8 pagesHexagon PPM - Concurrent Engineering Rev0edriceNo ratings yet
- DBMS ER DiagramDocument11 pagesDBMS ER DiagramAayushi ChowlaNo ratings yet
- RS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018Document70 pagesRS 1803 HFS BP Enterprise Artificial Intelligence (AI) Services 2018pantmukulNo ratings yet
- Structural Design PatternDocument34 pagesStructural Design PatternAkula SandeepNo ratings yet
- Virtual SIM Solution enDocument2 pagesVirtual SIM Solution entelephonicaNo ratings yet
- Denovo Voucher Script User ManualDocument55 pagesDenovo Voucher Script User ManualJulio CesarNo ratings yet
- Viewpoints For Requirements Elicitation: A Practical ApproachDocument8 pagesViewpoints For Requirements Elicitation: A Practical ApproachPhạm Phú TàiNo ratings yet
- SIP-I Tentative Marks 2021Document16 pagesSIP-I Tentative Marks 20210901AU201028 SARANSH BAIRAGINo ratings yet