Professional Documents
Culture Documents
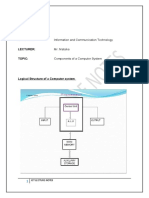
System Unit: Property of STI
System Unit: Property of STI
Uploaded by
Enimsaj CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TOPIC 4 ER ModelingDocument37 pagesTOPIC 4 ER ModelingNowlghtNo ratings yet
- 3 Examples of Multimedia ProductDocument4 pages3 Examples of Multimedia ProductSyukriah Mat YatyaNo ratings yet
- 2009 10 15 LIME Appendix B Erlang B TableDocument4 pages2009 10 15 LIME Appendix B Erlang B TableSardar A A KhanNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document8 pagesLect 1Ahmed SalihNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyDocument17 pagesChapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyAmruta DhengaleNo ratings yet
- Components of A Computer SystemDocument7 pagesComponents of A Computer SystemMbizi SamaitaNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarDocument5 pagesComputer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarChempa BalajiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document20 pagesLec 2smnepalschoolNo ratings yet
- Digitalization of DataDocument3 pagesDigitalization of DataAustin AgbasonNo ratings yet
- Components of System Units ReviewerDocument20 pagesComponents of System Units ReviewerMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2benazir masukatNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 COADocument23 pagesUnit - 2 COAArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument9 pagesIntroduction To ComputerMir Farhan Ali AbediNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument74 pagesIntroduction To ComputerJade TobiasNo ratings yet
- 1 Types and Components of Computer Systems: SectionDocument12 pages1 Types and Components of Computer Systems: Sectionkenneth gutayNo ratings yet
- 03 - Handout - 1 (2) CSADocument5 pages03 - Handout - 1 (2) CSAJudilyn Judy TomasNo ratings yet
- Overview of A Computer System.Document32 pagesOverview of A Computer System.grenamoNo ratings yet
- 5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Document19 pages5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Himanshi SainiNo ratings yet
- Computer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadaDocument18 pagesComputer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadakamalshrishNo ratings yet
- XI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Document20 pagesXI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6kemalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- System UnitDocument38 pagesSystem UnitBL A CKNo ratings yet
- Practical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?Document13 pagesPractical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?funny videosNo ratings yet
- IT1020 - Worksheet 01Document11 pagesIT1020 - Worksheet 01navithamaradasa2002No ratings yet
- Basics of ComputersDocument13 pagesBasics of ComputersFintonPaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document85 pagesUnit 4Chadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)Document10 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)rikzy rulaiwan100% (1)
- Ch-1 Computer SystemDocument23 pagesCh-1 Computer SystemVidushi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- COADocument137 pagesCOAThonta DariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Computer Systems: StructureDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Computer Systems: StructureCamilo AmarcyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Document24 pagesUnit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Ujjwal KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Document4 pagesIntroduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Jedekia kicaNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document4 pagesDocument 1mah almbroukNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ComputersLaira LicudineNo ratings yet
- CS2253 UwDocument131 pagesCS2253 UwVallam RameshNo ratings yet
- Mcrocomputer SystemDocument7 pagesMcrocomputer SystemVICTOR OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Computer CourseDocument20 pagesComputer CourseAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- CPDSDocument319 pagesCPDSrupakothurNo ratings yet
- Computer Essentials - Lecture 1Document6 pagesComputer Essentials - Lecture 1SHKO MAGDIDNo ratings yet
- Cfo Full NotesDocument48 pagesCfo Full Notessreeja sethuNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document7 pagesWeek 1nothaia morilloNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsDocument14 pagesCH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsIzzabelle Athena JayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2MUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument14 pagesComputer OrganizationahmedNo ratings yet
- System Unit LessonDocument10 pagesSystem Unit LessonUnknown TototNo ratings yet
- Hardware: Control UnitDocument8 pagesHardware: Control Unitigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Large Computers: (Mainframe and Super Computers)Document18 pagesLarge Computers: (Mainframe and Super Computers)Shivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Essential of ItDocument9 pagesNotes On Essential of ItDrRam Singh KambojNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarDocument5 pagesComputer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarGebBerheNo ratings yet
- 11 CSS Module Week 3Document23 pages11 CSS Module Week 3Alexander IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Computer Processing DevicesDocument21 pagesComputer Processing Devicesaluka porota75% (4)
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Sonu zehen001No ratings yet
- COA Notes For MCA UNIT-1Document6 pagesCOA Notes For MCA UNIT-1rashmi.bharadwajNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer HardwareDocument73 pagesBasics of Computer HardwareBalaji Rao NNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Computers, Smartphones and the InternetFrom EverandUnderstanding Computers, Smartphones and the InternetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5 Steps To Create A Massive Vocal Mix (FREE GUIDE)Document5 pages5 Steps To Create A Massive Vocal Mix (FREE GUIDE)Dávid BaltaváriNo ratings yet
- Case Study Managing Station Design Changes 2Document5 pagesCase Study Managing Station Design Changes 2Bereket KahsayNo ratings yet
- Overview On PVSystDocument10 pagesOverview On PVSystpreeti kumari sahuNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 8djh36 enDocument68 pagesCatalogue 8djh36 enGhasem KheirollahNo ratings yet
- Qualitywings Bae146 Flight Management Computer TutorialDocument27 pagesQualitywings Bae146 Flight Management Computer TutorialDaniel De AviaciónNo ratings yet
- PUB - 3373 - Actuator Charger & Tester - Instruction Manual - Issue 5Document17 pagesPUB - 3373 - Actuator Charger & Tester - Instruction Manual - Issue 5ABDUL GHAFOORNo ratings yet
- GAC Connection Diagram PDFDocument1 pageGAC Connection Diagram PDFThomasRudyNo ratings yet
- Transworld TW100 HS SSB Transceiver - Condensed Operating Instructions (Laminated Card Front and Back)Document2 pagesTransworld TW100 HS SSB Transceiver - Condensed Operating Instructions (Laminated Card Front and Back)Alexander J Rokowetz100% (1)
- Encore Parts List and Exploded v6 020520Document4 pagesEncore Parts List and Exploded v6 020520Roberto Damian HernándezNo ratings yet
- Bri OktoberDocument3 pagesBri OktoberMobilkamu JakartaNo ratings yet
- Miguel Angel Ariza SalazarDocument3 pagesMiguel Angel Ariza SalazarGreen InkNo ratings yet
- KivyDocument871 pagesKivySerge OngoloNo ratings yet
- DVP Series Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Document3 pagesDVP Series Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Sitaram TilekarNo ratings yet
- XCFR2.E60425 - Terminal Blocks - Component - UL Product IQDocument187 pagesXCFR2.E60425 - Terminal Blocks - Component - UL Product IQRahul Kumar Singh (IPR and Product Safety Compliance)No ratings yet
- L05 Topic1C Multimedia Element VideoDocument33 pagesL05 Topic1C Multimedia Element VideoRAYCHEAL VERONICA TONGNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document52 pagesLecture 26Cu BomNo ratings yet
- Sep 2010Document572 pagesSep 2010Shailesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Woofer - Wikipedia, The Fre..Document5 pagesWoofer - Wikipedia, The Fre..santamilNo ratings yet
- CETS HIGHVOLT Water TerminationsystemDocument4 pagesCETS HIGHVOLT Water TerminationsystemkmiqdNo ratings yet
- Cava PDFDocument2 pagesCava PDFSrideviNo ratings yet
- List of Students Who Applied For NCCDocument28 pagesList of Students Who Applied For NCCgurjot1234567890No ratings yet
- Written InterviewDocument4 pagesWritten Interviewcq8kd9rqh2No ratings yet
- BRKRST 2559Document85 pagesBRKRST 2559ritikaNo ratings yet
- Hyundair290lc 7crawlerexcavatorservicerepairfactorymanualinstantdownload 130422122642 Phpapp02Document7 pagesHyundair290lc 7crawlerexcavatorservicerepairfactorymanualinstantdownload 130422122642 Phpapp02codeyNo ratings yet
- NHPCDocument61 pagesNHPCSatyendra N Yadaw100% (2)
- MHYDocument24 pagesMHYhizbi7No ratings yet
- Working With Power Queries Using Blue PrismDocument11 pagesWorking With Power Queries Using Blue Prismemail2mesuryaNo ratings yet
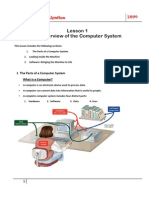
System Unit: Property of STI
System Unit: Property of STI
Uploaded by
Enimsaj CastroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
System Unit: Property of STI
System Unit: Property of STI
Uploaded by
Enimsaj CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
IT1707
System Unit
System unit – is the main hardware component of the computer system. It is the enclosure for all the essential electronic
components that make up a computer system. System units can be in a separated case, but can also be inside a portable
computer that share containers with other parts of the computer system.
Desktops – Most desktops have their system unit in a separate case. This case contains the system’s electronic
components and selected secondary storage devices. Input and output devices, such as mouse, keyboard, and
monitor are located outside the system unit.
Laptops – These are portable computers. Their system units are housed with selected secondary storage devices and
input devices.
Tablets – These portable computers have their system unit located behind the monitor.
Smartphones – The system unit of these mobile devices are located behind the display screen. There are other
mobile computers including wearable computers.
Personal computers come in a variety of different sizes, shapes, and capabilities. While they look different and each has its
own unique features, they share similar components, including system boards, microprocessors, and memory.
System Board
System board – This controls communications for the entire computer system. All devices and components connect to the
system board, including external devices like keyboards and monitors and internal components like hard-disk drives and
microprocessors.
The system board acts as a data path and traffic monitor, allowing the various components to communicate efficiently with
one another. This is a flat circuit board covered with a variety of different electronic components including sockets, slots, and
bus lines.
Sockets – Provide a connection point for small specialized electronic parts called chip. Chips consists of tiny circuit
boards. A chip is also called as integrated circuit (IC). Chips typically are mounted onto chip carriers. These carriers
plug either directly into sockets on the system board or onto cards that are then plugged into slots on the system
board. Sockets are used to connect the system board to a variety of different types of chips, including microprocessor
and memory chips.
Slots – These provide a connection point for specialized cards or circuit boards. These cards provide expansion
capability for a computer system.
Bus Lines – These are electrically conductive pathways of the system board. These carry the data from place to place.
These provide pathways that support communication among the various electronic components that are either
located on the system board or attached to the system board.
Microprocessor
Central Processing Unit (CPU) – This contains millions of tiny transistors and pathways (bus lines) that take in data and
instructions, process the data according to the instructions, and output the results of the calculations. It is contained on a
single chip called the microprocessor. It has three (3) basic sections: a control unit, ALU, and registers.
Control unit – This manages the flow of data through the CPU. It directs data to and from the other components
within the CPU. It directs the movement of electronic signals between memory, which temporarily holds data,
instructions, and processed information, and the arithmetic-logic unit. It also directs these control signals between
the CPU and input and output devices.
Arithmetic-logic unit (ALU) – This component does the actual processing. It receives data and instructions and
delivers a result. It performs two (2) types of operations: arithmetic and logical.
o Arithmetic operations are the fundamental math operations.
o Logical operations consist of comparisons.
Registers – These are holding areas for both data and instructions. There are many different registers, each with its
own special purpose. For example, there are registers that hold instructions and registers that hold data.
Chip processing capacities are often expressed in word sizes. A word is the number of bits (such as 32 or 64) that can be
accessed at one (1) time by the CPU. The more bits in a word, the more data a computer can process at one (1) time. A 32-
bit word CPU can access 4 bytes at a time. A 64-bit word CPU can access 8 bytes at a time. Therefore, the CPU designed to
process 64-bit words has greater processing capacity.
02 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 1 of 2
IT1707
The processing speed of a microprocessor is typically represented by its clock speed, which is related to the number of time
the CPU can process data or instructions in a second. The higher a microprocessor’s clock speed, the faster the
microprocessor.
Microprocessors that only support a single CPU is limited to processing one (1) program at a time. Multicore processors can
provide multiple independent CPUs. For multicore processors to be used effectively, computers must understand how to
divide tasks into parts that can be distributed across each core, this operation is called parallel processing.
Specialty Processors
In addition to microprocessor chips, a variety of more specialized processing chips have been developed.
Coprocessors are special chips designed to improve specific computing operations. For example, the graphics coprocessors
or graphics processing unit (GPU) and sound cards are considered as coprocessors.
Memory
Dynamic memory – also called as volatile memory. This memory does not retain its data unless it is electrically refreshed.
Static memory – also called as non-volatile memory. Memory that retains its data without electricity being constantly
applied.
Memory – It is a holding area for data, instructions, and information. It is contained on chips connected to the system board.
Three (3) types of memory chips:
Random-access Memory (RAM) – these are chips that holds the program (sequence of instructions) and data that
the CPU is presently processing. RAM is a dynamic memory because their contents are lost if power of the computer
is disrupted.
o Cache memory is a high-speed holding area for frequently used data and information.
o Dual in-line memory module (DIMM) is used to expand memory.
o Virtual memory divides large programs into parts that are read into RAM as needed.
Read-only Memory (ROM) – these chips have information stored in them by the manufacturer. Unlike RAM chips,
ROM chips are static and cannot be changed by the user. “Read only” means that the CPU can read or retrieve data
and programs written on the ROM chip. However, the computer cannot write or change the information or
instructions in ROM.
Flash Memory – this offers a combination of the features of RAM and ROM. Like RAM, it can be updated to store
new information. Like ROM, it does not lose that information when power to the computer system is turned off.
REFERENCES:
O’Leary, T., O’Leary L., & O’Leary D. (2017). Computing essentials 2017. USA: McGraw-Hill Education.
Wempen, F. (2014). Computing Fundamentals Digital Literacy Edition. United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
02 Handout 1 *Property of STI
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- TOPIC 4 ER ModelingDocument37 pagesTOPIC 4 ER ModelingNowlghtNo ratings yet
- 3 Examples of Multimedia ProductDocument4 pages3 Examples of Multimedia ProductSyukriah Mat YatyaNo ratings yet
- 2009 10 15 LIME Appendix B Erlang B TableDocument4 pages2009 10 15 LIME Appendix B Erlang B TableSardar A A KhanNo ratings yet
- Lect 1Document8 pagesLect 1Ahmed SalihNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyDocument17 pagesChapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyAmruta DhengaleNo ratings yet
- Components of A Computer SystemDocument7 pagesComponents of A Computer SystemMbizi SamaitaNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarDocument5 pagesComputer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarChempa BalajiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document20 pagesLec 2smnepalschoolNo ratings yet
- Digitalization of DataDocument3 pagesDigitalization of DataAustin AgbasonNo ratings yet
- Components of System Units ReviewerDocument20 pagesComponents of System Units ReviewerMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2benazir masukatNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 COADocument23 pagesUnit - 2 COAArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument9 pagesIntroduction To ComputerMir Farhan Ali AbediNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument74 pagesIntroduction To ComputerJade TobiasNo ratings yet
- 1 Types and Components of Computer Systems: SectionDocument12 pages1 Types and Components of Computer Systems: Sectionkenneth gutayNo ratings yet
- 03 - Handout - 1 (2) CSADocument5 pages03 - Handout - 1 (2) CSAJudilyn Judy TomasNo ratings yet
- Overview of A Computer System.Document32 pagesOverview of A Computer System.grenamoNo ratings yet
- 5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Document19 pages5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: Unit-I What Are Digital Computers?Himanshi SainiNo ratings yet
- Computer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadaDocument18 pagesComputer System: Prepared By: Suresh KhatiwadakamalshrishNo ratings yet
- XI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Document20 pagesXI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6kemalNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Computer SystemDocument34 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Computer Systemprasadnehra77No ratings yet
- System UnitDocument38 pagesSystem UnitBL A CKNo ratings yet
- Practical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?Document13 pagesPractical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?funny videosNo ratings yet
- IT1020 - Worksheet 01Document11 pagesIT1020 - Worksheet 01navithamaradasa2002No ratings yet
- Basics of ComputersDocument13 pagesBasics of ComputersFintonPaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document85 pagesUnit 4Chadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)Document10 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris 4 Makalah (Discussion Hardware and Software)rikzy rulaiwan100% (1)
- Ch-1 Computer SystemDocument23 pagesCh-1 Computer SystemVidushi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- COADocument137 pagesCOAThonta DariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Computer Systems: StructureDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Computer Systems: StructureCamilo AmarcyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Document24 pagesUnit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Ujjwal KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Document4 pagesIntroduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Jedekia kicaNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document4 pagesDocument 1mah almbroukNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ComputersLaira LicudineNo ratings yet
- CS2253 UwDocument131 pagesCS2253 UwVallam RameshNo ratings yet
- Mcrocomputer SystemDocument7 pagesMcrocomputer SystemVICTOR OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Computer CourseDocument20 pagesComputer CourseAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- CPDSDocument319 pagesCPDSrupakothurNo ratings yet
- Computer Essentials - Lecture 1Document6 pagesComputer Essentials - Lecture 1SHKO MAGDIDNo ratings yet
- Cfo Full NotesDocument48 pagesCfo Full Notessreeja sethuNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document7 pagesWeek 1nothaia morilloNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsDocument14 pagesCH 3 Computer Hardware For Information SystemsIzzabelle Athena JayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2MUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument14 pagesComputer OrganizationahmedNo ratings yet
- System Unit LessonDocument10 pagesSystem Unit LessonUnknown TototNo ratings yet
- Hardware: Control UnitDocument8 pagesHardware: Control Unitigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Large Computers: (Mainframe and Super Computers)Document18 pagesLarge Computers: (Mainframe and Super Computers)Shivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Essential of ItDocument9 pagesNotes On Essential of ItDrRam Singh KambojNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarDocument5 pagesComputer Concepts and C Language: - Prof. Niranjan N.ChiplunkarGebBerheNo ratings yet
- 11 CSS Module Week 3Document23 pages11 CSS Module Week 3Alexander IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Computer Processing DevicesDocument21 pagesComputer Processing Devicesaluka porota75% (4)
- Unit 1Document6 pagesUnit 1Sonu zehen001No ratings yet
- COA Notes For MCA UNIT-1Document6 pagesCOA Notes For MCA UNIT-1rashmi.bharadwajNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer HardwareDocument73 pagesBasics of Computer HardwareBalaji Rao NNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Computers, Smartphones and the InternetFrom EverandUnderstanding Computers, Smartphones and the InternetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5 Steps To Create A Massive Vocal Mix (FREE GUIDE)Document5 pages5 Steps To Create A Massive Vocal Mix (FREE GUIDE)Dávid BaltaváriNo ratings yet
- Case Study Managing Station Design Changes 2Document5 pagesCase Study Managing Station Design Changes 2Bereket KahsayNo ratings yet
- Overview On PVSystDocument10 pagesOverview On PVSystpreeti kumari sahuNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 8djh36 enDocument68 pagesCatalogue 8djh36 enGhasem KheirollahNo ratings yet
- Qualitywings Bae146 Flight Management Computer TutorialDocument27 pagesQualitywings Bae146 Flight Management Computer TutorialDaniel De AviaciónNo ratings yet
- PUB - 3373 - Actuator Charger & Tester - Instruction Manual - Issue 5Document17 pagesPUB - 3373 - Actuator Charger & Tester - Instruction Manual - Issue 5ABDUL GHAFOORNo ratings yet
- GAC Connection Diagram PDFDocument1 pageGAC Connection Diagram PDFThomasRudyNo ratings yet
- Transworld TW100 HS SSB Transceiver - Condensed Operating Instructions (Laminated Card Front and Back)Document2 pagesTransworld TW100 HS SSB Transceiver - Condensed Operating Instructions (Laminated Card Front and Back)Alexander J Rokowetz100% (1)
- Encore Parts List and Exploded v6 020520Document4 pagesEncore Parts List and Exploded v6 020520Roberto Damian HernándezNo ratings yet
- Bri OktoberDocument3 pagesBri OktoberMobilkamu JakartaNo ratings yet
- Miguel Angel Ariza SalazarDocument3 pagesMiguel Angel Ariza SalazarGreen InkNo ratings yet
- KivyDocument871 pagesKivySerge OngoloNo ratings yet
- DVP Series Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Document3 pagesDVP Series Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCS)Sitaram TilekarNo ratings yet
- XCFR2.E60425 - Terminal Blocks - Component - UL Product IQDocument187 pagesXCFR2.E60425 - Terminal Blocks - Component - UL Product IQRahul Kumar Singh (IPR and Product Safety Compliance)No ratings yet
- L05 Topic1C Multimedia Element VideoDocument33 pagesL05 Topic1C Multimedia Element VideoRAYCHEAL VERONICA TONGNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document52 pagesLecture 26Cu BomNo ratings yet
- Sep 2010Document572 pagesSep 2010Shailesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Woofer - Wikipedia, The Fre..Document5 pagesWoofer - Wikipedia, The Fre..santamilNo ratings yet
- CETS HIGHVOLT Water TerminationsystemDocument4 pagesCETS HIGHVOLT Water TerminationsystemkmiqdNo ratings yet
- Cava PDFDocument2 pagesCava PDFSrideviNo ratings yet
- List of Students Who Applied For NCCDocument28 pagesList of Students Who Applied For NCCgurjot1234567890No ratings yet
- Written InterviewDocument4 pagesWritten Interviewcq8kd9rqh2No ratings yet
- BRKRST 2559Document85 pagesBRKRST 2559ritikaNo ratings yet
- Hyundair290lc 7crawlerexcavatorservicerepairfactorymanualinstantdownload 130422122642 Phpapp02Document7 pagesHyundair290lc 7crawlerexcavatorservicerepairfactorymanualinstantdownload 130422122642 Phpapp02codeyNo ratings yet
- NHPCDocument61 pagesNHPCSatyendra N Yadaw100% (2)
- MHYDocument24 pagesMHYhizbi7No ratings yet
- Working With Power Queries Using Blue PrismDocument11 pagesWorking With Power Queries Using Blue Prismemail2mesuryaNo ratings yet