Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force
Force
Uploaded by
Wasiue Ahmed AbbasiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Force
Force
Uploaded by
Wasiue Ahmed AbbasiCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
Lecture no 2.
Force
COMPILED BY:
E NGR. MU HA MMA D A LI MORIYA NI
B.E (CIVIL E NGINEERING, MUET)
WHAT IS A FORCE?
Simple Definition: A force is a push or pull upon an object
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 1
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
PUSH
Pull
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 2
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
But the concept of Force is not as simple!
Let me know that do you think of any force ?
If a ball is Lying stationary on the ground ?
But the concept of Force is not as simple!
Let me know that do you think of any force ?
If a ball is Lying stationary on the ground ?
Normal Force(Reaction Force)
Weight due to gravitational Force
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 3
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
This means that it is not necessary if there is
no motion that there is no force !!
There has to be a net force or unbalanced
force for a object to move !!
Lets take this example
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 4
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
So again
Air Resistance
Lets take a frictionless surface and no air
resistance (Ideal case)
Normal Force(Reaction Force)
Weight due to gravitational Force
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 5
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
Let’s see this case
WHAT IS A FORCE?
Formal Definition: A Force can also be defined as an agent which
produces or tends to produce, destroys or tends to destroy
motion in an object.
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 6
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
CHARACTERISTICS OF A FORCE
1. Magnitude of the force
◦ (i.e., 100 N, 20 kN, 3 kips, etc.)
2. The direction of the line, along which the force acts
◦ (i.e., along OX, OY, at 30° North of East etc.)
3. Nature of the force
◦ (i.e., whether the force is push or pull)
4. The point of application of Force
◦ (i.e. the point at which (or through which) the force acts on the body)
CHARACTERISTICS OF A FORCE
Direction
60O
Point of
F = 20 N
Application
Magnitude
Push
Force
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 7
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
Effects of Forces
A force may produce the following effects in a body, on which it acts :
1. It may change the motion of a body. i.e. if a body is at rest, the force may set it
in motion.
And if the body is already in motion, the force may accelerate it.(Change the
motion)
2. It may retard the motion of a body.(Change the motion)
3. It may retard the forces, already acting on a body, thus bringing it to rest or in
equilibrium.
4. Change the direction of motion
5. It may give rise to the internal stresses in the body, on which it acts.
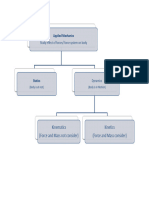
SYSTEM OF FORCES
When two or more forces act on a body, they are called to form a
system of forces
◦ Coplanar forces. The forces, whose lines of action lie on the same
plane, are known as coplanar forces.
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 8
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
SYSTEM OF FORCES
When two or more forces act on a body, they are called to form a
system of forces
◦ Collinear forces. The forces, whose lines of action lie on the
same line, are known as collinear forces.
SYSTEM OF FORCES
When two or more forces act on a body, they are called to form a
system of forces
◦ Concurrent forces. The forces, which meet at one point, are
known as concurrent forces. The concurrent forces may or may
not be collinear.
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 9
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
SYSTEM OF FORCES
◦ Coplanar concurrent forces. The forces, which meet at one point
and their lines of action also lie on the same plane, are known as
coplanar concurrent forces.
◦ Coplanar non-concurrent forces. The forces, which do not meet at
one point, but their lines of action lie on the same plane, are known
as coplanar non-concurrent forces.
◦ Non-coplanar concurrent forces. The forces, which meet at one
point, but their lines of action do not lie on the same plane, are
known as non-coplanar concurrent forces.
◦ Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces. The forces, which do not
meet at one point and their lines of action do not lie on the same
plane, are called non-coplanar non-concurrent forces.
Lets do an exercise
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 10
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
The solution !
Home assignment
1. Read page number 13, 14 and 15 of R.S Khurmi.
2. Find the practical examples of different system of forces.
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 11
Lecture notes of Applied Mechanics (CE-141) for 18-EL
Do it now;
because tomorrow will never come
Thank you !!
Compiled by: Engr. Muhammad Ali Moriyani 12
You might also like
- 2020 WTS 12 Work, Energy & PowerDocument22 pages2020 WTS 12 Work, Energy & PowerThabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Codes & Standards ListDocument27 pagesElectrical Codes & Standards ListKamalesh SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Unit-1Document35 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit-1M.suresh SureshNo ratings yet
- Engg MechanicsDocument20 pagesEngg MechanicsMamidi Pavan KishoreNo ratings yet
- Malawi University of Science and Technology (Must) : UNIT-1: Force SystemsDocument27 pagesMalawi University of Science and Technology (Must) : UNIT-1: Force SystemsChristella MacumiNo ratings yet
- 1st DraftDocument50 pages1st DraftDEVARAMANE DATTATREYANo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Introduction To Force SystemsDocument42 pagesUNIT 1 - Introduction To Force SystemsRK ShettyNo ratings yet
- 2.1lecture 2 (Force System)Document38 pages2.1lecture 2 (Force System)JIGME TENZINNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 FMEDocument59 pagesUnit-1 FMEAshish KhariNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture 2Document39 pages2.lecture 2JIGME TENZINNo ratings yet
- Emweek1class324 4 21Document13 pagesEmweek1class324 4 21Rakesh ThurpatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document18 pagesLecture 1Adame, Shira Marie - BerondoNo ratings yet
- SOM - English (2 & 3 Marks)Document25 pagesSOM - English (2 & 3 Marks)Kal Pathippagam75% (4)
- Unit 1Document89 pagesUnit 1gourav gargNo ratings yet
- Statics 101Document4 pagesStatics 101Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Conten T: Unit I:En Neerin Mechanics.......................................................................Document38 pagesConten T: Unit I:En Neerin Mechanics.......................................................................Mir Mustafa AliNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr.A.Vinoth JebarajDocument66 pagesPrepared by Dr.A.Vinoth JebarajMEGHA JAINNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document28 pagesUnit 1supraskyline2003No ratings yet
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1Document34 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS Module 1rout79858No ratings yet
- 2 Marks QA MOMDocument11 pages2 Marks QA MOMvasanthNo ratings yet
- Force Composition-2Document14 pagesForce Composition-2Aleksandra FerrabyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - LES #1 Force SystemDocument13 pagesMODULE 1 - LES #1 Force SystemJake BarettoNo ratings yet
- Tos 1: Unit 1 Forces: Equilibrium of Concurrent and Non-Concurrent ForcesDocument21 pagesTos 1: Unit 1 Forces: Equilibrium of Concurrent and Non-Concurrent Forcesbishal das50% (2)
- 2.2 - Mechanics (EN)Document90 pages2.2 - Mechanics (EN)André Luiz BragaNo ratings yet
- Lamis Theorem 6Document13 pagesLamis Theorem 6Sudhanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 UNIT-2 Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument44 pagesMODULE 1 UNIT-2 Introduction To Engineering MechanicsMANOJKUMAR MNo ratings yet
- 2 A-Lamis THMDocument2 pages2 A-Lamis THMsagarNo ratings yet
- Es11 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: Prepared By: Engr. Ruth Ann D Maningding 1Document16 pagesEs11 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: Prepared By: Engr. Ruth Ann D Maningding 1John Philip ParasNo ratings yet
- Theoryofstructures Ib 180903021950Document36 pagesTheoryofstructures Ib 180903021950Lance NabongNo ratings yet
- Theory of SpainDocument12 pagesTheory of SpainmarcosmsaroNo ratings yet
- 12-Engineering Mecahnics - Prof. AasimDocument45 pages12-Engineering Mecahnics - Prof. AasimYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Engg - Mechanics 2nd SemDocument97 pagesEngg - Mechanics 2nd Semmannatdhibar7No ratings yet
- MECHANICS OF DEFORMABLE BODIESDocument2 pagesMECHANICS OF DEFORMABLE BODIESJennie EmataNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - Girls Physics Solve ItDocument17 pagesCH 1 - Girls Physics Solve ItPdkNo ratings yet
- APM NotesDocument46 pagesAPM Notesvlavate79No ratings yet
- CE 1101 - Introduction and Equilibrium SystemDocument31 pagesCE 1101 - Introduction and Equilibrium SystemnayeemislammeghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 - Introduction To Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pagesLecture Notes 2 - Introduction To Statics of Rigid BodiesMark Recar AntequisaNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 1 Unit 1 (Principles of Statics)Document14 pagesMech 1 Module 1 Unit 1 (Principles of Statics)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Friction AutoDocument24 pagesFriction AutoSayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument1 pageTheoryDevansh VaidyaNo ratings yet
- GE6253 Engineering Mechanics 2 Mark With Answers R2013Document16 pagesGE6253 Engineering Mechanics 2 Mark With Answers R2013sivakumarNo ratings yet
- Composition of ForceDocument14 pagesComposition of ForcePari GuptaNo ratings yet
- EM - Lecture Notes - Module-1Document41 pagesEM - Lecture Notes - Module-1elinNo ratings yet
- Answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Document1 pageAnswer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Javin CaluyaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion-1Document4 pagesLaws of Motion-1prachi98601No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument11 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Mechanics of Deformable BodiesKobeNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Lab1Document7 pagesMechanics Lab1yogendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Ge6253: Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesGe6253: Engineering MechanicsMDR PRAPHUNo ratings yet
- Engineering-Mechanics Notes-8Document1 pageEngineering-Mechanics Notes-8Marius Ionut DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Dynamics of MachineryDocument35 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Dynamics of Machinerypraveen ajithNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force AnalysisDocument101 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force Analysissuneel kumar rathoreNo ratings yet
- Domunitinotes 180418054128 PDFDocument101 pagesDomunitinotes 180418054128 PDFsuneel kumar rathoreNo ratings yet
- Wave & OscillationDocument44 pagesWave & OscillationreduanulalamhridoyNo ratings yet
- Ge8292: Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesGe8292: Engineering MechanicsPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Course Code: DME-205Document16 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Course Code: DME-205HaradipMahilaryNo ratings yet
- Am 3Document18 pagesAm 3citowop670No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsDocument116 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsMiral_Kagathra100% (2)
- Engineering Mechanics - Chapter 2Document45 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Chapter 2Kishan PurohitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MechanicsDocument31 pagesModule 1 - MechanicsAsha AsokNo ratings yet
- Also Refer Last Year Question Papers in Stucor AppDocument10 pagesAlso Refer Last Year Question Papers in Stucor AppRaagul SNo ratings yet
- Quincke's ManualDocument13 pagesQuincke's ManualkrishnakumargmaliyilNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics ProblemsDocument8 pagesAerodynamics ProblemsPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- Carrier 42N TDB UnlockedDocument32 pagesCarrier 42N TDB UnlockedSvetla NikolovaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics (QB)Document21 pagesKinematics (QB)Toshi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Extra Materials Carnot EngineDocument21 pagesExtra Materials Carnot Enginetruffelove100% (1)
- 4029INSTRUMENTTRANSFORMERSDocument95 pages4029INSTRUMENTTRANSFORMERSmuaz_aminu1422100% (2)
- 09VORDocument12 pages09VORJosé MartinezNo ratings yet
- 5054 w11 QP 11Document20 pages5054 w11 QP 11mstudy123456No ratings yet
- RM10 12 15Document66 pagesRM10 12 15rodolfo moralesNo ratings yet
- Keystone - EPR Rubber CableDocument4 pagesKeystone - EPR Rubber CablekanarendranNo ratings yet
- Clasifica SaeDocument1,218 pagesClasifica SaeAlan G. GomezNo ratings yet
- Online Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDocument8 pagesOnline Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Electromagnetics by Matthew N.O. Sadiku 3rd Edition 5.1 Is Solution BookDocument27 pagesElements of Electromagnetics by Matthew N.O. Sadiku 3rd Edition 5.1 Is Solution BookMoon SkyNo ratings yet
- Dryer Selection and DesignDocument43 pagesDryer Selection and DesignMuluken DeaNo ratings yet
- SVC STATCOM Wind FirmDocument8 pagesSVC STATCOM Wind FirmFAIYAJ limonNo ratings yet
- Assignment (13th) WADocument11 pagesAssignment (13th) WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Hve ProjectDocument9 pagesHve ProjectramNo ratings yet
- Formelsamling TermodynamikDocument3 pagesFormelsamling TermodynamikConstantin AlexeNo ratings yet
- GMDSS Batteries Tests and Checks Mariners Must KnowDocument9 pagesGMDSS Batteries Tests and Checks Mariners Must KnowKunal Singh100% (2)
- Frenkel D. - Notes On Statistical Thermodynamics (2001)Document64 pagesFrenkel D. - Notes On Statistical Thermodynamics (2001)dhiraj.biswasNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic String Sizing Using Site-Specific ModelingDocument10 pagesPhotovoltaic String Sizing Using Site-Specific ModelingjackthonetNo ratings yet
- Indicator Cpi Vi - 3p - R EngDocument4 pagesIndicator Cpi Vi - 3p - R EngonatipakNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 1.1 Properties of Fluids: Problem 1Document4 pagesFormative Assessment 1.1 Properties of Fluids: Problem 1subyNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - AS - Unit1 - Quantum - 02 - Photoelectric - Effect - Questions SimiDocument2 pagesBenjamin Watson - AS - Unit1 - Quantum - 02 - Photoelectric - Effect - Questions SimiboobooNo ratings yet
- ITP EL - Gas EngineDocument19 pagesITP EL - Gas EngineRhadityo Shakti BudimanNo ratings yet
- WL005 - WL10: Silicon Bridge Rectifiers WOBDocument3 pagesWL005 - WL10: Silicon Bridge Rectifiers WOBtarpinoNo ratings yet
- Survey Formates ExcelDocument44 pagesSurvey Formates ExcelDANISH YASIN 064No ratings yet
- Mindanao Grid Loepp-08312022Document4 pagesMindanao Grid Loepp-08312022KianNo ratings yet