Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsOld Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Old Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Uploaded by
Khayzee AsesorInternal energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of atoms and molecules in a substance. Energy changes occur during chemical and physical processes and can be released or absorbed. There are different forms of energy including potential, kinetic, heat, and work. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can change forms but not be created or destroyed. Chemical processes involve substances changing, while physical processes do not change chemical composition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering) John Charles Slattery-Advanced Transport Phenomena-Cambridge University Press (1999) PDFDocument733 pages(Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering) John Charles Slattery-Advanced Transport Phenomena-Cambridge University Press (1999) PDFWY100% (2)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Materials Science & Engineering What Is Materials Science & Engineering?Document6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Materials Science & Engineering What Is Materials Science & Engineering?AruzhanNo ratings yet
- Physical Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Biochemistry Lecture Noteschc300No ratings yet
- Dela Torre Vs CA DocsDocument5 pagesDela Torre Vs CA DocsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicsMuhammed Muhasin. KNo ratings yet
- Nyetang P6Document7 pagesNyetang P6Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- 06 Thermochemistry EditDocument11 pages06 Thermochemistry EditYodaNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument52 pagesThermochemistryBiddut DasNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicsNitin BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Thermodynamics 1st LawDocument40 pagesChem 2 Thermodynamics 1st LawMaria RoelaJane A. CabisadaNo ratings yet
- Energy - CHEM 106Document29 pagesEnergy - CHEM 106Eunice MaeNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Summary - Libre TextsDocument4 pagesThermochemistry Summary - Libre Textsmacky 2No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 2 Chem131Document13 pagesLesson 1 2 Chem131Yessenia MontillaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Topic 2 (Reviewer)Document3 pagesChem Lab Topic 2 (Reviewer)Erianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- ثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Document35 pagesثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Al-Hassan NeimaNo ratings yet
- Heat Thermodynamics SlidesDocument19 pagesHeat Thermodynamics SlidesMd. Ibrahim Sani 2211043642No ratings yet
- C1 ThermochemistryDocument39 pagesC1 ThermochemistryaliesyaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsTshering TobdenNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry LectureDocument62 pagesThermochemistry LectureSiiveh DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2015Document27 pagesThermo 2015misganamarcos10No ratings yet
- Thermochemistry - Chapter 6Document45 pagesThermochemistry - Chapter 6Gokul MukundaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Nature of EnergyDocument5 pagesThermochemistry: Nature of EnergyChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- First Law Thermo PDFDocument45 pagesFirst Law Thermo PDFIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument38 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument26 pagesUnit II - Chemical ThermodynamicshvacsriniNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsajayyashpalNo ratings yet
- Which Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesWhich Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsSahada KanapiyaNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#4Document13 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#4maqsood3982No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics B Tech NotesDocument38 pagesThermodynamics B Tech NotesRajdeep ShawNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsManish SainiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledapi-233404189100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Cheat Notes (4th Semester) PDFDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Cheat Notes (4th Semester) PDFTalha AhsanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chemistry Chapter 6Document11 pagesThermodynamics Chemistry Chapter 6ajinkyarsingh2006No ratings yet
- Physics Topic 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPhysics Topic 3 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument32 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsRon allen ConconNo ratings yet
- Important Terms and DefinitionsDocument14 pagesImportant Terms and DefinitionsjustrandompersonshitNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 FinalsDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 FinalsSUASE GEMMALYNNo ratings yet
- TermokimiaDocument81 pagesTermokimiakeziaNo ratings yet
- ThermoChemistryDocument28 pagesThermoChemistryJOSHUA NYANGENANo ratings yet
- Energy & ChemistryDocument66 pagesEnergy & ChemistryAminNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Large Scale Response Kinetic Theory Thermodynamics, HeatDocument30 pagesThermodynamics: Large Scale Response Kinetic Theory Thermodynamics, HeatKritika KapoorNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryDocument58 pages03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryAko si GianNo ratings yet
- CO3 ThermodynamicsDocument72 pagesCO3 ThermodynamicsRonna IturaldeNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry CollegeDocument115 pagesThermochemistry CollegeBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- By Rachel & AmitDocument23 pagesBy Rachel & AmitAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesBasic Concept of Thermodynamicspanwarvinod22222No ratings yet
- CTD I PDFDocument10 pagesCTD I PDFarulrakkNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuestionsAntonioNo ratings yet
- Document of Che Chapter 6 NotesDocument10 pagesDocument of Che Chapter 6 NotesEstheruNo ratings yet
- CHEM20024 Lecture Notes 07 (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)Document27 pagesCHEM20024 Lecture Notes 07 (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)Lorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- Thermo - First SecondLawDocument35 pagesThermo - First SecondLawLiaquat NajmiNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument28 pagesThermochemistryMuhammad Nazif AzmiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ChapterDocument21 pagesChemistry ChapterappugmenonNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Chemistry FuelDocument11 pagesLESSON 3 Chemistry Fuelsimonjohn spanglerNo ratings yet
- L10 ThermodynamicsDocument39 pagesL10 ThermodynamicsfaresNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Activity SheetDocument15 pagesEnthalpy Activity SheetPrincess Fenix Sabio100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesThermodynamicsTejas SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Document24 pagesThermodynamics: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Vaibhav bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 1Document12 pagesThermodynamics Module 1Kirtan KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainDocument67 pagesThermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainfitriNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument19 pagesNoteslopa39018No ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- MemorandumDocument1 pageMemorandumKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Common Provisions of Pledge and MortDocument18 pagesCommon Provisions of Pledge and MortKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Section 5: An Order or Promise To Do Any ActDocument4 pagesSection 1 Section 5: An Order or Promise To Do Any ActKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Pan Pacific Vs EquitableDocument14 pagesPan Pacific Vs EquitableKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- PNB V. Ca, Ibarrola: As Payments For The Purchase of MedicinesDocument5 pagesPNB V. Ca, Ibarrola: As Payments For The Purchase of MedicinesKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Medel VS CaDocument9 pagesMedel VS CaKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Estate of Hemady VS Luzon SuretyDocument2 pagesEstate of Hemady VS Luzon SuretyKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- De Los Santos Vs Jarra: FactsDocument4 pagesDe Los Santos Vs Jarra: FactsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Stare DecisisDocument2 pagesStare DecisisKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Cases 31-40Document9 pagesCases 31-40Khayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Raw DigestsDocument6 pagesRaw DigestsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- AFLOW-QHA3P: Robust and Automated Method To Compute Thermodynamic Properties of SolidsDocument15 pagesAFLOW-QHA3P: Robust and Automated Method To Compute Thermodynamic Properties of SolidsadityamduttaNo ratings yet
- Routine Test Certificate: Purchaser's Name: Sale Order NoDocument2 pagesRoutine Test Certificate: Purchaser's Name: Sale Order NoPerumal PalaniNo ratings yet
- Lecithin As An EmulsifierDocument4 pagesLecithin As An EmulsifierAndrels7No ratings yet
- Balluff BES 516-325-S4-C BES01C8Document2 pagesBalluff BES 516-325-S4-C BES01C8celsocarneiroNo ratings yet
- Flexural Behavior of Composite BeamDocument4 pagesFlexural Behavior of Composite Beamasubhash11No ratings yet
- Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide DispersionsDocument34 pagesDielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersionszoex924No ratings yet
- Aluminium - Iron - SiliconDocument51 pagesAluminium - Iron - SiliconAnonymous HzbpFGY80No ratings yet
- Shineon Technical Description EnglishDocument19 pagesShineon Technical Description EnglishsrowbothamNo ratings yet
- Schering Bridge 09022020Document5 pagesSchering Bridge 09022020Cheem CoderNo ratings yet
- AET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SDocument5 pagesAET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- dESIGN OF D REGIONS STRUT AND TIE PDFDocument54 pagesdESIGN OF D REGIONS STRUT AND TIE PDFconsultor9010No ratings yet
- WewwDocument40 pagesWewwManoj Paul JohnNo ratings yet
- Capacitors JEE 2024Document100 pagesCapacitors JEE 2024Biden bhaiNo ratings yet
- Diploma Sittr 21 Revision Syllabus Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesDiploma Sittr 21 Revision Syllabus Strength of MaterialsYaduthilak YktNo ratings yet
- Properties:: Aniline FormaldehydeDocument3 pagesProperties:: Aniline FormaldehydeChaudhry BrothersNo ratings yet
- Split Tensile Strength of Brick MasonryDocument8 pagesSplit Tensile Strength of Brick Masonrymanish_shashikantNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Document12 pagesElectrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Ant Live100% (1)
- Information On PHD Qualification 2017 2018 SpringDocument3 pagesInformation On PHD Qualification 2017 2018 SpringErhan KapiciNo ratings yet
- Neuberovo Pravilo PDFDocument21 pagesNeuberovo Pravilo PDFMark JurichNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis and DesignDocument35 pagesFinite Element Analysis and Designchesspalace2100% (1)
- Sensors and Actuators A: PhysicalDocument10 pagesSensors and Actuators A: PhysicalBobby IgnatichNo ratings yet
- A Design Methodology of Resonant LLC DC-DC ConverterDocument10 pagesA Design Methodology of Resonant LLC DC-DC ConverterArsalan AtharNo ratings yet
- Compressive PropertiesDocument3 pagesCompressive PropertiesSh.nasirpurNo ratings yet
- PP - Braskem - CP 442 XP PDFDocument1 pagePP - Braskem - CP 442 XP PDFAdemilson Alves Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Die Attach Materials For High Temperature Applications - A ReviewDocument22 pagesDie Attach Materials For High Temperature Applications - A ReviewHanLe DuyNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Advanced Welding Kme055 2021Document2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Advanced Welding Kme055 2021Wizard ToxicNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Modeling of Ablation and Pyrolysis With Application To Rocket NozzlesDocument13 pagesTwo-Dimensional Modeling of Ablation and Pyrolysis With Application To Rocket NozzlesKamil El HanefiNo ratings yet
- CRCA Steel - Check Full Form, Meaning, FeaturesDocument5 pagesCRCA Steel - Check Full Form, Meaning, FeaturesSilambarasan KNo ratings yet
Old Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Old Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Uploaded by
Khayzee Asesor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesInternal energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of atoms and molecules in a substance. Energy changes occur during chemical and physical processes and can be released or absorbed. There are different forms of energy including potential, kinetic, heat, and work. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can change forms but not be created or destroyed. Chemical processes involve substances changing, while physical processes do not change chemical composition.
Original Description:
chem
Original Title
CHM035
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInternal energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of atoms and molecules in a substance. Energy changes occur during chemical and physical processes and can be released or absorbed. There are different forms of energy including potential, kinetic, heat, and work. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can change forms but not be created or destroyed. Chemical processes involve substances changing, while physical processes do not change chemical composition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesOld Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Old Units Cancel Out and Only The New Unit Will Remain
Uploaded by
Khayzee AsesorInternal energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of atoms and molecules in a substance. Energy changes occur during chemical and physical processes and can be released or absorbed. There are different forms of energy including potential, kinetic, heat, and work. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can change forms but not be created or destroyed. Chemical processes involve substances changing, while physical processes do not change chemical composition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CHM035 Internal energy (U) – the combined kinetic and
Conversion of Units potential energies of the atoms and molecules.
1. List down the given data and the required - Energy associated with the random,
quantity. disordered motion of molecules and with the
2. Find the appropriate conversion factors forces the molecules exert on each other
3. Write the unit multiplier in such a way that
old units cancel out and only the new unit will Energy changes during chemical reactions
remain. o The making or breaking of chemical bonds
4. Multiply the unit multiplier to the given changes the potential energy of the system
quantity and solve o If the amount of energy liberated in bond
5. If successive conversions are done, write the making is greater than that consumed in
unit multipliers in such a way that only the bond breaking, the overall process releases
required unit remains. chemical energy
Stoichiometry Calculations I Energy transfer: Heat
Molar mass (molecular weight) – the mass in grams Heat – the flow of energy between two objects, from
of one mole of a substance. the warmer one to the cooler one, because of a
Limiting reactant – the reactant that is used up difference in their temperatures
completely
o Stoichiometry computation must be based Energy transfer: Work
on the amount of limiting reactant Work – the transfer of energy accomplished by a
Excess reactant – reactant that is not used up force moving a mass some distance against
completely resistance
𝑊 = −𝑃∆𝑉
Heat in Physical Processes o A gas compresses when its pressure is less
Chemical properties – exhibited by matter as it than the surrounding pressure
undergoes changes in composition 𝑃𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑟 > 𝑃𝑠𝑦𝑠
o Ex. A chemical property of propane is that it Compression continues until the
combines with dioxygen, releasing energy in system and surrounding have equal
the process pressures (equilibrium)
Physical properties – observed in the absence of any Work is being done by the
change in composition atmosphere on the gas to compress it
o Ex. Color, density, hardness, melting point,
boiling point, and electrical and thermal o A gas expands when the pressure of the gas
conductivities is greater than the surroundings. It expands
Chemical Processes – involve one or more until it reaches equilibrium
substances getting used up (at least partially), and 𝑃𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑟 > 𝑃𝑠𝑦𝑠
one or more new substances are formed. Work is being done by the gas to push
Physical processes – occur with no change in against the pressure exerted by the
chemical composition; usually altered significantly as atmosphere.
matter undergoes physical changes
Temperature
Energy and Processes - Related to the average kinetic energy of the
o physical changes like changes in color etc., particles in a substance
can usually signify a chemical change - The higher the temperature, the faster the
o chemical and physical processes are usually movement of the particles
accompanied by energy changes - The lesser the temperature, the slower the
o energy may be either released (evolved) or movement of the particles
absorbed in a process
o burning fuels release a tremendous amount Law of Conservation of Energy
of energy o Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
o burning water to produce gaseous steam Energy is always changing from one kind to
requires the input of energy another.
o The total internal energy of the object never
Forms of Energy changes.
Potential energy (P) – associated with the relative ∆𝑈 = 𝑞 + 𝑤 = 𝑞 − 𝑝∆𝑉
position of an object ∆𝑈 = 𝑈𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 − 𝑈𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙
Kinetic energy (K) – associated with motion
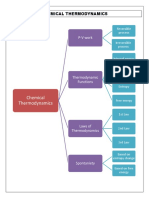
Definitions and sign conventions Comparing the internal energies of solid, liquid
System – part of the universe being studied and gases
o Energy, either in the form of heat or work,
being added to the system raises its INSERT PHOTO ABOUT IT
temperature, and vice versa
o Work being done on the system adds to the Processes at Constant Pressure
energy of the system. (+W) o It is more convenient to express the energy
o Work done by the system reduces the energy of the system associated with processes
of the system. (-W) carried out at constant pressure using a
different quantity than internal energy
Processes at constant volume called enthalpy.
o When a process is carried out at constant
volume, volume does not change. Enthalpy
Thus, ∆𝑉 = 0. Therefore, ∆𝐻 = ∆𝑈 + 𝑝∆𝑉
∆𝑈 = 𝑞 − 𝑝∆𝑉 = 𝑞𝑣 ∆𝐻 = (𝑞 − 𝑝∆𝑉) + 𝑝∆𝑉
∆𝐻 = 𝑞𝑝
Heating without change of phase: Heat Capacity ∆𝐻 = 𝐻𝑓𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 − 𝐻𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙
Specific heat – physical property of a material that
measures how much heat is required to raise the Exothermic and Endothermic Processes
temperature of one gram of that material by 1C. Exothermic process – heat evolves from the system
𝑞 = 𝑚𝑐∆𝑇 and the value of ∆𝐻 is less than zero
Molar heat capacity – physical property that Endothermic process – heat is absorbed by the
describes how much heat is required to raise the system and the value of ∆𝐻 is greater than zero.
temperature of one mole of a substance by 1C.
𝑞 = 𝑛𝐶𝑝 ∆𝑇 Heats of Formation
*subscript p indicates that this heat capacity is a Formation reaction – chemical reaction by which
constant pressure* one mole of a compound
Phase Changes
o The addition or removal of heat to a
substance may cause it to change its phase
o Temperature does not change during phase
changes
o Water vaporizes into steam at 100C.
INSERT PIC ABOUT PHASE CHANGE
Heating with change of phase: Latent Heats
Latent heat of Vaporization (Lv) – represents the
amount of heat for 1g of liquid at the boiling point
(100C) to turn into vapor (J/g)
- Liquid is vaporized = positive; vapor is
condensed = negative
𝑄𝑣 = 𝑚𝐿𝑣
Latent heat of Fusion (Lf) – represents the amount of
heat for 1g of liquid at the melting point (0C) to turn
into solid (J/g)
- Solid is melting = positive; liquid is freezing
= negative
𝑄𝑓 = 𝑚𝐿𝑓
Calorimetry
o When heat flow occurs between two bodies
that are isolated from their surroundings,
the amount of heat lost must by one body must
equal to the amount gained by the other.
−𝑞𝑐𝑜𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛 = 𝑞ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑢𝑝
You might also like
- (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering) John Charles Slattery-Advanced Transport Phenomena-Cambridge University Press (1999) PDFDocument733 pages(Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering) John Charles Slattery-Advanced Transport Phenomena-Cambridge University Press (1999) PDFWY100% (2)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Materials Science & Engineering What Is Materials Science & Engineering?Document6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Materials Science & Engineering What Is Materials Science & Engineering?AruzhanNo ratings yet
- Physical Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Biochemistry Lecture Noteschc300No ratings yet
- Dela Torre Vs CA DocsDocument5 pagesDela Torre Vs CA DocsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicsMuhammed Muhasin. KNo ratings yet
- Nyetang P6Document7 pagesNyetang P6Charles Daniel Torre MalolesNo ratings yet
- 06 Thermochemistry EditDocument11 pages06 Thermochemistry EditYodaNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument52 pagesThermochemistryBiddut DasNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThermodynamicsNitin BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Thermodynamics 1st LawDocument40 pagesChem 2 Thermodynamics 1st LawMaria RoelaJane A. CabisadaNo ratings yet
- Energy - CHEM 106Document29 pagesEnergy - CHEM 106Eunice MaeNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Summary - Libre TextsDocument4 pagesThermochemistry Summary - Libre Textsmacky 2No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 2 Chem131Document13 pagesLesson 1 2 Chem131Yessenia MontillaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Topic 2 (Reviewer)Document3 pagesChem Lab Topic 2 (Reviewer)Erianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- ثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Document35 pagesثرمو محاضرة 1 مرحلة 3Al-Hassan NeimaNo ratings yet
- Heat Thermodynamics SlidesDocument19 pagesHeat Thermodynamics SlidesMd. Ibrahim Sani 2211043642No ratings yet
- C1 ThermochemistryDocument39 pagesC1 ThermochemistryaliesyaNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsTshering TobdenNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry LectureDocument62 pagesThermochemistry LectureSiiveh DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2015Document27 pagesThermo 2015misganamarcos10No ratings yet
- Thermochemistry - Chapter 6Document45 pagesThermochemistry - Chapter 6Gokul MukundaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Nature of EnergyDocument5 pagesThermochemistry: Nature of EnergyChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- First Law Thermo PDFDocument45 pagesFirst Law Thermo PDFIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument38 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument26 pagesUnit II - Chemical ThermodynamicshvacsriniNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsajayyashpalNo ratings yet
- Which Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument19 pagesWhich Area of Chemistry Is Concerned With The Topic?: THERMOCHEMISTRY: Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsSahada KanapiyaNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#4Document13 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#4maqsood3982No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics B Tech NotesDocument38 pagesThermodynamics B Tech NotesRajdeep ShawNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesRevision Notes On Chemical ThermodynamicsManish SainiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledapi-233404189100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Cheat Notes (4th Semester) PDFDocument7 pagesThermodynamics Cheat Notes (4th Semester) PDFTalha AhsanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chemistry Chapter 6Document11 pagesThermodynamics Chemistry Chapter 6ajinkyarsingh2006No ratings yet
- Physics Topic 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPhysics Topic 3 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument32 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsRon allen ConconNo ratings yet
- Important Terms and DefinitionsDocument14 pagesImportant Terms and DefinitionsjustrandompersonshitNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 FinalsDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 FinalsSUASE GEMMALYNNo ratings yet
- TermokimiaDocument81 pagesTermokimiakeziaNo ratings yet
- ThermoChemistryDocument28 pagesThermoChemistryJOSHUA NYANGENANo ratings yet
- Energy & ChemistryDocument66 pagesEnergy & ChemistryAminNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Large Scale Response Kinetic Theory Thermodynamics, HeatDocument30 pagesThermodynamics: Large Scale Response Kinetic Theory Thermodynamics, HeatKritika KapoorNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryDocument58 pages03 Chapter 2 Part 2 ThermochemistryAko si GianNo ratings yet
- CO3 ThermodynamicsDocument72 pagesCO3 ThermodynamicsRonna IturaldeNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry CollegeDocument115 pagesThermochemistry CollegeBlanche Iris Estrel SiapnoNo ratings yet
- By Rachel & AmitDocument23 pagesBy Rachel & AmitAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesBasic Concept of Thermodynamicspanwarvinod22222No ratings yet
- CTD I PDFDocument10 pagesCTD I PDFarulrakkNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuestionsAntonioNo ratings yet
- Document of Che Chapter 6 NotesDocument10 pagesDocument of Che Chapter 6 NotesEstheruNo ratings yet
- CHEM20024 Lecture Notes 07 (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)Document27 pagesCHEM20024 Lecture Notes 07 (Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics)Lorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- Thermo - First SecondLawDocument35 pagesThermo - First SecondLawLiaquat NajmiNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument28 pagesThermochemistryMuhammad Nazif AzmiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ChapterDocument21 pagesChemistry ChapterappugmenonNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Chemistry FuelDocument11 pagesLESSON 3 Chemistry Fuelsimonjohn spanglerNo ratings yet
- L10 ThermodynamicsDocument39 pagesL10 ThermodynamicsfaresNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Activity SheetDocument15 pagesEnthalpy Activity SheetPrincess Fenix Sabio100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesThermodynamicsTejas SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Document24 pagesThermodynamics: Ashwani Tyagi Sir (Code: ATJEE)Vaibhav bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 1Document12 pagesThermodynamics Module 1Kirtan KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainDocument67 pagesThermodynamics: Specific Learning Objective at The End of The Session The Student Should Be Able To ExplainfitriNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument19 pagesNoteslopa39018No ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- MemorandumDocument1 pageMemorandumKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Common Provisions of Pledge and MortDocument18 pagesCommon Provisions of Pledge and MortKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Section 5: An Order or Promise To Do Any ActDocument4 pagesSection 1 Section 5: An Order or Promise To Do Any ActKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Pan Pacific Vs EquitableDocument14 pagesPan Pacific Vs EquitableKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- PNB V. Ca, Ibarrola: As Payments For The Purchase of MedicinesDocument5 pagesPNB V. Ca, Ibarrola: As Payments For The Purchase of MedicinesKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Medel VS CaDocument9 pagesMedel VS CaKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Estate of Hemady VS Luzon SuretyDocument2 pagesEstate of Hemady VS Luzon SuretyKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- De Los Santos Vs Jarra: FactsDocument4 pagesDe Los Santos Vs Jarra: FactsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Stare DecisisDocument2 pagesStare DecisisKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Cases 31-40Document9 pagesCases 31-40Khayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- Raw DigestsDocument6 pagesRaw DigestsKhayzee AsesorNo ratings yet
- AFLOW-QHA3P: Robust and Automated Method To Compute Thermodynamic Properties of SolidsDocument15 pagesAFLOW-QHA3P: Robust and Automated Method To Compute Thermodynamic Properties of SolidsadityamduttaNo ratings yet
- Routine Test Certificate: Purchaser's Name: Sale Order NoDocument2 pagesRoutine Test Certificate: Purchaser's Name: Sale Order NoPerumal PalaniNo ratings yet
- Lecithin As An EmulsifierDocument4 pagesLecithin As An EmulsifierAndrels7No ratings yet
- Balluff BES 516-325-S4-C BES01C8Document2 pagesBalluff BES 516-325-S4-C BES01C8celsocarneiroNo ratings yet
- Flexural Behavior of Composite BeamDocument4 pagesFlexural Behavior of Composite Beamasubhash11No ratings yet
- Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide DispersionsDocument34 pagesDielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersionszoex924No ratings yet
- Aluminium - Iron - SiliconDocument51 pagesAluminium - Iron - SiliconAnonymous HzbpFGY80No ratings yet
- Shineon Technical Description EnglishDocument19 pagesShineon Technical Description EnglishsrowbothamNo ratings yet
- Schering Bridge 09022020Document5 pagesSchering Bridge 09022020Cheem CoderNo ratings yet
- AET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SDocument5 pagesAET Question Bank For AUC R2013 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- dESIGN OF D REGIONS STRUT AND TIE PDFDocument54 pagesdESIGN OF D REGIONS STRUT AND TIE PDFconsultor9010No ratings yet
- WewwDocument40 pagesWewwManoj Paul JohnNo ratings yet
- Capacitors JEE 2024Document100 pagesCapacitors JEE 2024Biden bhaiNo ratings yet
- Diploma Sittr 21 Revision Syllabus Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesDiploma Sittr 21 Revision Syllabus Strength of MaterialsYaduthilak YktNo ratings yet
- Properties:: Aniline FormaldehydeDocument3 pagesProperties:: Aniline FormaldehydeChaudhry BrothersNo ratings yet
- Split Tensile Strength of Brick MasonryDocument8 pagesSplit Tensile Strength of Brick Masonrymanish_shashikantNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Document12 pagesElectrical Circuits and Internal Resistance (MCQ Only)Ant Live100% (1)
- Information On PHD Qualification 2017 2018 SpringDocument3 pagesInformation On PHD Qualification 2017 2018 SpringErhan KapiciNo ratings yet
- Neuberovo Pravilo PDFDocument21 pagesNeuberovo Pravilo PDFMark JurichNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis and DesignDocument35 pagesFinite Element Analysis and Designchesspalace2100% (1)
- Sensors and Actuators A: PhysicalDocument10 pagesSensors and Actuators A: PhysicalBobby IgnatichNo ratings yet
- A Design Methodology of Resonant LLC DC-DC ConverterDocument10 pagesA Design Methodology of Resonant LLC DC-DC ConverterArsalan AtharNo ratings yet
- Compressive PropertiesDocument3 pagesCompressive PropertiesSh.nasirpurNo ratings yet
- PP - Braskem - CP 442 XP PDFDocument1 pagePP - Braskem - CP 442 XP PDFAdemilson Alves Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Die Attach Materials For High Temperature Applications - A ReviewDocument22 pagesDie Attach Materials For High Temperature Applications - A ReviewHanLe DuyNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 5 Sem Advanced Welding Kme055 2021Document2 pagesBtech Me 5 Sem Advanced Welding Kme055 2021Wizard ToxicNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Modeling of Ablation and Pyrolysis With Application To Rocket NozzlesDocument13 pagesTwo-Dimensional Modeling of Ablation and Pyrolysis With Application To Rocket NozzlesKamil El HanefiNo ratings yet
- CRCA Steel - Check Full Form, Meaning, FeaturesDocument5 pagesCRCA Steel - Check Full Form, Meaning, FeaturesSilambarasan KNo ratings yet