Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radio Script Writing and Broadcasting
Radio Script Writing and Broadcasting
Uploaded by
Jehnn Benito0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
276 views2 pagesThis document provides guidance on writing scripts for radio broadcasting. It discusses different types of radio scripts, important considerations and formatting for script writing, and tips for structuring scripts. The key elements are:
1) There are different types of radio scripts including news, interviews, spots/plugs, drama, and documentaries.
2) When writing scripts, writers should double space, use clear formatting, keep sentences short, avoid difficult words, and attribute sources.
3) A well-structured radio script includes elements like a station ID, time check, news plug, intro, headlines, details, and outro.
Original Description:
RAdio Broadcasting script
Original Title
SCriPt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on writing scripts for radio broadcasting. It discusses different types of radio scripts, important considerations and formatting for script writing, and tips for structuring scripts. The key elements are:
1) There are different types of radio scripts including news, interviews, spots/plugs, drama, and documentaries.
2) When writing scripts, writers should double space, use clear formatting, keep sentences short, avoid difficult words, and attribute sources.
3) A well-structured radio script includes elements like a station ID, time check, news plug, intro, headlines, details, and outro.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
276 views2 pagesRadio Script Writing and Broadcasting
Radio Script Writing and Broadcasting
Uploaded by
Jehnn BenitoThis document provides guidance on writing scripts for radio broadcasting. It discusses different types of radio scripts, important considerations and formatting for script writing, and tips for structuring scripts. The key elements are:
1) There are different types of radio scripts including news, interviews, spots/plugs, drama, and documentaries.
2) When writing scripts, writers should double space, use clear formatting, keep sentences short, avoid difficult words, and attribute sources.
3) A well-structured radio script includes elements like a station ID, time check, news plug, intro, headlines, details, and outro.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Radio Script writing and Broadcasting
1. 1. -Mary Queen T. Bernardo-
2. 2. The Radio Script refers to the written material, which indicates the verbal and non-verbal
action that has to go into a radio program. It tells us what to do and say and when and how.
3. 3. • To ensure technical accuracy of information • To ensure continuity of program • To
maximize airtime
4. 4. 1. News Script 2. Interview Script 3. Spot/Plugs 4. Drama Script 5. Magazine Program
Script 6. The Documentary Script
5. 5. Things to Remember in Radio Scriptwriting • Double or triple space-typewrite all lines and
paragraphs. • Type copy in big letter so the newscaster can easily read it. • All spoken lines
should be typed in big and small letters. • All instructions and non-spoken lines should be
typed in big or capital letters.
6. 6. • Have a duplicate of each copy. • Make each sentence a paragraph. • Write a page
number on each script. • End each page with a paragraph before using another paper. •
Make your script clean. • Mark “x” for erroneous word.
7. 7. • Make the script short and simple. • Do not use words which are hard to pronounce. •
Don’t text-write. • Each sentence should not exceed 12 words. Break down long sentences
for easy readability. • Attribute the source of your story either at the beginning or at the end
of your news.
8. 8. Use short, ordinary conversation words Avoid “this, that, the former, the latter”
Avoid sibilants (words with hissing sounds) Use descriptive words when possible but use
them with care Do not string together a collection of ideas with “and”; sentences should be
kept short Other reminders
9. 9. keep subject and verb close together and use active rather than the passive voice for
verb Sample: X Ang naganap na sunud-sunod na nakawan sa mga paaralan ay
pinasisiyasat ni Tarlac City Mayor Aro Mendoza. Pinasisiyasat ni Tarlac City Mayor Aro
Mendoza ang naganap sunud sunod na nakawan sa mga paaralan Sentence Structure
10. 10. Round-off figures/numbers • Change 2.6123 million to more than 2 and a half million •
35.7002 percent to nearly 36 percent SAMPLE Umabot sa may 10.349 milyong piso…
Umabot sa mahigit sampung milyong piso… Write out symbols and fractions Avoid
abbreviations Other reminders
11. 11. Provide phonetic spelling Speech has rhythm and should be kept in mind when
writing a radio script A radio script should display an element of “nowness” Key repetitive
statements help the listener to get the message
12. 12. Get a good briefing, know your listener Do research about the topic Prepare content
outline Write the first draft Read it aloud. Time the material Visualize the script
Review the script Revise for style, correct timing and accuracy
13. 13. 05:00 (5-minute newscast program) 01:30 Ads and infomercials 00:10 Station ID 00:30
Intro, Bumpers and Teasers 02:50 Time left for news The remaining two minutes and fifty
seconds are to be apportioned to the news stories of the day.
14. 14. It is used between the news and commercial breaks. It tells the listener that there is a
break but that there will be some more news coming up. Example: “We’ll be back with more
news after these reminders from our sponsors…
15. 15. It is used to stimulate curiosity so that the listeners will stay tune in to hear what it’s all
about. Example: “Waling waling to replace sampaguita as national flower?”
16. 16. It is usually heard after the news. It reminds the listeners of what product sponsors
the said news. Example: “This news is brought to you by Dunkin Donut, ang pasalubong ng
bayan.”
17. 17. Title Page Program title - Mangyan Patrol 24/7 FORMAT - News Station - DWSJ 99.9
Airtime - 80:00 a.m – 8:05 a.m daily Date of Newscast - November 6, 2011 Talents Anchor:
Mary Queen T. Bernardo Reporters Ana M. Garcia Davis B. Tan Allan G. Gomez Field
Reporter Jinny-vi C. Panganiban 3. Format in Writing a Radio Script
18. 18. 18 The final step to indicate that the story has ended or has more details in the next
page. 1. Put ### at the end of page to indicate that the story has ended or put (more) at the
end of page to let the anchor knows that there is another page. 2. If you must split a story
into two pages, never break a sentence. Always end a page with a complete sentence.
19. 19. 1. Station ID 2. Time Check 3. News Plug 4. Intro 5. Headlines 6. Details 7. Extro
20. 20. ENGLISH Headlines National Local / Provincial Infomercial Foreign Showbiz
Sports Weather FILIPINO Ulo Pambansa Probinsiya Patalastas Ibayong Dagat
Showbis Palakasan Lagay ng Panahon
21. 21. Example of a Five-minute Radio Script
22. 22. Infomercials may be derived from subjects which have values related to government,
economy, health, environment, social, spiritual and/or moral responsibilities. Back
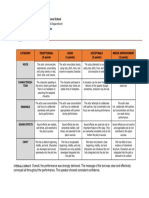
23. 23. Criteria for Radio Broadcast Criteria Percentage Script/production Application of
broadcast journalism principles Broadcast form of writing Clear & logical organization of
news scripts 30 Delivery & Presentation Clear presentation of items Modulation, volume
& quality Confidence 30 Style/Technique Creativity Uniqueness 30 Impression/Impact
Overall audience appeal Effect 10
24. 24. Example of an Individual Script 11/06/11 Lloyd’s Eye Bug 8:00 PM Hear! Hear! Hear!
Friends and avid fans of John Lloyd Cruz, the famous Yuri of “Kaytagal Kang Hinintay,”
never had an operation to eliminate his prominent eye bugs. Instead he had laser treatment
twice a month to lighten dark circles around his eyes! He is now filming “My First Romance”
with Bea Alonzo. So, wait and see for Star cinema’s heartwarming movie of the year. This is
Chikading Juday, Back to you, Queen! Castro/bello/09215457080
You might also like
- API Recommended Practice For ESPDocument104 pagesAPI Recommended Practice For ESPMaghfiraRamadhani100% (1)
- Using Correct and Appropriate Multimedia ResourcesDocument1 pageUsing Correct and Appropriate Multimedia Resourceseyah fajardoNo ratings yet
- Writing For RadioDocument14 pagesWriting For RadioShakthi Chinki0% (1)
- Sample Integrated Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSample Integrated Lesson Planapi-356301831No ratings yet
- Radio Drama RubricDocument2 pagesRadio Drama RubricAngelica Angeles100% (1)
- Author Study Research PaperDocument3 pagesAuthor Study Research PaperJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- A320 OralDocument5 pagesA320 OralNguyễn Trần Nam100% (1)
- Radio BroadcastingDocument45 pagesRadio BroadcastingHerman Jr AtipNo ratings yet
- Radio BroadcastingDocument43 pagesRadio BroadcastingAlemil Fontilar100% (1)
- Radio Script WritingDocument26 pagesRadio Script WritingJasper Christian L. MaralitNo ratings yet
- Broadcast News MaterialDocument5 pagesBroadcast News MaterialPauline Karen ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Radio BroadcastingDocument30 pagesRadio BroadcastingGeoffrey Tolentino-Unida100% (2)
- News Writing For Television and RadioDocument4 pagesNews Writing For Television and RadioRiko PratamaNo ratings yet
- Journ Training-RADIO SCRIPTWRITING AND BROADCASTINGDocument17 pagesJourn Training-RADIO SCRIPTWRITING AND BROADCASTINGrubieann_danzalan100% (1)
- Radio Drama ScriptDocument10 pagesRadio Drama Scriptapi-294976137No ratings yet
- Radio Drama: Powerpoint PresentationDocument10 pagesRadio Drama: Powerpoint PresentationLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Concepts On Radio & TV BroadcastingDocument94 pagesConcepts On Radio & TV BroadcastingAura Joy Otic-Mocorro PlanasNo ratings yet
- Writing A Script For The RadioDocument19 pagesWriting A Script For The RadioNK8No ratings yet
- Broadcast Announcing: Radio PerformanceDocument41 pagesBroadcast Announcing: Radio PerformanceLourdeliza Guarin Egaña100% (1)
- Radio Broadcasting Script NEWDocument6 pagesRadio Broadcasting Script NEWKristine Jill Fuentes LlegueNo ratings yet
- Radio Journalism/Broadcasting: Saldivia, Cloister Kevin C. & Sulmaca, Kimberly MDocument13 pagesRadio Journalism/Broadcasting: Saldivia, Cloister Kevin C. & Sulmaca, Kimberly MMark June B. GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Sample Radio Drama ScriptDocument3 pagesSample Radio Drama ScriptAnonymous QIeyxXkB0D100% (1)
- Journalism 9 NotesDocument7 pagesJournalism 9 NotesDIAYANARA ROSE CACHO100% (1)
- Radio Drama ScriptDocument7 pagesRadio Drama Scriptapi-477556951No ratings yet
- Script English FinalDocument9 pagesScript English FinalVilla Rose Gachon Delfin100% (1)
- Photojournalism SeminarDocument4 pagesPhotojournalism SeminarRodel AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Principles of Radio Scriptwriting and The Basic Radio Script FormatDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Radio Scriptwriting and The Basic Radio Script FormatFrancisRalfLlemit100% (1)
- English 10 Performance TaskDocument4 pagesEnglish 10 Performance TaskJello Perez CastañosNo ratings yet
- Radio Broadcasting PPT Region Speaker MMGDocument49 pagesRadio Broadcasting PPT Region Speaker MMGSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Structure of A Screenplay: Dr. Sailesh KolanuDocument35 pagesStructure of A Screenplay: Dr. Sailesh KolanuHelloNo ratings yet
- Unit III. The Radio Drama 2Document16 pagesUnit III. The Radio Drama 2RuthNo ratings yet
- WRITING FOR RADIO Lead ScriptDocument34 pagesWRITING FOR RADIO Lead ScriptYana kimNo ratings yet
- Communicative Style G9Document19 pagesCommunicative Style G9JTPH Music音シNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Writing For Desktop PublishingDocument21 pagesCollaborative Writing For Desktop PublishingJudith AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Coronation Script - Miss Conalum 2017Document7 pagesCoronation Script - Miss Conalum 2017Chkarliysle MhacoonsNo ratings yet
- RadioDocument36 pagesRadioMadhurika Goyal100% (1)
- Audio Editing QuizDocument8 pagesAudio Editing QuizAnonymous 3q6HiK100% (1)
- Gec 4 Lesson 12 - History of DramaDocument46 pagesGec 4 Lesson 12 - History of DramaGian Jane QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Radio Drama Script Title: No One But AmberDocument8 pagesRadio Drama Script Title: No One But AmberPatricia Ann Bustamante100% (1)
- Radio Scriptwriting and BroadcastingDocument32 pagesRadio Scriptwriting and BroadcastingKim SuarezNo ratings yet
- TV Production Syllabus SophmoresDocument4 pagesTV Production Syllabus Sophmoresapi-235345575No ratings yet
- Audio Play Criteria For Judging PDFDocument1 pageAudio Play Criteria For Judging PDFMark RonelNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Sociology and AnthropologyDocument12 pagesReviewer - Sociology and AnthropologyCherry CabadduNo ratings yet
- Radio Play ScriptDocument7 pagesRadio Play ScriptMaxene YbañezNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH-Grade 9: I. Learning SkillsDocument9 pagesENGLISH-Grade 9: I. Learning SkillsJohnnyNo ratings yet
- SPJ 10 Quarter HandoutDocument6 pagesSPJ 10 Quarter HandoutJo Ann Katherine ValledorNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint On Kinds of PropagandaDocument26 pagesPowerpoint On Kinds of PropagandaChynah Marie MonzonNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet CharactersDocument11 pagesRomeo and Juliet CharactersLeenie Anne Ang-Angco100% (1)
- Broadcasting JargonsDocument2 pagesBroadcasting JargonsEline LishNo ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet Diary Task PDFDocument14 pagesRomeo and Juliet Diary Task PDFsNo ratings yet
- 12 NewsravenDocument8 pages12 NewsravenmusicaBGNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document2 pagesWorksheet 1api-334911413No ratings yet
- Television Script Writing and BroadcastingDocument62 pagesTelevision Script Writing and BroadcastingSadiriNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Script WritingDocument2 pagesBroadcast Script Writingeojovmk0% (1)
- News WritingDocument47 pagesNews WritingJonabhelle ImpasNo ratings yet
- Radio Broadcasting ScriptDocument5 pagesRadio Broadcasting Scriptdonna belle m. intadNo ratings yet
- Structures of Headlines: Family Planning Seminar HeldDocument7 pagesStructures of Headlines: Family Planning Seminar HeldAvieNo ratings yet
- Radio Broad ScriptDocument10 pagesRadio Broad ScriptreyanaNo ratings yet
- Radio BroadcastingDocument41 pagesRadio BroadcastingWendel Matias100% (5)
- Radio Broadcasting and ScriptwritingDocument27 pagesRadio Broadcasting and ScriptwritingAllysa Mae Caleon100% (1)
- 160a936b140785 - BatoruDocument2 pages160a936b140785 - BatoruMauria PaglicawanNo ratings yet
- News Writing For Television and RadioDocument9 pagesNews Writing For Television and Radiojhon klein chavezNo ratings yet
- Stories Told through Sound: The Craft of Writing Audio Dramas for Podcasts, Streaming, and RadioFrom EverandStories Told through Sound: The Craft of Writing Audio Dramas for Podcasts, Streaming, and RadioNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Recognition: The Sumulong AdvocateDocument3 pagesCertificate of Recognition: The Sumulong AdvocateJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- Be Still. Rest But Never Quit.: For You, Who Never Ceased To Amaze MeDocument2 pagesBe Still. Rest But Never Quit.: For You, Who Never Ceased To Amaze MeJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- Juan Sumulong Memorial Junior College Taytay, Rizal S.Y. 2018-2019Document59 pagesJuan Sumulong Memorial Junior College Taytay, Rizal S.Y. 2018-2019Jehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- Capital: 3001 Buama Capital 3002 Buama, DrawingDocument2 pagesCapital: 3001 Buama Capital 3002 Buama, DrawingJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- ASSETS1Document1 pageASSETS1Jehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- JSMJC Conducts Parenting SeminarDocument1 pageJSMJC Conducts Parenting SeminarJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- HADO: Colliding Sports and Technology in The Field of Play HADO: The Future of SportsDocument5 pagesHADO: Colliding Sports and Technology in The Field of Play HADO: The Future of SportsJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- DIWA Led "Pasiklaban Sa Paaralan" Quiz BeeDocument1 pageDIWA Led "Pasiklaban Sa Paaralan" Quiz BeeJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Taytay Municipal Meet: JSMJC Diggers Snatch Gold and Silver MedalsDocument2 pages2019 Taytay Municipal Meet: JSMJC Diggers Snatch Gold and Silver MedalsJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- Respect The Feelings of Others 2. Refraining From The Words or Actions That May Offend Others 3. Observe Those Around You 4. Do Not Play Loud Music in Public 5. Be Careful On How You DressDocument1 pageRespect The Feelings of Others 2. Refraining From The Words or Actions That May Offend Others 3. Observe Those Around You 4. Do Not Play Loud Music in Public 5. Be Careful On How You DressJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- Letting Love Win: How My Parents' Love Made Me A WinnerDocument2 pagesLetting Love Win: How My Parents' Love Made Me A WinnerJehnn BenitoNo ratings yet
- CH II Key Feature of Development PoliciesDocument28 pagesCH II Key Feature of Development Policiessssshekhar100% (3)
- Datex-Ohmeda Avance - User Reference ManualDocument202 pagesDatex-Ohmeda Avance - User Reference ManualMariö OlveraNo ratings yet
- Emp-168 Analizador Bioquimico PDFDocument2 pagesEmp-168 Analizador Bioquimico PDFAlberto Ybañez CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Learning PlanDocument4 pagesSyllabus Learning PlanjessakiNo ratings yet
- Cruise Control 7.1: GeneralDocument22 pagesCruise Control 7.1: Generaljose fermin carrozaNo ratings yet
- Alinco DJ-X2000 Service ManualDocument58 pagesAlinco DJ-X2000 Service ManualYayok S. Anggoro100% (1)
- SPSS ImplicationsDocument3 pagesSPSS ImplicationsAnonymous MMNqiyxBUNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Independence PathfinderDocument2 pagesDeclaration of Independence PathfinderginaportfolioNo ratings yet
- 1.6. C. Cosin - Desalination Technologies and Economics - Capex, Opex and Technological Game Changers To Come - IlDocument56 pages1.6. C. Cosin - Desalination Technologies and Economics - Capex, Opex and Technological Game Changers To Come - IlEmad ElsaidNo ratings yet
- Compiled Question Ce 3227Document9 pagesCompiled Question Ce 3227Hamisi MzariNo ratings yet
- Tractors - Types and UtilitiesDocument14 pagesTractors - Types and UtilitiesZicoelyamny100% (2)
- Uncovering The Realities of Simulation, Part 1 (Of 1)Document11 pagesUncovering The Realities of Simulation, Part 1 (Of 1)bjsatola100% (2)
- Hydraulic Power UnitDocument2 pagesHydraulic Power UnitJosh SabimanNo ratings yet
- Watt Gearboxes-CatalogueDocument18 pagesWatt Gearboxes-CataloguecakhokheNo ratings yet
- Example - Software Architecture DocumentDocument14 pagesExample - Software Architecture DocumentAlejandro EspindolaNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument28 pagesSteelAshfaq SaudagarNo ratings yet
- Laser Guided BombsDocument20 pagesLaser Guided Bombsapi-382700075% (4)
- Lnvgy Util Asu Asu90f Anyos NoarchDocument158 pagesLnvgy Util Asu Asu90f Anyos NoarchAdrian StoicaNo ratings yet
- VTech My First Clock User ManualDocument15 pagesVTech My First Clock User ManualhaiyentanguyenNo ratings yet
- Turbo Pascal Graphix Toolbox Version 4.0 1987Document266 pagesTurbo Pascal Graphix Toolbox Version 4.0 1987Luiz Cesar NunesNo ratings yet
- Centrum &magnum C-3000Document12 pagesCentrum &magnum C-3000ศูนย์เครื่องจักรบางบอนโดยวงศ์ธนาวุฒิNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Notes DesignDocument24 pagesPile Foundation Notes DesignSnow YoshimaNo ratings yet
- Type-61 ElastomerSeatedButterflyValves 10 28 2022Document10 pagesType-61 ElastomerSeatedButterflyValves 10 28 2022viksursNo ratings yet
- Clinical Letter of Recommendation Request Cover SheetDocument3 pagesClinical Letter of Recommendation Request Cover SheetRaffy GutmanNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2Tarun BhatiaNo ratings yet
- PAKET 19 Pengetahuan Dan Pemahaman Umum (Inggris)Document2 pagesPAKET 19 Pengetahuan Dan Pemahaman Umum (Inggris)Felicia MaharaniNo ratings yet
- 543S 3 PDFDocument68 pages543S 3 PDFvaraprasad93No ratings yet