Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tabel Unutuk Q-Sytem
Tabel Unutuk Q-Sytem
Uploaded by
fadel muhammadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tabel Unutuk Q-Sytem
Tabel Unutuk Q-Sytem
Uploaded by
fadel muhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
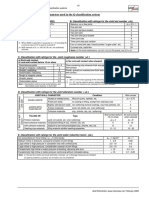
Input parameters to Q system
Rock quality designation (RQD) Joint set number (Jn)
Very poor RQD = 0 - 25% Massive, no or few joints Jn = 0.5 - 1
Poor 25 - 50 One joint set 2
Fair 50 - 75 One joint set plus random 3
Good 75 - 90 Two joint sets 4
Excellent 90 - 100 Two joint sets plus random 6
Notes: Three joint sets 9
(i) Where RQD is reported or measured as < 10 (inclu- Three joint sets plus random 12
ding 0), a nominal value of 10 is used to evaluate Q Four or more joint sets, heavily jointed, "sugar-cube", etc. 15
(ii) RQD intervals of 5, i.e. 100, 95, 90, etc. Crushed rock, earthlike 20
are sufficiently accurate Notes: (i) For tunnel intersections, use (3.0 x Jn); (ii) For portals, use (2.0 x Jn)
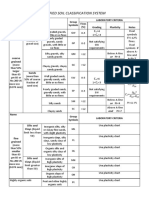
Desciption and ratings for the parameter Jr (joint roughness number)
a) Rock-wall contact,
c) No rock-wall contact when sheared
b) rock-wall contact before 10 cm shear
Discontinuous joints Jr = 4 Zone containing clay minerals thick enough to prevent rock-wall
Jr = 1.0
Rough or irregular, undulating 3 contact
Smooth, undulating 2 Sandy, gravelly or crushed zone thick enough to prevent rock-
1.0
Slickensided, undulating 1.5 wall contact
Rough or irregular, planar 1.5 Notes:
Smooth, planar 1.0 i) Add 1.0 if the mean spacing of the relevant joint set is greater than 3 m
Slickensided, planar 0.5 ii) Jr = 0.5 can be used for planar, slickensided joints having lineations,
Note : i) Descriptions refer to small scale features, provided the lineations are oreintated for minimum strength
and intermediate scale features, in that order
Descriptions and ratings for the parameter Ja (joint alteration number)
JOINT WALL CHARACTER Condition Wall contact
between joint
Healed or welded joints: filling of quartz, epidote, etc. Ja = 0,75
Contact
CLEAN JOINTS Fresh joint walls: no coating or filling, except from staining (rust) 1
walls
Slightly altered joint walls: non-softening mineral coatings, clay-free particles, etc. 2
COATING OR Friction materials: sand, silt calcite, etc. (non-softening) 3
THIN FILLING Cohesive materials: clay, chlorite, talc, etc. (softening) 4
Partly or no wall
FILLING OF: Type Partly wall contact No wall contact
Thin filling (< 5 mm) Thick filling
contact
Friction materials sand, silt calcite, etc. (non-softening) Ja = 4 Ja = 8
Hard cohesive materials compacted filling of clay, chlorite, talc, etc. 6 5 - 10
Soft cohesive materials medium to low overconsolidated clay, chlorite, talc, etc. 8 12
Swelling clay materials filling material exhibits swelling properties 8 - 12 13 - 20
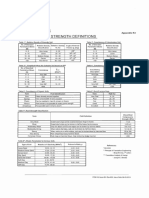
Description and ratings for the parameter Jw (joint water reduction factor)
Dry excavations or minor inflow, i.e. < 5 l/min locally pw < 1 kg/cm 2 Jw = 1
Medium inflow or pressure, occasional outwash of joint fillings 1 - 2.5 0.66
Large inflow or high pressure in competent rock with unfilled joints 2.5 - 10 0.5
Large inflow or high pressure, considerable outwash of joint fillings 2.5 - 10 0.3
Exceptionally high inflow or water pressure at blasting, decaying with time > 10 0.2 - 0.1
Exceptionally high inflow or water pressure continuing without noticeable decay > 10 0.1 - 0.05
Note: (i) The last four factors are crude estimates. Increase Jw if drainage measures are installed
(ii) Special problems caused by ice formation are not considered
Description and ratings for parameter SRF (stress reduction factor)
Multiple weakness zones with clay or chemically disintegrated rock, very loose surrounding rock (any depth) SRF = 10
zones intersecting
Single weakness zones containing clay or chemically disintegrated rock (depth of excavation < 50 m)
A. Weakness
5
excavation
Single weakness zones containing clay or chemically disintegrated rock (depth of excavation > 50 m) 2.5
Multiple shear zones in competent rock (clay-free), loose surrounding rock (any depth) 7.5
Single shear zones in competent rock (clay-free), loose surrounding rock (depth of excavation < 50 m) 5
Single shear zones in competent rock (clay-free), loose surrounding rock (depth of excavation > 50 m) 2.5
Loose, open joints, heavily jointed or "sugar-cube", etc. (any depth) 5
Reduce these valued of SRF by 25 - 50% if the relevant shear zones only influence, but do not
Note: (i)
intersect the excavation sc / s1 sq / sc
Low stress, near surface, open joints > 200 < 0.01 2.5
stress problems
B. Competent
Medium stress, favourable stress condition 200 - 10 0.01 - 0.3 1
rock, rock
High stress, very tight structure. Usually favourable to stability, may be except for walls 10 - 5 0.3 - 0.4 0.5 - 2
Moderate slabbing after > 1 hour in massive rock 5-3 0.5 - 0.65 5 - 50
Slabbing and rock burst after a few minutes in massive rock 3-2 0.65 - 1 50 - 200
Heavy rock burst (strain burst) and immediate dynamic deformation in massive rock <2 >1 200 - 400
For strongly anisotropic stress field (if measured): when 5 < s 1 / s 3 <10, reduce s c to 0.75 s c .
(ii)
When s 1/ s 3 > 10, reduce s c to 0.5 s c
Notes:
Few case records available where depth of crown below surface is less than span width. Suggest SRF increase
(iii)
from 2.5 to 5 for low stress cases sq / sc
Plastic flow of incompetent rock under the Mild squeezing rock pressure 1-5 5 - 10
C. Squeezing rock
influence of high pressure Heavy squeezing rock pressure >5 10 - 20
Chemical swelling activity depending on Mild swelling rock pressure 5 - 10
D. Swelling rock
presence of water Heavy swelling rock pressure 10 - 15
You might also like
- Rock Cavern in SingaporeDocument24 pagesRock Cavern in SingaporepabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Plaxis ParametersDocument3 pagesPlaxis ParametersAsif Mostafa AnikNo ratings yet
- Field Soil Description ASTM 2487Document17 pagesField Soil Description ASTM 2487Muhamad Naufan NurfarisaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Flow Assurance PDFDocument123 pagesAdvanced Flow Assurance PDFMarcoNo ratings yet
- 5471Document3 pages5471Mihai-Eugen Popa100% (2)
- System Dynamics, Third Edition: Using Simscape ™ For Modeling Hydraulic Systems: Dynamics of A Hydraulic Piston and LoadDocument40 pagesSystem Dynamics, Third Edition: Using Simscape ™ For Modeling Hydraulic Systems: Dynamics of A Hydraulic Piston and LoadredwaneNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Description and Ratings For The Input Parameters of The Q-System (Simplified From Grimstad and Barton, 1993)Document1 pageTable 1. Description and Ratings For The Input Parameters of The Q-System (Simplified From Grimstad and Barton, 1993)Trương Đoàn Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
- Combining - RMR Q RMiDocument2 pagesCombining - RMR Q RMilaxmikant1983No ratings yet
- Short On Q-System PDFDocument3 pagesShort On Q-System PDFjuan davidNo ratings yet
- A) Rock Wall Contact, and B) Wall Contact Before 10 CM ShearDocument1 pageA) Rock Wall Contact, and B) Wall Contact Before 10 CM ShearJio MarnnNo ratings yet
- Tabel Gsi, RMR, RmiDocument4 pagesTabel Gsi, RMR, RmiPup BooNo ratings yet
- Q Course For PERU PPT 2Document7 pagesQ Course For PERU PPT 2jhonaroniNo ratings yet
- Rock Tunelling Quality Index, QDocument8 pagesRock Tunelling Quality Index, QMilthonNo ratings yet
- ISRM2019 BB QslopeFaultedRocksAndFaultZonesDocument9 pagesISRM2019 BB QslopeFaultedRocksAndFaultZonesJuan Fernando Joya NuñezNo ratings yet
- Q - Method 2013 Summary For Field UseDocument2 pagesQ - Method 2013 Summary For Field UsePatricio CisternasNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 Q-Rock Mass ClassificationDocument21 pagesLec-11 Q-Rock Mass ClassificationUmair AshrafNo ratings yet
- 2022 10 06 Tutorial 2 Q-Value Ref TablesDocument5 pages2022 10 06 Tutorial 2 Q-Value Ref TablesQhamani QhamaniNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pendahuluan: A. Core Drilling, Core, Coring B. Sampel, Sampling, Preparasi C. Rock Mass D. Intack RockDocument3 pagesTugas Pendahuluan: A. Core Drilling, Core, Coring B. Sampel, Sampling, Preparasi C. Rock Mass D. Intack RockOdit Adams OditNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Rock Mass Classification: 4.6 Tunnelling Quality Index (Q)Document7 pagesModule 4: Rock Mass Classification: 4.6 Tunnelling Quality Index (Q)tanujaayerNo ratings yet
- Table 6: Classification of Individual Parameters Used in The Tunnelling Quality Index QDocument3 pagesTable 6: Classification of Individual Parameters Used in The Tunnelling Quality Index QSameer ShashwatNo ratings yet
- Hoek-Brown Critera and GSIDocument112 pagesHoek-Brown Critera and GSIMohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Properties of Rock MassesDocument31 pagesEngineering Properties of Rock Massessuchismita majhiNo ratings yet
- Table: Rock Mass Rating System (After Bieniawski 1989) : RQD 115-3.3 JDocument1 pageTable: Rock Mass Rating System (After Bieniawski 1989) : RQD 115-3.3 JSubeg SeaikhNo ratings yet
- ChartDocument4 pagesChartGopal VermaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Description of SoilsDocument4 pagesEngineering Description of SoilsSRISHTI SHAKYANo ratings yet
- Slides For ThermalDocument6 pagesSlides For Thermaladil abidNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass Classification: Ashok Kumar Director Geological Survey of IndiaDocument44 pagesRock Mass Classification: Ashok Kumar Director Geological Survey of IndiazmnerNo ratings yet
- Is 13365 Part4 DraftDocument15 pagesIs 13365 Part4 DraftPalak Shivhare0% (1)
- Korelasi Parameter GeoteknikDocument9 pagesKorelasi Parameter GeoteknikMasita FikaahNo ratings yet
- As1726 1993Document16 pagesAs1726 1993Nguyen Quoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 09 SolutionDocument3 pagesTutorial 09 Solution秦瑋駿No ratings yet
- 8 - Rock Mass Characterization (Pg. 7)Document7 pages8 - Rock Mass Characterization (Pg. 7)sudhakarNo ratings yet
- Emailing Logueo Geotecnico_MDEng-QuimsacochaDocument8 pagesEmailing Logueo Geotecnico_MDEng-QuimsacochaELVA MILAGROS ALAVEDRA SIMBRONNo ratings yet
- Codes For BoltsDocument15 pagesCodes For Boltsc.m.jibeeshNo ratings yet
- RMR Table ClassificationDocument22 pagesRMR Table ClassificationPrasetya Adi RinantoNo ratings yet
- 5 FinevscoarseDocument4 pages5 FinevscoarseRana Mudssar KhanNo ratings yet
- Rockmass Classification SystemDocument11 pagesRockmass Classification SystemChandrani PrasadNo ratings yet
- Uscs ChartDocument2 pagesUscs Chartchopin123456No ratings yet
- Soil Descriptions - Figure 1 and 2 Revised ISSMFE - Rev. Oct, 2012Document2 pagesSoil Descriptions - Figure 1 and 2 Revised ISSMFE - Rev. Oct, 2012Terobau111No ratings yet
- Min3210 Support Doc Mid-Term Exam Nov 10 2022Document23 pagesMin3210 Support Doc Mid-Term Exam Nov 10 2022Abdelghafour ElmchiekNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 09Document2 pagesTutorial 09秦瑋駿No ratings yet
- Rock Classification 1994Document5 pagesRock Classification 1994Asnake KefelegnNo ratings yet
- RMRXDocument1 pageRMRXFrancisco Javier Solis NuñezNo ratings yet
- Chapter - III (Draft Earthwork) 07.09.2019Document30 pagesChapter - III (Draft Earthwork) 07.09.2019rtyrty12No ratings yet
- 10 - RMR SYSTEM OF ROCKMASS CLASSIFICATION - Pg. 10Document9 pages10 - RMR SYSTEM OF ROCKMASS CLASSIFICATION - Pg. 10Mike Eugene CollinsNo ratings yet
- SoilClassification SivakuganDocument15 pagesSoilClassification SivakuganAman JainNo ratings yet
- Laser ProfilometerDocument11 pagesLaser ProfilometerJuan David Roldán MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Geo-Mechanics Classification of Rock Masses: No UCS Test DoneDocument2 pagesGeo-Mechanics Classification of Rock Masses: No UCS Test DonesandipNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of RockDocument19 pagesBearing Capacity of RockAhmad PooladiNo ratings yet
- Lec7-CEM&G Session 7 Soils Classification - 07112018Document75 pagesLec7-CEM&G Session 7 Soils Classification - 07112018Sarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- 12 AllDocument17 pages12 Allधीरज कुमारNo ratings yet
- Properties of Soils: AppendixDocument32 pagesProperties of Soils: AppendixMd. Nahid HossainNo ratings yet
- Annex: A 1: Relative Density of Cohesionless SoilsDocument16 pagesAnnex: A 1: Relative Density of Cohesionless Soilsjems patelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04-Chapter 4 Classification PDFDocument86 pagesLesson 04-Chapter 4 Classification PDFYasser Alghrafy100% (1)
- Classifications of Some Discontinuity FeaturesDocument3 pagesClassifications of Some Discontinuity FeaturesrichkyutamaNo ratings yet
- Identification and Classification ofDocument40 pagesIdentification and Classification ofDevang GajeraNo ratings yet
- Discontinuity Characterization - QueensMineDesignWikiDocument4 pagesDiscontinuity Characterization - QueensMineDesignWikiImranNo ratings yet
- Short On Q-SystemDocument3 pagesShort On Q-SystemChandraAndySaputraNo ratings yet
- Horizon Borehole Log Key Sheet and Soil Description Guide: Sample / Test SymbolsDocument2 pagesHorizon Borehole Log Key Sheet and Soil Description Guide: Sample / Test SymbolsJose Leo MissionNo ratings yet
- Application of The Q-Slope Method To Highly Weathered and Saprolitic RocksDocument6 pagesApplication of The Q-Slope Method To Highly Weathered and Saprolitic RocksWalt ArcherNo ratings yet
- Interfacial Friction Between Soils and Solid SurfacesDocument81 pagesInterfacial Friction Between Soils and Solid SurfacesStressDyn ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- Recent Format Discotinuty Data SheetDocument10 pagesRecent Format Discotinuty Data SheetSusett M TNo ratings yet
- BHDS2003Document1 pageBHDS2003Neeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- TS 02025 - 1.00 - Testing of Cast-in-Place Concrete PilesDocument13 pagesTS 02025 - 1.00 - Testing of Cast-in-Place Concrete PilespabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Risk and Performance: With A Focus On Earthworks Compaction and Data ManagementDocument11 pagesGeotechnical Risk and Performance: With A Focus On Earthworks Compaction and Data ManagementpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- MRTS140Document23 pagesMRTS140pabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Care 2023 08 22Document16 pagesSepsis Care 2023 08 22pabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Transport For NSW (TFNSW) Specification D&C R31 Vertical Wick DrainsDocument16 pagesTransport For NSW (TFNSW) Specification D&C R31 Vertical Wick DrainspabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Swelling Rocks Strain in Tunneling: D. Parsapour and A. FahimifarDocument11 pagesPrediction of Swelling Rocks Strain in Tunneling: D. Parsapour and A. FahimifarpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Removable Single Bore Multiple AnchorsDocument7 pagesRemovable Single Bore Multiple AnchorspabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Pain Relief CompressedDocument64 pagesPain Relief Compressedpabulumzeng100% (1)
- Procedure For Sampling and Quality Evaluation Testing of Rock For Riprap Slope ProtectionDocument9 pagesProcedure For Sampling and Quality Evaluation Testing of Rock For Riprap Slope ProtectionpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Current Practice of Cfa Piling in Australia and New Zealand: Martinla@fcc - Co.nzDocument9 pagesCurrent Practice of Cfa Piling in Australia and New Zealand: Martinla@fcc - Co.nzpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- 9 TBM Boreability I Hard BergmasseDocument43 pages9 TBM Boreability I Hard BergmassepabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Sec683 Soil Nail WallsDocument14 pagesSec683 Soil Nail Wallspabulumzeng100% (1)
- FULLTEXT01 GroutingDocument58 pagesFULLTEXT01 GroutingMehran RezvaniNo ratings yet
- Sec682 Reinforced Soil StructuresDocument10 pagesSec682 Reinforced Soil StructurespabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Earthworks SpecDocument30 pagesEarthworks SpecpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Application of Reinforcing Methods For Existing Pile Foundation On Soft Ground (In-Cap Method)Document9 pagesApplication of Reinforcing Methods For Existing Pile Foundation On Soft Ground (In-Cap Method)pabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis in Stiff Fissured Clays - Stark and Eid 1997 PDFDocument9 pagesSlope Stability Analysis in Stiff Fissured Clays - Stark and Eid 1997 PDFpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical FailureDocument25 pagesGeotechnical FailurepabulumzengNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Pressure Relief ValvesDocument4 pagesThe Basics of Pressure Relief ValvesSud GawaliNo ratings yet
- G G G G G: HapterDocument19 pagesG G G G G: HapterAnnNo ratings yet
- ss1 2nd Term Chem Note1 1Document35 pagesss1 2nd Term Chem Note1 1Victor Okosun86% (7)
- The Edrizzi System: User Manual March 2020/4Document58 pagesThe Edrizzi System: User Manual March 2020/4Kaya Eralp AsanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 61-Derivation of Bernoullis Equation PDFDocument6 pagesLesson 61-Derivation of Bernoullis Equation PDFSaravanan MathiNo ratings yet
- XE SampleDocument31 pagesXE SampleJerome HarinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Underground Environment - Mine VentilationDocument23 pagesChapter-2-Underground Environment - Mine VentilationSahil SokhalNo ratings yet
- Flow-After-flow Tests For Gas WellsDocument6 pagesFlow-After-flow Tests For Gas WellsTino Nassel100% (1)
- Manometer NotesDocument5 pagesManometer NotesRaju100% (1)
- Mercury Porosimetry: A General (Practical) OverviewDocument11 pagesMercury Porosimetry: A General (Practical) OverviewMilene EloyNo ratings yet
- SofregazDocument26 pagesSofregazAbdulkadir Berk MalkoçNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Design Exercise PDFDocument1 pageDistillation Column Design Exercise PDFHari PurwitoNo ratings yet
- Section - 2 - Champ IV PackerDocument2 pagesSection - 2 - Champ IV PackerBekir OnayNo ratings yet
- Civil and MechnicalDocument15 pagesCivil and MechnicalLokeshNo ratings yet
- Combined Heat and Power Systems: Reference Manual ForDocument284 pagesCombined Heat and Power Systems: Reference Manual ForKamyab PakistanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Allocation Measurement Api Chapter 20.1: Weathered Oil Has Lost Most of Its DissolvedDocument7 pagesLiquid Allocation Measurement Api Chapter 20.1: Weathered Oil Has Lost Most of Its DissolvedSE CristobalNo ratings yet
- Density of Methanol + Water Between 250 K and 440 K and Up To 40Document9 pagesDensity of Methanol + Water Between 250 K and 440 K and Up To 40DanielRicardoDelgadoNo ratings yet
- Name: Teo Mahatmana K.M Nim: K2218076 Class: 2BDocument7 pagesName: Teo Mahatmana K.M Nim: K2218076 Class: 2BTeo mahatmana Ksatria MuktiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Long-Term Performance of EPS Geofoam On Lateral Earth Pressures On Retaining WallsDocument19 pagesEffect of Long-Term Performance of EPS Geofoam On Lateral Earth Pressures On Retaining WallsBao TruongNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - LPP-3Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics - LPP-3Lester LewisNo ratings yet
- System Description Fuel Gas Draining PDFDocument4 pagesSystem Description Fuel Gas Draining PDFsivamNo ratings yet
- S1 Hyd Thrust T+answersDocument22 pagesS1 Hyd Thrust T+answersprabathiyaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of BinsDocument34 pagesStructural Design of Binsjayaraman3No ratings yet
- Enzymelabreport DaliahagebDocument4 pagesEnzymelabreport Daliahagebapi-337922708No ratings yet
- Smoke Control: Section 4/chapter 12Document12 pagesSmoke Control: Section 4/chapter 12Ramyaa LakshmiNo ratings yet
- GMV5 Service Manual 2014Document120 pagesGMV5 Service Manual 2014Артур БобкинNo ratings yet
- Grundfos MQ Leaflet-210x297 GB LowDocument2 pagesGrundfos MQ Leaflet-210x297 GB LowPetros IosifidisNo ratings yet