Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Copy of How It Works
Copy of How It Works
Uploaded by
api-473894609Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Copy of How It Works
Copy of How It Works
Uploaded by
api-473894609Copyright:
Available Formats
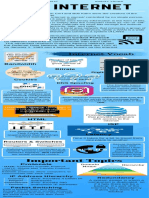
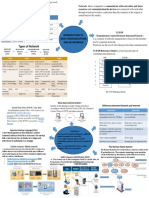
THE
INTERNET Created by
VINTON G. CERF AND ROBERT E. KAHN
IET WHO OWNS
LAN AND
F THE INTERNET?
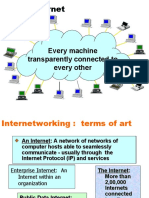
WAN THE International community of those
interested in the evolution and No one, the internet is not
DIFFERENCE operation of the internet.
controlled by anyone. It is a
LAN(Local Area Network): platform in which data is
A connection between shared between the entire
computers within a world.
limited area.
WAN(Wide Area WHAT DATA
Network): Multiple LAN's
DOES IT USE?
that are connected
together
IP Address: The internet uses bits for data
and even bigger
An Internet Protocol that assigns a given
numerical value consisting of bits to each
device that is connected to a network.
WHAT ARE THE
Packet: METHODS?
Formatted unit of data that is carried in bits
Electricity, light, and radio
waves are used to transfer
data.
Things to know
Bandwidth; The maximum
data transfer rate.
Domain Name: Characters
that form the main part of
an Internet address.
IPv4 vs IPv6: Are protocols
that are used to identify ne Rou
tw te
machines. IPv6 are 128 bits o rs
co Swi rks, : Co
while IPv4 is only 32 bits. nne tche dir nn
ct s: ect ect
co m
u De s d s l
m lti vic ata oca
Bit rate: The speed/rate at ut ple e u tra l
p
er d s
which bits are transferred. ne evi ed ffic.
tw ces to
or
Along with the quality of k. on
a
video or audio files.
DNS,IP,
ISP,& DHCP
DNS: System of converting alphabetical names
into numerical IP addresses.
IP: Technical rules that controls communication
on the internet
ISP: An organization that provides access to
the internet. Can range from international to
regional service providers.
DHCP: Network protocol that allows a server to
assign and IP address to a given computer from
a defined range of numbers
Modem: A unit that maintains connection between
"Get" Request: Requests data ISP and router.
from a specified resource. Router: Forwards information destined for the
"Post" Request: Used to send internet to the modem, while keeping internal traffic
data to a server to create/update inside the network.
a resource.
DNS Spoofing: When a DNS
server's records are maliciously
altered to redirect traffic to an
Cookies: Messages that contains information
attacker
HTML: Is a standard markup language
about any volunteered information that the
for websites, tells computer what the browser stores.
website looks like. Latency: The measure of time used for data
TCP: Manages the sending and being sent over a round-trip. Usually measured
recieving of all packets of data. Makes in milliseconds.
sure that all packets are received Digital Certificates: Uses public key
SSL/TLS: Layer of security aroundcryptography to identify that an identity of an
information to protect it. individual site is true.
HTTP/HTTPS:Defines how messages are formatted and
transferred. HTTPS is the secure version.
URL: The complete address of a website,
including domain and other details. n g
Protocols: System of rules that allows for
communication between two devices. Zha
r y
r
Je
You might also like
- API Co-Signer Setup - FireblocksDocument10 pagesAPI Co-Signer Setup - FireblocksCaracas Blockchain WeekNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Communicate With Other Ict Users Using EmailDocument5 pages10.1 Communicate With Other Ict Users Using EmailmartinNo ratings yet
- Internet InfographicDocument1 pageInternet Infographicapi-473864903No ratings yet
- The Internet 3Document1 pageThe Internet 3api-473696806No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Telecommunications, The Internet and Wireless TechnologyDocument28 pagesChapter 6 - Telecommunications, The Internet and Wireless TechnologyDyg Nademah Pengiran MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Internet InfographicDocument1 pageInternet Infographicapi-473859381No ratings yet
- HeadingDocument1 pageHeadingapi-473862799No ratings yet
- The InternetDocument1 pageThe Internetapi-473715855No ratings yet
- Internet Research Info-GraphicDocument1 pageInternet Research Info-Graphicapi-473693811No ratings yet
- 06-Network LayerDocument49 pages06-Network LayerLuân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- A World Connected An Internet Info-Graphic by Kabir MaindarkarDocument1 pageA World Connected An Internet Info-Graphic by Kabir Maindarkarapi-473711334No ratings yet
- WorkDocument45 pagesWork2019bakereNo ratings yet
- The Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OtherDocument58 pagesThe Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every Otherਜਸਪ੍ਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਬਾਹਰਾNo ratings yet
- The Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OtherDocument58 pagesThe Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OtherVarish GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OtherDocument58 pagesThe Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every Otherben4u33No ratings yet
- The Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OtherDocument58 pagesThe Internet: Every Machine Transparently Connected To Every OthersanritaNo ratings yet
- The Internet-2Document1 pageThe Internet-2api-473857199No ratings yet
- The InternetDocument1 pageThe Internetapi-473923074No ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document31 pagesLecture 8Alpengolden MoonderlandNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and The InternetDocument45 pagesComputer Networks and The InternetSUNDAS FATIMANo ratings yet
- 13.internet Meaning, History and Basic Terminology-2194,2250,2286Document25 pages13.internet Meaning, History and Basic Terminology-2194,2250,2286ShipraNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Internet, Brief History and Basic Internet TermsDocument25 pagesMeaning of Internet, Brief History and Basic Internet TermsShipraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 2 - NETWORK ADMINISTRATIONDocument7 pagesTopic 1 2 - NETWORK ADMINISTRATIONLanz CatamisanNo ratings yet
- InfographicDocument1 pageInfographicapi-473693776No ratings yet
- Infographic ProjectDocument1 pageInfographic Projectapi-473864587No ratings yet
- Comp Sci Networks NotesDocument9 pagesComp Sci Networks NotesLilyRadhikaNo ratings yet
- Internet InfographicDocument1 pageInternet Infographicapi-473862476No ratings yet
- The Internet 2Document1 pageThe Internet 2api-473710345No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction NetworkingDocument60 pages1 Introduction NetworkingAlemayehu GetachewNo ratings yet
- TermsDocument5 pagesTermstajwar967No ratings yet
- Journey of The Internet 2Document1 pageJourney of The Internet 2api-473866871No ratings yet
- Lecture - 01 Part01Document8 pagesLecture - 01 Part01Irfan Haider Munir HussainNo ratings yet
- Internet 1Document1 pageInternet 1api-473714616No ratings yet
- WCMC Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument35 pagesWCMC Chapter 1 - IntroductionOla MilesNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Presented ByDocument24 pagesComputer Networks: Presented ByDjordje OrasaninNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Chapter 1 SlidesDocument87 pagesData Communication Chapter 1 SlidesSaad KhalilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Data Communication, Networks, Internet, ProtocolDocument34 pagesLecture 1 - Data Communication, Networks, Internet, ProtocolNahid ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CS 108 Week 11 Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesCS 108 Week 11 Computer NetworksFarshad yazdiNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking - Cyber Security - Ethical HackingDocument25 pagesBasic Networking - Cyber Security - Ethical HackingShanzida Anika MimNo ratings yet
- Osi and ProtocolsDocument7 pagesOsi and ProtocolsGilgamesh berserkerNo ratings yet
- A Signal Goes Out Via Radio Waves To The RouterDocument1 pageA Signal Goes Out Via Radio Waves To The Routerapi-473862808No ratings yet
- Ict NetworksDocument23 pagesIct NetworksmihikakashikarNo ratings yet
- COMP 3324: Chapter 1 ReviewDocument41 pagesCOMP 3324: Chapter 1 ReviewIsmail YurtNo ratings yet
- Networking: Network ComponentsDocument8 pagesNetworking: Network ComponentstemNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument55 pagesNetworkingRey Allen TenosoNo ratings yet
- A2 It NotesDocument18 pagesA2 It NotesnyereceoNo ratings yet
- Types of Network: Introduction To Data Communications and NetworkingDocument2 pagesTypes of Network: Introduction To Data Communications and NetworkingleeyiwenNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Introduction - IIDocument35 pagesLec 1 - Introduction - IIHamna YounisNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument21 pagesNetworksShubham waghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks: KVS Regional Office Jaipur - Session 2020-21 Page 14 of 19Document3 pagesIntroduction To Networks: KVS Regional Office Jaipur - Session 2020-21 Page 14 of 19adamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networking.Document40 pagesIntroduction To Networking.Md Fareed JuneidNo ratings yet
- Internet Info GraphicDocument1 pageInternet Info Graphicapi-473870124No ratings yet
- Network Protcols: ThroughputDocument16 pagesNetwork Protcols: Throughputsandhu408No ratings yet
- CN IntroductionDocument74 pagesCN IntroductionSivaraman EswaranNo ratings yet
- Questions From Chapter 7Document4 pagesQuestions From Chapter 7Syeda Wahida SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Internet & World Wide WebDocument30 pagesDifference Between Internet & World Wide Webs sNo ratings yet
- Network Basics ProtocolsDocument5 pagesNetwork Basics ProtocolsChandraksha ShantigoduNo ratings yet
- INTRO To Fundamentals of Internet and Networks PDFDocument40 pagesINTRO To Fundamentals of Internet and Networks PDFSuhail QadirNo ratings yet
- WNF Wlan 3-1Document17 pagesWNF Wlan 3-1oobaa bbbssaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument18 pagesComputer NetworkRaju LalNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks ITMDocument43 pagesComputer Networks ITMGreeshmaNo ratings yet
- Net - Httplistener With HTTPS Support - Stack OverflowDocument13 pagesNet - Httplistener With HTTPS Support - Stack Overflowmuji onoNo ratings yet
- Dell Wyse Management Suite 1.1 QSGDocument58 pagesDell Wyse Management Suite 1.1 QSGsajithNo ratings yet
- 10.1.4.8 Lab - Configure ASA 5505 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDMDocument40 pages10.1.4.8 Lab - Configure ASA 5505 Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDMerojasNo ratings yet
- Fiori ErrorDocument3 pagesFiori ErrorpatiranNo ratings yet
- ProxySG 6.6. Basic Student PDFDocument232 pagesProxySG 6.6. Basic Student PDFfahmiNo ratings yet
- Sonicwall Gen 7 Nsa Series: HighlightsDocument10 pagesSonicwall Gen 7 Nsa Series: HighlightsIT DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Check Point Web Visualization ToolDocument91 pagesCheck Point Web Visualization ToolJohn PeterNo ratings yet
- ViewPower Pro User ManualDocument71 pagesViewPower Pro User ManualMuhammad Aslam ZahidNo ratings yet
- API Mepro Data Package - v1.4Document12 pagesAPI Mepro Data Package - v1.4Ahsan ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Brava! HTML Viewer 4.0 Administration GuideDocument8 pagesBrava! HTML Viewer 4.0 Administration GuideDébora AraújoNo ratings yet
- Ruckus Wireless Zonedirector: Release NotesDocument23 pagesRuckus Wireless Zonedirector: Release NotesredplayNo ratings yet
- PII, PHI, PCI Data HandlingDocument2 pagesPII, PHI, PCI Data HandlingKhaled SaifNo ratings yet
- PHP Whole PDFDocument284 pagesPHP Whole PDFKshitij NayakNo ratings yet
- Headers and PropetiesDocument8 pagesHeaders and PropetiescvcllvNo ratings yet
- CTHSEC-1001-The Future of Transport Layer SecurityDocument28 pagesCTHSEC-1001-The Future of Transport Layer Securityhabib kamaieNo ratings yet
- COIT20262 - Advanced Network Security, Term 2, 2017: Assignment 2Document8 pagesCOIT20262 - Advanced Network Security, Term 2, 2017: Assignment 2Karambir SinghNo ratings yet
- Cyber Threat Assessment-2020-08-01-0001Document20 pagesCyber Threat Assessment-2020-08-01-0001Bon Ber Amad OrofeoNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Ultimate Asp Net Core Web Api 2Nd Edition Marinko Spasojevic Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Ultimate Asp Net Core Web Api 2Nd Edition Marinko Spasojevic Online Ebook All Chapter PDFmichael.thompson124100% (9)
- Scan Report: June 4, 2023Document63 pagesScan Report: June 4, 2023BruhNo ratings yet
- Full Disclosure: The Internet Dark AgeDocument60 pagesFull Disclosure: The Internet Dark Agekitty katNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Product MatrixDocument7 pagesFortinet Product Matrixsaqer_11No ratings yet
- Yealink SIP-T20P DatasheetDocument2 pagesYealink SIP-T20P DatasheetmartinsNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesCybersecurity Interview QuestionsLuke R. Corde100% (1)
- Cloudvue Catalog With Updated SpecsDocument26 pagesCloudvue Catalog With Updated SpecsVarunaviNo ratings yet
- B Tesla-Release-2 5 8Document42 pagesB Tesla-Release-2 5 8Mustafa HussienNo ratings yet
- Forcepoint Ipsec Guide: Forcepoint Web Security CloudDocument36 pagesForcepoint Ipsec Guide: Forcepoint Web Security CloudJorge SuazaNo ratings yet
- Hacking - 101 Hacking Guide 2ndDocument28 pagesHacking - 101 Hacking Guide 2ndKiên PT100% (2)
- Fortigate 200f SeriesDocument10 pagesFortigate 200f SeriesPablo Daniel MiñoNo ratings yet