Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Upper Respiratory Tract: Parts of The Respiratory System
Upper Respiratory Tract: Parts of The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Naomi Lorraine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesThe document summarizes key concepts about the respiratory, circulatory, and cardiovascular systems. It describes the major parts of each system and their functions in transporting oxygen, nutrients, waste, etc. throughout the body. It also discusses common diseases that can affect these systems like asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, hypertension, heart attacks, and more. Genetics concepts are introduced around heredity, traits, genes, DNA, chromosomes, and how traits are inherited. The work of Gregor Mendel, who discovered the laws of inheritance through plant experiments, is also mentioned.
Original Description:
Original Title
SCIENCE_REVIEWER_MT1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key concepts about the respiratory, circulatory, and cardiovascular systems. It describes the major parts of each system and their functions in transporting oxygen, nutrients, waste, etc. throughout the body. It also discusses common diseases that can affect these systems like asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, hypertension, heart attacks, and more. Genetics concepts are introduced around heredity, traits, genes, DNA, chromosomes, and how traits are inherited. The work of Gregor Mendel, who discovered the laws of inheritance through plant experiments, is also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract: Parts of The Respiratory System
Upper Respiratory Tract: Parts of The Respiratory System
Uploaded by
Naomi LorraineThe document summarizes key concepts about the respiratory, circulatory, and cardiovascular systems. It describes the major parts of each system and their functions in transporting oxygen, nutrients, waste, etc. throughout the body. It also discusses common diseases that can affect these systems like asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, hypertension, heart attacks, and more. Genetics concepts are introduced around heredity, traits, genes, DNA, chromosomes, and how traits are inherited. The work of Gregor Mendel, who discovered the laws of inheritance through plant experiments, is also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
jkfm
Respiratory System Bronchitis - Is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes,
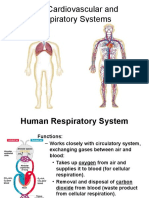
⤷ is the system in the human body that enables us to the airways that carry air to your lungs. It causes a cough
breathe. that often brings up mucus.
Parts of the Respiratory System Four Phases of Human Respiration
Upper Respiratory Tract Breathing or ventilation
- nose External Respiration, which is the exchange of gases
- nasal cavity (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between inhaled air and the
- mouth blood.
- pharynx Internal Respiration, which is the exchange of gases
- larynx (voice box) between the blood and tissue fluids.
Lower Respiratory Tract Cellular Respiration, which is the process of breaking
- trachea (windpipe) sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy.
- main bronchi
- bronchioles Circulatory System
- alveoli (air sacs) ⤷ is a network consisting of blood, blood vessels, and the
- lungs heart. This network supplies tissues in the body with
- diaphragm oxygen and other nutrients, transports hormones, and
removes unnecessary waste products.
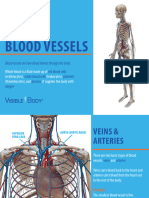
Blood Vessels: Alleys and Highways
⤷ passageway that distribute blood throughout the body
3 Types of Blood Vessels
Arteries: carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart
(except pulmonary arteries)
Veins: carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart
(except pulmonary veins)
Capillaries: fine branching blood vessels that form a
network between the arterioles and venules.
Aorta – largest artery
Vena Cava (Superior and Inferior) – largest veins
Blood: River of Life
⤷ serves as an important role in the maintenance of
Flow of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide internal conditions
Nose → Nasal Cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea
→ Main Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli Components of Blood
Plasma
Ailments of the Respiratory System ↠ pale, yellowish liquid
Asthma - Asthma is defined as a common, chronic ↠ 90% water and 10% soluble substances
respiratory condition that causes difficulty breathing due ↠ transports substances needed by cells and removes
to inflammation of the airways. waste products
Emphysema – Emphysema is a serious respiratory Red Blood Cells or Erythrocytes
disease, those who suffer from emphysema have trouble ↠ biconcave, disc-shaped
exhaling air from their lungs. Cigarette smoke damages ↠ carries oxygen
the air sacs in the lungs to a point where they can no ↠ does not contain nucleus
longer repair themselves. ↠ made in the red marrow of the flat and long bones
Lung Cancer - DNA mutations in the lungs cause White Blood Cells or Leukocytes
irregular cells to multiply and create an uncontrolled ↠ irregular in shape
growth of abnormal cells, or a tumor. ↠ contains nucleus
Pneumonia - Pneumonia is a common lung disease ↠ protects the body against diseases and fights infection
caused by an infection in the air sacs in the lungs. The
infections can be bacterial, viral or fungal.
jkfm
Platelets or Thrombocytes Heredity and Variation
↠ small fragments of cells Genetics: Branch of biology, the study of heredity
↠ made in the bone marrow Heredity: Passing of generic information of traits from
↠ does not contain nucleus parents to offspring
↠ helps in blood clotting Traits: Observable characteristics, determined by genes
in chromosomes
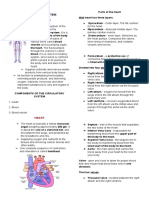
Types of Circulation Chromosomes: Found in the nucleus of a cell, storage
Pulmonary: blood flow between the heart and lungs units of genes, double stranded
Coronary: blood flow within the heart
Systemic: blood flow between the heart and the other Chromatid (each strand)
parts of the body Sister chromatid (both strands)
Connected by a centromere
Cardiovascular Diseases 23 pairs of chromosomes
Heart 22 pairs – traits
Hypertension 23rd pair – sex chromosomes (XX: male XY: female)
↠ High Blood Pressure – “The Silent Killer”
↠ Results from the tightening of the arterioles Gene: Section of DNA that carries information for a
increasing the resistance of blood flow particular trait
↠ Heart muscles may thicken, enlarges, and become DNA/Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Double helix molecule
overworked. that contains generic material, major chemical
Stroke component of chromosomes
↠ Death of brain cells due to lack of oxygen for having Alleles: Different form of the same gene
poor blood flow
Arteriosclerosis/Coronary Heart Disease Example:
↠ Narrowing of the artery because of plaque build-up Gene: eye color
Rheumatic Heart Disease Allele: black, brown, green, etc.
↠ Usually occurs in children a compilation of rheumatic
fever in which the heart valves are damaged Pairs:
Heart Attack Adenine & Thymine
↠ Refers to the damage or death of the heart muscle due Cytosine & Guanine
to a blockage of the coronary artery from a blood clot
Aneurysm
↠ A bulge formed on the arterial wall of the brain that
supplies to the brain
Blood
Hemophilia
↠ The blood does not clot properly; bleeding thus
persists
↠ Caused by the lack of one of the plasma proteins
associated with clotting
Anemia
↠ Is a deficiency of the red blood cells or hemoglobin
(protein molecule in red blood cells) in the blood
Leukemia
↠ Characterized by an abnormal increase in the number CELL
of white blood cells; cancer of the blood
⇓
NUCLEUS
Flow of
⇓
blood
CHROMOSOME
⇓
DNA
⇓
BASE PAIR
⇓
GENE
jkfm
Karyotyping Ways how Traits are inherited
↠ used to determine number and size of chromosome 1. Controlled by a single gene but with two
↠ used to detect chromosomal oberration (changes in contrasting alleles
the chromosomes) 2. Controlled by a single gene but with two
multiple alleles
Genetic Mutations 3. Controlled by several genes interacting to one
another
Gregor Johann Mendel
- Raised on a farm and understood the value of
plant breeding
- At 21, entered priesthood and studied plant
breeding in a monastery in the Czech Republic
- Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants
(28,000)
Mendel’s Three Laws of Inheritance
Formation of gametes (sex cells): Where the generic
information of an individual starts
Cell division of gametes: to maintain the chromosome
number of organisms
Somatic Cells (Body Cells) Sperm and Egg Cells
Diploid (2n) Haploid (n)
Produced by mitosis Produced by meiosis Genetic Crosses using the Punnett Square
Monohybrid Cross: cross involving a single trait
Dihybrid Cross: cross involving two traits
During fertilization, the haploid cells become diploid Genotype: gene combination
cells Phenotype: physical feature
Homologous Chromosomes: structurally alike Monohybrid Cross
chromosomes
Spermatogenesis Oogenesis
Production of egg cells or
Production of sperm
ova
Takes place in the outer
Takes place in the testes
region of the ovaries
Starts to puberty until Starts during fetal
old age development Dihybrid Cross
Crossing Over: exchange of generic material between
homologous chromosomes
Variation: result of the transfer of similar/different
alleles of traits, from parents to offspring
You might also like
- 500 Mcqs Surgery and RadiologyDocument66 pages500 Mcqs Surgery and RadiologyJihad Anad81% (59)
- BTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesBTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Cardiovascular SystemMPNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Test QuestionsDocument20 pagesAbdomen Test QuestionsRuth AlooNo ratings yet
- Emergency in DermatologyDocument47 pagesEmergency in DermatologyKenzo Adhi WiranataNo ratings yet
- Science 1.1Document42 pagesScience 1.1Ina SuzaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System FunctionsDocument23 pagesHuman Respiratory System FunctionsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer 2018Document3 pagesSci Reviewer 2018Sai KabilingNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Docx2Document8 pagesScience Reviewer - Docx2Vaughn Siegfried FuertezNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document5 pagesNotes 1kwekNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument38 pagesCirculatory SystemNilesh SahaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - CirculatoryDocument5 pagesModule 5 - CirculatoryRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ReviewerDocument7 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewerVictoria Ellex TiomicoNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LEC Module 3Document8 pagesPMLS 2 LEC Module 3Peach DaquiriNo ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation PDFDocument47 pagesBlood and Circulation PDFeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Hand-OutDocument3 pagesRespiratory Hand-Outstilla lonerNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumansDocument19 pages3.2.2 Blood Circulatory System in HumanslovenialawNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Organisms: Circulatory SystemDocument36 pagesMulticellular Organisms: Circulatory SystemSpidervaitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Transport in AnimalDocument46 pagesChapter 9. Transport in AnimalCharxd zzNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerWayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Transport in Human (Notes)Document21 pagesTopic 11 Transport in Human (Notes)nizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1qprelimsDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 1qprelimsAlyanna SagcalNo ratings yet
- Double CirculationDocument3 pagesDouble Circulationmubasherkatbar562No ratings yet
- Topic 7: Transport in HumansDocument19 pagesTopic 7: Transport in HumansAmyrul Darwisy ZafranNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Pulmonary EmbolismDocument12 pagesCase Study On Pulmonary EmbolismJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System: Ronmar T. Riňo Abegail Bersamin Maila C. TamondongKelly Troy Alano100% (13)
- Class 9-Biology-Lesson 8-Circulatory System3Document7 pagesClass 9-Biology-Lesson 8-Circulatory System3Shlok JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy L9 PPDocument22 pagesAnatomy L9 PPTara WifaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Study Guides - The Respiratory System and The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesStudy Guides - The Respiratory System and The Circulatory SystemMara R. VergaraNo ratings yet
- The Mass Transport in AnimalsDocument45 pagesThe Mass Transport in AnimalsCereal KillerNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 Reviewer q1-4Document8 pagesSCIENCE 9 Reviewer q1-4garciathomas0210No ratings yet
- Unit10Chapter37Respiration Circulation Excretion 2Document26 pagesUnit10Chapter37Respiration Circulation Excretion 2Jaya TurnerNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Blood VesselsDocument20 pagesVisibleBody Blood VesselscascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyRoger RonconiNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Human Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesLecture On Human Circulatory SystemolandiolettyNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument6 pagesTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument30 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportElaine McDholicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 KSSM FORM 4 BIODocument12 pagesChapter 10 KSSM FORM 4 BIOYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument42 pagesBlood CirculationAshu kumar100% (1)
- Endocardial Tubes EpimyocardiumDocument3 pagesEndocardial Tubes EpimyocardiumAngel IsalesNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B byDocument33 pagesThe Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B bykaranarorarafaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDocument16 pagesGrade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDane Gian Angelo TanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10Document9 pagesBiology Chapter 10wongchengen2006No ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument5 pagesBlood VesselsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Haematology. BaharDocument14 pagesHaematology. BaharJustin OmwengaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 First Quarter ALL NotesDocument9 pagesScience 9 First Quarter ALL Notesliannicole884No ratings yet
- Body Fluids & RespirationDocument1 pageBody Fluids & RespirationNabinNo ratings yet
- Ciculatory SystemDocument21 pagesCiculatory SystemSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonNo ratings yet
- Student Notes - Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesStudent Notes - Circulatory SystemJanith VimukthiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerfluyuuyyyNo ratings yet
- Life's Transport, Exchange and Defense SystemsDocument7 pagesLife's Transport, Exchange and Defense SystemshjNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System What Is A Circulatory System?: HeartDocument4 pagesCirculatory System What Is A Circulatory System?: HeartVianney LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BloodDocument85 pagesCardiovascular System BloodEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals: The Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesTransport in Animals: The Circulatory SystemAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument10 pagesTransport in Animalswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Specimen Collection GuidelinesDocument16 pagesMicrobiology Specimen Collection Guidelines1DaddictNo ratings yet
- Lab Lesson 16: The Kato-Katz Technique For Helminths EggsDocument5 pagesLab Lesson 16: The Kato-Katz Technique For Helminths EggsRalph B. BarsanalinaNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsDocument20 pagesHigh-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The SkinDocument22 pagesAssessing The Skinjasnate84No ratings yet
- 30 Dec JoBs BY KHALIQ HASSAN - Watermarked PDFDocument4 pages30 Dec JoBs BY KHALIQ HASSAN - Watermarked PDFKamran Talpur100% (1)
- Dr. Cahyarini - Ppi TB RSP KarsDocument44 pagesDr. Cahyarini - Ppi TB RSP KarsMohammad SutamiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 6asDocument15 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9 6askilatmarielleann.cte.cpcNo ratings yet
- CHD2 - DR Shirley L ADocument74 pagesCHD2 - DR Shirley L ARaihan Luthfi100% (1)
- Soya-Based Infant FormulaDocument2 pagesSoya-Based Infant FormulaVegan Future100% (2)
- EritrositDocument12 pagesEritrositNatasya HerinNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Urine FormationDocument19 pagesKidney and Urine FormationXee JayNo ratings yet
- Genetic Improvement of Buffaloes For Milk Production: R.K. SethiDocument11 pagesGenetic Improvement of Buffaloes For Milk Production: R.K. Sethik.srikiran5427No ratings yet
- Anatomy of TH Brain: BrainstemDocument2 pagesAnatomy of TH Brain: BrainstemHanna RamosNo ratings yet
- DLL AgricultureDocument15 pagesDLL AgricultureAntartica AntarticaNo ratings yet
- D100 of Tricks, Puzzles and RiddlesDocument4 pagesD100 of Tricks, Puzzles and RiddlesJohn WilksNo ratings yet
- DRILLING #3 Classification of Living ThingDocument6 pagesDRILLING #3 Classification of Living ThingMuhammad MunawarNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument103 pagesBirth InjuriesAruna ApNo ratings yet
- Salivary SecretionDocument23 pagesSalivary SecretionSamridhi SinghNo ratings yet
- 10 Importance of Clean WaterDocument3 pages10 Importance of Clean Waterchelci14No ratings yet
- For External Review: Draft Good Practice Note: Improving Animal Welfare in Livestock OperationsDocument37 pagesFor External Review: Draft Good Practice Note: Improving Animal Welfare in Livestock OperationsIFC SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Basic Haematological Techniques: Carol Briggs - Barbara J. BainDocument1 pageBasic Haematological Techniques: Carol Briggs - Barbara J. BainRahmat SatriadiNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Vertebrate Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesStructure of The Vertebrate Nervous SystemMadhavan MbbsNo ratings yet
- Breathing Affects Our Thoughts and EmotionsDocument127 pagesBreathing Affects Our Thoughts and EmotionsarbetaNo ratings yet
- Bissonnette (2008)Document7 pagesBissonnette (2008)swagatarcNo ratings yet
- GURPS Hit Locations OnlyDocument1 pageGURPS Hit Locations OnlyJames GeustNo ratings yet
- Scientific Saddle FittingDocument25 pagesScientific Saddle Fittinginventor6623No ratings yet
- Assessment of The AbdomenDocument6 pagesAssessment of The Abdomenmalyn1218No ratings yet