Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generation First Second Third Fourth Fifth Year
Generation First Second Third Fourth Fifth Year
Uploaded by
keerthana vijayakumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the five generations of computers from 1942 to the present. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were very large, expensive, and consumed significant energy. The second generation introduced transistors, were smaller and faster than the first. The third generation saw the introduction of integrated circuits and microprocessors, making computers cheaper, more accurate, and portable. The fourth generation featured microcomputers and microprocessors, while the fifth generation is characterized by super large scale integration, artificial intelligence, and examples like laptops and mobile phones.
Original Description:
5 generation of computers in tabulation
Original Title
Generation of computers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the five generations of computers from 1942 to the present. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were very large, expensive, and consumed significant energy. The second generation introduced transistors, were smaller and faster than the first. The third generation saw the introduction of integrated circuits and microprocessors, making computers cheaper, more accurate, and portable. The fourth generation featured microcomputers and microprocessors, while the fifth generation is characterized by super large scale integration, artificial intelligence, and examples like laptops and mobile phones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesGeneration First Second Third Fourth Fifth Year
Generation First Second Third Fourth Fifth Year
Uploaded by
keerthana vijayakumarThe document summarizes the five generations of computers from 1942 to the present. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were very large, expensive, and consumed significant energy. The second generation introduced transistors, were smaller and faster than the first. The third generation saw the introduction of integrated circuits and microprocessors, making computers cheaper, more accurate, and portable. The fourth generation featured microcomputers and microprocessors, while the fifth generation is characterized by super large scale integration, artificial intelligence, and examples like laptops and mobile phones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
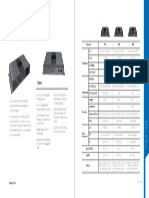
Generation of computers
Generation First Second Third Fourth Fifth
Year 1942-1955 1955-1964 1964-1975 1975-1989 1989-now
Super Large
Integrated circuits Scale
Components Vacuum tubes Transistors Microprocessor chip
(IC) Integration
(SLSI)
Millions of
Nanoseconds &
Speed milliseconds Microseconds nanoseconds instruction per
Picoseconds
second
Punched Monitors,
i/o components Punched cards monitors, printers Monitors, printers
cards printers
Floppy disk,
Magnetic hard disk,
Storage Devices Magnetic tape Magnetic Tape Floppy disk, hard disk
drums optical storage,
USB
Natural
High level language
Programming Machine Assembly level High level language Language like
like BASIC,
Languages Language language like C, C++ PROLOG,
PASCAL
SQL etc
Smaller than 1st Much Smaller than
Size Very Large Micro computers Tiny computers
generation Previous
Accuracy Less High than 1st High than previous More improved High
Portability Non-portable Better than 1st Better than previous Portable Hand held
Examples ENIAC, IBM 400, IBM IBM 360, IBM 370, IBM 3033, CRAY- 1 LAPTOP,
UNIVAC, IBM 1600, UNIVAC III UNIVAC 9000 Mobile phones
705 etc
Available
only Heat reduced than Less expensive Small size Artificial
Advantages
component 1st Better accuracy cheaper Intelligence
those days
Consume Cooling system
more energy, required Air conditioning Latest technology is Some faults
Disadvantages
low speed Costly and non- required required are there
High cost versatile
ROBOTS
You might also like
- KSPTDocument3 pagesKSPTSherin Manoj75% (4)
- Signage Design Manual V23-LAMS SectionDocument6 pagesSignage Design Manual V23-LAMS Sectionmmcdaid13No ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To ComputerDocument13 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To ComputerPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.0Document3 pagesAssignment 1.0Riyad HasanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Tubes: Main Electronic ComponentDocument1 pageVacuum Tubes: Main Electronic Componentalqryshybas963No ratings yet
- Generation of ComputersDocument1 pageGeneration of ComputersSuraj BhattNo ratings yet
- CRM FinalDocument10 pagesCRM Finaljaiswaljyoti148No ratings yet
- L2 Ict - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision DoneDocument8 pagesL2 Ict - UNIT 2: Technology Systems Revision Template: Subject Notes Revision Doneapi-448604259No ratings yet
- Zkteco Europe Zpad Plus 4g LeafletDocument2 pagesZkteco Europe Zpad Plus 4g LeafletKamal KannanNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheets: Learning Task 3Document9 pagesAnswer Sheets: Learning Task 3Zyrille MojicaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.0Document3 pagesAssignment 1.0Riyad HasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.0Document3 pagesAssignment 1.0Riyad HasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3-It Hardware and SoftwareDocument78 pagesLecture-3-It Hardware and SoftwarerizaNo ratings yet
- Computer SystemDocument16 pagesComputer Systemgrace bulawitNo ratings yet
- Office Productivity Las Week 3Document3 pagesOffice Productivity Las Week 3Erizza PastorNo ratings yet
- GenerationsDocument25 pagesGenerationscharan kaurNo ratings yet
- Computer Book - Klgfmtoi0q9et6zz1kpwDocument128 pagesComputer Book - Klgfmtoi0q9et6zz1kpwvamsikrishna.cNo ratings yet
- Ecdl v5.0 Module 1 Windows Vista OutlineDocument2 pagesEcdl v5.0 Module 1 Windows Vista OutlineTirta ChairulNo ratings yet
- Arihant CCC Courses - RemovedDocument138 pagesArihant CCC Courses - RemovedSPEAK UP UniversalNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 01Document1 pageMind Map 01Dr. Suna PaanaNo ratings yet
- مذكرات الرخصة الدولية باللغة الانجليزيةDocument94 pagesمذكرات الرخصة الدولية باللغة الانجليزيةMohammed Abd-elatyNo ratings yet
- ICT - Chapter 1 - Revision NotesDocument8 pagesICT - Chapter 1 - Revision Notesjoshua.ananth-smchsNo ratings yet
- Draft SylabbusDocument146 pagesDraft SylabbusKiambisNo ratings yet
- Dict001 Fundamentals in Ict: Erangi Piumika BSC Mis (SP)Document60 pagesDict001 Fundamentals in Ict: Erangi Piumika BSC Mis (SP)Ashani LakshikaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document47 pagesCH 1abdiimohammedadamNo ratings yet
- JzbxusDocument3 pagesJzbxusDipan SahooNo ratings yet
- BR Imc2000 Imc2500Document4 pagesBR Imc2000 Imc2500Aivars LīpenītsNo ratings yet
- Atsel HMI SP113 DatasheetDocument3 pagesAtsel HMI SP113 Datasheetmetwar ankitNo ratings yet
- Generations of ComputersDocument10 pagesGenerations of Computershassansagheer894No ratings yet
- Generations of ComputerDocument2 pagesGenerations of Computermahambadar786No ratings yet
- Advanced ProcessorsDocument31 pagesAdvanced ProcessorsPraveen GovindNo ratings yet
- ComputersDocument86 pagesComputersmahesh jagadaleNo ratings yet
- Computer Terminology ICET Exam Updated 8th July 2022Document60 pagesComputer Terminology ICET Exam Updated 8th July 2022RishwaNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi Dalam PendidikanDocument52 pagesAplikasi Teknologi Informasi Dalam PendidikanTri RahayuNo ratings yet
- CZUR ET Series User Manual - English-20220211 ADocument15 pagesCZUR ET Series User Manual - English-20220211 AasdfafdsgNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems - CS 2364Document97 pagesEmbedded Systems - CS 2364S_Gunasekar100% (1)
- Copnotes 1Document32 pagesCopnotes 1api-554428889No ratings yet
- 2.1 Input Devices and Their UsesDocument12 pages2.1 Input Devices and Their UsesDhrisha GadaNo ratings yet
- Design of Embedded SystemsDocument44 pagesDesign of Embedded SystemssivajiNo ratings yet
- ICT 2nd Lesson Grade 1Document13 pagesICT 2nd Lesson Grade 1vtgrules105No ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument4 pagesComputer ScienceTariro h j HamadziripiNo ratings yet
- Computer PDFDocument49 pagesComputer PDFPratyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Employability Skill Unit - I It Literacy: Short Form - Long FormDocument19 pagesEmployability Skill Unit - I It Literacy: Short Form - Long FormAkAY'sNo ratings yet
- Ricoh IM 2702 BrochureDocument4 pagesRicoh IM 2702 BrochureMandylaNo ratings yet
- 1 1 5 How-Do-We-Enable-Tinyml 3Document53 pages1 1 5 How-Do-We-Enable-Tinyml 3MumtazNo ratings yet
- Ready Recknor - Grade IX - CA - 2020-21Document109 pagesReady Recknor - Grade IX - CA - 2020-21HALOLLOLNo ratings yet
- Diploma of Intel 12 Gen Laptop Chiplevel Course New Time TableDocument8 pagesDiploma of Intel 12 Gen Laptop Chiplevel Course New Time TabletekleNo ratings yet
- IIT Blackfin PresentationDocument121 pagesIIT Blackfin Presentationjeevan432No ratings yet
- HarewareDocument44 pagesHarewareBBA Jnu AIS 14thNo ratings yet
- Embedded System IntroductionDocument23 pagesEmbedded System IntroductionVinayagam MariappanNo ratings yet
- Smart WarehouseDocument18 pagesSmart Warehousebigumbara1981No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Computer 101: Health InformaticsCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Computer: Generations of Computer First Generation Technology: FeaturesDocument5 pagesComputer: Generations of Computer First Generation Technology: FeaturesAshraf JamalNo ratings yet
- Taurus BoxDocument1 pageTaurus BoxWalefi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Install Computer Systems and Networks EditedDocument101 pagesInstall Computer Systems and Networks EditedviptoneytNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals by Anita GoelDocument5 pagesComputer Fundamentals by Anita GoelSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 90548S WPAN HomeRF TutorialDocument27 pages90548S WPAN HomeRF TutorialFanirisoa SylvieNo ratings yet
- Visi Smart Campus 2.1Document34 pagesVisi Smart Campus 2.1Junita RianyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Keyboard BBDocument16 pagesVirtual Keyboard BBWIKNo ratings yet
- 03 Mind Map TheoryDocument24 pages03 Mind Map TheorylinacathoedspruithighNo ratings yet
- Chapter1a Embedded System IntroDocument19 pagesChapter1a Embedded System IntroSorin NicolaNo ratings yet
- Plainchant For Children-1Document46 pagesPlainchant For Children-1mrsalex055581No ratings yet
- Furashadii HargeysaDocument9 pagesFurashadii HargeysaGaryaqaan Muuse YuusufNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument32 pagesComputer Softwaremarieta bandialaNo ratings yet
- Navarathri Stotrams CompilationDocument77 pagesNavarathri Stotrams CompilationvlaxmananNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument3 pagesDownloadBruno Soares de CastroNo ratings yet
- English Starters Sample Statement of Results 1Document2 pagesEnglish Starters Sample Statement of Results 1MNo ratings yet
- Khoso Soonhan: Resident Address:-Postal AddressDocument3 pagesKhoso Soonhan: Resident Address:-Postal AddressSoonhanNo ratings yet
- Singular and Plural NounsDocument10 pagesSingular and Plural NounsIrina MBNo ratings yet
- Instant Words - Instant VocabularyDocument46 pagesInstant Words - Instant VocabularyMarisol GarcíaNo ratings yet
- C1 Olap Quick StartDocument80 pagesC1 Olap Quick StarthiepltsdsgthhNo ratings yet
- A Listening Lesson Plan in English IVDocument4 pagesA Listening Lesson Plan in English IVSara Danica Herjas Ariza100% (1)
- Displaying The Directory Tree Using The TreeView Control in VBNETDocument8 pagesDisplaying The Directory Tree Using The TreeView Control in VBNETapi-3813141100% (3)
- Logical PuzzicalDocument16 pagesLogical PuzzicalSamarth PawaskarNo ratings yet
- Spanish BrothersDocument284 pagesSpanish BrothersPaul SimonNo ratings yet
- Postmortem Y5 2017Document2 pagesPostmortem Y5 2017Shakti GanesNo ratings yet
- Own It 3 Unit7 W1Document1 pageOwn It 3 Unit7 W1Gaye ColakNo ratings yet
- LPDocument3 pagesLPKimberlyAnneAlbaciteBabantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document38 pagesChapter 1-3Lara SeptiaNo ratings yet
- Serafin Talagtag (Resume)Document2 pagesSerafin Talagtag (Resume)Unified Mechnical Engineering nad Technology SocietyNo ratings yet
- Assumption of Normality Dr. Azadeh AsgariDocument27 pagesAssumption of Normality Dr. Azadeh AsgariDr. Azadeh AsgariNo ratings yet
- Early New Orleans JazzDocument8 pagesEarly New Orleans JazzDiana Fox100% (1)
- Multi - Dimensional Fuzzy ReasoningDocument13 pagesMulti - Dimensional Fuzzy ReasoningEdgar Maya PerezNo ratings yet
- L3new Comp ASyntDocument77 pagesL3new Comp ASyntmolalign tekalignNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Introduction To PythonDocument11 pagesLecture 8 Introduction To PythonMOMEKEM KUEFOUET DUREL HERVANENo ratings yet
- Grammar Mid-Sem Test Practice: Set 2 Part ADocument5 pagesGrammar Mid-Sem Test Practice: Set 2 Part AAuni RazaliNo ratings yet
- Numerical Reasoning Test SamplesDocument10 pagesNumerical Reasoning Test Samplesemmsadelaine0% (1)
- Let' S Celebrate! Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLet' S Celebrate! Lesson PlanStelli Oana100% (1)