Professional Documents
Culture Documents
28 - Performance Enhancement Sheet
28 - Performance Enhancement Sheet
Uploaded by
Naveen GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
28 - Performance Enhancement Sheet
28 - Performance Enhancement Sheet
Uploaded by
Naveen GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
Biomentors classes online, Mumbai
Performance Enhancement Sheet- 28
Chemical bonding and molecular structure
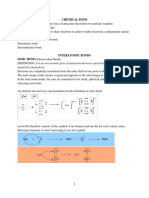
Ionic bond
Ionic compound bond formed between elements with comparatively low ionization enthalpies and
elements with comparatively high negative value of electron gain enthalpy
Properties of ionic compounds
1. Crystal structure
The crystalline ionic compound have well defined crystal structure or crystal lattice eg. In NaCl each
𝑁𝑎+ is surrounded by six 𝐶𝑙 − ions and vice versa
2.Melting and boiling point
Ionic compound have high melting point and boiling point due to powerful electrostatic force
between ions
3.Solubility
They are generally soluble in polar solvents(having dielectric constant). The solubility of ionic
compound decreases with increases in covalent character of ionic compounds. It is govern by
a. Lattice energy: More the lattice energy, lesser is the solubility, e.g. sulphates and
phosphates of Ba and Sr are insoluble in water due to high lattice energy.
b. Heat of hydration: More the heat of hydration, more is the solubility.
4.Electrical conductivity
In a solid state they do not conduct electricity since there is no free movement of electrons but in
molten state and in solution they conduct electricity
5. Isomorphism
𝑁𝑎𝐹 and 𝑀𝑔𝑂 are isomorphous due to similar electronic structure
𝑁𝑎+ 𝐹 − 𝑀𝑔 2+ 𝑂2−
2,8 2,8 2,8 2,8
Similarly K2S and CaCl2 are isomorphous
𝐾 + 𝑆 2− 𝐾 + 𝐶𝑙 − 𝐶𝑎2+ 𝐶𝑙 −
2,8,8 2,8,8 2,8,8 2,8,8 2,8,8 2,8,8
You might also like
- Unit 1Document35 pagesUnit 1Tangent ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Structure of MoleculesDocument11 pagesStructure of MoleculesalxsxxdNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingAsilah AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument22 pagesChemical Bondakuakwartemaamensah123No ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular ShapeDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Shapeshivakafle039No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding IIDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding IIdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 1105Document51 pagesChemical Bond 1105Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding76241717abelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding1Document35 pagesChemical Bonding1drchewieNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument87 pagesChemical BondingMichael Dela Torre Diaz Jr.No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- SGC Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesSGC Chemical Bondingcassandraolmido18No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Document26 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Gautam SinghNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument14 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- F&Q - Segundo Examen - Presentación de IdoyaDocument15 pagesF&Q - Segundo Examen - Presentación de IdoyaSamuel Echeverría MuroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 2Document32 pagesChemical Bond 2Yak Raj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document26 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Bhupinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYTES Mechanics AssignmentDocument4 pagesELECTROLYTES Mechanics Assignmentbighnesh.2006.singhNo ratings yet
- Revision Chem Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesRevision Chem Bonding Notesrania samirNo ratings yet
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocument4 pagesIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument39 pagesIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Ib CHEM Topic 4 Chemical BondingDocument45 pagesIb CHEM Topic 4 Chemical Bondingyasser khairyNo ratings yet
- HO-Chemical-BondsDocument3 pagesHO-Chemical-BondsbiswektylerNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Two Classes of Compounds: Covalent Bonding Between Hydrogen Atomssince Each Hydrogen Atom Has OneDocument2 pagesTwo Classes of Compounds: Covalent Bonding Between Hydrogen Atomssince Each Hydrogen Atom Has OnetaeNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Chemical Bonding (Chem +1)Document52 pagesCH 3. Chemical Bonding (Chem +1)nitinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part1Document30 pagesUnit 1 Part1Gem khyle VelascoNo ratings yet
- Properties of BondsDocument36 pagesProperties of BondsPaulNo ratings yet
- Matthew McClain Lab Report Period 4Document4 pagesMatthew McClain Lab Report Period 4mmcclain2014No ratings yet
- Structure & BondingDocument30 pagesStructure & Bondingytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument51 pagesChemical BondingAzariah GobinNo ratings yet
- VBT MotDocument23 pagesVBT Motskyanan592No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document31 pagesModule 01Pacha Praneeth35No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument40 pagesChemical BondingabuhurairabscNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Igcses Chemistry SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Igcses Chemistry Summarytaliaamjad771No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFDocument110 pagesChemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdDocument49 pagesEnc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdSri VanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- L7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesDocument19 pagesL7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- 8 Thhourlab 9 BakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderDocument5 pages8 Thhourlab 9 Bakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderapi-297169088No ratings yet
- BondingDocument25 pagesBondingnya72505No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Is A Type ofDocument5 pagesIonic Bonding Is A Type ofNadya IkaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsShreyas KamathNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Chemical BondinG EDDocument77 pagesChapter Two Chemical BondinG EDnasec38602No ratings yet
- Electron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingDocument50 pagesElectron Dot Diagrams / Lewis Structures: Atom and Covalent Compound DiagrammingJoan Clarice CorlaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet