Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V Characteristic Around The Quiescent Point Is An Accurate Estimation of The Forward Resistance R of The Diode
V Characteristic Around The Quiescent Point Is An Accurate Estimation of The Forward Resistance R of The Diode
Uploaded by
Sniper ArcheryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V Characteristic Around The Quiescent Point Is An Accurate Estimation of The Forward Resistance R of The Diode
V Characteristic Around The Quiescent Point Is An Accurate Estimation of The Forward Resistance R of The Diode
Uploaded by
Sniper ArcheryCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electrical Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
ESc 102 Home Assignment #8 Assigned: 7.9.18
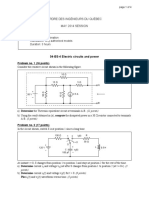
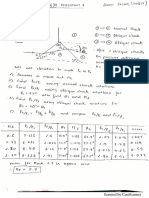
1. In the circuit shown in Fig.1, plot V0 as a function of Vi (for 0 +
Vi 5 V), highlighting all salient features. For both diodes, use + 20
D1
D2
the 2nd-order diode model with V = 0.6 V and rF = 10 . Vi 50 V0
+
1.5 V
– –
2. The diode D used in the circuit shown in Fig.2 has I0 = 1015 A. –
The input signal vs has both dc and ac components, and is given
Fig.1
by vs = [5 + 0.1sin(t)] V. First, using iterations, find the dc
quiescent current flowing through the diode and the dc quiescent
voltage appearing across it. What is the dc power dissipated by
1 k
the diode? Then, determine the peak-to-peak value of the ac +
diode current. Note that the inverse slope of the diode ID-VD vs D
characteristic around the quiescent point is an accurate
–
estimation of the forward resistance rF of the diode.
3. In a simple half wave rectifier circuit as shown in Fig.2 (with the diode D and Fig.2
the 1 k resistor exchanging their positions, and the output being taken across
the 1 k resistor), using 1st-order diode model (with V = 0.6 V), and assuming
vs to be a pure sinusoid, determine its rms value, so that conduction should begin during each positive
half cycle at an angle no greater than 5. Determine the average value of the output voltage under this
condition. Also, find the peak and average values of the current flowing through the load (i.e., the 1
k resistor).
4. In an unregulated power supply using bridge rectifiers, as shown in Fig.3, we need to develop V0 = 5
V across an 8 load (RL), with no more than 5% ripple present in V0. Determine: i) the transformer
turns ratio N, ii) the value of the filter capacitor C, iii) the minimum breakdown voltage of the diodes
(using a safety factor of 2), and iv) the peak and average diode currents (compare these values with the
dc load current). Use first order diode model with V = 0.6 V. This is a very primitive design of a
power pack for your electronic appliances.
5. Sketch the voltage transfer characteristic (i.e., v0 versus instantaneous amplitude of vs) for the circuit
shown in Fig.4. Assume vs = 10sin(t) V, and use 2nd order diode model (V = 0.6 V and rF = 20 ).
6. Determine the minimum and maximum values of the series resistor used in a Zener regulator circuit,
whose output voltage is to be 25 V, the input voltage varies between 35 V and 40 V, and the maximum
load current is 75 mA. The minimum and maximum current ratings of the Zener is 10 mA and 250 mA
respectively. Neglect Zener resistance rZ.
+
+
10 +
D1 D2 +
230 V D
50 Hz vs 10 v0
D4 D3 + +
– – 4V
– C RL V0 – –
N:1
–
Fig.4
Fig.3
You might also like
- Assignment 1 - Analog CircuitDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Analog CircuitSV MNo ratings yet
- Midterm1 F2021Document2 pagesMidterm1 F202160 beatsNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4-1Document4 pagesSheet 4-1bodesaid2002No ratings yet
- DiodeDocument198 pagesDiodeAamir AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DiodeDocument246 pagesChapter 3 Diodeabdala67No ratings yet
- 04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014Document4 pages04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014LuisAranaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab Junction Diode Basics I. PurposeDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab Junction Diode Basics I. Purposekstu1112No ratings yet
- EE230 Lab 5Document3 pagesEE230 Lab 5AnnirudhNo ratings yet
- 3 DiodeRectifiers HLDocument10 pages3 DiodeRectifiers HLRimsha pervaizNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Homework ProblemsDocument21 pagesSolutions of Homework ProblemsHusni MustafaNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesPurpose: Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsshahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Saksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Analog Crash Course Workbook GaDocument54 pagesAnalog Crash Course Workbook GaAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1-Analog Diode Application CircuitsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1-Analog Diode Application Circuitsnaim yuslieNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2013 SolutionDocument5 pagesMidterm 2013 SolutionArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Lab3 2015Document6 pagesLab3 2015MichNo ratings yet
- Review Problems SolutionsDocument6 pagesReview Problems SolutionsDimitrios PanaNo ratings yet
- ConverterDocument17 pagesConverterJimmy TanNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics: I-TheoryDocument4 pagesDiode Characteristics: I-TheoryShubham PatelNo ratings yet
- Universidad Politecnica Salesiana. Laboratorio Analogica: Practica 5: Análisis de Característica de Un Diodo A SilicioDocument3 pagesUniversidad Politecnica Salesiana. Laboratorio Analogica: Practica 5: Análisis de Característica de Un Diodo A SiliciojefersonNo ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment #2 - Key PDFDocument11 pagesElectronics Assignment #2 - Key PDFKhairi SalehNo ratings yet
- Temasek Polytechnic School of Engineering AY 2015/2016 TERM TEST (Apr Semester)Document6 pagesTemasek Polytechnic School of Engineering AY 2015/2016 TERM TEST (Apr Semester)Justin NgNo ratings yet
- 1 DiodesDocument28 pages1 DiodesiamthebasselNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab Report 4Document5 pagesEdc Lab Report 4aneesNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurDocument27 pagesEsc201: Introduction To Electronics: Shilpi Gupta Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurShreyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document8 pagesLecture 8Centvie Joie F. AlbeosNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryArda Deniz EryiğitNo ratings yet
- Assignments 5Document4 pagesAssignments 5Ahmed Jamal100% (1)
- ELTR 270 - Diode Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument33 pagesELTR 270 - Diode Practice Problems and SolutionsKirk100% (1)
- Transformer Equivalent CircuitDocument14 pagesTransformer Equivalent CircuitJeans GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Final Examination: Tuesday, June 29, 2004 Time: 3:30 - 6:30 PMDocument6 pagesENGG 325 - Electric Circuits and Systems Final Examination: Tuesday, June 29, 2004 Time: 3:30 - 6:30 PMTaha EtemNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Laws: Experiment No.3 Aim of Experiment ApparatusDocument4 pagesKirchhoff's Laws: Experiment No.3 Aim of Experiment Apparatusfatima qasimNo ratings yet
- Beee Unit - 05Document75 pagesBeee Unit - 05sidduanji1431No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document10 pagesLecture 1Dr. Saad Saffah HresheeNo ratings yet
- Buku DiodaDocument8 pagesBuku Diodanaru_chan1003No ratings yet
- L16Document41 pagesL16Deepti SaraswatNo ratings yet
- 11.types of DiodesDocument13 pages11.types of DiodesAmmar HussamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instrumentation: Experiment 8: DiodesDocument55 pagesElectronic Instrumentation: Experiment 8: DiodesCharie MaeNo ratings yet
- Colour Coded ResistorsDocument28 pagesColour Coded ResistorsEd JudgeNo ratings yet
- 03 AE Applications DiodesDocument29 pages03 AE Applications Diodesrakibnabil800No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperDocument38 pagesChapter 3 - Rectifier Filter ClipperfaizalabdullahNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Document5 pagesTutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Arthur MoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 DiodeDocument246 pagesChapter 3 DiodeGabriel Medina EncaladaNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicDocument2 pagesBasic ElectronicNayab AlamNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of Puerto Rico Mechanical Engineering Department Mechatronics ME-5250 Professor: Sandra L. OrdóñezDocument15 pagesPolytechnic University of Puerto Rico Mechanical Engineering Department Mechatronics ME-5250 Professor: Sandra L. OrdóñezGabriel PachecoNo ratings yet
- 2020 TestDocument8 pages2020 Testhenry.yapeterNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab ManualRohan KatkamNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 2 - Diode Characteristicsdonatello84100% (3)
- 21pwmct0790 Lab 2 EPDDocument8 pages21pwmct0790 Lab 2 EPDSinan MasoomNo ratings yet
- # 1 (7 Problems)Document8 pages# 1 (7 Problems)wl0o0dyNo ratings yet
- S D B A: Emiconductor Iodes IN Asic PplicationsDocument9 pagesS D B A: Emiconductor Iodes IN Asic PplicationsNafi SiamNo ratings yet
- 電子學一 第三章Document24 pages電子學一 第三章電機二 12黃聖祐No ratings yet
- Clipper Clamper CircuitsDocument15 pagesClipper Clamper CircuitsAnilaSaghirNo ratings yet
- Circuits and Electronics Chapter 3 and NotesDocument49 pagesCircuits and Electronics Chapter 3 and NotesDr. S. DasNo ratings yet
- Diode Lecture MineDocument34 pagesDiode Lecture MineSaud AloufiNo ratings yet
- EG1108 T6 - Ans PDFDocument8 pagesEG1108 T6 - Ans PDFLeong ssNo ratings yet
- Lecture 40 OF PHY101 Virtual UniversityDocument4 pagesLecture 40 OF PHY101 Virtual UniversityHamza IhsanNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 Diode Apps LL-RectifiersDocument32 pagesLecture-2 Diode Apps LL-RectifiersMister X100% (1)
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsDocument11 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsTalha RiazNo ratings yet
- JEE (MAIN) - 2015 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - ADocument28 pagesJEE (MAIN) - 2015 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - ASniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- IITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - EDocument22 pagesIITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - ESniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- IITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - E Solutions Part-A: Physics 1. Correct OptionDocument48 pagesIITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - E Solutions Part-A: Physics 1. Correct OptionSniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE - 2012 Paper - 1Document15 pagesIIT JEE - 2012 Paper - 1Sniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- IITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - EDocument22 pagesIITJEE (MAIN) - 2014 (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics) Code - ESniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Part A: ChemistryDocument26 pagesPart A: ChemistrySniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- AE311Document8 pagesAE311Sniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- H"' - Ry", 4 1r: 1, ' ':LT"R D Ry T (Ol'o''''lr ,: Rllri-NilDocument3 pagesH"' - Ry", 4 1r: 1, ' ':LT"R D Ry T (Ol'o''''lr ,: Rllri-NilSniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy and C O Bond StrengthDocument29 pagesInfrared (IR) Spectroscopy and C O Bond StrengthSniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Sniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Sniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Mechanics With Vectors: ESO202A: Mechanics of Solids, 2019Document15 pages1.0 Mechanics With Vectors: ESO202A: Mechanics of Solids, 2019Sniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Recap of Toy Problems & Introducing H-AtomDocument8 pagesRecap of Toy Problems & Introducing H-AtomSniper ArcheryNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Bendix 2150Document32 pagesAir Compressor Bendix 2150Juan RiveraNo ratings yet
- 9 V Regulator Using 7809Document4 pages9 V Regulator Using 7809sarsm56No ratings yet
- TripwireDocument16 pagesTripwirePranshu RastogiNo ratings yet
- GEA17904 Zero Liquid Discharge BrochureDocument2 pagesGEA17904 Zero Liquid Discharge BrochureThanh Dat PhamNo ratings yet
- Development of High Performance UOE Pipe For Linepipe: AbstractDocument13 pagesDevelopment of High Performance UOE Pipe For Linepipe: AbstractKK SinghNo ratings yet
- TF April 2014 WebDocument20 pagesTF April 2014 WebNick SNo ratings yet
- L&T Seawoods ResidencesDocument5 pagesL&T Seawoods ResidencesMD IRSHAD ALAMNo ratings yet
- AP - Oracle R12 Account Payables (AP) SetupsDocument39 pagesAP - Oracle R12 Account Payables (AP) Setupssatyam shashi100% (1)
- H1 Educationist ProfileDocument13 pagesH1 Educationist ProfileAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- 355 TDS-11S Parts Manual CC Rev1 GDSDocument170 pages355 TDS-11S Parts Manual CC Rev1 GDSrig602.mechanicNo ratings yet
- 02.GPM DPR L1 Product Format Documentation EDocument82 pages02.GPM DPR L1 Product Format Documentation EMaxi GarzonNo ratings yet
- Commscope HBX-6517DS-VTMDocument4 pagesCommscope HBX-6517DS-VTMniuniuniNo ratings yet
- $SysAdm Made Easy 46cd (Entire Book-2002)Document781 pages$SysAdm Made Easy 46cd (Entire Book-2002)Avijit RoyNo ratings yet
- ECG Abstract PDFDocument2 pagesECG Abstract PDFgangadhara0% (1)
- ORIG - Oxygen Cylinder Checks and StorageDocument8 pagesORIG - Oxygen Cylinder Checks and StorageImnot Realanymore ImanillusionNo ratings yet
- Courses ListDocument2 pagesCourses Listapi-281148847No ratings yet
- Fb-274 GB Paladin1200dDocument2 pagesFb-274 GB Paladin1200dchaudhasNo ratings yet
- DTC P0135 Oxyge (A/F) Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)Document3 pagesDTC P0135 Oxyge (A/F) Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)Erln Lima100% (1)
- Surface Miner #UdaiDocument38 pagesSurface Miner #UdaiChandan Kumar100% (1)
- SC-PT560 Operating Instructions PDFDocument44 pagesSC-PT560 Operating Instructions PDFLeonardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Oceanographic Winch, Wire and Cable TechnologyDocument566 pagesHandbook of Oceanographic Winch, Wire and Cable Technologysuresh_501No ratings yet
- 2014 Survey of Living Conditions QuestionnaireDocument59 pages2014 Survey of Living Conditions QuestionnaireabguyNo ratings yet
- YZJ2015-2223-SED 轴接地 - FinalDocument18 pagesYZJ2015-2223-SED 轴接地 - Finalmarine ShanghaiNo ratings yet
- Design of Rectangular Water TankDocument242 pagesDesign of Rectangular Water Tankmumarbsc7244No ratings yet
- ENA ManualDocument60 pagesENA ManualAbdul Munim100% (1)
- TCW450Document2 pagesTCW450Richard GriffithNo ratings yet
- Mobox - Log 342Document3 pagesMobox - Log 342micaelsouzarodrigues0No ratings yet
- Energy Audit in Textile Industry-A Study With Ring Frame MotorDocument5 pagesEnergy Audit in Textile Industry-A Study With Ring Frame MotorNarender Mehra SethNo ratings yet
- GPS Users GuideDocument9 pagesGPS Users GuideSimple SimonNo ratings yet
- SWT 2000 LeafletDocument4 pagesSWT 2000 LeafletphucgenjiNo ratings yet