Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Light: Fluorescence, Triboluminescence, Etc
Types of Light: Fluorescence, Triboluminescence, Etc
Uploaded by
Felix Hu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesThe document discusses different types of light including sunlight, incandescent light, light from electric discharge, fluorescence, and various forms of luminescence. The sun's light is produced through nuclear fusion, which excites atoms and causes them to emit photons. Incandescent lightbulbs get hot when electric current passes through their tungsten filaments. Fluorescent and some street lights use electric discharge through gases like mercury and sodium to produce light. Fluorescence involves absorbing ultraviolet light and re-emitting it as visible light. Luminescence produces light through chemical reactions, extended atomic excitation, or friction without heat.
Original Description:
The different types of light and how they are used/different properties
Original Title
Types of Light
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of light including sunlight, incandescent light, light from electric discharge, fluorescence, and various forms of luminescence. The sun's light is produced through nuclear fusion, which excites atoms and causes them to emit photons. Incandescent lightbulbs get hot when electric current passes through their tungsten filaments. Fluorescent and some street lights use electric discharge through gases like mercury and sodium to produce light. Fluorescence involves absorbing ultraviolet light and re-emitting it as visible light. Luminescence produces light through chemical reactions, extended atomic excitation, or friction without heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesTypes of Light: Fluorescence, Triboluminescence, Etc
Types of Light: Fluorescence, Triboluminescence, Etc
Uploaded by
Felix HuThe document discusses different types of light including sunlight, incandescent light, light from electric discharge, fluorescence, and various forms of luminescence. The sun's light is produced through nuclear fusion, which excites atoms and causes them to emit photons. Incandescent lightbulbs get hot when electric current passes through their tungsten filaments. Fluorescent and some street lights use electric discharge through gases like mercury and sodium to produce light. Fluorescence involves absorbing ultraviolet light and re-emitting it as visible light. Luminescence produces light through chemical reactions, extended atomic excitation, or friction without heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Types of light: Fluorescence, triboluminescence, etc.
The Sun’s light
ℵ The atoms in our sun are fusing together, and releases a huge amount of energy at all different
wavelengths. (without this, we would die)
ℵ Hydrogen atoms combine to produce helium - excited atoms release energy released in the
form of light (photons)
Incandescent light
ℵ the emission of visible light by a body, caused by its high temperature
o Incandescent light bulbs have tiny tungsten wires that get very hot when an electric
current passes through it (5% efficiency)
Light from Electric Discharge
ℵ The process of producing light by passing current through a gas
o Some streetlights are sodium vapour bulbs.
o An electric current passes through the bulbs, which contain a small amount of mercury
and sodium, with most of the air removed.
o The current excites the atoms, and a yellowish light, is emitted as the atoms release
their energy.
o Different gases could emit different colors.
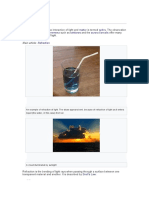
Fluorescence
ℵ The immediate emission of visible light as a result of the absorption of ultraviolet light
ℵ Occurs when an object absorbs UV light and immediately releases energy as light
o A fluorescent light bulb is a discharge tube with an electrode at the end.
o The bulb contains mercury vapour and an inert gas such as argon.
o The inside of the bulb is coated with a powdery substance called phosphor.
o Electrons are emitted from an electrode and collide with mercury atoms, exciting them.
o The excited mercury atoms emit the energy in the form of UV light. (not visible)
o The UV light is absorbed by the phosphor which emits the energy as visible light.
o Fluorescent LBs are 4x (20% efficient) as good as incandescent ones.
Luminescence
ℵ Light generated without heating the object
Chemiluminescence
ℵ Light generated by the energy released in a chemical reaction (e.g glow in the dark sticks)
ℵ No heat produced
Phosphorescence
ℵ The process of producing light by the absorption of ultraviolet light resulting in the emission of
visible light over an extended period of time
ℵ Similar to fluorescence, but the materials glow long after they have absorbed UV light (e.g glow
in the dark material)
Bioluminescence
ℵ Light produced by living organisms as a result of a chemical reaction, like deep-sea (e.g fireflies)
Triboluminescence
ℵ The production of light from friction as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain
crystals
ℵ Certain crystals can release tiny amounts of light when crushed (e.g mint lifesavers)
You might also like
- Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice 2021Document230 pagesInfusion Therapy Standards of Practice 2021rseer100% (2)
- 144 SQRRDocument19 pages144 SQRRcaptainamerica201390% (20)
- WWW Scribd Com Document 523146465 Fraud Bible 1Document20 pagesWWW Scribd Com Document 523146465 Fraud Bible 1Ohi0100% (3)
- You'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshDocument272 pagesYou'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshtaeBoNo ratings yet
- Light SourceDocument4 pagesLight Sourcesana.incubationNo ratings yet
- How Fluorescent Lamps Work: Let There Be LightDocument9 pagesHow Fluorescent Lamps Work: Let There Be Lightlahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- How Fluorescent Lamps Work by NafeesDocument14 pagesHow Fluorescent Lamps Work by NafeesnafeesNo ratings yet
- Sources of LightDocument3 pagesSources of LightTami AbordoNo ratings yet
- 2.1. LightDocument34 pages2.1. Light6h4gxcf7jbNo ratings yet
- Utilities - Light SourceDocument34 pagesUtilities - Light SourceSidisGarciaNo ratings yet
- Visible LightDocument2 pagesVisible LightYvannah CodmNo ratings yet
- Light SourcesDocument2 pagesLight SourcesNinggen HoomanNo ratings yet
- Types of Light SourcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Light SourcesBiniam100% (1)
- Discharge LampsDocument26 pagesDischarge LampsFemi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Sources of Light StudentDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Sources of Light Studentwardah.ishaqueNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument4 pagesReaction PaperNedz StarkNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230427 071710 0000Document1 pagePDF 20230427 071710 0000JENZENE EDIOSNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Arc LampDocument8 pagesWorking Principle of Arc LamphimNo ratings yet
- How Does A Fluorescent Starter WorkDocument4 pagesHow Does A Fluorescent Starter Workhardmanperson100% (1)
- LuminescenceDocument1 pageLuminescenceKristiyan GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Principle of Arc LampDocument8 pagesPrinciple of Arc Lampanon_135607575No ratings yet
- What Is Light Energy?Document2 pagesWhat Is Light Energy?Rosalyn Gaurana Alagon FriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Light WavesDocument27 pagesChapter 10 Light WavesDom Christian LastNo ratings yet
- Class LightingDocument46 pagesClass LightingOnajinrin OluwakemiNo ratings yet
- TLE 9 Aristotle Group 2Document7 pagesTLE 9 Aristotle Group 2mariviebuendia777No ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument8 pagesSCIENCEdive iveNo ratings yet
- Activity 13: Basic Science & Modeling Solar Energy PV Panels & Energy Sources (Solar-Sunlight)Document3 pagesActivity 13: Basic Science & Modeling Solar Energy PV Panels & Energy Sources (Solar-Sunlight)Leonard ChanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Fluorescent LightDocument3 pagesExperiment 4: Fluorescent Lightud54No ratings yet
- Iiiumination2 Incandesent LampDocument6 pagesIiiumination2 Incandesent LampPushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Understanding Light:: Properties & ClassificationsDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Light:: Properties & ClassificationsColtonNo ratings yet
- Nature of LightDocument4 pagesNature of Lightalleaheunice29No ratings yet
- OpticsDocument3 pagesOpticsLeo CerenoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Light SourcesDocument21 pagesArtificial Light SourcesAljomar Bas JularbalNo ratings yet
- Light Sources and Its CharacteristicDocument26 pagesLight Sources and Its CharacteristicVarisa RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Analysis Final2Document8 pagesAssignment Analysis Final2Mahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Light Light Sources Daylight DaylightingDocument2 pagesLight Light Sources Daylight DaylightingStephen GomezNo ratings yet
- LightDocument41 pagesLightqwertasdfgNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsAmy OliverNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Visible Light PresentationDocument16 pagesScience 10 - Visible Light PresentationTrexie Joy TamonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes ShortXDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Notes ShortXdsckln/cmakNo ratings yet
- LASER Introduction: What Is Light?Document13 pagesLASER Introduction: What Is Light?Morosan DimitrieNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsAlzon Joseph SamboNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document49 pagesUnit 2mexebi1971No ratings yet
- US Iran ConflictDocument6 pagesUS Iran ConflictIhsaan GulzarNo ratings yet
- LASER07022023Document39 pagesLASER07022023Akhyaya PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Group IiiDocument7 pagesGroup Iiibreakitdown yoyoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument22 pagesElectromagnetic WavesAgus SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Artificial SubjectDocument22 pagesArtificial SubjectJamaica MinandangNo ratings yet
- The Nature of LightDocument27 pagesThe Nature of LightvlsiprabhuNo ratings yet
- Luminescence Applications Few Basics: K.V.R. MurthyDocument14 pagesLuminescence Applications Few Basics: K.V.R. MurthyA Xuan PhuNo ratings yet
- Introduction - About LasersDocument3 pagesIntroduction - About LasersIrwan SiburianNo ratings yet
- Light SourcesDocument4 pagesLight SourcesSooraj AroraNo ratings yet
- All About Light DiscussionDocument29 pagesAll About Light DiscussionMika MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent LampDocument4 pagesFluorescent Lampprateek mishraNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties PDFDocument27 pagesOptical Properties PDFaljhon100% (1)
- Difference Between Fluorescence and LuminescenceDocument1 pageDifference Between Fluorescence and LuminescenceDhrubajyoti Ghosh100% (1)
- Light and Light ProductionDocument19 pagesLight and Light Productionangeladel484No ratings yet
- 2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 2 Lecture 4 LIGHT SOURCES (S)Document39 pages2021 BUILDING UTILITIES 3 - Module 2 Lecture 4 LIGHT SOURCES (S)Sophia Manila Silla100% (1)
- LuminescenceDocument12 pagesLuminescenceMamta GargNo ratings yet
- Emission and Absorption - Principles of Structural ChemistryDocument2 pagesEmission and Absorption - Principles of Structural ChemistryLeon MpalsNo ratings yet
- Compact Fluorescent Lighting CFL Construction and Working and ComparisonDocument23 pagesCompact Fluorescent Lighting CFL Construction and Working and ComparisonAnimesh Verma100% (7)
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument32 pagesConduction Convection RadiationShalini Kulshrestha100% (2)
- NCERT Science, Physics, Chemistry and Biology.Document84 pagesNCERT Science, Physics, Chemistry and Biology.Honey SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fundamentals An Introduction To Engineering Chapter 01Document31 pagesEngineering Fundamentals An Introduction To Engineering Chapter 01Ana ChavezNo ratings yet
- Newsletter May 2022 Vol 3 Issue 3.0Document24 pagesNewsletter May 2022 Vol 3 Issue 3.0Google UserNo ratings yet
- Literary Reading Through A Biographical ContextDocument1 pageLiterary Reading Through A Biographical ContexthaydeeNo ratings yet
- Principle/S Involved:: Chemical Formula of The Reagent Used Role/Use in The Experiment Naoh Na H Y - 2H O MGCL - 6H ODocument2 pagesPrinciple/S Involved:: Chemical Formula of The Reagent Used Role/Use in The Experiment Naoh Na H Y - 2H O MGCL - 6H OCathrina Andrea RamosNo ratings yet
- Natural DisastersDocument1 pageNatural DisastersAela VinayNo ratings yet
- Daifuku MIT BrochureDocument5 pagesDaifuku MIT BrochureZiqi LinNo ratings yet
- How To Build An End To End Bi SolutionDocument9 pagesHow To Build An End To End Bi Solutionviviana luque sallucoNo ratings yet
- Aluminum 6061Document3 pagesAluminum 6061Achmad Rizal MustaqimNo ratings yet
- Arts-1 Q2Document35 pagesArts-1 Q2Alvin MellaNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing Business LettersDocument60 pagesLetter Writing Business LettersAvery Jan SilosNo ratings yet
- SHARP-mxm350n M350u m450n M450uDocument12 pagesSHARP-mxm350n M350u m450n M450uIoas IodfNo ratings yet
- Teacher Timesavers, Volume 2Document47 pagesTeacher Timesavers, Volume 2Mohamed Abdalla Mohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document15 pagesClass 1eisha123No ratings yet
- Exalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsDocument92 pagesExalco Albio 102 Curtain Wall SystemsAdmir MatoshiNo ratings yet
- 09ns2 InstallDocument9 pages09ns2 InstallTanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing StandartsDocument28 pagesAdditive Manufacturing StandartssefaydesNo ratings yet
- Operating Characteristic (OC) CurveDocument4 pagesOperating Characteristic (OC) CurveSaquib Bin Habib100% (2)
- TOPIC: Ethics, Anonymity, and Personal Identity in The Wired World I. Multiple Choice (10 Items)Document3 pagesTOPIC: Ethics, Anonymity, and Personal Identity in The Wired World I. Multiple Choice (10 Items)Espresso LanNo ratings yet
- Major VFP Encryption Update - SweetPotato Software BlogDocument8 pagesMajor VFP Encryption Update - SweetPotato Software BlogAntonio BeltránNo ratings yet
- Jalil Akhtar 058Document7 pagesJalil Akhtar 058Malik JalilNo ratings yet
- The Perception of Students On The Utilization of Google Translate To Acquire VocabularyDocument9 pagesThe Perception of Students On The Utilization of Google Translate To Acquire VocabularyARSI SYAHID YUSUF MI'RAJNo ratings yet
- Free Emotional IntelligenceDocument9 pagesFree Emotional IntelligencesolangeNo ratings yet
- Taes Padhihary Potd, Jee 2023 KidDocument2 pagesTaes Padhihary Potd, Jee 2023 KidmonyNo ratings yet
- Smoke & Ventilation CalculationsDocument7 pagesSmoke & Ventilation CalculationsZine Models100% (2)
- PDMS Forum TipsDocument3 pagesPDMS Forum TipsSudheepNo ratings yet
- Anna University EDDocument48 pagesAnna University EDSivaji SivaNo ratings yet