Professional Documents
Culture Documents
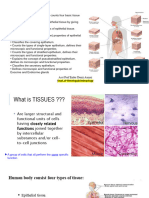
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Uploaded by
veniceCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of ZombiesDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ZombiesdsolisNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- HistocologyDocument10 pagesHistocologyKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Edited 2020Document44 pagesHISTOLOGY Edited 2020lifeeternaltointerveneNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Document4 pagesEpithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Mirriam Joy CortezNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Epithelium TissueDocument9 pagesHistology of The Epithelium TissueKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument39 pagesLaboratory ManualChelsea Chadwick100% (1)
- Epithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti BhattacharjeeDocument125 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti Bhattacharjeelochi gmNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument13 pagesEpithelial TissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- EpituleinDocument3 pagesEpituleinAlexandra JunchayaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Activity#2 - THE EPITHELIUMDocument13 pages2.0 Activity#2 - THE EPITHELIUMaragon.sariNo ratings yet
- Tissues and CellsDocument14 pagesTissues and Cellsstormigirl017No ratings yet
- Epithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument124 pagesEpithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesBahasa Inggrisahmad jamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The EpitheliumDocument3 pagesChapter 3 The EpitheliumGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument28 pagesIntroduction To AnatomyConstantin JegertNo ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Epithelium (Epithelial Tissue)Document64 pagesEpithelium (Epithelial Tissue)Nihal BilalNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesEpithelial TissueAmmar ShahidNo ratings yet
- 4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology MariebDocument12 pages4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology Mariebmine2515No ratings yet
- Topic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Document71 pagesTopic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Test CaseDocument54 pagesTest CaseEmil BoseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHDocument6 pagesLesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHLoraine Andrei DeLeonNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- 6 - TissueDocument7 pages6 - TissueJocelyn AtisNo ratings yet
- De Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALDocument6 pagesDe Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALCHRISTINE JOY DE RAMANo ratings yet
- Ciliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumDocument20 pagesCiliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumMisnawatiNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesLAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemMickey Ayle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- Surface EpitheliumDocument17 pagesSurface EpitheliumKareem VictorNo ratings yet
- Microscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesMicroscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Epithelium TissueDocument13 pagesEpithelium TissueasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Histo 1Document9 pagesHisto 1carloNo ratings yet
- L2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022Document32 pagesL2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022TalarNo ratings yet
- Vet Histo Notes Chap 2Document10 pagesVet Histo Notes Chap 2Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals (Content)Document15 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals (Content)kevenliamwilliam.exampointNo ratings yet
- Basic TissueDocument60 pagesBasic TissueSantoshini RaviNo ratings yet
- MT 100 Lab Notes 1Document11 pagesMT 100 Lab Notes 1Nilo Golosino IIINo ratings yet
- Tissues: Lecture OutlineDocument87 pagesTissues: Lecture OutlineJed Esperidion Solivio JumillaNo ratings yet
- Tob 2.1Document32 pagesTob 2.1LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialtissueDocument84 pages1 EpithelialtissueDeniz asmazNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument6 pagesHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Zoology Animal TissueDocument54 pagesZoology Animal TissueasuhassNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial TissueMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument87 pagesTissuesEDLYN BRAZILNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ana Histology PDFDocument79 pagesAna Histology PDFNagesh NNo ratings yet
- Histopathology I: Epithelium Tissue Part IDocument44 pagesHistopathology I: Epithelium Tissue Part ICarinaJongLeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy U-1 Introduction To Anatomy PharmacyDocument116 pagesAnatomy U-1 Introduction To Anatomy Pharmacysinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganismsDocument58 pagesStructural Organismssivarigil1918No ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument23 pagesCombine PDFsigninNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Epithelial TissueDocument65 pagesDilek Akakin Epithelial TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionveniceNo ratings yet
- Art (1) Through Ages by Helen GardnerDocument2 pagesArt (1) Through Ages by Helen GardnerveniceNo ratings yet
- Listening Exam PDFDocument1 pageListening Exam PDFveniceNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Refraction of Light Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Refraction of Light Laboratory ReportveniceNo ratings yet
- Ethoxy Ethane: 32 Chastine B. Parker 1BbcDocument6 pagesEthoxy Ethane: 32 Chastine B. Parker 1BbcveniceNo ratings yet
- Thomas Hanna - Explorers of Humankind (1979)Document158 pagesThomas Hanna - Explorers of Humankind (1979)franco6araujo100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromeDocument36 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromekotraeNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument35 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesanjayNo ratings yet
- Science Continuous Assessment (Chapter 1 & 2)Document10 pagesScience Continuous Assessment (Chapter 1 & 2)Catherine ChanNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1189) Celeste M. Nelson (Eds.) - Tissue Morphogenesis - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Document365 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1189) Celeste M. Nelson (Eds.) - Tissue Morphogenesis - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Pranav Vyas100% (1)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Biomedical Engineering Graduate Concentrations: Advisor: Prof. Tim BrunsDocument8 pagesBiomedical Engineering Graduate Concentrations: Advisor: Prof. Tim BrunsDelfina HuangNo ratings yet
- Ecology Review Questions 2 With AnswersDocument4 pagesEcology Review Questions 2 With AnswersJanrhey DarNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated Immune ResponsesDocument44 pagesCell-Mediated Immune Responsesvivin100% (1)
- How To Check Blood Test Report PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Check Blood Test Report PDFDenise CssNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology 8th Edition by Castro - Test BankDocument16 pagesMarine Biology 8th Edition by Castro - Test Bankshaista.azizNo ratings yet
- 20130415035811876Document206 pages20130415035811876WillAsherNo ratings yet
- Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli - Written Report PDFDocument6 pagesEnteropathogenic Escherichia Coli - Written Report PDFuypaul97No ratings yet
- Zoono Brand-BrochureDocument10 pagesZoono Brand-BrochureMichael TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Cilia Microvilli Stereocilia ComparisonDocument1 pageCilia Microvilli Stereocilia ComparisonSophiaNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer Overview: ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesColon Cancer Overview: ElectrolytesPranaliNo ratings yet
- Lab 17Document5 pagesLab 17harman parmarNo ratings yet
- Jawaban:: Kata Yang Sama Penulisannya, Tetapi Beda Ketika Dibunyikan KatanyaDocument2 pagesJawaban:: Kata Yang Sama Penulisannya, Tetapi Beda Ketika Dibunyikan KatanyaUkhty Putri TrianaNo ratings yet
- Dot Blot ProtocolDocument2 pagesDot Blot ProtocolSuki BlytheNo ratings yet
- (Labgenomics) Biz Collaboration - LabGun™ COVID-19 Assay PCR Kit (Information 20200304) - ENDocument15 pages(Labgenomics) Biz Collaboration - LabGun™ COVID-19 Assay PCR Kit (Information 20200304) - ENJoana SampaioNo ratings yet
- Applied Haematology SynopsisDocument6 pagesApplied Haematology SynopsisPARAS BHATIANo ratings yet
- BIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Document72 pagesBIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Parveen BrarNo ratings yet
- Helichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDDocument373 pagesHelichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDAthina Margatina100% (1)
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Document8 pagesPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Parts and FunctionGem CarpioNo ratings yet
- Imunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifDocument55 pagesImunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifAnthony UchihaNo ratings yet
- MdsDocument570 pagesMdsAgus SusantoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ModuleDocument2 pagesBiodiversity ModuleKaren Ocon EstelaNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology William Carroll FrazierDocument490 pagesFood Microbiology William Carroll FrazierK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Uploaded by
veniceOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Simple Squamous and Pseudo Epithelium
Uploaded by
veniceCopyright:
Available Formats
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
1. IDENTIFY THE TISSUE SAMPLES PER CLASSIFICATION
ANIMAL ORIGIN OF THE TISSUE SAMPLE
Organs in animals are composed of a number of different tissue types. For example, the stomach
has epithelial tissue making linings and secreting gastric juices
TISSUE TYPE - SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM is composed of one layer of uniform
flat cells, which rest on the basement membrane. Apical surfaces are
smooth, and the width of the cells is greater than their height. The
nuclei appear flattened and can easily be recognized following
hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) because of the basophilia
(affinity for blue stains) of the nucleic acids in the nuclei. This type of
epithelium is found lining the posterior surface of the cornea; lining
blood vessels and lymphatic vessels (where it is called endothelium);
lining the surface of the body cavities, including the pericardial,
pleural, and peritoneal cavities (where it is called mesothelium); and
lining the alveoli of the lungs.
2. DETERMINE THE PARTS (DISTINGUISHING PARTS) OF THE
TISSUE SAMPLE;
In our specimen, we can see the ff parts:
Plasma membrane – is a network of lipids and proteins that
forms the boundary of the cell’s contents and the outside of
the cell
Cytoplasm – made up of mostly water and salt and helps to fill out the cell and keeps organelles
in their place
Nucleus – contains the majority of cell’s genetic material
3. PROVIDE BASIC AND CLINICAL CORRELATION TO THE TISSUE SAMPLE
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
1. IDENTIFY THE TISSUE SAMPLES PER CLASSIFICATION
ANIMAL ORIGIN OF THE TISSUE SAMPLE
TISSUE TYPE - PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION
The cells of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium vary in shape and height, and their nuclei are
staggered, giving the false impression of being arranged in two or three layers of cells. However, the
basal aspect of each cell is in contact with the basement membrane. Most cells are tall and columnar,
but there are also short basal cells, some of which are stem cells. The most widespread type of
pseudostratified columnar epithelium is ciliated and is found lining the trachea and primary bronchi, the
auditory tube, and part of the tympanic cavity. Nonciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium is
found throughout the epididymis and vas deferens in the male reproductive tract. Cilia on the apical
surfaces of some cells are closely packed like bristles of a brush. The pink line indicated by the arrow
(inset) is formed by the basal bodies, from which the cilia arise. The arrangement of the nuclei in
pseudostratified columnar epithelium is more irregular than in stratified columnar epithelium.
2. DETERMINE THE PARTS (DISTINGUISHING PARTS) OF THE TISSUE SAMPLE;
In our specimen, we can see the ff parts:
Lamina Propria – conditioning (warming, moistening and removal of particulate materials) of the
air, prevention the epithelium from dehydration by moving air.
Basement membrane – maintaining individual cell replacement in the epithelium
Goblet cells – These cells secrete mucus, which moistens the epithelial surface (so the ciliated
cells can function) and adheres to inhaled particles (so dust and bacteria are caught before they
are carried all the way into alveoli).
Cilia – provide a coordinated sweeping motion of the mucus coat -"ciliary escalator" - that
serves as an important protective mechanism for removing small inhaled particles
Nucleus
3. PROVIDE BASIC AND CLINICAL CORRELATION TO THE TISSUE SAMPLE
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of ZombiesDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ZombiesdsolisNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueSofia LiNo ratings yet
- HistocologyDocument10 pagesHistocologyKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Edited 2020Document44 pagesHISTOLOGY Edited 2020lifeeternaltointerveneNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Epithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Document4 pagesEpithelium: (Edit) Classification (Structural)Mirriam Joy CortezNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Epithelium TissueDocument9 pagesHistology of The Epithelium TissueKelvin HillsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument39 pagesLaboratory ManualChelsea Chadwick100% (1)
- Epithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti BhattacharjeeDocument125 pagesEpithelium: Dr. Kalpajyoti Bhattacharjeelochi gmNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument13 pagesEpithelial TissueJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Week 1Document35 pagesGenbio2 Week 1Noel Vincent Agonoy100% (1)
- EpituleinDocument3 pagesEpituleinAlexandra JunchayaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Activity#2 - THE EPITHELIUMDocument13 pages2.0 Activity#2 - THE EPITHELIUMaragon.sariNo ratings yet
- Tissues and CellsDocument14 pagesTissues and Cellsstormigirl017No ratings yet
- Epithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument124 pagesEpithelium: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesBahasa Inggrisahmad jamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The EpitheliumDocument3 pagesChapter 3 The EpitheliumGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument28 pagesIntroduction To AnatomyConstantin JegertNo ratings yet
- Histology 2018 1Document38 pagesHistology 2018 1Marvin Ndashimye100% (1)
- Epithelium (Epithelial Tissue)Document64 pagesEpithelium (Epithelial Tissue)Nihal BilalNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument3 pagesEpithelial TissueAmmar ShahidNo ratings yet
- 4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology MariebDocument12 pages4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology Mariebmine2515No ratings yet
- Topic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Document71 pagesTopic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Test CaseDocument54 pagesTest CaseEmil BoseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHDocument6 pagesLesson 4 - Activity 2 1 TBHLoraine Andrei DeLeonNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- 6 - TissueDocument7 pages6 - TissueJocelyn AtisNo ratings yet
- De Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALDocument6 pagesDe Rama - Activity Worksheet #02 - HHIS FINALCHRISTINE JOY DE RAMANo ratings yet
- Ciliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumDocument20 pagesCiliated Epithelium Is A Category of EpitheliumMisnawatiNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesLAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues - Integumentary SystemMickey Ayle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Histology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesHistology: (1) - Epithelial TissueDTM FHKNo ratings yet
- Surface EpitheliumDocument17 pagesSurface EpitheliumKareem VictorNo ratings yet
- Microscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesMicroscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Epithelium TissueDocument13 pagesEpithelium TissueasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Histo 1Document9 pagesHisto 1carloNo ratings yet
- L2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022Document32 pagesL2.1 - Simple Epithelium, 2march 2022TalarNo ratings yet
- Vet Histo Notes Chap 2Document10 pagesVet Histo Notes Chap 2Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals (Content)Document15 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals (Content)kevenliamwilliam.exampointNo ratings yet
- Basic TissueDocument60 pagesBasic TissueSantoshini RaviNo ratings yet
- MT 100 Lab Notes 1Document11 pagesMT 100 Lab Notes 1Nilo Golosino IIINo ratings yet
- Tissues: Lecture OutlineDocument87 pagesTissues: Lecture OutlineJed Esperidion Solivio JumillaNo ratings yet
- Tob 2.1Document32 pagesTob 2.1LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- 1 EpithelialtissueDocument84 pages1 EpithelialtissueDeniz asmazNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument6 pagesHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Zoology Animal TissueDocument54 pagesZoology Animal TissueasuhassNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial TissueMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument87 pagesTissuesEDLYN BRAZILNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ana Histology PDFDocument79 pagesAna Histology PDFNagesh NNo ratings yet
- Histopathology I: Epithelium Tissue Part IDocument44 pagesHistopathology I: Epithelium Tissue Part ICarinaJongLeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy U-1 Introduction To Anatomy PharmacyDocument116 pagesAnatomy U-1 Introduction To Anatomy Pharmacysinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganismsDocument58 pagesStructural Organismssivarigil1918No ratings yet
- Crissman Epithelial ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCrissman Epithelial Objectiveskkonci01No ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument23 pagesCombine PDFsigninNo ratings yet
- Dilek Akakin Epithelial TissueDocument65 pagesDilek Akakin Epithelial TissueErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionveniceNo ratings yet
- Art (1) Through Ages by Helen GardnerDocument2 pagesArt (1) Through Ages by Helen GardnerveniceNo ratings yet
- Listening Exam PDFDocument1 pageListening Exam PDFveniceNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Refraction of Light Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Refraction of Light Laboratory ReportveniceNo ratings yet
- Ethoxy Ethane: 32 Chastine B. Parker 1BbcDocument6 pagesEthoxy Ethane: 32 Chastine B. Parker 1BbcveniceNo ratings yet
- Thomas Hanna - Explorers of Humankind (1979)Document158 pagesThomas Hanna - Explorers of Humankind (1979)franco6araujo100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromeDocument36 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Metabolic SyndromekotraeNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument35 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesanjayNo ratings yet
- Science Continuous Assessment (Chapter 1 & 2)Document10 pagesScience Continuous Assessment (Chapter 1 & 2)Catherine ChanNo ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1189) Celeste M. Nelson (Eds.) - Tissue Morphogenesis - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Document365 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 1189) Celeste M. Nelson (Eds.) - Tissue Morphogenesis - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2015)Pranav Vyas100% (1)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Biomedical Engineering Graduate Concentrations: Advisor: Prof. Tim BrunsDocument8 pagesBiomedical Engineering Graduate Concentrations: Advisor: Prof. Tim BrunsDelfina HuangNo ratings yet
- Ecology Review Questions 2 With AnswersDocument4 pagesEcology Review Questions 2 With AnswersJanrhey DarNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated Immune ResponsesDocument44 pagesCell-Mediated Immune Responsesvivin100% (1)
- How To Check Blood Test Report PDFDocument3 pagesHow To Check Blood Test Report PDFDenise CssNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology 8th Edition by Castro - Test BankDocument16 pagesMarine Biology 8th Edition by Castro - Test Bankshaista.azizNo ratings yet
- 20130415035811876Document206 pages20130415035811876WillAsherNo ratings yet
- Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli - Written Report PDFDocument6 pagesEnteropathogenic Escherichia Coli - Written Report PDFuypaul97No ratings yet
- Zoono Brand-BrochureDocument10 pagesZoono Brand-BrochureMichael TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Cilia Microvilli Stereocilia ComparisonDocument1 pageCilia Microvilli Stereocilia ComparisonSophiaNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer Overview: ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesColon Cancer Overview: ElectrolytesPranaliNo ratings yet
- Lab 17Document5 pagesLab 17harman parmarNo ratings yet
- Jawaban:: Kata Yang Sama Penulisannya, Tetapi Beda Ketika Dibunyikan KatanyaDocument2 pagesJawaban:: Kata Yang Sama Penulisannya, Tetapi Beda Ketika Dibunyikan KatanyaUkhty Putri TrianaNo ratings yet
- Dot Blot ProtocolDocument2 pagesDot Blot ProtocolSuki BlytheNo ratings yet
- (Labgenomics) Biz Collaboration - LabGun™ COVID-19 Assay PCR Kit (Information 20200304) - ENDocument15 pages(Labgenomics) Biz Collaboration - LabGun™ COVID-19 Assay PCR Kit (Information 20200304) - ENJoana SampaioNo ratings yet
- Applied Haematology SynopsisDocument6 pagesApplied Haematology SynopsisPARAS BHATIANo ratings yet
- BIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Document72 pagesBIOL200 Midterm Review Session 2022WT1 - V2Parveen BrarNo ratings yet
- Helichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDDocument373 pagesHelichrysum Umbreculigerum Better Than CBDAthina Margatina100% (1)
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Document8 pagesPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Parts and FunctionGem CarpioNo ratings yet
- Imunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifDocument55 pagesImunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifAnthony UchihaNo ratings yet
- MdsDocument570 pagesMdsAgus SusantoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity ModuleDocument2 pagesBiodiversity ModuleKaren Ocon EstelaNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology William Carroll FrazierDocument490 pagesFood Microbiology William Carroll FrazierK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHNo ratings yet