Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water Soluble Vitamins
Water Soluble Vitamins
Uploaded by
nreena aslam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
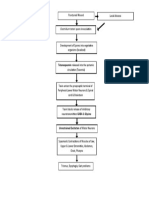
19 views2 pagesWater soluble vitamins play important roles as enzyme cofactors in many metabolic pathways. Deficiencies can result in diseases. Vitamin B1 is important for the TCA cycle and deficiencies can cause Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Vitamin B2 is involved in fatty acid metabolism and its deficiency can cause eye and mouth issues. Vitamin B3 deficiency results in pellagra with diarrhea, dementia and dermatitis. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy with poor wound healing and bleeding.
Original Description:
high yield table
Original Title
Vitamins
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWater soluble vitamins play important roles as enzyme cofactors in many metabolic pathways. Deficiencies can result in diseases. Vitamin B1 is important for the TCA cycle and deficiencies can cause Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Vitamin B2 is involved in fatty acid metabolism and its deficiency can cause eye and mouth issues. Vitamin B3 deficiency results in pellagra with diarrhea, dementia and dermatitis. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy with poor wound healing and bleeding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesWater Soluble Vitamins
Water Soluble Vitamins
Uploaded by
nreena aslamWater soluble vitamins play important roles as enzyme cofactors in many metabolic pathways. Deficiencies can result in diseases. Vitamin B1 is important for the TCA cycle and deficiencies can cause Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Vitamin B2 is involved in fatty acid metabolism and its deficiency can cause eye and mouth issues. Vitamin B3 deficiency results in pellagra with diarrhea, dementia and dermatitis. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy with poor wound healing and bleeding.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Water Soluble vitamins
Vitamin Enzyme Pathway Deficiency Disease
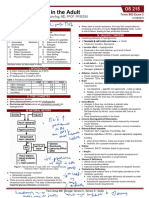
B 1 (Thiamine) Associated with Alcoholism Wernicke’s encephalopathy:
dehydrogenases: TCA cycle CNS damage
-Pyruvate dehydrogenase Interferes with absorption Korsakoff’s syndrome:
-α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase Amnesia & psychiatric manifestations
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome:
Both neurologic and psychiatric manifestations
In regions dependent on Beriberi syndrome:
polished or dehusked rice (husk A. Wet beriberi: high output cardiac failure due to inadequate ATP
is the source of thiamine) and accumulation of keto-acids in the cardiac muscle.
B. Dry beriberi: Without fluid retention
`-Transketolase (activity requires HMP shunt
only thiamine) and its activity is
used to diagnose thiamine
deficiency.
-Branched chain keto acid Metabolism of branched Maple syrup disease
dehydrogenase chain amino acids
B 2 (Riboflavin) -Succinate dehydrogenase TCA -Ariboflavinosis -Corneal neovascularization
Used to make FAD(H2) -Fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase Β-Oxidation of F.A. Dietary deficiency (TPN) -Stomatitis
-Glycerol phosphate GP shuttle -Angular stomatitis
dehydrogenase
B 3 (Niacin) -Cofactor for dehydrogenases In large doses it can inhibit -Malnutrition -Pellagra:
-Used to make NAD(H) & hormone sensitive lipase -tea and toast diet in elderly Diarrhea, Dementia, Dermatitis & Death
NADP(H) (Antihyperlipidemic drug)
B 5 (Pantothenic Used to make Co-enzyme A
acid) -Fatty acid synthase
-Fatty acyl-CoA synthase -Fatty acid metabolism
-Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase -TCA
B 6 (Pyridoxine) Used as Pyridoxal-Phosphate by -Detoxify ammonia -Alcoholic liver disease -Sideroblastic anemia
all Aminotransferases -Heme synthesis -Liver damage ( increase -Stomatitis
(Transaminases) transaminases) -Encephalopathy
-Isoniazid
Also used by cystathionine β-
synthase -Supplemented in pts with homocysteinuria
B 7 (Biotin) Associated with carboxylases
(ABC enzymes: ATP, Biotin, and
Carbon). -Gluconeogenesis -Excessive ingestion of raw -Fasting hypoglycemia
-Pyruvate carboxylase -Fatty acid synthesis eggs which contains Avidin
-Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (biotin binding protein)
-Odd chain fatty acid Alopecia
-Propionyl-CoA metabolism and metabolism Bowel inflammation
of Val, Met, Ile and Thr. Muscle pain
Vitamin Enzyme Pathway Deficiency Disease
B 9 (Folic acid) -Thymidylate synthase (U T) -Thymidine (Pyrimidine -Pregnancy (depletion of the - Increase risk of NTD.
THF is the active form synthesis) stores within 3 months).
-Purine synthesis - Alcoholics -Megaloblastic anemia
-Buildup of homocysteine (homocystinemia) DVT and
atheroma formation.
-Supply of B12 , folate or pyridoxine lowers homocysteine
levels
B 12 -Homocysteine methyltransferase - reactivate folate - No dietary deficiency. -Megaloblastic anemia (no folate reactivation)
(Cyanocobalamine) - pernicious anemia (most
-Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase -Odd chain fatty acid common)
metabolism and -Bacterial overgrowth
metabolism of Val, Met, Ile -Terminal ileum resection
and Thr. -Pancreatitis
-Crohn’s disease
-Source of succinyl-CoA -Vegans -Subacute degeneration of spinal cord
-Diphyllobothrium latum Degeneration of posterior and lateral columns
Vitamin C -Prolyl & Lysyl hydroxylase -Collagen synthesis -Diet deficient in citrus fruits& -Scurvy:
(Ascorbate) -Dopamine hydroxylase -Catecholamine synthesis green vegetables Poor wound healing, easy bruisability, bleeding gums,
increase bleeding time, glossitis and anemia
-Iron absorption from GIT from plant
sources
You might also like
- Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties: Thomas E. CreightonDocument1 pageProteins: Structures and Molecular Properties: Thomas E. CreightonNisanth Ravichandran0% (1)
- Problems: 4: The Aminoglycoside AntibioticsDocument3 pagesProblems: 4: The Aminoglycoside AntibioticsSaul RuizNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Family CaseDocument17 pagesFamily Medicine Family Casecorina_oliverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document24 pagesChapter 3Dawlat Slama0% (1)
- 2019 Arbor Acre Nutritional SpecsDocument8 pages2019 Arbor Acre Nutritional SpecsGail Margarette ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role DeficiencyDocument9 pagesVitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role Deficiencykristian markus delos santosNo ratings yet
- 02-04 2022 Pharm Mens and Womens Health 2022 R4Document86 pages02-04 2022 Pharm Mens and Womens Health 2022 R4Amira HelayelNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaDocument45 pagesLymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaOmar Mohammed100% (1)
- Laboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPDocument41 pagesLaboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPmarieNo ratings yet
- Protein Energy MalnutritionDocument16 pagesProtein Energy MalnutritionAisha Abdullah ManzurNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathology For Dentistry Students - Surgical Pathology of Thyroid and Adrenal GlandsDocument38 pagesSurgical Pathology For Dentistry Students - Surgical Pathology of Thyroid and Adrenal Glandssorin niky mocanu100% (1)
- Id MCQDocument6 pagesId MCQGalaleldin Ali100% (1)
- EndoDocument8 pagesEndoSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue ProtozoaDocument32 pagesBlood and Tissue ProtozoaFort SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Critical Care: Version 2 (2020)Document56 pagesCritical Care: Version 2 (2020)yazzNo ratings yet
- 2016 CPG Ent PDFDocument21 pages2016 CPG Ent PDFCamelle CelisNo ratings yet
- Management of Hypertensive Emergency and UrgencyDocument20 pagesManagement of Hypertensive Emergency and UrgencyOersted EdwardNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Document3 pagesPharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Ahmedshaker21No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Dyslipidemia by DR SarmaDocument123 pagesPharmacotherapy of Dyslipidemia by DR Sarmamae2003No ratings yet
- Cancer Chemotherapy: Acronym of RegimenDocument13 pagesCancer Chemotherapy: Acronym of RegimenVaibhav Bharat100% (1)
- Protocol - IM DyspneaDocument7 pagesProtocol - IM DyspneaTrisNo ratings yet
- NSAIDs, DMARDs & Antigout1Document69 pagesNSAIDs, DMARDs & Antigout1Melissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- GI Diarrheal Micro ChartDocument3 pagesGI Diarrheal Micro ChartEvan MillerNo ratings yet
- Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonists: Namwase Hadijja KatabiraDocument77 pagesAdrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonists: Namwase Hadijja KatabiraSamson100% (1)
- 1 LiverDocument10 pages1 LiverAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Infra-Auricular Mass Case PresDocument8 pagesInfra-Auricular Mass Case PresEjay Jacob RicamaraNo ratings yet
- 07 EndocrineDocument44 pages07 Endocrineandirio7486No ratings yet
- SympathomimeticDocument56 pagesSympathomimeticvarish0% (1)
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsDocument5 pagesPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- CPG DyslipidemiaDocument26 pagesCPG DyslipidemiaRenzy SalumbreNo ratings yet
- CVA or StrokeDocument14 pagesCVA or StrokeJoenalyn AliguinNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Document106 pagesPEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Raven EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida - GDMDocument1 pageOral Revalida - GDMMary Loise VillegasNo ratings yet
- Tetanus PathophyDocument1 pageTetanus PathophydicksonNo ratings yet
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Functions Characteristics Deficiency RDA Food SourcesDocument9 pagesVitamin Functions Characteristics Deficiency RDA Food SourcesJoren Angela GalangNo ratings yet
- NEET PG Syllabus 2024 - Detailed Subject-Wise TopicsDocument70 pagesNEET PG Syllabus 2024 - Detailed Subject-Wise Topicsmayur TNo ratings yet
- 5: Diarrhea and Constipation: MedicineDocument7 pages5: Diarrhea and Constipation: MedicineDia DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Bone - Infection Tanpa AnotasiDocument75 pagesBone - Infection Tanpa AnotasirifanirdNo ratings yet
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- Path Concept MapsDocument113 pagesPath Concept MapsAndleeb ImranNo ratings yet
- Vicks Drug of Choice ListDocument17 pagesVicks Drug of Choice Listethank211No ratings yet
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pharma CollectionDocument40 pagesPharma CollectionMuhd Nico DariyantoNo ratings yet
- OS 215 02 Diabetes in AdultsDocument11 pagesOS 215 02 Diabetes in AdultsMigs Medina100% (1)
- Beers CriteriaDocument16 pagesBeers CriteriaNickolasMarllesNo ratings yet
- EmergencyDocument86 pagesEmergencyyazzNo ratings yet
- Hyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019Document7 pagesHyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019HannaNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy: Its Applications &Document39 pagesGene Therapy: Its Applications &Rose DeymNo ratings yet
- OCHA PH - Measles OutbreakDocument1 pageOCHA PH - Measles OutbreakPhilippe Ceasar C. BascoNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument19 pagesOsteoporosisLasa SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Abdominal PainDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Abdominal PainCherry Faith Merisco LabtangNo ratings yet
- Classification of The DrugsDocument50 pagesClassification of The DrugsGlena SalamNo ratings yet
- NEET-PG 2014 - 2015: Important One Liners For Neet - 5Document22 pagesNEET-PG 2014 - 2015: Important One Liners For Neet - 5adiNo ratings yet
- A To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGDocument5 pagesA To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGQworldNo ratings yet
- Antiemetics and ProkineticsDocument29 pagesAntiemetics and ProkineticsGilbert Girising100% (1)
- GoutDocument3 pagesGoutMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- 24th Lecture - Upper Motor Neuron and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions - CNS PhysiologyDocument15 pages24th Lecture - Upper Motor Neuron and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions - CNS PhysiologySirima Makura100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaDocument25 pagesPathophysiology: Rectal CarcinomaCristina CristinaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity FINAL V4 Sheet1Document1 pageAntibiotic Sensitivity FINAL V4 Sheet1JHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ncov RecordOfAchievementDocument1 pageIntroduction To Ncov RecordOfAchievementnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- File 128 - Zohaib Biopsy Marked4!6!2019Document6 pagesFile 128 - Zohaib Biopsy Marked4!6!2019nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- File 128 - Zohaib Biopsy Marked4!6!2019Document6 pagesFile 128 - Zohaib Biopsy Marked4!6!2019nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Y 2013Document11 pagesY 2013nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- ECG Cheat Sheet: Atrial Fibrillation. Treatment?Document2 pagesECG Cheat Sheet: Atrial Fibrillation. Treatment?nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- CK 9Document11 pagesCK 9nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- 2016 Coccidiomycosis1777978430-1Document4 pages2016 Coccidiomycosis1777978430-1nreena aslam100% (1)
- 24 Hour ECG Monitoring: HSV, MycoplasmaDocument3 pages24 Hour ECG Monitoring: HSV, Mycoplasmanreena aslam100% (1)
- Melina 7-2019Document11 pagesMelina 7-2019nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Uterine Synechae Formation: No Need To Remove InitiallyDocument20 pagesUterine Synechae Formation: No Need To Remove Initiallynreena aslam100% (1)
- Ajay Biopsy. 260+Document43 pagesAjay Biopsy. 260+nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- CK 11Document2 pagesCK 11nreena aslam100% (1)
- CK Recalls 1Document12 pagesCK Recalls 1nreena aslam100% (3)
- CK 9Document11 pagesCK 9nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Online Bank Challan Form PDFDocument1 pageOnline Bank Challan Form PDFnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- January 2020Document5 pagesJanuary 2020nreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Online Bank Challan Form PDFDocument1 pageOnline Bank Challan Form PDFnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Noor Part 2Document7 pagesNoor Part 2nreena aslam100% (1)
- 2 Application For Provisional License (For One Year House Job Only) PDFDocument2 pages2 Application For Provisional License (For One Year House Job Only) PDFnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Tricarboxylic Acid CycleDocument25 pagesTricarboxylic Acid CycleJulia Mae LabajoNo ratings yet
- C3 Written Test Question PaperDocument1 pageC3 Written Test Question PaperPrakhar JalanNo ratings yet
- Animal Feed Science and Technology: J.F.X. Silva, K. Ribeiro, J.F. Silva, T.B. Cahú, R.S. BezerraDocument11 pagesAnimal Feed Science and Technology: J.F.X. Silva, K. Ribeiro, J.F. Silva, T.B. Cahú, R.S. BezerrasanbifiqarNo ratings yet
- Genetics Questions Exam NEET BiologyDocument10 pagesGenetics Questions Exam NEET BiologySadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- MetalloenzymesDocument11 pagesMetalloenzymesimsrinu100% (9)
- Nutrient QuizDocument4 pagesNutrient Quizapi-297371665No ratings yet
- Tips SPS574Document4 pagesTips SPS574AriffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionDocument4 pagesChapter 9 &10 - Gene ExpressionMahmOod GhNo ratings yet
- Rna World: GENETICS/Molecular Basis of Inheritance /BIBATSU SALAM / /page No.29Document3 pagesRna World: GENETICS/Molecular Basis of Inheritance /BIBATSU SALAM / /page No.29Salty ChipsNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates LipidsDocument1 pageBiological Macromolecules: Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates LipidsJoan PamatNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For CLDocument5 pagesBiochemistry For CLGashaw TilahunNo ratings yet
- Transcription ProcessDocument85 pagesTranscription Processshruti shahNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)Document53 pages1.3 Cell Membranes (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- Membrane ProteinsDocument47 pagesMembrane ProteinsStanley ChikoveNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1.4 Enzymes Classification and KineticsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry 1.4 Enzymes Classification and Kineticslovelots1234100% (1)
- Chapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes)Document11 pagesChapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes)ToXicNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document18 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Rista AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- Pmbi130 FT 10 2022 1Document8 pagesPmbi130 FT 10 2022 1Kaoma MofyaNo ratings yet
- Lahore University of Management Sciences: Shahzad - Hussan@lums - Edu.pk Ahmed - Afzal@lums - Edu.pkDocument5 pagesLahore University of Management Sciences: Shahzad - Hussan@lums - Edu.pk Ahmed - Afzal@lums - Edu.pkQasim FarooqNo ratings yet
- Essentiality of and Recommended Dietary Intakes For Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty AcidsDocument4 pagesEssentiality of and Recommended Dietary Intakes For Omega-6 and Omega-3 Fatty AcidsRicardo CorreaNo ratings yet
- Biosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachDocument10 pagesBiosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachMohamed MounirNo ratings yet
- Time Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortDocument3 pagesTime Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortShidevNo ratings yet
- Mutation Chromosome Change in Number and StructureDocument53 pagesMutation Chromosome Change in Number and StructureyukbhuviNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument10 pagesEnzyme Kineticskedirwoliy100% (1)
- Biochem Assignment 2Document5 pagesBiochem Assignment 2Hadia SajidNo ratings yet
- Bukti Evaluasi Ketersediaan Obat Terhadap FormulariumDocument70 pagesBukti Evaluasi Ketersediaan Obat Terhadap Formulariumchandrapurwitasari14No ratings yet
- Answers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark SchemesDocument2 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark Schemeshshshs hshs sshdgNo ratings yet