Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsStructuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Structuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Uploaded by
Sebastiao SilvaStructural basics in architecture focuses on folded slab roofs and thin shell structures. Folded slab roofs are thin-walled structures made of reinforced concrete or steel plates formed into prismatic, pyramidal, or prismoidal shapes. Thin shell structures are also called plate and shell structures, which are lightweight constructions using curved shell elements like concrete shells, lattice shells, and membrane structures. Examples of curved thin shell structures include hyperbolic shells, parabolic shells, and double curve shells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Folded Plate Structures FinalDocument27 pagesFolded Plate Structures FinalJ 3 E100% (1)
- Shell Structures and Cable StructuresDocument33 pagesShell Structures and Cable StructuresSanika Kadam100% (1)
- Shell StructureDocument18 pagesShell StructureYachika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2D Plane Strain PlasticityDocument4 pages2D Plane Strain PlasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Shell Structure Cargo Fabian Lising Ramos HannahDocument30 pagesShell Structure Cargo Fabian Lising Ramos HannahRyana Rose CristobalNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates 6.2Document16 pagesFolded Plates 6.2vamshi bodaNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures: Ar.C.Naga Vaishnavi Ar.M.PadmaDocument25 pagesShell Structures: Ar.C.Naga Vaishnavi Ar.M.Padmasindhura100% (1)
- Vinay Katariya ABCM REPORT 6 PDFDocument10 pagesVinay Katariya ABCM REPORT 6 PDFVinay KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Shells and Folded PlatesDocument15 pagesShells and Folded PlatesSyed K INo ratings yet
- Part-B Shell-2Document3 pagesPart-B Shell-2studio surfaceNo ratings yet
- Braced Barrel VaultsDocument26 pagesBraced Barrel VaultsYong Athirah Zamzuri100% (1)
- BT115-RESEARCH 4A-Husana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Section ADocument21 pagesBT115-RESEARCH 4A-Husana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Section AThessaly HusanaNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates - : Theory OF StructureDocument24 pagesFolded Plates - : Theory OF StructureShrea ZopeNo ratings yet
- ABCM DOMES, SHELLS & VAULTS - Report 4 - Group B3Document10 pagesABCM DOMES, SHELLS & VAULTS - Report 4 - Group B3Amey DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument40 pagesShell StructuresBharath AkurathiNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures-13-4-20Document19 pagesShell Structures-13-4-20sanket pawarNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument12 pagesShell Structuresdevang92100% (1)
- Special Structures Chapter 5Document55 pagesSpecial Structures Chapter 5Syed K INo ratings yet
- Building Structure and AesthaeticsDocument22 pagesBuilding Structure and AesthaeticsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Space Frames: Submitted By:-Akshay RishabhDocument7 pagesSpace Frames: Submitted By:-Akshay RishabhASHRAF TAMBOLINo ratings yet
- Folded Plate StructureDocument23 pagesFolded Plate StructureVvvg J100% (1)
- North Light Truss & Space FrameDocument28 pagesNorth Light Truss & Space FrameArshi Khan100% (2)
- Roofing System PDFDocument85 pagesRoofing System PDFAashi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument17 pagesShell Structuresdeepanshusoni100% (1)
- Shell Structure: S.Atchaya N.Ramupriya J.Sanofar Navreen S.Srividhya R.SwathyDocument29 pagesShell Structure: S.Atchaya N.Ramupriya J.Sanofar Navreen S.Srividhya R.Swathysrividhya raghavanNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates: Group Members: Subject: Theory of StructuresDocument20 pagesFolded Plates: Group Members: Subject: Theory of StructuresSoham SatamNo ratings yet
- Shell Roof and Membrane Structures1Document28 pagesShell Roof and Membrane Structures1Ar Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Shell RoofDocument13 pagesShell RoofvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Tensile StructureDocument49 pagesLecture 03 Tensile StructureDEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Shell Structure-Regulto, Maria CArmela D.Document20 pagesShell Structure-Regulto, Maria CArmela D.Carmela RegultoNo ratings yet
- CofferdamDocument41 pagesCofferdamSukhwinder Singh Gill0% (1)
- Advanced Structures: Unit 2 - Structural ElementsDocument98 pagesAdvanced Structures: Unit 2 - Structural ElementsSamreen Khan100% (1)
- Shell Structures: Shijo JoseDocument31 pagesShell Structures: Shijo Joseaksh dNo ratings yet
- CofferdamDocument42 pagesCofferdamRavi Shankar Kaushik60% (5)
- TENSILEDocument16 pagesTENSILESahithi SahiNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures-060139Document57 pagesShell Structures-060139Sonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Space Frame: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument11 pagesSpace Frame: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchRafia HassanNo ratings yet
- Shells 150918104334 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument30 pagesShells 150918104334 Lva1 App6891 PDFTasneem JraiNo ratings yet
- Shell and Cable StructuresDocument17 pagesShell and Cable StructuresShubham RautNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures - SEM IX - Folded Plates and ShellsDocument70 pagesTheory of Structures - SEM IX - Folded Plates and Shellsdavid100% (1)
- Midterm Module 3Document17 pagesMidterm Module 3CarloNo ratings yet
- CompositeDocument13 pagesCompositeklerdumdum02No ratings yet
- Shelled StructureDocument10 pagesShelled Structurenandu shahNo ratings yet
- Part-B SHELL - STRUCTURES-1Document31 pagesPart-B SHELL - STRUCTURES-1studio surfaceNo ratings yet
- Shaped StructuresDocument26 pagesShaped StructureskgatoNo ratings yet
- Space FrameDocument46 pagesSpace FrameAnonymous Y9dgyXhA100% (2)
- Tension Structure Connection Details Fabric ArchitectureDocument17 pagesTension Structure Connection Details Fabric Architecturejanhavi28No ratings yet
- Folded PlatesDocument23 pagesFolded Platesbhushruti100% (1)
- Shell and Dome - Lecture Note - 2023Document18 pagesShell and Dome - Lecture Note - 2023tsehay3737No ratings yet
- Shells and Domes Sec 201Document33 pagesShells and Domes Sec 201dplpthk1502No ratings yet
- Brief On Tensile StructuresDocument34 pagesBrief On Tensile StructuresShikhaNo ratings yet
- Structural SystemsDocument39 pagesStructural Systemstejaswini91% (11)
- ShellDocument64 pagesShellAishwarya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures - B.M.C. - V PDFDocument21 pagesShell Structures - B.M.C. - V PDFAvi Korat100% (1)
- Folded PlateDocument14 pagesFolded PlateTanvi Yadav100% (3)
- 01 Omkar Pilankar 5thb Folded Plates A.B.C.MDocument20 pages01 Omkar Pilankar 5thb Folded Plates A.B.C.MHeramb MaratheNo ratings yet
- Folded Plate StructureDocument9 pagesFolded Plate StructureMohit BansalNo ratings yet
- Other Long Span Structures: Construction VIDocument46 pagesOther Long Span Structures: Construction VIShruti TareNo ratings yet
- 16bar002,16bar005,16bar017,16bar024,16bar028 Space FrameDocument28 pages16bar002,16bar005,16bar017,16bar024,16bar028 Space Framenij balarNo ratings yet
- What Are Folded Plates?Document10 pagesWhat Are Folded Plates?Sadhana PatilNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Elastoplasticidade Com AbaqusDocument6 pagesElastoplasticidade Com AbaqusSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Funções de FormaDocument9 pagesFunções de FormaSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Technique in Plasticity Including Solution Advancement ControlDocument20 pagesNumerical Technique in Plasticity Including Solution Advancement ControlSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Matlab InterfaceDocument128 pagesMatlab InterfaceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3 BalanceDocument7 pages3 BalanceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 5 ElasticityDocument8 pages5 ElasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- TensorDocument7 pagesTensorSebastiao Silva100% (1)
- Creo Help CenterDocument1 pageCreo Help CenterSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- How To Implement Elastoplasticity in A Model Using External Materials - COMSOL BlogDocument17 pagesHow To Implement Elastoplasticity in A Model Using External Materials - COMSOL BlogSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- UMAT Theory - Nader Abedrabbo, PH.DDocument2 pagesUMAT Theory - Nader Abedrabbo, PH.DSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 08 Plasticity CompleteDocument85 pages08 Plasticity CompleteSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 122 TD4Document15 pages122 TD4Sebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 5Document25 pages14 Chapter 5Sebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- PlasticityDocument16 pagesPlasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Siemens Brazil enDocument5 pagesSiemens Brazil ensterilemovieNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks ExamDocument3 pagesNeural Networks Examfruit1991No ratings yet
- Catalog Siemens DetectieDocument340 pagesCatalog Siemens DetectieDamian OvidiuNo ratings yet
- ABS Welding With Backing StripDocument1 pageABS Welding With Backing StripAbuBakarSiddkeRumiNo ratings yet
- Planetary UrbanisationDocument5 pagesPlanetary UrbanisationFaris DzulfikarNo ratings yet
- Survey On Physical Layer Security For 5G Wireless NetworksDocument20 pagesSurvey On Physical Layer Security For 5G Wireless NetworksjavaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Skill Integration Challenge ReflectionDocument2 pagesPacket Tracer - Skill Integration Challenge Reflectionapi-250744553No ratings yet
- Planning and Designing of Bridge Over Solani RiverDocument5 pagesPlanning and Designing of Bridge Over Solani RiverCurious RajNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinDocument6 pagesPhysic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinNurl AinaNo ratings yet
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Unit4 PDFDocument36 pagesUnit4 PDFDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- Control Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFDocument8 pagesControl Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFmurugan1984No ratings yet
- Evs Project & SeminarDocument21 pagesEvs Project & Seminarpratibhaawari01No ratings yet
- SPE Data Analytics in Reservoir EngineeringDocument108 pagesSPE Data Analytics in Reservoir EngineeringNindy Sherli ParamitaNo ratings yet
- ASME SEC IX 2017-Pages-361-367Document7 pagesASME SEC IX 2017-Pages-361-367RahulNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1st Periodical TestDocument4 pagesScience 9 1st Periodical TestKebu Yen100% (1)
- Handicraft Production LMDocument82 pagesHandicraft Production LMmjcNo ratings yet
- Benito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFDocument81 pagesBenito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFcalenduloNo ratings yet
- BARBED WIRe DPRDocument22 pagesBARBED WIRe DPRGateway ComputersNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muet 1Document15 pagesMuet 1Sity Noor QiyahNo ratings yet
- Per. Dev. Week 2Document21 pagesPer. Dev. Week 2Mi ChellNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - MTH401 Fall 2006 Final Term Paper Session 1Document6 pagesDifferential Equations - MTH401 Fall 2006 Final Term Paper Session 1Faizan Zafar SahiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument18 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpurk krishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Is-Criteria For Structural Design of Penstock-11639 - 3Document19 pagesIs-Criteria For Structural Design of Penstock-11639 - 3duldar docNo ratings yet
- Hall - Panikkar Trusting The OtherDocument23 pagesHall - Panikkar Trusting The OtherOscar Emilio Rodríguez CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Isopropyl Alcohol Solution 91, 400682 - HLK - SDSDocument7 pagesIsopropyl Alcohol Solution 91, 400682 - HLK - SDSAman BaigNo ratings yet
- Wolfgang Pauli and Modern PhysicsDocument17 pagesWolfgang Pauli and Modern PhysicsahsbonNo ratings yet
- HVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & InstallationDocument3 pagesHVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & Installationnoha azamali50% (2)
Structuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Structuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Uploaded by
Sebastiao Silva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views26 pagesStructural basics in architecture focuses on folded slab roofs and thin shell structures. Folded slab roofs are thin-walled structures made of reinforced concrete or steel plates formed into prismatic, pyramidal, or prismoidal shapes. Thin shell structures are also called plate and shell structures, which are lightweight constructions using curved shell elements like concrete shells, lattice shells, and membrane structures. Examples of curved thin shell structures include hyperbolic shells, parabolic shells, and double curve shells.
Original Description:
Original Title
structuresshells-170517142559.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStructural basics in architecture focuses on folded slab roofs and thin shell structures. Folded slab roofs are thin-walled structures made of reinforced concrete or steel plates formed into prismatic, pyramidal, or prismoidal shapes. Thin shell structures are also called plate and shell structures, which are lightweight constructions using curved shell elements like concrete shells, lattice shells, and membrane structures. Examples of curved thin shell structures include hyperbolic shells, parabolic shells, and double curve shells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views26 pagesStructuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Structuresshells 170517142559 PDF
Uploaded by
Sebastiao SilvaStructural basics in architecture focuses on folded slab roofs and thin shell structures. Folded slab roofs are thin-walled structures made of reinforced concrete or steel plates formed into prismatic, pyramidal, or prismoidal shapes. Thin shell structures are also called plate and shell structures, which are lightweight constructions using curved shell elements like concrete shells, lattice shells, and membrane structures. Examples of curved thin shell structures include hyperbolic shells, parabolic shells, and double curve shells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 26
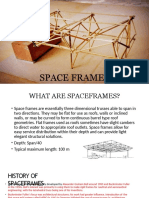
Structural basics in architecture
FOLDED SLAB ROOFS
• A thin-walled building structure of the shell type
• Movable form work can be employed.
• Form work required is relatively simpler.
• Design involves simpler calculations.
• Folded plate consumes more material than shells.
Folded slab roof
• Modern folded plate structures are typically
made of cast in site or precast reinforced
concrete, or steel plate.
Prismatic:
Rectangular
plates.
Pyramidal: Non-
rectangular
plates.
Prismoidal:
Triangular or
trapezoidal plates
Folded plate hut-japan
Air force academy chapel u.s.a.
Stairs....
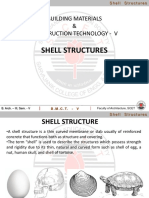
CONCEPT OF SHELLS
• Thin shell structures are also called plate and shell structures.
• They are Light weight constructions using shell elements.
Thin shells-types
• Concrete shells- monolithic dome or stressed ribbon bridge
or saddle roof.
• Lattice shell structures(grid shell)-geodesic dome or
hyperboloid structure.
• Membrane structures- fabric structures, other tensile
structures, cable domes, pneumatic structures.
Thin shells - examples
• Concrete shell- • Membrane structures-
Deitingen Service Birdair
Station
Double curve shells
• Curved surface shell
structures can be used
to create very useful,
lightweight, rigid
structural forms.
Double curve shells
CYLINDERICAL SHELLS
Hyperbolic shells
• Doubly curved surface- shape of a saddle.
• It has a convex form along one axis and
concave form on along the other.
• Easy to construct using a series of straight
structural members
• Constructed using concrete.
• The curvature reduces its tendency to buckle
in compression and achieves stiffness.
Parabolic shells
• Series of parabolas stung together.
• The use of reinforcing steel in the upward
curvature of the parabola allows for the
tensile forces to flow into first the neutral sag,
or catenary then the thrust of the forces flow
into the compression on the downward
parabola.
• Both the axial parabolas are compressed and
in tension.
Saddle dome in Calgary, Alberta
Lee valley velopark, Londan
Parabolic shells
PARABOLOID
A paraboloid is a particular kind of three-dimensional
surface. In the simplest case, it is the revolution of a
parabola along its axis of symmetry. This kind of surface
will open upwards in both sideways dimensions. A
hyperbolic paraboloid will open upward in one dimension
and downward in the other, resembling a saddle. Like in a
two-dimensional parabola, scaling factors can be applied
to the curvature of a paraboloid.
y = x2
Examples :
• TWA terminal,NYC Intl. Airport
•Zeiss Planatarium,Germany
• l'oceanogràfic,Spain
The variants of Paraboloids are:
•Elliptical paraboloid (silmilar to paraboloid)
•Hyperbolic “
Hyperbolic:
A saddle-shaped quadric surface whose sections by
planes parallel to one coordinate plane are
hyperbolas while those sections by planes
parallel to the other two are parabolas if proper
orientation of the coordinate axes is assumed
In simple words, I is a combination of hyperbolae
and parabola within a single entity.
Examples:
•Lee Valley Velo Park
•House by James R. Mowry
•Scotiabank Saddledome,Canada
The end
You might also like
- Folded Plate Structures FinalDocument27 pagesFolded Plate Structures FinalJ 3 E100% (1)
- Shell Structures and Cable StructuresDocument33 pagesShell Structures and Cable StructuresSanika Kadam100% (1)
- Shell StructureDocument18 pagesShell StructureYachika SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2D Plane Strain PlasticityDocument4 pages2D Plane Strain PlasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Shell Structure Cargo Fabian Lising Ramos HannahDocument30 pagesShell Structure Cargo Fabian Lising Ramos HannahRyana Rose CristobalNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates 6.2Document16 pagesFolded Plates 6.2vamshi bodaNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures: Ar.C.Naga Vaishnavi Ar.M.PadmaDocument25 pagesShell Structures: Ar.C.Naga Vaishnavi Ar.M.Padmasindhura100% (1)
- Vinay Katariya ABCM REPORT 6 PDFDocument10 pagesVinay Katariya ABCM REPORT 6 PDFVinay KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Shells and Folded PlatesDocument15 pagesShells and Folded PlatesSyed K INo ratings yet
- Part-B Shell-2Document3 pagesPart-B Shell-2studio surfaceNo ratings yet
- Braced Barrel VaultsDocument26 pagesBraced Barrel VaultsYong Athirah Zamzuri100% (1)
- BT115-RESEARCH 4A-Husana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Section ADocument21 pagesBT115-RESEARCH 4A-Husana, Thessaly Aubrey S. - Section AThessaly HusanaNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates - : Theory OF StructureDocument24 pagesFolded Plates - : Theory OF StructureShrea ZopeNo ratings yet
- ABCM DOMES, SHELLS & VAULTS - Report 4 - Group B3Document10 pagesABCM DOMES, SHELLS & VAULTS - Report 4 - Group B3Amey DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument40 pagesShell StructuresBharath AkurathiNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures-13-4-20Document19 pagesShell Structures-13-4-20sanket pawarNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument12 pagesShell Structuresdevang92100% (1)
- Special Structures Chapter 5Document55 pagesSpecial Structures Chapter 5Syed K INo ratings yet
- Building Structure and AesthaeticsDocument22 pagesBuilding Structure and AesthaeticsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Space Frames: Submitted By:-Akshay RishabhDocument7 pagesSpace Frames: Submitted By:-Akshay RishabhASHRAF TAMBOLINo ratings yet
- Folded Plate StructureDocument23 pagesFolded Plate StructureVvvg J100% (1)
- North Light Truss & Space FrameDocument28 pagesNorth Light Truss & Space FrameArshi Khan100% (2)
- Roofing System PDFDocument85 pagesRoofing System PDFAashi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shell StructuresDocument17 pagesShell Structuresdeepanshusoni100% (1)
- Shell Structure: S.Atchaya N.Ramupriya J.Sanofar Navreen S.Srividhya R.SwathyDocument29 pagesShell Structure: S.Atchaya N.Ramupriya J.Sanofar Navreen S.Srividhya R.Swathysrividhya raghavanNo ratings yet
- Folded Plates: Group Members: Subject: Theory of StructuresDocument20 pagesFolded Plates: Group Members: Subject: Theory of StructuresSoham SatamNo ratings yet
- Shell Roof and Membrane Structures1Document28 pagesShell Roof and Membrane Structures1Ar Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Shell RoofDocument13 pagesShell RoofvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Tensile StructureDocument49 pagesLecture 03 Tensile StructureDEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Shell Structure-Regulto, Maria CArmela D.Document20 pagesShell Structure-Regulto, Maria CArmela D.Carmela RegultoNo ratings yet
- CofferdamDocument41 pagesCofferdamSukhwinder Singh Gill0% (1)
- Advanced Structures: Unit 2 - Structural ElementsDocument98 pagesAdvanced Structures: Unit 2 - Structural ElementsSamreen Khan100% (1)
- Shell Structures: Shijo JoseDocument31 pagesShell Structures: Shijo Joseaksh dNo ratings yet
- CofferdamDocument42 pagesCofferdamRavi Shankar Kaushik60% (5)
- TENSILEDocument16 pagesTENSILESahithi SahiNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures-060139Document57 pagesShell Structures-060139Sonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Space Frame: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument11 pagesSpace Frame: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchRafia HassanNo ratings yet
- Shells 150918104334 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument30 pagesShells 150918104334 Lva1 App6891 PDFTasneem JraiNo ratings yet
- Shell and Cable StructuresDocument17 pagesShell and Cable StructuresShubham RautNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures - SEM IX - Folded Plates and ShellsDocument70 pagesTheory of Structures - SEM IX - Folded Plates and Shellsdavid100% (1)
- Midterm Module 3Document17 pagesMidterm Module 3CarloNo ratings yet
- CompositeDocument13 pagesCompositeklerdumdum02No ratings yet
- Shelled StructureDocument10 pagesShelled Structurenandu shahNo ratings yet
- Part-B SHELL - STRUCTURES-1Document31 pagesPart-B SHELL - STRUCTURES-1studio surfaceNo ratings yet
- Shaped StructuresDocument26 pagesShaped StructureskgatoNo ratings yet
- Space FrameDocument46 pagesSpace FrameAnonymous Y9dgyXhA100% (2)
- Tension Structure Connection Details Fabric ArchitectureDocument17 pagesTension Structure Connection Details Fabric Architecturejanhavi28No ratings yet
- Folded PlatesDocument23 pagesFolded Platesbhushruti100% (1)
- Shell and Dome - Lecture Note - 2023Document18 pagesShell and Dome - Lecture Note - 2023tsehay3737No ratings yet
- Shells and Domes Sec 201Document33 pagesShells and Domes Sec 201dplpthk1502No ratings yet
- Brief On Tensile StructuresDocument34 pagesBrief On Tensile StructuresShikhaNo ratings yet
- Structural SystemsDocument39 pagesStructural Systemstejaswini91% (11)
- ShellDocument64 pagesShellAishwarya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Shell Structures - B.M.C. - V PDFDocument21 pagesShell Structures - B.M.C. - V PDFAvi Korat100% (1)
- Folded PlateDocument14 pagesFolded PlateTanvi Yadav100% (3)
- 01 Omkar Pilankar 5thb Folded Plates A.B.C.MDocument20 pages01 Omkar Pilankar 5thb Folded Plates A.B.C.MHeramb MaratheNo ratings yet
- Folded Plate StructureDocument9 pagesFolded Plate StructureMohit BansalNo ratings yet
- Other Long Span Structures: Construction VIDocument46 pagesOther Long Span Structures: Construction VIShruti TareNo ratings yet
- 16bar002,16bar005,16bar017,16bar024,16bar028 Space FrameDocument28 pages16bar002,16bar005,16bar017,16bar024,16bar028 Space Framenij balarNo ratings yet
- What Are Folded Plates?Document10 pagesWhat Are Folded Plates?Sadhana PatilNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Elastoplasticidade Com AbaqusDocument6 pagesElastoplasticidade Com AbaqusSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Funções de FormaDocument9 pagesFunções de FormaSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Technique in Plasticity Including Solution Advancement ControlDocument20 pagesNumerical Technique in Plasticity Including Solution Advancement ControlSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Matlab InterfaceDocument128 pagesMatlab InterfaceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 3 BalanceDocument7 pages3 BalanceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 5 ElasticityDocument8 pages5 ElasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- TensorDocument7 pagesTensorSebastiao Silva100% (1)
- Creo Help CenterDocument1 pageCreo Help CenterSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- How To Implement Elastoplasticity in A Model Using External Materials - COMSOL BlogDocument17 pagesHow To Implement Elastoplasticity in A Model Using External Materials - COMSOL BlogSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- UMAT Theory - Nader Abedrabbo, PH.DDocument2 pagesUMAT Theory - Nader Abedrabbo, PH.DSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 08 Plasticity CompleteDocument85 pages08 Plasticity CompleteSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 122 TD4Document15 pages122 TD4Sebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 5Document25 pages14 Chapter 5Sebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- PlasticityDocument16 pagesPlasticitySebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Siemens Brazil enDocument5 pagesSiemens Brazil ensterilemovieNo ratings yet
- Neural Networks ExamDocument3 pagesNeural Networks Examfruit1991No ratings yet
- Catalog Siemens DetectieDocument340 pagesCatalog Siemens DetectieDamian OvidiuNo ratings yet
- ABS Welding With Backing StripDocument1 pageABS Welding With Backing StripAbuBakarSiddkeRumiNo ratings yet
- Planetary UrbanisationDocument5 pagesPlanetary UrbanisationFaris DzulfikarNo ratings yet
- Survey On Physical Layer Security For 5G Wireless NetworksDocument20 pagesSurvey On Physical Layer Security For 5G Wireless NetworksjavaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Skill Integration Challenge ReflectionDocument2 pagesPacket Tracer - Skill Integration Challenge Reflectionapi-250744553No ratings yet
- Planning and Designing of Bridge Over Solani RiverDocument5 pagesPlanning and Designing of Bridge Over Solani RiverCurious RajNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinDocument6 pagesPhysic Lab Report 6: Sherry Carentona GalinNurl AinaNo ratings yet
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Unit4 PDFDocument36 pagesUnit4 PDFDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- Control Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFDocument8 pagesControl Valve CV - What It Means and How To Calculate It - Visaya PDFmurugan1984No ratings yet
- Evs Project & SeminarDocument21 pagesEvs Project & Seminarpratibhaawari01No ratings yet
- SPE Data Analytics in Reservoir EngineeringDocument108 pagesSPE Data Analytics in Reservoir EngineeringNindy Sherli ParamitaNo ratings yet
- ASME SEC IX 2017-Pages-361-367Document7 pagesASME SEC IX 2017-Pages-361-367RahulNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1st Periodical TestDocument4 pagesScience 9 1st Periodical TestKebu Yen100% (1)
- Handicraft Production LMDocument82 pagesHandicraft Production LMmjcNo ratings yet
- Benito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFDocument81 pagesBenito Canfield - Rule of Perfection PDFcalenduloNo ratings yet
- BARBED WIRe DPRDocument22 pagesBARBED WIRe DPRGateway ComputersNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- FuturaPC EngDocument36 pagesFuturaPC EngRashika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muet 1Document15 pagesMuet 1Sity Noor QiyahNo ratings yet
- Per. Dev. Week 2Document21 pagesPer. Dev. Week 2Mi ChellNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations - MTH401 Fall 2006 Final Term Paper Session 1Document6 pagesDifferential Equations - MTH401 Fall 2006 Final Term Paper Session 1Faizan Zafar SahiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument18 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpurk krishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Is-Criteria For Structural Design of Penstock-11639 - 3Document19 pagesIs-Criteria For Structural Design of Penstock-11639 - 3duldar docNo ratings yet
- Hall - Panikkar Trusting The OtherDocument23 pagesHall - Panikkar Trusting The OtherOscar Emilio Rodríguez CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Isopropyl Alcohol Solution 91, 400682 - HLK - SDSDocument7 pagesIsopropyl Alcohol Solution 91, 400682 - HLK - SDSAman BaigNo ratings yet
- Wolfgang Pauli and Modern PhysicsDocument17 pagesWolfgang Pauli and Modern PhysicsahsbonNo ratings yet
- HVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & InstallationDocument3 pagesHVAC Designing Drafting Estimation & Installationnoha azamali50% (2)