Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019
Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019
Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019
Uploaded by
Nicole cuencosCopyright:
Available Formats
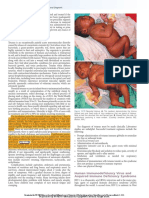
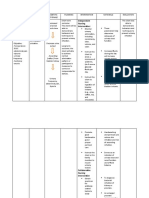
TYPOID- is a bacterial infection transmitted by Serological Tests : Typhidot – confirmatory Muscle spasm & stiffness, difficulty of swallowing,
contaminated water, milk, shellfish and other foods. It ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunoassay) difficulty of breathing and spine will arch backward
is an infection of the GIT affecting lymphoid tissues of Widal test
the small intestines called Peyer’s patches. DIAGNOSIS: Physical Examination
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT &TREATMENT: TRETAMENT: Within 72 hours, administration of
CAUSATIVE AGENT: Salmonella typhosa, Antibiotics- ampicillin, chloramphenicol(Drug of ATS, TAT or TIG, especially if no previous
Salmonella paratyphi choice for treatment of typhoid fever ), immunization
SIGN & SYMPTOMS:
fluoroquinolone Amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin Tetanus toxoid
NURSING MANAGEMENT Antibiotic- Pen G
1. Prodromal Stage- headache, fever, 1. Isolation by the medical aseptic technique Muscle relaxant
anorexia, lethargy, diarrhea or constipation, 2. Maintain or restore fluid and electrolyte
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
vomiting, abdominal pain, feeling of un balance by giving nourishing fluids in small
quantities at frequent intervals. Isolation
wellness
3. Monitor the patient’s vital signs. Protect the child from any stimuli
2. Fastigial Stage / Pyrexial Stage-the
4. Prevent further injury (such as falls) of patient Administer oxygen if dyspnea and cyanosis occur.
following signs appear: ladder like curve of
with typhoid psychosis. For tetanic spams,
tempt, splenomegaly ,Rose spots 5. Maintain good personal hygiene and mouth Protect the child from falling
(Pathognomonic sign of Typhoid fever) care. Note the number, duration and frequency
usually occur between the second and fourth 6. Cooling measures are necessary during the
of convulsion
week of illness. febrile state.
7. Administer medication as prescribed Record any change in trismus or inability
3. Defervescent stage- fever gradually
Prevention: to swallow
subsides severity of previous conditions
1. Sanitary and proper disposal of excreta For inability to swallow
,onset of complications
2. Enteric isolation IV therapy for nutrition and balance
4. Convalescent Stage- gradual disappearance 3. Provision of adequate amounts of safe
of signs and symptoms Gavage feeding
drinking water supply
Incubation Period: 7 -14 days Accurate I and O
4. Education of the general public on the mode
Source of Infection: of transmission Oral care
Feces, urine and vomitus of infected person 5. Immunization Prevention:
Ingestion of shellfish (oysters) taken from 6. Handwashing Active immunization with TT, DPT
waters contaminated with sewage disposal 7. Avoid mode of transmission (Diphtheria, Pertussis, and Tetanus) vaccine;
can be a source of infection. 8. Decontamination of water sources Passive immunization-TIG, ATS
DIAGNOSTIC TEST TETANUS (Lockjaw)- serious infection; this
bacterium produces a toxin that affects the brain and
Clinical examination
nervous system leading to stiffness in the muscles.
Culture of Blood, bone marrow, urine , stool
CAUSE: Clostridium tetani.
for S. typhi, rectal swab
SIGN & SYMPTOMS: diarrhea, fever, and headache
MENINGITIS-inflammation of the meninges, which CAUSATIVE AGENT: Dengue virus- DEN-1, DEN-2,
2. Monitor patient's general condition.
cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. DEN-3, and DEN-4. Spread by Aedes mosquitoes
& Aedes albopictus 3. Provide tepid Sponge bath
CAUSATIVE AGENTS: SIGN & SYMPTOMS:
4. Encourage the client to drink water
Meningococcus (Neisseria meningitidis)
Streptococcus pneumonia 1. Sudden-onset fever 5. Explain to patients and families sign of
Mycobacterium 2. Headache (typically located behind the eyes)
3. Muscle and joint pain bleeding, and immediately report if there
4. Rash is bleeding
SIGN & SYMPTOMS: Head ache (steady or
5. Chills (shivering)
throbbing) fever, Neck immobility , Positive Kernig’s 6. Facial flushing 6. Anticipation of bleeding: use a soft
sign, Positive Brudzinki’s sign, Photophobia 7. Loss of appetite
DIAGNOSTIC TEST: CT SCAN or MRI, BLOOD 8. Sore throat toothbrush, maintain oral hygiene, apply
TEST, CHEST X-RAY, LUMBAR PUNCTURE 9. Abnormal bleeding such as nosebleeds,
pressure take 5-10 minutes after each
bleeding gums and/or blood in your urine.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT &TREATMENT: blood.
Penicillin G, Dexamethasone, Phenytoin, DIAGNOSTIC TEST: 7. Monitor signs of decreased platelets
NURSING MANAGEMENT: Hematocrit, accompanied by clinical signs.
1. Infection control precaution until 24 hours CBC, 8. Give the medication as prescribe by the
after initiation of antibiotic therapy
2. Assist with pain management and rest Seroloy Test (MAC-ELISA –IgM antibody physician
3. Encourage the patient to stay hydrated capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay PREVENTION:
4. Ensure neurologic monitoring
(MAC- ELISA), &IgGELISA, Health teachings about Do’s & Don’ts of Dengue
5. Monitor daily body weight and I & O
Molecular testing (polymerase chain reaction,
Prevention:
PCR) JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS - is an infection
Antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis: Rifampin
(Rifadin), Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (Cipro), MEDICAL MANAGEMENT &TREATMENT: of the Central Nervous System (CNS) caused by a
Ceftrioxone sodium (Rocephin); Vaccination
Paracetamol for fever, pain relievers with virus CAUSATIVE AGENT: (Flavivirus) transmitted
(Meningococcal conjugated);
acetaminophen, rest, and Increase fluid intake to the man by a mosquito.
DEUNGUE- also known as breakbone fever, is a SIGN & SYMPTOMS: headache, high fever, tremors,
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
mosquito-borne infection that can lead to a severe
flu-like illness 1. Monitor Vital signs and I & O nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, spastic paralysis.
DIAGNOSTIC TEST:
Serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to detect virus- CHIKUNGUNYA is an infection caused by NURSING MANAGEMENT
specific IgM antibodies the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). 1. Monitor Neurologic Status with GCS & Vital
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT &TREATMENT: SIGN & SYMPTOMS : signs
2. Administration of non-steroidal anti-
Suramin -a drug used to treat trypanosomal disease, Fever and joint pain. These typically occur two to inflammatory drugs help in relieving pain.
and diethyldithiocarbamate have shown reasonably twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may 3. Antiviral drugs like acyclovir are also given
(but given only in complicated cases as
good antiviral efficacy against Japanese encephalitis include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a prescribed by doctor).
4. Fluid intake: Plenty of fluids intake helps in
virus in vitro rash. keeping hydrated.
5. Infected persons should be isolated from
anticonvulsants for seizure control COMPLICATION-long term joint pain.
mosquitoes as much as possible in order to
NURSING MANAGEMENT: avoid transmission of infection to other
people.
1. Monitor Neurologic Status with GCS & Vital DIAGNOSTIC TEST:
signs Reverse transcription–polymerase chain PREVENTION
2. Provide security for patients by providing reaction (RT-PCR)
1. Use insect repellent containing DEET,
assistance on the bed use the side rails Enzyme-Linked Immuno-sorbent Assay Picaridin, oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed
skin. Always follow the directions on the
3. Increase patient awareness and sensory (ELISA) may confirm the presence of IgM and
package.
function IgG anti-Chikungunya antibodies. 2. Wear long sleeves and pants (ideally treat
clothes with permethrin or another repellent).
PREVENTION: Prevent mosquito bites. Mosquitoes 3. Have secure screens on windows and doors
to keep mosquitoes out.
bite during the day and night. Use insect repellent, MEDICAL MANAGEMENT TREATMENT: 4. Additionally, a person with chikungunya fever
wear long-sleeved shirts and pants, treat clothing and ibuprofen, naproxen, acetaminophen, or should limit his exposure to mosquito bites to
avoid further spreading the infection. The
gear, and get vaccinated before traveling, if paracetamol person should use repellents when outdoors
exposed to mosquito bites or stay indoors in
vaccination is recommended for you. chloroquine phosphate- for Chikungunya areas with screens or under a mosquito net.
Bed rest & Increase fluid intake
RABIES- a contagious and fatal viral disease of dogs 1. Washing the wound thoroughly with soap and
and other mammals that causes madness and water
convulsions, transmissible through the saliva to 2. Provide wound care
humans. 3. Give Ainti-rabies vaccine as prescribe by the
physician
CAUSATIVE AGENT: Rabies Virus 4. Manage the patient with rabies:
SIGN & SYMPTOMS Isolate the patient
Flu-like symptoms such as a fever, headache, muscle Encourage family to provide care &
aches, loss of appetite, nausea, and tiredness. company
Neurological symptoms develop, including: Give food if the patient is hungry
irritability or aggressiveness Keep water out of sight
excessive movements or agitation
Observe Universal precautions
confusion, bizarre or strange thoughts, or
PREVENTION
hallucinations
muscle spasms and unusual postures Instruct to have regular antirabies vaccinations for
seizures (convulsions) all pets and domestic animals
weakness or paralysis (when a person cannot move Provide educational information and awareness
some part of the body)
extreme sensitivity to bright lights, sounds, or touch
DIAGNOSTIC TEST
Serum and spinal fluid test
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT &TREATMENT
Fast-acting shot (rabies immune globulin)
Anti -rabies vaccines
NURSING MANAGEMENT
You might also like
- Medical Abbreviations Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMedical Abbreviations Worksheet PDFRupert Bautista100% (1)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (3)
- Vision Therapy in The Modern Behavioural Optometry Practice History of Vision TherapyDocument8 pagesVision Therapy in The Modern Behavioural Optometry Practice History of Vision TherapyPierre A. RodulfoNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Care of The Older Adult Emelie Jalandoni Tan, RN., DnsDocument7 pagesNCM 114 Care of The Older Adult Emelie Jalandoni Tan, RN., DnsPatricia Vasquez100% (4)
- CHN ReviewersDocument5 pagesCHN ReviewersAngelina Nicole G. TungolNo ratings yet
- Finals 3Document5 pagesFinals 3Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Case StudyDocument5 pagesActivity 2 - Case StudyGrace MendozaNo ratings yet
- Case 3Document27 pagesCase 3Eduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Vector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Document20 pagesVector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Nina OaipNo ratings yet
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocument16 pagesSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory & Immunologic Diseases IIIDocument252 pagesInflammatory & Immunologic Diseases IIIiamaldrinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Lesson HealthDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Lesson HealthJulyfer CabisoNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Moleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IDocument11 pagesMoleno April Mariebsn Ii F Case Scenario 1 Pediatric-Community Acquired Pneumonia Pcap-C IyounggirldavidNo ratings yet
- MedsurgDocument11 pagesMedsurgJuana ToriomNo ratings yet
- Principles of Medicine - Infectious Diseases Part 2 NotesDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Medicine - Infectious Diseases Part 2 NotesRianne MagalongaNo ratings yet
- Childhood Infectious DiseasesDocument17 pagesChildhood Infectious DiseasesRNStudent1No ratings yet
- Group 2 TetanusDocument43 pagesGroup 2 TetanusDaymon, Ma. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Erythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineDocument6 pagesErythromycin & Pneumococcal VaccineNikki Joy NavarroNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- CHN Presentaion-1Document23 pagesCHN Presentaion-1Sada AlakNo ratings yet
- Enteric DiseaseDocument2 pagesEnteric DiseaseHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox (Varicella) - Acute MUMPS (Epidemic Parotitis) - An AcuteDocument7 pagesChicken Pox (Varicella) - Acute MUMPS (Epidemic Parotitis) - An AcutejunlynNo ratings yet
- CHN TransDocument5 pagesCHN TransRica MariaeNo ratings yet
- Health and DiseaseDocument32 pagesHealth and DiseaseAlejandro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument101 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKira100% (4)
- NCP PediaDocument9 pagesNCP Pediajuworski1No ratings yet
- Baccilary DysenteryDocument2 pagesBaccilary DysenteryZam PamateNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument3 pagesDiseasestamizharasiNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Is The Inflammation of The Protective MembranesDocument7 pagesMeningitis Is The Inflammation of The Protective MembranesAtinder PalNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of RhabdoviridaeDocument3 pagesRabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of RhabdoviridaeFhaye LitucoNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument3 pagesTETANUSfxbukenyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 AllDocument50 pagesNCM 112 AllNathaniel BudayNo ratings yet
- Tetanus NeonatorumDocument1 pageTetanus Neonatorumeagame gamersNo ratings yet
- VITALSIGNSIMMUNIZATIONDocument6 pagesVITALSIGNSIMMUNIZATIONGlaiza Mae TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Commmon Communcable Diseases Affecting The Gastointestinal System Final-1Document113 pagesCommmon Communcable Diseases Affecting The Gastointestinal System Final-1fulolorenzNo ratings yet
- Brosure Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesBrosure Dengue FeverMadvi TadeoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in PaediatricsDocument19 pagesPneumonia in PaediatricsBhintuna ChaNo ratings yet
- NCM109 - Reviewer-Lp-1-To-Lp-4Document54 pagesNCM109 - Reviewer-Lp-1-To-Lp-4princessNo ratings yet
- 1) Epi DiseasesDocument58 pages1) Epi DiseasesdaveNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals!Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals!Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- 17 Agromed Tutor 2Document22 pages17 Agromed Tutor 2FatimahNo ratings yet
- RabiesDocument22 pagesRabiesDivine IncilloNo ratings yet
- TF FinalDocument13 pagesTF FinalAiraa ShaneNo ratings yet
- CHN RleDocument3 pagesCHN RleCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- High Risk PreschoolerDocument7 pagesHigh Risk PreschoolerAngela Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument7 pagesBacterial InfectionsLarissaNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Presented by Sharlin MacalintalDocument18 pagesTyphoid Fever: Presented by Sharlin MacalintalPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- CD PresentationDocument225 pagesCD PresentationHersy Marie Azores GarayNo ratings yet
- Biostat Finals p2Document8 pagesBiostat Finals p2Kystrel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Infectious and Inflammatory DisordersDocument11 pagesInfectious and Inflammatory DisordersdivineNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DiseaseDocument7 pagesPediatric DiseaseTomasina Portia OrteaNo ratings yet
- Terapi Kejang DemamDocument5 pagesTerapi Kejang DemamWulan MeilaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiacand Respiratory CMsDocument23 pagesCardiacand Respiratory CMsday alcoberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Human HealthDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Human HealthREKSHENA A/P PERKAS MoeNo ratings yet
- Cte #2: Matrix of Communicable DiseasesDocument7 pagesCte #2: Matrix of Communicable Diseasesjoannamae molagaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Leptospirosis Dengue Fever Malaria Filariais EncephalitisDocument95 pages1.2 Leptospirosis Dengue Fever Malaria Filariais Encephalitisesbercinio8528valNo ratings yet
- Chikunguniya PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument6 pagesChikunguniya PATHOPHYSIOLOGYAngad GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Diseases at A Glance by Dr. NK Sharma Chapter: Human Health & DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseases at A Glance by Dr. NK Sharma Chapter: Human Health & DiseaseRahul DixitNo ratings yet
- CHN Midterm ReviewerDocument54 pagesCHN Midterm ReviewerJoi PreconesNo ratings yet
- Module 3B.2 Puerperial InfectionDocument17 pagesModule 3B.2 Puerperial InfectionEmmanuel BillenaNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeFrom EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CLEFT LIP AND CLEFT PALATENicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Fdar-Labor PainDocument5 pagesFdar-Labor PainNicole cuencos100% (1)
- Depression Case StudyDocument1 pageDepression Case StudyNicole cuencos100% (1)
- APPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Document3 pagesAPPENDIC CASES Cuenco2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain Case StudyDocument7 pagesLabor Pain Case StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Case Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Document7 pagesCase Ana-Hypothyroidism 2020Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- COLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONDocument3 pagesCOLON CANCER NCP-impaired nutrITIONNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Weigght Gain NCPDocument1 pageWeigght Gain NCPNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaire Urinary EliminationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Spinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesSpinal Bifida Ncp-Impaired Physical MobilityNicole cuencos50% (2)
- Deficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid Volume Related To Polyuria and Dehydration AEB Dry Mucus MembraneNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Alteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesDocument3 pagesAlteration of The Starling Forces Which Control Transfer of Fluid From The Vascular Compartment To Surrounding Tissue SpacesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESDocument5 pagesDrug Classification/Indicati ON Mechanis MOF Action Contraindication Adverse Reaction Dose, Route, Frequenc Y Nursing Responsibiliti ESNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Significance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Document1 pageSignificance of The Study & Scope, Limitations and Delimitations-HIV2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective CuesNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Duavent Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Computation FormulasDocument1 pageComputation FormulasNicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and HygieneDocument28 pagesAdvanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and Hygienejane entunaNo ratings yet
- Medical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashDocument13 pagesMedical Student Amnesia USMLE Step 1 - Flash Cards by CueFlashMuhammad Farhan KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : By, Ms. Ekta. S. Patel, I Yr M.SC NursingDocument71 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : By, Ms. Ekta. S. Patel, I Yr M.SC NursingannisanabilaasNo ratings yet
- Patient History Form: Dow Executive CheckupDocument6 pagesPatient History Form: Dow Executive CheckupAkhtar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Senarai Nama Anggota Unit Rawatan Rapi, Hospital Queen Elizabeth Ii 2014Document8 pagesSenarai Nama Anggota Unit Rawatan Rapi, Hospital Queen Elizabeth Ii 2014Rosyta DawatNo ratings yet
- Pocket Pediatric Hematologi OnkologiDocument5 pagesPocket Pediatric Hematologi OnkologiAdrian KhomanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing POST TEST Day 1Document1 pageMental Health and Psychiatric Nursing POST TEST Day 1Mcbry TiongNo ratings yet
- HapDocument15 pagesHapWinariieeyy Nayy100% (1)
- admin,+14-18+JPS+Alya+Rahma+Trishna+1 RemovedDocument8 pagesadmin,+14-18+JPS+Alya+Rahma+Trishna+1 RemovedadekirmayulianiNo ratings yet
- Screw Retained Vs Cement Retained Implant-Supported FDP, Closed-Tray Vs Open-Tray Dental Implant ImpressionDocument5 pagesScrew Retained Vs Cement Retained Implant-Supported FDP, Closed-Tray Vs Open-Tray Dental Implant ImpressionMazen T. ShembeshNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant and Antipsychotic Side-Effects and Personalised Prescribing, A Systematic Review and Digital Tool Development. Lancet 2023Document17 pagesAntidepressant and Antipsychotic Side-Effects and Personalised Prescribing, A Systematic Review and Digital Tool Development. Lancet 2023tomil.hoNo ratings yet
- Institute of Human Behaviour and Allied SciencesDocument52 pagesInstitute of Human Behaviour and Allied SciencesCMO Bestla GroupNo ratings yet
- My ThesisDocument10 pagesMy Thesishinduja reddipilliNo ratings yet
- Acute Calculous CholecystitisDocument9 pagesAcute Calculous CholecystitisNoel LoayzaNo ratings yet
- The Smoker's BodyDocument1 pageThe Smoker's BodyAnna Rose CabuncalNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya PolavarapuDocument18 pagesInsulin Therapy: by Dr. Adithya Polavarapuadithya polavarapuNo ratings yet
- Ciy745 PDFDocument35 pagesCiy745 PDFPhúc LâmNo ratings yet
- Gmail Maxicare EReady Advance PDFDocument7 pagesGmail Maxicare EReady Advance PDFShirelyNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Complications: Mandibular Anterior: Intraosseous VesselsDocument2 pagesIntraoperative Complications: Mandibular Anterior: Intraosseous VesselsRoenteiqNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro To Health AssessmentDocument30 pagesWeek 2 - Intro To Health AssessmentGLADYS MAY GUDELOS MEJIASNo ratings yet
- Answer Intermediate LifeDocument1 pageAnswer Intermediate LifeDAvid HallasiNo ratings yet
- CLONORCHISDocument23 pagesCLONORCHISodysseyfairy2739No ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument81 pagesPoliomyelitisKaycee Glene CalubNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta Drug StudyDocument5 pagesAbruptio Placenta Drug StudyJayne Angelie A. NuevaespañaNo ratings yet
- Extended Trochanteric Osteotomy in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty - Contemporary Outcomes of 612 HipsDocument12 pagesExtended Trochanteric Osteotomy in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty - Contemporary Outcomes of 612 Hips阿欧有怪兽No ratings yet
- Journal Collodion BabyDocument5 pagesJournal Collodion BabyLidia MdNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 18Document8 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 18sarasjunk100% (1)