Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LP in Logarithms
LP in Logarithms
Uploaded by
Don Joey Loyola PontevedraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Distance FormulaDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Distance FormulaKenneth Sedonio Arrubio-Guiral88% (8)
- Lesson Plan - Day 1.Document4 pagesLesson Plan - Day 1.Jocelyn Baculi AutenticoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Operation of Functions (Discovery and Lectured)Document15 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Operation of Functions (Discovery and Lectured)Jameson SalazarNo ratings yet
- Exponential Equation LP FinalDocument3 pagesExponential Equation LP FinalAngelo Belandres Llonora100% (4)
- Performance Task AND Project IN Basic CalculusDocument4 pagesPerformance Task AND Project IN Basic CalculusBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Manipulating Rational Expressions Ad EquationsDocument9 pagesLesson Plan For Manipulating Rational Expressions Ad Equationslaurice benal100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For Exponential Equation Using Same BaseDocument5 pagesLesson Plan For Exponential Equation Using Same Baseアンジェロドン100% (2)
- LP STEM - BC11D IIIf 2 Rules of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesLP STEM - BC11D IIIf 2 Rules of DifferentiationLeopold Laset100% (2)
- Learning Module: MODULE 6: Solving Problems Involving Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocument9 pagesLearning Module: MODULE 6: Solving Problems Involving Rational Algebraic ExpressionsMaria Martina Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Flexobox-Gu8ia Rapida PDFDocument1 pageFlexobox-Gu8ia Rapida PDFFanytta LarahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in General MathematicsDerren Nierras Gaylo100% (1)
- Rational Function RepresentationDocument3 pagesRational Function RepresentationJM Panganiban IINo ratings yet
- STEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Document10 pagesSTEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Chad Lowe Verdan Villarroya100% (3)
- Week 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Document6 pagesWeek 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Dindin Oromedlav LoricaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General Mathematics 11Document2 pagesLesson Plan in General Mathematics 11marystel b. BorbonNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 2Document7 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 2Rod ManachoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan Iin Statistics and ProbabilityDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan Iin Statistics and ProbabilitySHARMINE CABUSAS0% (1)
- Probability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPDocument3 pagesProbability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPJoshua OticNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningLily Anne Ramos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Sample Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath 10 Sample Lesson PlanAce SundiamNo ratings yet
- Gen Math First QuarterDocument194 pagesGen Math First QuarterDindin Oromedlav Lorica100% (8)
- Lesson No.11 Domain and Range of Rational FunctionsDocument3 pagesLesson No.11 Domain and Range of Rational FunctionsDian Jane Gaylawan75% (4)
- LP Rational FunctionDocument10 pagesLP Rational FunctionJaiNo ratings yet
- TOS For Gen MathDocument3 pagesTOS For Gen MathAbegail PanangNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusDocument46 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusLeah Mae France100% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsJoanMurilloSimanganNo ratings yet
- III. Lesson 10 Inverse of One-To One FunctionDocument3 pagesIII. Lesson 10 Inverse of One-To One Functionalejandro diyaoNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 8.3Document8 pagesDLP Math 8.3Val Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- GM Week2 Summative Assessment 2a Rational Functions October 12 16Document2 pagesGM Week2 Summative Assessment 2a Rational Functions October 12 16Lee Russel CoronelNo ratings yet
- Gen Math STEM B Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesGen Math STEM B Daily Lesson Logjun del rosario100% (1)
- SHS Learning Plan (General Mathematics)Document3 pagesSHS Learning Plan (General Mathematics)MeYo San100% (1)
- Compound Interest DLLDocument5 pagesCompound Interest DLLOmengMagcalas100% (1)
- Culminating Performance Standard Performance Task Enabling Performance Standard Performance CheckDocument1 pageCulminating Performance Standard Performance Task Enabling Performance Standard Performance CheckJap TVNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLogarithmic Lesson PlanAzza ZzinNo ratings yet
- WHLP General Mathematics Week 1 - 4Document8 pagesWHLP General Mathematics Week 1 - 4Christine YnotNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanRaquel NavarezNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability DLL-MaligayaDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability DLL-MaligayaMARIA CARMELA MALIGAYANo ratings yet
- 1st PT GEN MATHDocument7 pages1st PT GEN MATHErnie LahaylahayNo ratings yet
- Marjorie B. Malveda Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesMarjorie B. Malveda Detailed Lesson PlanMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MATH2Document4 pagesLesson Plan MATH2Jomar AbreuNo ratings yet
- Khai Lesson Plan 2Document10 pagesKhai Lesson Plan 2api-299009301100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanLauren Erickson0% (1)
- A Lesson Plan On Exponential Functions in RealityDocument3 pagesA Lesson Plan On Exponential Functions in RealityMarnellie Bautista-Valdez100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in General Mathematics PDFDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in General Mathematics PDFAgatha Jane Francisco100% (1)
- Simple Interest Lesson EDTECH 541Document2 pagesSimple Interest Lesson EDTECH 541Jennifer Marrott80% (5)
- Arithmetic Sequence 1Document2 pagesArithmetic Sequence 1Eric de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- One-To-One FunctionsDocument2 pagesOne-To-One FunctionsDominic Dalton Caling100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in StatisticsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in StatisticsJulovern MolvizarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Daily Lesson LogMa. Wilma Q. SevilloNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (BOW) - GenMathDocument2 pagesBudget of Work (BOW) - GenMathJENETTE SABURAO50% (2)
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityJay ReyesNo ratings yet
- SEPTEMBER 14 118 DLL Rational ExpressionDocument4 pagesSEPTEMBER 14 118 DLL Rational ExpressionIsrael Arthel IlaoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument22 pagesQ4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityAngeleehNo ratings yet
- Equivalence of A StatementDocument7 pagesEquivalence of A StatementkiahjessieNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Jeanelyn SegotierNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsHazel Recites Bernaldez100% (1)
- Orig LP Luyun 03-13-2023Document12 pagesOrig LP Luyun 03-13-2023api-651752332No ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsDocument25 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsPOTENCIANO JR TUNAYNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 6Document6 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 6Ram GazerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Laws of ExponentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - Laws of ExponentMarizel VillaluzNo ratings yet
- DLL 6Document4 pagesDLL 6REALIZA B. BELCHEZNo ratings yet
- Cs245 F16 Part 1Document310 pagesCs245 F16 Part 1needecon102notesNo ratings yet
- Spanning TreeDocument2 pagesSpanning TreefxtrendNo ratings yet
- Sap MRP ConfigDocument23 pagesSap MRP Configsharadapurv100% (1)
- Control System Competitive Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesControl System Competitive Questions With AnswersAnonymous D0FSPtyI8No ratings yet
- Guia ZDocument30 pagesGuia ZJonathan ChafloqueNo ratings yet
- TRIAL MATH M 950-2 2015 Jong SrawakDocument9 pagesTRIAL MATH M 950-2 2015 Jong SrawakmasyatiNo ratings yet
- CPP Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesCPP Model Question PaperRaja GuruNo ratings yet
- 6 Thomas Intergraph Partnership SPRDDocument28 pages6 Thomas Intergraph Partnership SPRDManoj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Apache HiveDocument77 pagesApache HiveAshok Kumar K RNo ratings yet
- Helpful Transactions, Tools, Programs, Tables, Etc. For A SAP GRC ConsultantDocument11 pagesHelpful Transactions, Tools, Programs, Tables, Etc. For A SAP GRC Consultantxylas_zeusNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial 9 Ball Plate Impact PDFDocument8 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 9 Ball Plate Impact PDFhansNo ratings yet
- Exp No.: 6 Aim: To Study Dos, Arp Spoofing and Buffer Overflow Attack. Theory A) Dos AttackDocument7 pagesExp No.: 6 Aim: To Study Dos, Arp Spoofing and Buffer Overflow Attack. Theory A) Dos AttacksanjayNo ratings yet
- CXEx Tutorial - Creating Mac Ports of Games & Applications - The Porting TeamDocument15 pagesCXEx Tutorial - Creating Mac Ports of Games & Applications - The Porting TeamIndrick BorealeNo ratings yet
- Co 2020Document12 pagesCo 2020Sinley PatelNo ratings yet
- OpenStage HFA V2R0.98.0 Release Notes V13.0 ExternDocument22 pagesOpenStage HFA V2R0.98.0 Release Notes V13.0 Externfantasy247No ratings yet
- Logicore Ip Fast Simplex Link (FSL) V20 Bus (V2.11C) : Ffs Block RamsDocument9 pagesLogicore Ip Fast Simplex Link (FSL) V20 Bus (V2.11C) : Ffs Block RamswachutunaiNo ratings yet
- Review and Critical Thinking QuesionDocument2 pagesReview and Critical Thinking QuesionIkmal AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is Hiper-VDocument21 pagesWhat Is Hiper-Vhinjak hakaloNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann Nicdao Resume Khit Ano BastaDocument2 pagesMary Ann Nicdao Resume Khit Ano BastapatmanderNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Graphs of Functions 2Document123 pages2.0 Graphs of Functions 2juriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Configuration Guide - Multicast (V100R006C01 - 01)Document298 pagesConfiguration Guide - Multicast (V100R006C01 - 01)indra_uhuiiNo ratings yet
- Workshop02 Nguyễn-Tuấn-Minh DE170598Document9 pagesWorkshop02 Nguyễn-Tuấn-Minh DE170598Minh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Adv OS MCQDocument16 pagesAdv OS MCQsraveshNo ratings yet
- Business StudiesDocument15 pagesBusiness StudiesdiolpNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Unix and Linux Programming PR Cot 218 and It 214Document7 pagesLab Manual Unix and Linux Programming PR Cot 218 and It 214sameerroushanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Visual Test SoftwareDocument12 pagesAdvanced Visual Test SoftwareCHOCHO2009No ratings yet
- ME3400e SCG PDFDocument1,274 pagesME3400e SCG PDFsergioNo ratings yet
- ClarioNET 6301Document117 pagesClarioNET 6301jpg67No ratings yet
- Wavelet Families and Properties - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument2 pagesWavelet Families and Properties - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaAtul ManiNo ratings yet
LP in Logarithms
LP in Logarithms
Uploaded by
Don Joey Loyola PontevedraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LP in Logarithms
LP in Logarithms
Uploaded by
Don Joey Loyola PontevedraCopyright:
Available Formats
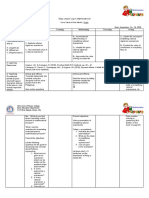
Detailed Lesson Plan
in General Math
I. Objectives
At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
a.) express exponential form into logarithmic expression and vice-
versa;
b.) solve logarithms manually and with the aid of Microsoft Excel;
c.) value the importance of logarithms by knowing its application in
Science, DRRM and other related subjects.
II. Subject Matter
Content : Functions and their Graphs
Content Standards : Key concepts of exponential functions and
logarithmic functions.
Performance Standards : apply the concepts of exponential functions
and logarithmic functions to formulate and
solve real-life problems with precision and
accuracy.
Learning Competencies : 1.) Represent real-life situations using
logarithmic functions. (M11GM – Ih – 1)
Topic : Introduction to Logarithms
Reference : Gen. Mathematics Teaching Guide,
pp. 112 – 121.
Materials : Multi-media
III. Procedures:
A. Preliminaries
- Prayer
- Checking of Attendance
- Checking of assignment (If there’s any)
B. Preparatory Activity
- Review of the previous lesson
Ask the student to find the value of the variable.
a.) 5x = 625
1
b.) x-2 = 9
c.) 102 = x
Answers:
a. x = 4
b. x = 3
c. x = 100
C. Developmental Activities
ACTIVITY
Video about earthquake will be shown to the students.
ANALYSIS
The following questions will be asked:
1. What have you observed in the video?
2. How devastating is the earthquake?
3. What are the magnitudes that were reported? Can we compute
these magnitudes manually?
ABSTRACTION
(Indicators No. 4 and 5)
The teacher will employ scaffolding teaching technique and auction
system as a game to stimulate the students learning. It is by providing
worksheets to the group of students then engaging them to a game. (See
attachment for the sample of the worksheets).
Examples:
Think of a logarithm of x to the base b (denoted by logbx as the exponent
of b that gives x. For example, log381 = 4 because 34 = 81. Some
additional examples are given below:
a.) Log232 = 5 because 25 = 32
b.) Log51 = 0 because 50 = 1
1 1
c.) Log66 = -1 because 6-1 = 6
Auction System:
(Indicators No. 2 and 3)
The students are provided with strips of paper. The strips of paper
is color coded. White for 1 point, Green for 2 points and Yellow for 5
points. Each group is given a 10 white strips, 10 green strips and 4 yellow
strips, a total of 50 points. Before the question is given, the leader of the
group will choose 1 member of his/her team to fight with other group
(each member has only one chance of answering the question). After
the question is given, the teacher will be asking for bets. The highest
bidder will have the 1st chance to answer the question. However, if the
answer of the highest bidder is wrong, the 2nd bidder will answer the
question. The member who got a correct answer will collect all the bets.
At the end of the game the number of strips of paper will be the basis of
ranking. However, the group who has no more strips of paper will be out
from the game.
Round 1.
Example 1. Without using a calculator, find the value of the following
logarithmic expression.
a.) log9729
b.) log 10, 000
c.) log1/216
1
d.) log5
√5
Solution.
a.) What exponent of 9 will give 729? Answer: 3
b.) What exponent of 10 will give 10, 000? Answer: 4
c.) What exponent of ½ will give 16? Answer: -4
1
d.) What exponent of 5 will give ? Answer: -1/2
√5
Round 2. (Indicator no. 8)
Example 2. Using a Microsoft excel, compute for the value of the natural
logarithm.
a. ln 100
b. ln 250
APPLICATION
(Indicator 1, Science Integration)
The teacher will ask the following question:
1. Do you know the meaning of the magnitude that is being reported right after
the earthquake?
To fully understand on the meaning of each magnitude, the students will
be given piece of paper with numbers 1 to 10 as magnitude. With these
numbers they are to assign descriptions that describes the magnitude of the
earthquake. The descriptions are as follows: Scarcely Perceptible, Slightly Felt,
Weak, Moderately Strong, Strong, Very Strong, Destructive, Very Destructive,
Devastating, Completely Devastating. The role of the teacher is to check if the
students made it correctly.
2. How is this magnitude computed?
In Richter Scale the magnitude R of an earthquake is given by
2 𝐸
R= 3 (log104.40 )
Where E (in joules) in the energy released by the earthquake.
(The quantity 104.40 is the energy released by a very small reference
earthquake).
IV. Evaluation
I. Valuing the topic through real life application.
(Indicator no.1, DRRM Integration)
Based on the video that we have watched,
1. How important is emergency or first aid kit?
2. How can we reduce the risks and damages of an earthquake?
After gaining ideas from the students, the teacher then will show the things to
be done before, during and after the earthquake.
II. Refer to Seatwork in Teaching Guide, Seatwork 1, 2 and 3 on page 121.
V. Assignment
1. Research on decibel levels that are already harmful to our auditory
health, and seek ways to prevent hearing loss.
Prepared by:
JOEYNEL L. PONTEVEDRA
SST - II
Checked by:
CHARLIE C. ROMERO, MST
School Principal
Earthquake’s Magnitude in Richter Scale
Magnitude Description
10
Arrange the following description on the magnitude given on the table.
WEAK STRONG DESTRUCTIVE
MODERATELY STRONG VERY STRONG SCARCELY PERCEPTIBLE
COMPLETELY DEVASTATING VERY DESTRUCTIVE
DEVASTATING VERY DEVASTATING
You might also like
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Distance FormulaDocument3 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Distance FormulaKenneth Sedonio Arrubio-Guiral88% (8)
- Lesson Plan - Day 1.Document4 pagesLesson Plan - Day 1.Jocelyn Baculi AutenticoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Operation of Functions (Discovery and Lectured)Document15 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan For Operation of Functions (Discovery and Lectured)Jameson SalazarNo ratings yet
- Exponential Equation LP FinalDocument3 pagesExponential Equation LP FinalAngelo Belandres Llonora100% (4)
- Performance Task AND Project IN Basic CalculusDocument4 pagesPerformance Task AND Project IN Basic CalculusBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Manipulating Rational Expressions Ad EquationsDocument9 pagesLesson Plan For Manipulating Rational Expressions Ad Equationslaurice benal100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For Exponential Equation Using Same BaseDocument5 pagesLesson Plan For Exponential Equation Using Same Baseアンジェロドン100% (2)
- LP STEM - BC11D IIIf 2 Rules of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesLP STEM - BC11D IIIf 2 Rules of DifferentiationLeopold Laset100% (2)
- Learning Module: MODULE 6: Solving Problems Involving Rational Algebraic ExpressionsDocument9 pagesLearning Module: MODULE 6: Solving Problems Involving Rational Algebraic ExpressionsMaria Martina Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Flexobox-Gu8ia Rapida PDFDocument1 pageFlexobox-Gu8ia Rapida PDFFanytta LarahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in General MathematicsDerren Nierras Gaylo100% (1)
- Rational Function RepresentationDocument3 pagesRational Function RepresentationJM Panganiban IINo ratings yet
- STEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Document10 pagesSTEM - PC11AG-If-1 (Systems of Nonlinear Equations-Illustrate System of Nonlinear Equation)Chad Lowe Verdan Villarroya100% (3)
- Week 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Document6 pagesWeek 1. Day 2 (Lesson 2)Dindin Oromedlav LoricaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General Mathematics 11Document2 pagesLesson Plan in General Mathematics 11marystel b. BorbonNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 2Document7 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 2Rod ManachoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan Iin Statistics and ProbabilityDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan Iin Statistics and ProbabilitySHARMINE CABUSAS0% (1)
- Probability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPDocument3 pagesProbability Distribution On Discrete Random Variables DLPJoshua OticNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningLily Anne Ramos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Sample Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesMath 10 Sample Lesson PlanAce SundiamNo ratings yet
- Gen Math First QuarterDocument194 pagesGen Math First QuarterDindin Oromedlav Lorica100% (8)
- Lesson No.11 Domain and Range of Rational FunctionsDocument3 pagesLesson No.11 Domain and Range of Rational FunctionsDian Jane Gaylawan75% (4)
- LP Rational FunctionDocument10 pagesLP Rational FunctionJaiNo ratings yet
- TOS For Gen MathDocument3 pagesTOS For Gen MathAbegail PanangNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusDocument46 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Pre-CalculusLeah Mae France100% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsJoanMurilloSimanganNo ratings yet
- III. Lesson 10 Inverse of One-To One FunctionDocument3 pagesIII. Lesson 10 Inverse of One-To One Functionalejandro diyaoNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 8.3Document8 pagesDLP Math 8.3Val Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- GM Week2 Summative Assessment 2a Rational Functions October 12 16Document2 pagesGM Week2 Summative Assessment 2a Rational Functions October 12 16Lee Russel CoronelNo ratings yet
- Gen Math STEM B Daily Lesson LogDocument6 pagesGen Math STEM B Daily Lesson Logjun del rosario100% (1)
- SHS Learning Plan (General Mathematics)Document3 pagesSHS Learning Plan (General Mathematics)MeYo San100% (1)
- Compound Interest DLLDocument5 pagesCompound Interest DLLOmengMagcalas100% (1)
- Culminating Performance Standard Performance Task Enabling Performance Standard Performance CheckDocument1 pageCulminating Performance Standard Performance Task Enabling Performance Standard Performance CheckJap TVNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLogarithmic Lesson PlanAzza ZzinNo ratings yet
- WHLP General Mathematics Week 1 - 4Document8 pagesWHLP General Mathematics Week 1 - 4Christine YnotNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanRaquel NavarezNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability DLL-MaligayaDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability DLL-MaligayaMARIA CARMELA MALIGAYANo ratings yet
- 1st PT GEN MATHDocument7 pages1st PT GEN MATHErnie LahaylahayNo ratings yet
- Marjorie B. Malveda Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesMarjorie B. Malveda Detailed Lesson PlanMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MATH2Document4 pagesLesson Plan MATH2Jomar AbreuNo ratings yet
- Khai Lesson Plan 2Document10 pagesKhai Lesson Plan 2api-299009301100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanLauren Erickson0% (1)
- A Lesson Plan On Exponential Functions in RealityDocument3 pagesA Lesson Plan On Exponential Functions in RealityMarnellie Bautista-Valdez100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in General Mathematics PDFDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in General Mathematics PDFAgatha Jane Francisco100% (1)
- Simple Interest Lesson EDTECH 541Document2 pagesSimple Interest Lesson EDTECH 541Jennifer Marrott80% (5)
- Arithmetic Sequence 1Document2 pagesArithmetic Sequence 1Eric de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- One-To-One FunctionsDocument2 pagesOne-To-One FunctionsDominic Dalton Caling100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in StatisticsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in StatisticsJulovern MolvizarNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Daily Lesson LogMa. Wilma Q. SevilloNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (BOW) - GenMathDocument2 pagesBudget of Work (BOW) - GenMathJENETTE SABURAO50% (2)
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityJay ReyesNo ratings yet
- SEPTEMBER 14 118 DLL Rational ExpressionDocument4 pagesSEPTEMBER 14 118 DLL Rational ExpressionIsrael Arthel IlaoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument22 pagesQ4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityAngeleehNo ratings yet
- Equivalence of A StatementDocument7 pagesEquivalence of A StatementkiahjessieNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (Domain and Range)Jeanelyn SegotierNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsHazel Recites Bernaldez100% (1)
- Orig LP Luyun 03-13-2023Document12 pagesOrig LP Luyun 03-13-2023api-651752332No ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsDocument25 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsPOTENCIANO JR TUNAYNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 6Document6 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 6Ram GazerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Laws of ExponentDocument4 pagesLesson Plan - Laws of ExponentMarizel VillaluzNo ratings yet
- DLL 6Document4 pagesDLL 6REALIZA B. BELCHEZNo ratings yet
- Cs245 F16 Part 1Document310 pagesCs245 F16 Part 1needecon102notesNo ratings yet
- Spanning TreeDocument2 pagesSpanning TreefxtrendNo ratings yet
- Sap MRP ConfigDocument23 pagesSap MRP Configsharadapurv100% (1)
- Control System Competitive Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesControl System Competitive Questions With AnswersAnonymous D0FSPtyI8No ratings yet
- Guia ZDocument30 pagesGuia ZJonathan ChafloqueNo ratings yet
- TRIAL MATH M 950-2 2015 Jong SrawakDocument9 pagesTRIAL MATH M 950-2 2015 Jong SrawakmasyatiNo ratings yet
- CPP Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesCPP Model Question PaperRaja GuruNo ratings yet
- 6 Thomas Intergraph Partnership SPRDDocument28 pages6 Thomas Intergraph Partnership SPRDManoj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Apache HiveDocument77 pagesApache HiveAshok Kumar K RNo ratings yet
- Helpful Transactions, Tools, Programs, Tables, Etc. For A SAP GRC ConsultantDocument11 pagesHelpful Transactions, Tools, Programs, Tables, Etc. For A SAP GRC Consultantxylas_zeusNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial 9 Ball Plate Impact PDFDocument8 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 9 Ball Plate Impact PDFhansNo ratings yet
- Exp No.: 6 Aim: To Study Dos, Arp Spoofing and Buffer Overflow Attack. Theory A) Dos AttackDocument7 pagesExp No.: 6 Aim: To Study Dos, Arp Spoofing and Buffer Overflow Attack. Theory A) Dos AttacksanjayNo ratings yet
- CXEx Tutorial - Creating Mac Ports of Games & Applications - The Porting TeamDocument15 pagesCXEx Tutorial - Creating Mac Ports of Games & Applications - The Porting TeamIndrick BorealeNo ratings yet
- Co 2020Document12 pagesCo 2020Sinley PatelNo ratings yet
- OpenStage HFA V2R0.98.0 Release Notes V13.0 ExternDocument22 pagesOpenStage HFA V2R0.98.0 Release Notes V13.0 Externfantasy247No ratings yet
- Logicore Ip Fast Simplex Link (FSL) V20 Bus (V2.11C) : Ffs Block RamsDocument9 pagesLogicore Ip Fast Simplex Link (FSL) V20 Bus (V2.11C) : Ffs Block RamswachutunaiNo ratings yet
- Review and Critical Thinking QuesionDocument2 pagesReview and Critical Thinking QuesionIkmal AhmadNo ratings yet
- What Is Hiper-VDocument21 pagesWhat Is Hiper-Vhinjak hakaloNo ratings yet
- Mary Ann Nicdao Resume Khit Ano BastaDocument2 pagesMary Ann Nicdao Resume Khit Ano BastapatmanderNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Graphs of Functions 2Document123 pages2.0 Graphs of Functions 2juriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Configuration Guide - Multicast (V100R006C01 - 01)Document298 pagesConfiguration Guide - Multicast (V100R006C01 - 01)indra_uhuiiNo ratings yet
- Workshop02 Nguyễn-Tuấn-Minh DE170598Document9 pagesWorkshop02 Nguyễn-Tuấn-Minh DE170598Minh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Adv OS MCQDocument16 pagesAdv OS MCQsraveshNo ratings yet
- Business StudiesDocument15 pagesBusiness StudiesdiolpNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Unix and Linux Programming PR Cot 218 and It 214Document7 pagesLab Manual Unix and Linux Programming PR Cot 218 and It 214sameerroushanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Visual Test SoftwareDocument12 pagesAdvanced Visual Test SoftwareCHOCHO2009No ratings yet
- ME3400e SCG PDFDocument1,274 pagesME3400e SCG PDFsergioNo ratings yet
- ClarioNET 6301Document117 pagesClarioNET 6301jpg67No ratings yet
- Wavelet Families and Properties - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaDocument2 pagesWavelet Families and Properties - MATLAB & Simulink - MathWorks IndiaAtul ManiNo ratings yet