Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nonprofit Organization
Nonprofit Organization
Uploaded by
Venz LacreOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nonprofit Organization
Nonprofit Organization
Uploaded by
Venz LacreCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER
BLUE NOTES
57 S
L
A nonprofit organization is an entity that is operated for the benefit of society as a whole rather than for the
benefit of an individual proprietor or a group of partners or shareholders. The concept of income is irrelevant and
NPOs strive only to obtain revenue sufficient to cover up expenses.
Accounting for NPOs is based on US GAAP, namely FASB SFAS 116, SFAS 117, SFAS 124 and AICPA Audit and
Accounting Guide for health care organizations.
Examples of NPOs:
1. Voluntary health and welfare organizations
2. Schools, colleges and universities
3. Hospitals
4. Cooperatives
5. Labor unions
6. Performing arts organizations
7. Foundations
8. Religious organizations
9. Country clubs
10. Professional associations
Fund Accounting
Internal accounting for many nonprofit organizations is the fund which is an accounting entity with a self-balancing set
of accounts recording cash and other financial resources together with related liabilities and changes therein.
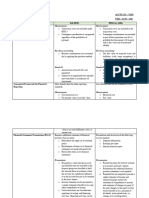
Contributions or donations
Type of contribution Recognition Measurement Corresponding Journal Entries
A. Cash Recognize as revenue in Face value of cash Cash xx
the year received even received Contributions revenue xx
in the presence of
restrictions
Note: If restrictions are
present- reported as
'temporary restricted
revenue' in the
statement of activities.
Still revenue.
B. Materials Recognize as revenue in Fair value of materials Inventory xx
the year received even received Contributions revenue xx
in the presence of
restrictions
Note: If restrictions are
present- reported as
Practical Accounting 1 Theory of Accounts
Chapter 57 – Nonprofit Organization USL Blue Notes 209
'temporary restricted
revenue' in the
statement of activities.
C. Services the services require Going rate for Salaries expense xx
specialized skills, are comparable employees Contributions revenue xx
provided by individuals or contractors of the
possessing those skills entity, less any meals or
and would typically other living costs
need to be purchased if absorbed by the
not provided by nonprofit organization
donation
D. Facilities Recognize as revenue in Fair value of the Building xx
the year received even facilities received and Contributions revenue xx
in the presence of this could be either to
restrictions an asset or expense
Note: If restrictions are account
present- reported as
'temporary restricted
revenue' in the
statement of activities.
Expenses for NPOs
Type Definition Reporting in the Statement of activities
A. Program services The organization's activities that Reported as unrestricted in the SOA
result in the distribution of
goods and services to
beneficiaries, customers or
members that fulfill the
purposes or mission of the
organization
B. Support activities Activities of the organization Reported as unrestricted in the SOA
other than program services,
such as management and
general expenses, fund raising
and membership development
activities
Note: Due to the fact that all expenses of NPOs are unrestricted, these expenses can only be deducted from unrestricted revenue.
Theory of Accounts Practical Accounting 1
210 USL Blue Notes Chapter 57 – Nonprofit Organization
Funds of an NPO
A. Unrestricted fund
This includes all the assets of a NPO that are available for use as authorized by the governing board and are not
restricted for specific purposes.
B. Restricted fund
This is used to account for assets available for current use but expendable only as authorized by the donor of
the assets. The donor may impose either 'use' or 'time' restrictions or both.
C. Endowment fund
Classified as:
- permanent endowment fund - one w/c the principal must be maintained indefinitely (permanently restricted)
in revenue producing investments. Only the revenue from the investments may be expended(temporarily
restricted). Also known as 'regular endowment'
- term endowment fund - one for which the principal may be expended after the passage of certain period or
the occurrence of an event specified by the donor(temporarily restricted).
-quasi-endowment fund - a fund established by the governing board of the nonprofit organization. At the
option of the board, the principal may later be expended. Accordingly, this type of fund is included in
'unrestricted net assets' because this is established using unrestricted net assets.
D. Agency fund
Used to account for assets held by the nonprofit organization as custodian. The assets held by the organization
is reported as liability of the NPOs agency fund because most NPOs have no equity in the fund
E. Annuity fund
Established when assets are contributed to the nonprofit organization with the stipulation that the
organization shall pay specified fixed amount to a designated beneficiary periodically during a specified period
of time. At the end of that period, the unexpended assets of the annuity fund are transferred to the
unrestricted fund, restricted fund or endowment fund as instructed by the donor.
F. Life income fund
This is used to account for stipulated payments to a named beneficiary during the beneficiary's lifetime.
However, only the income on the fund is paid to the beneficiary. Thus, payments from a life income fund vary
from period to period.
G. Loan fund
This is usually established by colleges and universities for the purpose of granting loans to students to satisfy
their school needs. Student loan funds generally are resolving, meaning, as old loans are repaid; new loans are
made from the receipts.
H. Plant fund
The fund established for land, building and equipment of the nonprofit organization. In addition to plant
assets, the plant fund may include cash and investments earmarked for additions to plant or payments of
liabilities collateralized by the plant assets. Sinking fund assets set aside for the retirement of debt incurred to
acquire plant assets may also be included in the plant fund.
The components of the financial statements of a nonprofit organization:
1. The Statement of financial position – This statement shall report that “assets should equal liabilities and net
assets”.
Net assets must be broken down into unrestricted, temporarily restricted and permanently restricted.
For hospitals, SFP discloses amounts for unrestricted, temporarily restricted and permanently restricted net
Practical Accounting 1 Theory of Accounts
Chapter 57 – Nonprofit Organization USL Blue Notes 211
assets as of a specific date.
2. Statement of activities – This statement shall report the “changes in net assets” and the revenue, gains,
expenses and losses of a nonprofit organization. This is the equivalent of the income statement for commercial
accounting. The statement of activities shall report expenses by functional classification as program services
and supporting services. However, a voluntary health and welfare organization is required to prepare a
“statement of functional expenses”. The statement of functional expenses shall report expenses both by
function (program and support) and by natural classification (salaries, depreciation, etc.).
For hospitals, SOA reports changes in unrestricted, temporarily restricted and permanently restricted net
assets for a period.
3. Statement of cash flows
4. Notes to financial statements
5. Statement of Operations – For hospitals, this discloses only the changes in unrestricted net assets for a period.
Classifications of the “net assets” of a nonprofit organization:
1. Unrestricted net assets – Typically, these are the assets in the “unrestricted fund”.
2. Temporarily restricted net assets – Generally, these are the assets in the restricted fund, loan fund, term
endowment fund, annuity fund, life income fund and plant fund.
3. Permanently restricted net assets – The most significant source of permanently restricted net assets is a
“permanent endowment fund”.
Unconditional promises:
Unconditional promises to give are reported in the period the pledges are made and not in the period of cash
collection.
Accordingly, if the contribution will not be received until next year, the contribution will be reported increase in
the temporarily restricted net assets for the current year because of the time restriction.
A “conditional promise” to give is considered unconditional if the possibility that the condition will not be met is
remote.
Reclassifications of net assets:
For example, in a prior year, a benefactor made a contribution to a private nonprofit university with the stipulation
that the donation be used for faculty travel during the current year.
This contribution is reported under temporarily restricted net assets in the prior year.
When the contribution is used for faculty travel in the current year, it is reported as a “reclassification” in the
current year’s statement of activities.
Reclassifications are reported in the statement of financial activities as “net assets release from restrictions.”
This reclassification is reported in the current year as a negative amount for temporarily restricted net assets and
positive amount for unrestricted net assets.
The travel expense is reported in the current year’s statement of activities as a deduction from unrestricted net
assets. All expenses are decreases in unrestricted net assets.
This means that the use if the contribution for faculty travel has no effect on unrestricted net assets at the current
year-end.
The reason is that the effect is offsetting, meaning, increase in unrestricted net assets upon reclassification from
“temporarily restricted to unrestricted” and decrease in unrestricted net assets when the contribution is used or
expended.
Theory of Accounts Practical Accounting 1
212 USL Blue Notes Chapter 57 – Nonprofit Organization
Classification of cash flows for a nonprofit organization:
Operating activities – This include “unrestricted” cash contributions, unrestricted revenue and expenses.
Investing activities include cash flows from acquisition and disposal of property, plant and equipment,
investments and other long-term assets.
Financing activities include temporarily or permanently “restricted” cash contributions and cash flows from
borrowings and repayment of borrowings.
Practical Accounting 1 Theory of Accounts
You might also like
- Growth Management Consultants: Finance ReportDocument4 pagesGrowth Management Consultants: Finance ReportNgọc VânNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting: Accounting For Non-Profit OrganizationsDocument28 pagesGovernment Accounting: Accounting For Non-Profit OrganizationsJanine LerumNo ratings yet
- SS&C GlobeOp - FA ModuleDocument34 pagesSS&C GlobeOp - FA ModuleAnil Dube100% (1)
- Non Profit OrganizationsDocument26 pagesNon Profit OrganizationsAngelica Allanic67% (3)
- Hotel Audit PolicyDocument6 pagesHotel Audit PolicyZiaul Huq50% (2)
- Financial StatementsDocument6 pagesFinancial StatementsLuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Afar - Not For Profit OrganizationsDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Afar - Not For Profit OrganizationsJem Valmonte100% (1)
- Afar 3215-NpoDocument5 pagesAfar 3215-Npoj.galagar.127531.tcNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Afar G/N/E de Leon 3015 - Not For Profit Organizations M A Y 2 0 2 1Document6 pagesLecture Notes: Afar G/N/E de Leon 3015 - Not For Profit Organizations M A Y 2 0 2 1TatianaNo ratings yet
- 36 Retained EarningsDocument7 pages36 Retained EarningsShenna Mae LibradaNo ratings yet
- ACCTG 013 - Module 6Document33 pagesACCTG 013 - Module 6Andrea Lyn Salonga CacayNo ratings yet
- AC16 601A HONSON Comparing Financial Statements of The GovernmentDocument8 pagesAC16 601A HONSON Comparing Financial Statements of The GovernmentAlyssa Mae HonsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5Azi LheyNo ratings yet
- Villamor - Activity in Module 4 Part 1Document3 pagesVillamor - Activity in Module 4 Part 1CPAREVIEWNo ratings yet
- Ngos-Accounting and Legal IntricaciesDocument7 pagesNgos-Accounting and Legal IntricaciesShrey DNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument66 pagesPresentation of Financial StatementsCherryvic Alaska - KotlerNo ratings yet
- NPOs - ADVACC - GOV'T ACCDocument6 pagesNPOs - ADVACC - GOV'T ACCblack hudieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 First 10 Pages (Corporate Governance)Document10 pagesChapter 7 First 10 Pages (Corporate Governance)muhammadNo ratings yet
- Acctg Part 3Document6 pagesAcctg Part 3Irish Claire BaquiranNo ratings yet
- BusfinanzDocument4 pagesBusfinanzfrancine ًNo ratings yet
- RECEIVABLESDocument12 pagesRECEIVABLESNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Sample Questions On Audit of Specialized IndustriesDocument8 pagesImportant Points and Sample Questions On Audit of Specialized IndustriesIra Grace De CastroNo ratings yet
- Business and Accounting REVIEWERDocument8 pagesBusiness and Accounting REVIEWERMoon 7044No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - CorporationDocument7 pagesChapter 8 - CorporationNyah MallariNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - ResumosDocument10 pagesFinancial Management - ResumosBeatriz BastosNo ratings yet
- Accounting Management: Public Accounting School University of Sinú - Sectional CartagenaDocument12 pagesAccounting Management: Public Accounting School University of Sinú - Sectional CartagenaSusana Luz Rubio VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Non-Profit OrganizationsDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Non-Profit OrganizationsAngelica Joy ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesAcccob 2 Revieweranika bordaNo ratings yet
- To Accounting: Accounting and Its EnvironmentDocument13 pagesTo Accounting: Accounting and Its EnvironmentNajima MangontawarNo ratings yet
- Accounting Conventions: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesAccounting Conventions: Learning Objectivesjerrylove069No ratings yet
- AuditingDocument9 pagesAuditingLiezel MonteronNo ratings yet
- Learning Module In: Grade 11Document11 pagesLearning Module In: Grade 11Esvee TyNo ratings yet
- IAS 28 - IFRS 9 (Accounting For Associates and Financial Instruments)Document29 pagesIAS 28 - IFRS 9 (Accounting For Associates and Financial Instruments)Hiền MỹNo ratings yet
- Not For Profit OrganizationDocument30 pagesNot For Profit Organizatione.ortiz.531130No ratings yet
- Ccfas Chapter 8 15Document5 pagesCcfas Chapter 8 15Ceann RapadasNo ratings yet
- P5 - Chapter 9 DIVISIONAL PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL AND TRANSFER PRICINGDocument10 pagesP5 - Chapter 9 DIVISIONAL PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL AND TRANSFER PRICINGDhruvi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Non Profit OrganizationsDocument28 pagesChapter 16 Non Profit Organizationslou-924No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting-1Document10 pagesFinancial Accounting-1Dharmik UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Receivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromDocument3 pagesReceivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromMjhayeNo ratings yet
- ACTG 21B (CH4) - Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesACTG 21B (CH4) - Lecture Notesraimefaye seduconNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PAS 1 PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTSDocument8 pagesChapter 3 PAS 1 PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTSJeanette LampitocNo ratings yet
- Non-Proft Organizations: Barredo, Michelle Cruzat, Mary Ann Tesoro, Joshua Bs Acc 5-1 Ludivinia F. Victorino, Cpa, MbaDocument41 pagesNon-Proft Organizations: Barredo, Michelle Cruzat, Mary Ann Tesoro, Joshua Bs Acc 5-1 Ludivinia F. Victorino, Cpa, MbaAngelica EstolatanNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping Group 1 KainaDocument20 pagesBookkeeping Group 1 KainaRhodge BustilloNo ratings yet
- Accounting Textbook GlossaryDocument13 pagesAccounting Textbook Glossaryandzani2008No ratings yet
- 18 AIS 012 (MD Jubayed Hossen)Document9 pages18 AIS 012 (MD Jubayed Hossen)Md JubayedNo ratings yet
- Fme Accounting Terminology ChecklistDocument6 pagesFme Accounting Terminology ChecklistLATIFNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting MechanicsDocument34 pagesFinancial Reporting Mechanicsb6muddasar100% (1)
- Fa 3 Chapter 6 Statement of Comprehensive IncomeDocument11 pagesFa 3 Chapter 6 Statement of Comprehensive IncomeKristine Florence TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Non Profit OrganizationsDocument62 pagesChapter 16 Non Profit OrganizationsJanine LerumNo ratings yet
- Pfs Project WebinarDocument31 pagesPfs Project WebinarNeji HergliNo ratings yet
- PRIA AFAR03003 Corporate Liquidation and Home Office and Branch Accounting No AnswerDocument33 pagesPRIA AFAR03003 Corporate Liquidation and Home Office and Branch Accounting No AnswerViannice Acosta100% (3)
- The Basic Financial Statement FinalDocument69 pagesThe Basic Financial Statement FinalKaren Annica Astrero MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Us Gaap Ind As and Indian Gaap Similarities and DifferencesDocument4 pagesIfrs Us Gaap Ind As and Indian Gaap Similarities and DifferencesDrpranav SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Cfas Chapter 7Document2 pagesCfas Chapter 7danielisaiahasdNo ratings yet
- CA P.S. Beniwal: Member of IND AS Implementation Committee of ICAIDocument11 pagesCA P.S. Beniwal: Member of IND AS Implementation Committee of ICAIChhaya JajuNo ratings yet
- 03 Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesDocument5 pages03 Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesJAMES ANDROE TANNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framew Ork and Accountin G Standards: Justiniano L. Santos, CPA, MBADocument46 pagesConceptual Framew Ork and Accountin G Standards: Justiniano L. Santos, CPA, MBACarmela BuluranNo ratings yet
- Cfas Chapter 8Document4 pagesCfas Chapter 8danielisaiahasdNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Chart of AccountsDocument37 pagesCooperative Chart of AccountsGianena MarieNo ratings yet
- Business Combinations - Ifrs 3Document39 pagesBusiness Combinations - Ifrs 3Valerie Verity MarondedzeNo ratings yet
- Provision and ReserveDocument4 pagesProvision and ReservePrabhakar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Adjusting AccountsDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Adjusting AccountsIESHA JAESAMIN TWAYE BASTIANNo ratings yet
- INC Resume TemplateDocument1 pageINC Resume TemplateVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Afar Crc-Ace PW SolutionsDocument18 pagesAfar Crc-Ace PW SolutionsVenz Lacre100% (1)
- 00 Test Bank Title PageDocument1 page00 Test Bank Title PageVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Storytelling Etc 2019 Guidelines and Mechanics 1Document4 pagesStorytelling Etc 2019 Guidelines and Mechanics 1Venz LacreNo ratings yet
- CAT B I Can Save The Earth PDFDocument2 pagesCAT B I Can Save The Earth PDFVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1Document15 pagesChapter 5 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1Mayeth BotinNo ratings yet
- Chapter11.Flexible Budgeting and The Management of Overhead and Support Activity CostsDocument38 pagesChapter11.Flexible Budgeting and The Management of Overhead and Support Activity CostsMangoStarr Aibelle Vegas75% (4)
- CAT A If Trees Could Talk PDFDocument1 pageCAT A If Trees Could Talk PDFVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Tariff and Custom CodeDocument12 pagesTariff and Custom CodeAmy Olaes Dulnuan100% (1)
- Joint Arrangements: Problem 6-1: True or FalseDocument18 pagesJoint Arrangements: Problem 6-1: True or FalseVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Consignment Sales: Problem 9-1: True or FalseDocument4 pagesConsignment Sales: Problem 9-1: True or FalseVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Partnership - Part 2: Problem 2-1: True or FalseDocument8 pagesPartnership - Part 2: Problem 2-1: True or FalseVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Resa Aud PT PDFDocument16 pagesResa Aud PT PDFVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Home Office, Branch and Agency Accounting: Problem 11-1: True or FalseDocument13 pagesHome Office, Branch and Agency Accounting: Problem 11-1: True or FalseVenz Lacre100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1-1Document10 pagesChapter 1 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1-1Mayeth BotinNo ratings yet
- Pmecpar FT AP InvestingDocument12 pagesPmecpar FT AP InvestingVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1Document15 pagesChapter 5 - Teacher's Manual - Afar Part 1Mayeth BotinNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Definitions: Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument5 pagesDerivatives Definitions: Financial Accounting and ReportingVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- #02 Conceptual FrameworkDocument5 pages#02 Conceptual FrameworkZaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Framework For Business Transactions Other Laws Guide QuestionsDocument22 pagesRegulatory Framework For Business Transactions Other Laws Guide QuestionsVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Acidity of WaterDocument4 pagesAcidity of WaterVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- UP 2010 Civil Law Credit Transactions .PDocument34 pagesUP 2010 Civil Law Credit Transactions .PVenz Lacre100% (1)
- Acidity of WaterDocument1 pageAcidity of WaterVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of The FMCG IndustryDocument58 pagesFundamental Analysis of The FMCG Industryavinash singhNo ratings yet
- !'JIII, All.,.. - , - , - , - : InvoiceDocument5 pages!'JIII, All.,.. - , - , - , - : InvoiceLouie SyNo ratings yet
- Reading 24 Income TaxesDocument27 pagesReading 24 Income TaxesARPIT ARYANo ratings yet
- Alteo Annual Report 2014Document85 pagesAlteo Annual Report 2014s.sabapathy100% (1)
- V-Ride MASDocument5 pagesV-Ride MASDave Castillo Bangisan100% (1)
- Project Sunrise: Molson Coors International, India SAP Implementation - Project Sunrise Module: ControllingDocument43 pagesProject Sunrise: Molson Coors International, India SAP Implementation - Project Sunrise Module: ControllingKaveri BangarNo ratings yet
- Sector Specific Ratios and ValuationDocument10 pagesSector Specific Ratios and ValuationAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Public MarketDocument16 pagesPublic MarketPrecious Joy SaminNo ratings yet
- Audit Module 1 - Variance Analysis TemplateDocument9 pagesAudit Module 1 - Variance Analysis Templatehai saskiNo ratings yet
- Sno Company Name Employees On Linkedin LocationDocument33 pagesSno Company Name Employees On Linkedin LocationUdaya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Solution 4 27Document12 pagesSolution 4 27hind alteneijiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementDocument15 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementMohsin Qayyum0% (2)
- Pradip Kumar Shrivastava: SAP FICO, BI and BPC Techno-Functional Program/Project Manager Email: PH: 512-426-3961Document11 pagesPradip Kumar Shrivastava: SAP FICO, BI and BPC Techno-Functional Program/Project Manager Email: PH: 512-426-3961Pandit Katti NarahariNo ratings yet
- Akn p5 3a Pa1Document10 pagesAkn p5 3a Pa1Alche MistNo ratings yet
- Da Nang University Vietnam - Korea University of Information and Communication Technology Faculty of Digital Economy & E - TradeDocument34 pagesDa Nang University Vietnam - Korea University of Information and Communication Technology Faculty of Digital Economy & E - TradeTrí PhạmNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING - MIDTERM - 2019-2020 - 2nd Semester - PART5Document3 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING - MIDTERM - 2019-2020 - 2nd Semester - PART5Renalyn ParasNo ratings yet
- English - Glossary Business TermsDocument7 pagesEnglish - Glossary Business TermsChoy DanNo ratings yet
- Buckwold 21e - CH 5 Selected SolutionsDocument13 pagesBuckwold 21e - CH 5 Selected SolutionsLucy100% (1)
- CDP Katni English PDFDocument268 pagesCDP Katni English PDFAjay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting: by Debra Jeter and Paul ChaneyDocument37 pagesAdvanced Accounting: by Debra Jeter and Paul ChaneyRose SpringNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2 MBA Financial and Managerial AccountingDocument7 pagesAssignment # 2 MBA Financial and Managerial AccountingSelamawit MekonnenNo ratings yet
- ACC 213 SylabusDocument5 pagesACC 213 Sylabusfbicia218No ratings yet
- CIMA - Question Bank (Relevant For F2)Document12 pagesCIMA - Question Bank (Relevant For F2)bebebam100% (1)
- Ate Bec EssayDocument17 pagesAte Bec EssayMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- VVDocument30 pagesVVHans WeirlNo ratings yet
- IJRESSSep 15 Anu KHDocument18 pagesIJRESSSep 15 Anu KHGreen EarthNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Equity Analysis & Analyst Recommendations - FTSE China 25 IndexDocument53 pagesFundamental Equity Analysis & Analyst Recommendations - FTSE China 25 IndexQ.M.S Advisors LLCNo ratings yet