Professional Documents
Culture Documents
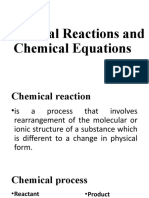
Direct Combination or Synthesis Reaction A + B Ab
Direct Combination or Synthesis Reaction A + B Ab
Uploaded by
Alvianica Nanda Utami0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesThe document describes several types of chemical reactions:
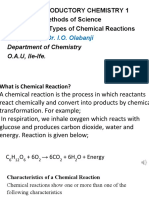
1) Synthesis reactions involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. An example is the reaction of iron and sulfur to form iron sulfide.
2) Decomposition reactions involve breaking a single compound into smaller constituents. An example is the electrolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas.
3) Single displacement reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound. Zinc replacing hydrogen in hydrochloric acid is provided as an example.
4) Double displacement reactions involve the exchange of ions between two reactants to form two new compounds. The reaction of sodium chloride and silver nitrate is given.
Original Description:
synthesis
Original Title
synthesis reaction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes several types of chemical reactions:
1) Synthesis reactions involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. An example is the reaction of iron and sulfur to form iron sulfide.
2) Decomposition reactions involve breaking a single compound into smaller constituents. An example is the electrolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas.
3) Single displacement reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound. Zinc replacing hydrogen in hydrochloric acid is provided as an example.
4) Double displacement reactions involve the exchange of ions between two reactants to form two new compounds. The reaction of sodium chloride and silver nitrate is given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesDirect Combination or Synthesis Reaction A + B Ab
Direct Combination or Synthesis Reaction A + B Ab
Uploaded by
Alvianica Nanda UtamiThe document describes several types of chemical reactions:
1) Synthesis reactions involve the combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. An example is the reaction of iron and sulfur to form iron sulfide.
2) Decomposition reactions involve breaking a single compound into smaller constituents. An example is the electrolysis of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas.
3) Single displacement reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound. Zinc replacing hydrogen in hydrochloric acid is provided as an example.
4) Double displacement reactions involve the exchange of ions between two reactants to form two new compounds. The reaction of sodium chloride and silver nitrate is given.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
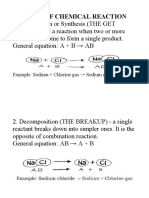
Direct Combination or Synthesis Reaction
A + B → AB
The combination of iron and sulfur to form iron (II) sulfide is an example of a
synthesis reaction:
8 Fe + S8 → 8 FeS
Chemical Decomposition
In a decomposition reaction, a compound is broken into smaller chemical species.
AB → A + B
The electrolysis of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas is an example of a
decomposition reaction:
2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2
Single Displacement or Substitution Reaction
A substitution or single displacement reaction is characterized by one element
being displaced from a compound by another element.
A + BC → AC + B
An example of a substitution reaction occurs when zinc combines with
hydrochloric acid. The zinc replaces the hydrogen:
Zn + 2 HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Double Displacement Reaction
In a double displacement or metathesis reaction two compounds exchange bonds or
ions in order to form different compounds.
AB + CD → AD + CB
An example of a double displacement reaction occurs between sodium chloride
and silver nitrate to form sodium nitrate and silver chloride.
NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s)
Acid-Base Reaction
An acid-base reaction is a type of double displacement reaction that occurs
between an acid and a base. The H+ ion in the acid reacts with the OH- ion in the
base to form water and an ionic salt:
HA + BOH → H2O + BA
The reaction between hydrobromic acid (HBr) and sodium hydroxide is an
example of an acid-base reaction:
HBr + NaOH → NaBr + H2O
Combustion
A combustion reaction is a type of redox reaction in which a combustible
materialcombines with an oxidizer to form oxidized products and generate heat
(exothermic reaction). Usually, in a combustion reaction oxygen combines with
another compound to form carbon dioxide and water. An example of a combustion
reaction is the burning of naphthalene:
C10H8 + 12 O2 → 10 CO2 + 4 H2O
You might also like
- What Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypekamilbismaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EqnsDocument17 pagesChemical Eqnsmacff217No ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction TypesDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction TypesKomal RamzaanNo ratings yet
- HELIN .H ١Document7 pagesHELIN .H ١Helin HassanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions TypesDocument1 pageChemical Reactions TypesGraciella BeduyaNo ratings yet
- Body Paragraph Uas EnglishDocument4 pagesBody Paragraph Uas EnglishazkaamandafNo ratings yet
- What Is A Chemical Reaction?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Chemical Reaction?Endslie LuceroNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument1 pageChemical ReactionReymark MutiaNo ratings yet
- The Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument1 pageThe Types of Chemical Reactionskumush.toymasova999No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions: Combination Decomposition Single Displacement Double Displacement Oxidation and ReductionDocument14 pagesChemical Reactions: Combination Decomposition Single Displacement Double Displacement Oxidation and ReductionRishika Garg JainNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations VeeDocument20 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations VeeSanjay JagarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Types of Chemical ReactionDocument4 pagesModule 12 Types of Chemical ReactionmaningdingkendrickNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions:, Is A Reaction in Which Two or More Substances Combine To Form A Single New SubstanceDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions:, Is A Reaction in Which Two or More Substances Combine To Form A Single New Substanceabdallrahman elmiNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionLyrah ManioNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument20 pagesChemical Reactiongenevieruiz19No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument40 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionschhajuramNo ratings yet
- TEST PAPER 10th ch1Document10 pagesTEST PAPER 10th ch1Sumit Kumar KarnNo ratings yet
- Science Revision STUDY MATERIALDocument94 pagesScience Revision STUDY MATERIALYoNo ratings yet
- Chmical ReactionDocument30 pagesChmical Reactionarshasaraf114No ratings yet
- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Question and AnswerDocument6 pagesPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES Question and AnswerKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsROn Arellano100% (2)
- Classifying Chemical Reactions TableDocument2 pagesClassifying Chemical Reactions TableSamLuoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 02 Types of Chemical Reactions 1Document1 pageWorksheet 02 Types of Chemical Reactions 1Maria Jane GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ChemmyDocument3 pagesChemmyjaelajeanine326No ratings yet
- Assignment - 3Document12 pagesAssignment - 3padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument79 pagesChemical Reactionss.rosa.nicholejoyNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985617Document9 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-985617abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1VrindaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions EquationsDocument13 pagesChemical Reactions EquationsShubham ShawNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESISDocument3 pagesSYNTHESISJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactionsnknawada1324No ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988058Document9 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY Solution-988058abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- IOC Chemical-ReactionsDocument37 pagesIOC Chemical-ReactionsUwe JasmiraNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9-Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsDocument32 pagesLESSON 9-Chemical Reactions and Chemical EquationsAlthea CeroNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Types Ofchemical ReactionsDocument22 pagesGrade 8 Types Ofchemical ReactionsreddypoulomiNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Document10 pagesUnit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Farah AounNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument6 pagesScience NotesKhushal BachwaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsanjayjoshi.jnvNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Sandhya RaniNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument11 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangesBarkha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Paradise Cbse: Join For MoreDocument202 pagesParadise Cbse: Join For MoreDeepak GoyalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemical Reaction & Equation, Carbon &its Compounds Mock Paper SolutionsDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Chemical Reaction & Equation, Carbon &its Compounds Mock Paper SolutionsadvikanuragNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Chemical Reactions: Trishalyn Mickaela T. Roberto BSMT 1-IDocument3 pagesThe Different Types of Chemical Reactions: Trishalyn Mickaela T. Roberto BSMT 1-Ijohn dave tanNo ratings yet
- 10TH SEM-1 PS NOTESDocument31 pages10TH SEM-1 PS NOTESsrinivasarao.thangaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsdsarika61No ratings yet
- Types RXDocument1 pageTypes RXazeezsharique4No ratings yet
- Reaction Types PowerpointDocument7 pagesReaction Types Powerpointapi-267743846No ratings yet
- Chem Test 3 Study SheetDocument3 pagesChem Test 3 Study SheetDarren SischyNo ratings yet
- VSA Type QuestionsDocument7 pagesVSA Type QuestionsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 145_AnswersDocument4 pages145_Answersnjbhange6418No ratings yet
- CH 1 Chemistry Creatve Learning NotesDocument10 pagesCH 1 Chemistry Creatve Learning NotesMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument42 pagesChemistry NotesDhanraj BarkalitaNo ratings yet
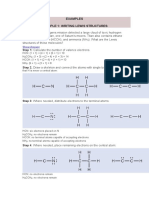
- Step 1: Calculate The Number of Valence Electrons.: Examples Example 1: Writing Lewis StructuresDocument31 pagesStep 1: Calculate The Number of Valence Electrons.: Examples Example 1: Writing Lewis Structureslucia h. enriquezNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument28 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsIvan PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- ChemChapter7 RojasDocument6 pagesChemChapter7 RojasTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionAlvin GultiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint Presentation.Document16 pagesChapter 7 - Chemical Reactions and Equations - Powerpoint Presentation.Nicholas KoerbitzNo ratings yet
- checical 4Document1 pagechecical 4Parmjeet DhandaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Motion (Multiple Choice) QPDocument26 pagesMotion (Multiple Choice) QPAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)
- Science V Bukit Sion Reproduction in Flowering 20181102-BersihDocument7 pagesScience V Bukit Sion Reproduction in Flowering 20181102-BersihAlvianica Nanda UtamiNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetDocument6 pagesElements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)
- Persuasive Essay Structure and FormatDocument3 pagesPersuasive Essay Structure and FormatAlvianica Nanda UtamiNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument16 pagesMath PDFAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)