Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Basics of Game Theory
The Basics of Game Theory
Uploaded by
bilalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Basics of Game Theory
The Basics of Game Theory
Uploaded by
bilalCopyright:
Available Formats
EDUCATION MARKETS SIMULATOR YOUR MONEY ADVISORS ACADEMY
FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS SECTORS & INDUSTRIES ANALYSIS
Fundamental The Basics Of Game Theory
Analysis
TOOLS FOR FUNDAMENTAL
ANALYSIS
Do You Want to Become BY DANIEL MCNULTY | Updated Mar 30, 2019
a Better Investor?
SECTORS & INDUSTRIES
Game theory is the process of modeling the strategic interaction between two or
ANALYSIS
more players in a situation containing set rules and outcomes. While used in a
GET AHEAD OF
THE GAME
number of disciplines, game theory is most notably used as a tool within the study
of economics. The economic application of game theory can be a valuable tool to
NO THANKS aide in the fundamental analysis of industries, sectors and any strategic
interaction between two or more firms. Here, we'll take an introductory look at
game theory and the terms involved, and introduce you to a simple method of
solving games, called backwards induction.
Game Theory Definitions
Any time we have a situation with two or more players that involves known
payouts or quantifiable consequences, we can use game theory to help determine
the most likely outcomes.
Let's start out by defining a few terms commonly used in the study of game theory:
Game: Any set of circumstances that has a result dependent on the actions of
two of more decision-makers (players).
Players: A strategic decision-maker within the context of the game.
Strategy: A complete plan of action a player will take given the set of
circumstances that might arise within the game.
Payoff: The payout a player receives from arriving at a particular outcome. The
payout can be in any quantifiable form, from dollars to utility.
Information set: The information available at a given point in the game. The
term information set is most usually applied when the game has a sequential
component.
Equilibrium: The point in a game where both players have made their decisions
and an outcome is reached.
Assumptions in Game Theory
As with any concept in economics, there is the assumption of rationality. There is
also an assumption of maximization. It is assumed that players within the game
are rational and will strive to maximize their payoffs in the game.
When examining games that are already set up, it is assumed on your behalf that
the payouts listed include the sum of all payoffs associated with that outcome.
This will exclude any "what if" questions that may arise.
The number of players in a game can theoretically be infinite, but most games will
be put into the context of two players. One of the simplest games is a sequential
game involving two players.
Solving Sequential Games Using Backwards Induction
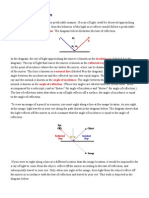
Below is a simple sequential game between two players. The labels with Player 1
and Player 2 within them are the information sets for players one or two,
respectively. The numbers in the parentheses at the bottom of the tree are the
payoffs at each respective point. The game is also sequential, so Player 1 makes
the first decision (left or right) and Player 2 makes its decision after Player 1 (up or
down).
Figure 1
Backwards induction, like all game theory, uses the assumptions of rationality and
maximization, meaning that Player 2 will maximize his payoff in any given
situation. At either information set we have two choices, four in all. By eliminating
the choices that Player 2 will not choose, we can narrow down our tree. In this way,
we will bold the lines that maximize the player's payoff at the given information
set.
Figure 2
After this reduction, Player 1 can maximize its payoffs now that Player 2's choices
are made known. The result is an equilibrium found by backwards induction of
Player 1 choosing "right" and Player 2 choosing "up." Below is the solution to the
game with the equilibrium path in bold.
Figure 3
For example, one could easily set up a game similar to the one above using
companies as the players. This game could include product release scenarios. If
Company 1 wanted to release a product, what might Company 2 do in response?
Will Company 2 release a similar competing product? By forecasting sales of this
new product in different scenarios, we can set up a game to predict how events
might unfold. Below is an example of how one might model such a game. (For
related reading, see: Why Is Game Theory Useful in Business?)
Figure 4
The Bottom Line
By using simple methods of game theory, we can solve for what would be a
confusing array of outcomes in a real-world situation. Using game theory as a tool
for financial analysis can be very helpful in sorting out potentially messy real-
world situations, from mergers to product releases. (For related reading, see:
Advanced Game Theory Strategies for Decision-Making.)
Related Articles
BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS
Game Theory: Beyond the Basics
BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS
How Game Theory Strategy Improves
Decision Making
Partner Links
BUSINESS ESSENTIALS
How Is Game Theory Useful in
Business?
ECONOMICS
5 Nobel Prize-Winning Economic
Theories You Should Know About
MICROECONOMICS
Comparing Dominant Strategy Solution
vs. Nash Equilibrium Solution
BUSINESS ESSENTIALS
Using Appreciative Inquiry to Solve
Management Problems
Related Terms
How Game Theory Works
Game theory is a framework for modeling scenarios in which conflicts of interest exist
among the players. more
Backward Induction
In game theory, backward induction is the process of deducing backward from the end of a
problem or scenario to infer a sequence of optimal actions. more
Zero-Sum Game
A situation in which one person’s gain is equivalent to another’s loss, so that the net
change in wealth or benefit is zero. A zero-sum game may have as few as two players, or
millions of participants. more
Centipede Game Definition
The centipede game in game theory involves two players alternately getting a chance to
take the larger share of an increasing money stash. more
Traveler's Dilemma
The traveler's dilemma demonstrates the paradox of rationality - that making decisions
illogically often produces a better payoff in game theory. more
Nash Equilibrium
The Nash Equilibrium is a concept within game theory where the optimal outcome of a
game is where there is no incentive to deviate from their initial strategy. more
Terms About Us Privacy Policy
News Advertise Terms of Use
Tutorials Contact Careers
# A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Investopedia is part of the Dotdash publishing family. The Balance | Lifewire | TripSavvy | The Spruce and more
You might also like
- Biological AstronautDocument5 pagesBiological AstronautMirza Faraz BaigNo ratings yet
- Yasser M. Awaad - Absolute Pediatric Neurology (2018, Springer International Publishing)Document735 pagesYasser M. Awaad - Absolute Pediatric Neurology (2018, Springer International Publishing)Miguel Angel Villarreal Ybazeta100% (3)
- The Teacher Magazine PDFDocument28 pagesThe Teacher Magazine PDFSole Carapella86% (7)
- Water Filter ActivityDocument7 pagesWater Filter Activityapi-312859548No ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsDocument15 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Please Read Carefully: T17024 4.3L Digital Air FryerDocument24 pagesPlease Read Carefully: T17024 4.3L Digital Air FryerMitch CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Teaching English As A Foreign / Second Language - A HandoutsDocument34 pagesTeaching English As A Foreign / Second Language - A HandoutsAsma Haseeb QaziNo ratings yet
- Control (Management) : Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesControl (Management) : Navigation SearchnishejprakashNo ratings yet
- Heatpump ApplicationDocument2 pagesHeatpump ApplicationsandyolkowskiNo ratings yet
- (ML) Canon EOS Features ComparisonDocument42 pages(ML) Canon EOS Features Comparisona5OolNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsDocument23 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Systems ArchitectureDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Information Systems Architecturevicrattlehead2013No ratings yet
- Taguchi Matrix-Worked Out ExampleDocument3 pagesTaguchi Matrix-Worked Out ExampleshekarthimmappaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic MechinesDocument24 pagesHydraulic Mechinesdr hs govardhana swamyNo ratings yet
- Time StudyDocument341 pagesTime StudyrasheamNo ratings yet
- Time Study WorksheetDocument1 pageTime Study WorksheetAjibola H. MartinsNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump ProposalDocument5 pagesHeat Pump ProposalSyamim HamizanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Game TheoryDocument8 pagesGlossary of Game TheoryK Krishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument19 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysisssophal100% (2)
- Module 5 - DECISION MAKINGDocument28 pagesModule 5 - DECISION MAKINGjuneid al jarwanNo ratings yet
- Regional Maritime UniversityDocument16 pagesRegional Maritime Universitysydney brownNo ratings yet
- Stedimate ManualDocument44 pagesStedimate Manualpedro navor100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics: Lecture Notes ofDocument22 pagesFluid Mechanics: Lecture Notes ofAlsharksi AviationNo ratings yet
- NPF Rule For Sharp StarsDocument16 pagesNPF Rule For Sharp StarsSebastian GirandoNo ratings yet
- XII Linear Programming AssignmentDocument2 pagesXII Linear Programming AssignmentCRPF SchoolNo ratings yet
- Popatlal Ashok: Name Start Time End Time NameDocument55 pagesPopatlal Ashok: Name Start Time End Time NameshahharshilNo ratings yet
- Tom's TEFL - Teacher's Easter Egg Hunt KeyDocument2 pagesTom's TEFL - Teacher's Easter Egg Hunt KeyTom's TEFLNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsDocument34 pagesBTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsBrendan Burr100% (1)
- Management Accounting ControlDocument166 pagesManagement Accounting ControlKumara Uluwatta (K.H.U.D. Nandana Kumara)100% (4)
- Gantt Chart FormatDocument1 pageGantt Chart FormatamanNo ratings yet
- Name - Period - Date - Newton'S Laws WebquestDocument5 pagesName - Period - Date - Newton'S Laws WebquestsohiNo ratings yet
- Focal Length of A Lens Boys MethodDocument2 pagesFocal Length of A Lens Boys MethodGonKilNo ratings yet
- Electrical Tape (Or Insulating Tape) Is A Type ofDocument2 pagesElectrical Tape (Or Insulating Tape) Is A Type ofToy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Processing X Ray FilmDocument5 pagesProcessing X Ray Filmkanwar1992singhNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanKevin Paul DeañoNo ratings yet
- Tom's TEFL - Animal DominosDocument2 pagesTom's TEFL - Animal DominosTom's TEFLNo ratings yet
- 83 Ways To Reduce Your Energy Needs 2.0 PDFDocument14 pages83 Ways To Reduce Your Energy Needs 2.0 PDFM Imran AleeNo ratings yet
- Applied CalculasDocument15 pagesApplied Calculasmohammad rashid tkNo ratings yet
- Brooke Science Lesson Plan 1Document15 pagesBrooke Science Lesson Plan 1api-455384768No ratings yet
- How To Make A Simple DC MotorDocument1 pageHow To Make A Simple DC MotorQuen AñanaNo ratings yet
- Yamazumi BoardsDocument2 pagesYamazumi BoardsBetoAlbaCruz100% (1)
- Tresspass NoticeDocument3 pagesTresspass NoticeBobby Sludds100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Sensation and PerceptionDocument66 pagesChapter 8 Sensation and Perceptionapi-726122866No ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law MC Questions PDFDocument7 pagesCoulomb's Law MC Questions PDFLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Image FormedDocument2 pagesReflection and Image FormedFaith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Energy ExperimentDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Energy Experimentapi-380820076No ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsDocument16 pagesBTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Thoughts To Ponder ..: Horizontal Motion Vertical MotionDocument5 pagesThoughts To Ponder ..: Horizontal Motion Vertical MotionSer Oca Dumlao LptNo ratings yet
- New LP On Climate ExtremesDocument3 pagesNew LP On Climate ExtremesJacquelyn celestialNo ratings yet
- 7e Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument28 pages7e Lesson Plan in ScienceLorenzz ZaffNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Impulseand MomentumDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Impulseand MomentumLawrence Fabregas Delima100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanHeina NadiaNo ratings yet
- A Premier of TaguchiDocument259 pagesA Premier of Taguchikushalsingh2000100% (2)
- Detailed LPDocument14 pagesDetailed LPQueenie Narciso PacalangNo ratings yet
- Experiment Reflection of LightDocument6 pagesExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759No ratings yet
- PDF - Geothermal Power PlantDocument43 pagesPDF - Geothermal Power PlantTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanellenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Wave WorksheetDocument1 pageAnatomy of A Wave WorksheetYuzhao XiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science General CHEMISTRY 2 (Grade 12)Document11 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science General CHEMISTRY 2 (Grade 12)noel baldozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Physical ScienceDocument7 pagesLesson Plan - Physical Scienceapi-390871957No ratings yet
- Game TheoryDocument5 pagesGame TheoryJoseph AyodejiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering Lectures First SeasonDocument122 pagesIndustrial Engineering Lectures First SeasonAli Hassan AHNo ratings yet
- Computational Game TheoryDocument6 pagesComputational Game TheoryNishiya VijayanNo ratings yet
- Score and Tabulation SheetDocument5 pagesScore and Tabulation SheetYronne ArsolonNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Learning and CommunicationDocument24 pagesFactors Influencing Learning and CommunicationYamith J. FandiñoNo ratings yet
- CCSC 19Th CommencementDocument10 pagesCCSC 19Th CommencementShimmer CrossbonesNo ratings yet
- School Guidebook 2013-14-1 PDFDocument230 pagesSchool Guidebook 2013-14-1 PDFarchitectfemil6663No ratings yet
- Linstad Assure Model Instructional Plan - Animal HabitatsDocument4 pagesLinstad Assure Model Instructional Plan - Animal Habitatsapi-270439059No ratings yet
- De Thi CPEDocument15 pagesDe Thi CPETrongTanNo ratings yet
- Tecle Gebremichael ResumeDocument3 pagesTecle Gebremichael Resumeapi-665020557No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Education in Malaysia: A Critical ReviewDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship Education in Malaysia: A Critical Reviewuthman98No ratings yet
- PT English6 q3 DraftDocument8 pagesPT English6 q3 DraftVener Madia Mabunga-CastrodesNo ratings yet
- THESISDocument28 pagesTHESISMilbert Loyloy SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Candidate Admitted List: Session:OLODE 03 of 2023 Center:AllDocument10 pagesCandidate Admitted List: Session:OLODE 03 of 2023 Center:AllAshish RanaNo ratings yet
- Adult Personality Development (2001)Document6 pagesAdult Personality Development (2001)Kesavan ManmathanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management TipsDocument6 pagesClassroom Management TipsJavier BahenaNo ratings yet
- English Literature Teacher S Guide UG013031Document78 pagesEnglish Literature Teacher S Guide UG013031Rebecca TsangNo ratings yet
- Idaho Core Standards Danielson FrameworkDocument21 pagesIdaho Core Standards Danielson Frameworkapi-518329053No ratings yet
- Prospectus 2022Document41 pagesProspectus 2022api-285503905No ratings yet
- Negotiat I On Process Interview: TítuloDocument4 pagesNegotiat I On Process Interview: TítuloKenji MishimaNo ratings yet
- (Garcia Et Al, 2020) - Self-Eficacy Among Users of Information and Communication Technologies in The Brazilian School EnvironmentDocument4 pages(Garcia Et Al, 2020) - Self-Eficacy Among Users of Information and Communication Technologies in The Brazilian School EnvironmentMaico XuriNo ratings yet
- Notification ISRO Hindi Typist VacanciesDocument1 pageNotification ISRO Hindi Typist VacanciesYogesh DagarNo ratings yet
- WHRPC Nomination Form Honoris Causa ''Document2 pagesWHRPC Nomination Form Honoris Causa ''sheikjilanbashaNo ratings yet
- Maths 1H May 2021Document28 pagesMaths 1H May 2021redbrickfireballNo ratings yet
- Bigsaywit NarrativeDocument4 pagesBigsaywit Narrativejein_amNo ratings yet
- Leadership IN Organization: Ambesh Kumar Srivastava Aditi Khanna Hitali Makkar Deepesh Sharma Abhishek SharmaDocument19 pagesLeadership IN Organization: Ambesh Kumar Srivastava Aditi Khanna Hitali Makkar Deepesh Sharma Abhishek Sharmaambesh Srivastava100% (4)
- Science 2010 Pearson 459 63Document6 pagesScience 2010 Pearson 459 63Lucas DutraNo ratings yet
- Add Math SPM Trial 2008 Kedah p1 Ans1Document21 pagesAdd Math SPM Trial 2008 Kedah p1 Ans1KOW ZHEN QUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- IITM BSC Degree - Ambassadors - PresentationDocument9 pagesIITM BSC Degree - Ambassadors - Presentationabdul quabizNo ratings yet
- Peer Coach Training June 2016Document1 pagePeer Coach Training June 2016Peer Coach Academy ColoradoNo ratings yet