Professional Documents
Culture Documents
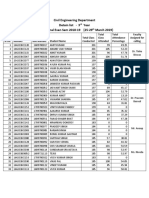
COURSE FILE Nce 702 WRE
COURSE FILE Nce 702 WRE
Uploaded by
Mohd AmirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COURSE FILE Nce 702 WRE
COURSE FILE Nce 702 WRE
Uploaded by
Mohd AmirCopyright:
Available Formats
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
COURSE FILE
Subject Name: Water Resource Engineering
Subject Code: NCE 702
Semester/ Year: VIIth/ 4thYear
Faculty Name: : Mr. Shailendra Singh
Department: Civil Engineering
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Vision of Institute
To be a leading educational institution recognized for excellence in engineering education and
research producing globally competent and socially responsible technocrats.
Mission of Institute
IM1: To provide state-of-art infrastructural facilities that support achieving academic
excellence.
IM2: To provide a work environment that is conducive for professional growth of faculty
and staff.
IM3: To collaborate with industry for achieving excellence in research, consultancy and
entrepreneurship development.
Vision of Civil Engineering Department:
To be a centre of excellence for practical oriented education in Civil Engineering.
Mission of Civil Engineering Department:
DM1: To impart excellent engineering education and produce competent professionals capable
to analyse, design and supervise construction of Civil Engineering structures for societal and
environmental needs.
DM2: To provide global avenues to the students and faculty to enhance their professional
careers.
DM3: To collaborate with the industries to ensure efficient project management and
entrepreneurship development.
Program Educational Objectives (PEOs)
Civil Engineering Graduates will be able to:
PEO1: Acquire knowledge and expertise in analysis, design and construction of Civil
Engineering structures with cost economics, structural safety, functional aesthetics and harmony
conducive to the environment.
PEO2: Ensure right engineering attitude for professional Civil Engineering roles and enhance
competency in work culture and higher education.
PEO3: Inculcate an attitude for lifelong learning to become ethical civil engineers and imbibe a
sense of responsible citizen to serve the society and the nation
Program Outcomes (POs)
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
1. Engineering knowledge: Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering
fundamentals, and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering
problems.
2. Problem analysis: Identify, formulate, review research literature, and analyze complex
engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of
mathematics, natural sciences, and engineering sciences.
3. Design/development of solutions: Design solutions for complex engineering problems
and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs with
appropriate consideration for the public health and safety, and the cultural, societal,
and environmental considerations.
4. Conduct investigations of complex problems: Use research-based knowledge and
research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data,
and synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
5. Modern tool usage: Create, select, and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and
modern engineering and I T tools including prediction and modeling to complex
engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.
6. The engineer and society: Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to
assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent
responsibilities relevant to the professional engineering practice.
7. Environment and sustainability: Understand the impact of the professional
engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts, and demonstrate the
knowledge of, and need for sustainable development.
8. Ethics: Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities
and norms of the engineering practice.
9. Individual and team work: Function effectively as an individual, and as a member or
leader in diverse teams, and in multidisciplinary settings.
10. Communication: Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the
engineering community and with society at large, such as, being able to comprehend
and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations,
and give and receive clear instructions.
11. Project management and finance: Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the
engineering and management principles and apply these to one’s own work, as a
member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
12. Life-long learning: Recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability to
engage in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological
change.
Program Specific Outcomes (PSOs) Program
Civil Engineering Graduates will be able to:
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
PSO 1. Plan and design for construction of civil engineering systems to meet the changing
needs of the society within realistic constraints of economy and environment with thrust on
social and ethical issues to ensure construction management, safety, quality and sustainability.
PSO 2. Design for construction of hydraulics structures, multi-storeyed buildings and industrial
structures, roads, railways, bridges, water supply and sewage treatment plants using various
principles of civil engineering.
Course Outcomes:
Water Resources Engineering
(NCE702): On completion of this course, the students will be able to
analyse the hydrologic cycle, hydrologic systems precipitation,
C 406.1
evaporation and infiltration
analyse the direct runoff and hydrographs used for the analysis of
C 406.2
runoff
learn the irrigation systems and development of irrigation in
C 406.3
India.
learn sediment transport theories of lined and unlined canal
C 406.4
system
design of the regulation and control systems of canal and types of
C 406.5
canal irrigation works
C 406.6 analyse the ground water hydraulics.
CO-PO Mapping:
PO10
PO11
PO12
PO1
PO2
PO3
PO4
PO5
PO6
PO7
PO8
PO9
PO
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
CO
C 406.1 2 2 - - - 1 - - - - - 2
C 406.2 3 2 - - - 2 1 - - - - 2
C 406.3 3 3 - - - 2 1 - - - - 1
C 406.4 3 3 - - - 3 1 - - - - 2
C 406.5 3 3 2 1 - 2 1 - - - - 2
C 406.6 3 2 - - - 2 1 - - - - 2
C-406 2.83 2.50 2.00 1.00 - 2.00 1.00 - - - - 1.83
CO-PSO MAPPING:
PSO 1
PSO 2
PSO
CO
C 406.1 2 2
C 406.2 2 2
C 406.3 3 2
C 406.4 3 3
C 406.5 3 3
C 406.6 3 3
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Time Table:
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Department of Civil Enginnering (CE)
Even Semester - Session 2017-18
8th Semester / 4th Year
SECTION - Q
CLASS ROOM NO. : Block B-103
2:3
TIM 1:40 3:20
09:30- 10:20- 11:10- 12:00- 12:50 0- 4:10-
E - -
10:20 11:10 12:00 12:50 -1:40 3:2 5:00
DA 2:30 4:10
0
Y
P P
L L NCE851 NCE851
L L A B
MO NCE NCE
NOE 081 NOE 081 C-109 C-109
N 061/063 061/063
B-103/C- B-103/C-
C-109 C-109
109 109
L L L L
NCE
NOE 081 NCE 801 NCE 801
TU 052/053
LUNCH BREAK
E B-103/C-
C-109 C-109 C-109
109
P P
L L L NCE851 NCE851
L C D
WE NCE NCE NCE
NCE 801 C-109 C-109
D 052/053 052/053 061/063
B-103/C- B-103/C- B-103/C-
C-109
109 109 109
P P
L L L L NCE851 NCE851
TH E F
UR NCE NCE
NCE 801 NCE 801 C-109 C-109
052/053 052/053
C-109 C-109 B-103/C- B-103/C-
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
109 109
L L L L
NCE NCE
NOE 081 NOE 081
061/063 061/063
FRI
B-103/C- B-103/C-
C-109 C-109
109 109
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &
TECHNOLOGY
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Department of Civil Enginnering (CE)
Odd Semester - Session 2017-2018
7th Semester / 4th Year
SECTION -NO. : Block B-103
09:30- 11:10- 12:00- 12:50- 3:20- 4:10-
TIME 10:20-11:10 1:40-2:30 2:30-3:20
10:20 12:00 12:50 1:40 4:10 5:00
DAY
L L L L
NCE
702 P NCE751
MON
/B 103
B-103
L L L
NCE
702 P
TUE
NCE753/B -103
B-103
LUNCH BREAK
L L L L
NCE
702 P
WED
NCE753 /B 103
B-103
L L L L
THUR
L L L L
NCE
702 P
FRI
NCE751 /B-103
B-103
Syllabus
NCE – 702 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
UNIT – I
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Hydrology : Hydrologic Cycle. Water Budget Equation, Hydrologic system, Precipitation :
Types, measurements and analysis, error in estimation, missing data,
consistency of rainfall records, Intensity during frequency (IDF) and probabilitic maximum
Precipitation (PMP) curves.
Evaporation and consumptive use: Process affecting factors, estimation and measurement
techniques.
Infiltration : Process affecting factors, measurement and estimation, Infiltration Indices. 8
UNIT – II
Surface Runoff: Components and factors affecting runoff, methods of estimation of runoff
volume and peak runoff, rating curve, Rainfall – runoff relationships Hydrograph analysis:
components, factors affecting hydrographs, base flow separation, Direct Runoff Hydrograph,
Unit Hydrograph: Theory and assumptions. Derivation of Unit Hydrograph, Synthetic Unit
Hydrograph Introduction to computer models for rainfall runoff analysis.
Irrigation: Developments in India, Necessity and types Advantages & disadvantages of
irrigation. Functions of water in plant growth, Methods of Irrigation, Water requirement of crops.
Irrigation frequency, Irrigation efficiencies, Principal crops and crop season, crop rotation.
Canal irrigation: Classes and alignment, Parts of a canal system, Commanded area, curves in
channels, channel losses. 8
UNIT – III
Sediment Transportation: Suspended and Bed load and its estimation
Irrigation channels: Types: lined and unlined, silt theories: Kennedy’s and Lacey’s Design
procedure for irrigation channels, Longitudinal cross section, Schedule of area
statistics and channel dimensions, use of Garret’s Diagrams in channel design, cross sections of
an Irrigation channel, Computer programs for design of channels
Lining of Irrigation Canals: Advantages and types, factors for selection of a particular type,
design of lined channels, cross section of lined channels, Economics of canal lining. Water
Logging: Definition, effects, causes and anti-water logging measures, Drainage of water logged
land, Types of drains open and closed, spacing of closed drains. 8
UNIT – IV
Regulation and control of canal system: Purpose, Types of canal regulation works and their
functional aspects
Irrigation Outlets: Requirements, types, non-modular, semi-module and rigid module, selection
criterion
River Training: Objective and need, classification of rivers, and river training works,
meandering, stages, methods of river training, bank protection, Methods for measurement of
discharge. 8
UNIT – V
Ground Water Hydrology: Zones of underground water, Aquifers and their types, important
terms, Determination of discharge through unconfined and confined aquifers with steady flow
conditions, Interference among wells, determination of aquifer constants, Well loss and specific
capacity, efficiency of a well, types of water wells, bored and open wells, specific yield of a well,
Relative merits of well and canal irrigation, type of tube wells, well surrounding and well
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
development, Suitable site selection for a tube well, Types of open wells, Methods of lifting
water. Infiltration galleries. 8
Text Book
1. Irrigation Engg. and Hydraulic Structures by S.K. Garg, Khanna Publishers.
2. Irrigation and water Power engineering by B.C. Punmia, Laxmi Publications.
3. Engineering Hydrology by K. Subramanya, TMH.
4. Irrigation Water Power and Water Resource Engg. by K.R. Arrora.
5. Water resource engineering by Ralph A. Wurbs & Wesley P. James, Pearson Publication.
References
1. Water Resources Engg. By Larry W. Mays, John Wiley India
2. Water resources Engg. By Wurbs and James, John wiley India
3. Water Resources Engg. By R. K. Linsley, McGraw Hill
4. Irrigation and water Resources Engg. By G L Asawa, New age International Publishers
5. Irrigation Theory and practices by A.M. Michel.
6. Fundamental of Hydraulic Engineering System by Houghalen, Pearson Publication.
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Lecture Plan:
Lect. Date Lecture Topic Mapping Reference/ Page No.
No. with CO Book
1 Hydrology : Hydrologic CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 1-15
Cycle. Water Budget and Hydraulic
Equation Structures by
S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers.
2 , Hydrologic system CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 20-35
Precipitation : Types, and Hydraulic
measurements and Structures by
analysis S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
3 error in estimation, CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 36-45
missing data and Hydraulic
consistency of rainfall Structures by
records S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
4 Intensity during CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 48-62
frequency (IDF) and and Hydraulic
probabilitic maximum Structures by
Precipitation (PMP) S.K. Garg,
curves. Khanna
estimation and Publishers
measurement techniques.
5 Evaporation and CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 63-80
consumptive use: Process and Hydraulic
affecting factors Structures by
S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
6 Evaporation estimation CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 81-90
and measurement and Hydraulic
techniques. Structures by
S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
7 Infiltration : Process CO 1 Irrigation Engg. 94-115
affecting factors, and Hydraulic
measurement and Structures by
estimation Infiltration S.K. Garg,
Indices Khanna
Publishers
8 Surface Runoff: CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 120-143
Components and factors and Hydraulic
affecting runoff methods Structures by
of estimation of runoff S.K. Garg,
volume Khanna
Parts of a canal system, Publishers
Commanded area, curves
in channels, channel
losses.
9 peak runoff, rating curve, CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 146-165
Rainfall – runoff and Hydraulic
relationships Hydrograph Structures by
analysis: components, S.K. Garg,
factors affecting Khanna
hydrographs, base flow Publishers
separation.
10 Direct Runoff CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 166-194
Hydrograph, Unit and Hydraulic
Hydrograph: Theory and Structures by
assumptions. Derivation S.K. Garg,
of Unit Hydrograph. Khanna
Publishers
11 Class test CO 2 Irrigation Engg.
and Hydraulic
Structures by
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
12 Synthetic Unit CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 196-225
Hydrograph Introduction and Hydraulic
to computer models for Structures by
rainfall runoff analysis. S.K. Garg,
Khanna
Publishers
13 Irrigation: Developments CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 226- 241
in India, Necessity and and Hydraulic
types Advantages & Structures by
disadvantages of S.K. Garg
irrigation.
14 Functions of water in CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 242-262
plant growth, Methods of and Hydraulic
Irrigation, Water Structures by
requirement of crops. S.K. Garg
15 Irrigation frequency, CO 2 Irrigation Engg. 265-281
Irrigation efficiencies, and Hydraulic
Principal crops and crop Structures by
season, crop rotation. S.K. Garg
Canal irrigation: Classes
and alignment,Planning.
16 Sediment Transportation: CO 3 Irrigation Engg. 282- 301
Suspended and Bed load and Hydraulic
and its estimation Structures by
S.K. Garg
17 Irrigation channels: CO 3 Irrigation Engg. 335-345
Types: lined and unlined, and Hydraulic
silt theories: Structures by
S.K. Garg
18 Kennedy’s and Lacey’s CO 3 Irrigation Engg. 346-362
Design procedure for and Hydraulic
irrigation channels, Structures by
Longitudinal cross S.K. Garg
section
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
19 Schedule of area CO 3 Irrigation Engg. 365-384
statistics and channel and Hydraulic
dimensions, use of Structures by
Garret’s Diagrams in S.K. Garg
channel design
20 cross sections of an CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 250-264
Irrigation channel, and Hydraulic
Computer programs for Structures by
design of channels S.K. Garg
21 Lining of Irrigation CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 265-281
Canals: Advantages and and Hydraulic
types, factors for Structures by
selection of a particular S.K. Garg
type.
22 Design of lined channels, CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 282-300
cross section of lined and Hydraulic
channels. Structures by
S.K. Garg
23 Economics of canal CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 301-320
lining. Water Logging: and Hydraulic
Definition, effects, Structures by
causes and anti-water S.K. Garg
logging measures.
24 Drainage of water logged CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 322-336
land, Types of drains and Hydraulic
open and closed, spacing Structures by
of closed drains. S.K. Garg
25 Regulation and control of CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 185-212
canal system: Purpose, and Hydraulic
Types of canal regulation Structures by
works and their S.K. Garg
functional aspects
26 Irrigation Outlets: CO 4 Irrigation Engg. 214-232
Requirements, types, and Hydraulic
non-modular, semi- Structures by
module and rigid S.K. Garg
module, selection
criterion
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
27 River Training: CO 5 Irrigation Engg. 1-17
Objective and need, and Hydraulic
classification of rivers Structures by
S.K. Garg
28 River training works, CO 5 Irrigation Engg. 445-453
meandering, stages and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
29 Methods of river CO 5 Irrigation Engg. 306-324
training, bank protection and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
30 Class test CO 5 Irrigation Engg.
and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
31 Methods for CO 5 Irrigation Engg. 266-276
measurement of and Hydraulic
discharge. Structures by
S.K. Garg
32 Ground Water CO 5 Irrigation Engg. 166-212
Hydrology: Zones of and Hydraulic
underground water, Structures by
Aquifers and their types. S.K. Garg
33 Determination of CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 139-165
discharge through and Hydraulic
unconfined and confined Structures by
aquifers with steady flow S.K. Garg
conditions
34 Interference among CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 250-257
wells, determination of and Hydraulic
aquifer constants. Structures by
S.K. Garg
35 Well loss and specific CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 260-294
capacity, efficiency of a and Hydraulic
well, types of water wells Structures by
S.K. Garg
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
36 bored and open wells, CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 298-329
specific yield of a well, and Hydraulic
Relative merits of well Structures by
and canal irrigation S.K. Garg
37 type of tube wells, well CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 331-365
surrounding and well and Hydraulic
development Structures by
S.K. Garg
38 Suitable site selection for CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 380-386
a tube well, and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
39 Types of open wells, CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 387-406
Methods of lifting water. and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
40 Infiltration galleries CO 6 Irrigation Engg. 407-409
and Hydraulic
Structures by
S.K. Garg
Total Hrs: ___40_______
Text Books:
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Water Resource Engineering
GALGOTIAS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
1, Knowledge Park-II, Greater Noida, U.P.
Water Resource Engineering (NCE-702) ( 2017-18)
Details of Online resources
1. http://nptel.ac.in/courses/105102088/
2. http://nptel.ac.in/courses/105102088/27
Value Added Topics
Methods for measurement of discharge
Suitable site selection for a tube well
Types of open wells
Methods of lifting water
Water Resource Engineering
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Environmental Governance in The PhilippinesDocument37 pagesEnvironmental Governance in The PhilippinesEira Raye100% (2)
- RCE 503-CIVIL-attainment - CODocument17 pagesRCE 503-CIVIL-attainment - COMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Format Result AnalysisDocument38 pagesFormat Result AnalysisMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Assessment ToolsDocument1 pageAssessment ToolsMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Latestyearcoursefile Nce043Document54 pagesLatestyearcoursefile Nce043Mohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Ocf 2018Document8 pagesQuestion Paper Ocf 2018Mohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Question Paper OcfDocument8 pagesQuestion Paper OcfMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Co Based Assisgnmen T OcfDocument6 pagesCo Based Assisgnmen T OcfMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Innovative Questions Related To The Open Channel FlowDocument2 pagesInnovative Questions Related To The Open Channel FlowMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Application For IncrementDocument1 pageApplication For IncrementMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- COURSE FILE Nce 702 WREDocument19 pagesCOURSE FILE Nce 702 WREMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Co Based Assisgnmen T OcfDocument6 pagesCo Based Assisgnmen T OcfMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument1 pageCivil Engineering DepartmentMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Course Exit Survey Transportation LabDocument1 pageCourse Exit Survey Transportation LabMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Questions Related To Open Channel Flow.Document3 pagesQuestions Related To Open Channel Flow.Mohd AmirNo ratings yet
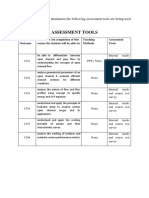
- Assessment Tools: For Finding Out Overall Attainment The Following Assessment Tools Are Being UsedDocument1 pageAssessment Tools: For Finding Out Overall Attainment The Following Assessment Tools Are Being UsedMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Assessment Tools: For Finding Out Overall Attainment The Following Assessment Tools Are Being UsedDocument1 pageAssessment Tools: For Finding Out Overall Attainment The Following Assessment Tools Are Being UsedMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Gradually Varied FlowDocument43 pagesGradually Varied FlowMohd Amir100% (1)
- Innovative Questions Related To The Open Channel FlowDocument2 pagesInnovative Questions Related To The Open Channel FlowMohd AmirNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Why Humans Need WaterDocument2 pagesPart 3 Why Humans Need WaterSimon DruryNo ratings yet
- FTAITA, Toufik. Community Water Management. Is It Still Possible. Anthropological PerspectivesDocument18 pagesFTAITA, Toufik. Community Water Management. Is It Still Possible. Anthropological PerspectivesMari MachiniNo ratings yet
- Thukela Water Management AreaDocument32 pagesThukela Water Management AreaTyron PillayNo ratings yet
- Principles of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Water Resources Engineering: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurVivekChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Awbare Water Supply Distrabution Agency Structure1Document6 pagesAwbare Water Supply Distrabution Agency Structure1engkader bc143No ratings yet
- Settling Parties' Motion To Approve Settlement AgreementDocument93 pagesSettling Parties' Motion To Approve Settlement AgreementL. A. PatersonNo ratings yet
- 1250 FTPDocument14 pages1250 FTPPress EscapeNo ratings yet
- Sub Theme 1 - Full PaperDocument249 pagesSub Theme 1 - Full PaperDedi ApriadiNo ratings yet
- TS3 L9 TNB Overview of Hydropower in Malaysia PDFDocument32 pagesTS3 L9 TNB Overview of Hydropower in Malaysia PDFAhmad BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- Economic Development and EnvironmentDocument25 pagesEconomic Development and EnvironmentNiloy KrittikaNo ratings yet
- Tar Lock LectureDocument32 pagesTar Lock LectureRachel TreichlerNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Cabanatuan CityDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology Cabanatuan CityJosiah CruzNo ratings yet
- Water Supply & Treatment ModuleDocument170 pagesWater Supply & Treatment Modulemsea86% (7)
- Consultancy With Distinction inDocument51 pagesConsultancy With Distinction inabadullahNo ratings yet
- Water: Review: Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) in Abandoned Coal Mines of Shanxi, ChinaDocument21 pagesWater: Review: Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) in Abandoned Coal Mines of Shanxi, ChinaSilvia MachadoNo ratings yet
- Water DemandDocument11 pagesWater DemandDali MondalNo ratings yet
- CHILE, Enviromental, Political and Social IssuesDocument302 pagesCHILE, Enviromental, Political and Social IssuesAlexNo ratings yet
- Interlinking of RiversDocument31 pagesInterlinking of Riversbisu100% (1)
- The Roles of The IMF, The World Bank, and The WTO in Liberalization and Privatization of The Water Services SectorDocument30 pagesThe Roles of The IMF, The World Bank, and The WTO in Liberalization and Privatization of The Water Services SectorShivam SinghalNo ratings yet
- Hydrology HadoutDocument13 pagesHydrology HadoutKubaNo ratings yet
- En PPT Evs SWP RainwaterDocument32 pagesEn PPT Evs SWP Rainwaternaveengargns100% (1)
- Jps Strategic PlanDocument67 pagesJps Strategic PlanLim Shwe WenNo ratings yet
- Arid Lands Water Evaluation and ManagementDocument1,068 pagesArid Lands Water Evaluation and Managementካሳ አለም ፍርዱNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination and Syllabus For B.Tech (Civil Engineering)Document57 pagesScheme of Examination and Syllabus For B.Tech (Civil Engineering)हुडदंग हास्य कवि सम्मलेनNo ratings yet
- 7 Crucial Problems Faced by Urban Society in IndiaDocument39 pages7 Crucial Problems Faced by Urban Society in IndiaShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Dư A N Lo C Da U Nghi Sơn PDFDocument418 pagesDư A N Lo C Da U Nghi Sơn PDFVăn Đại - BKHN100% (1)
- MyBook 11Document278 pagesMyBook 11ali mustafaNo ratings yet
- Pub 00037207Document236 pagesPub 00037207Quinsya AqilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ResourcesDocument69 pagesChapter 1 ResourcesGovindNo ratings yet