Professional Documents
Culture Documents
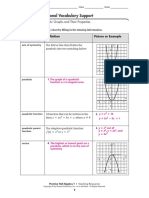
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Uploaded by
danasli7607245Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Korean Grammar in Use Beginner PDFDocument344 pagesKorean Grammar in Use Beginner PDFdanasli760724583% (6)
- AROC and IROC PracticeDocument4 pagesAROC and IROC PracticeAayan Khan100% (1)
- Chapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y IsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y Isunknown :)No ratings yet
- G7.M1.v3 Teacher EditionDocument224 pagesG7.M1.v3 Teacher EditionTuyếnĐặng67% (3)
- Volumes of A Revolution ExerciseDocument1 pageVolumes of A Revolution ExercisewolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- TAD1641GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineDocument2 pagesTAD1641GE: Volvo Penta Genset EnginesIMPEX sHARMANo ratings yet
- Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 2 Tips For ParentsDocument2 pagesEureka Math Grade 7 Module 2 Tips For ParentsEmily Greaves100% (1)
- Placement Test 1Document2 pagesPlacement Test 1GothamSchools.orgNo ratings yet
- Distributing Balls Into Boxes PDFDocument3 pagesDistributing Balls Into Boxes PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m3 Teacher MaterialsDocument374 pagesMath g7 m3 Teacher MaterialsMohammad Abdul OhabNo ratings yet
- MHF4U - Workbook 2022-2023Document91 pagesMHF4U - Workbook 2022-2023ashitha2goveasNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemDocument18 pagesAlgebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemMichelle Corpuz IballaNo ratings yet
- A1AG12ADocument3 pagesA1AG12AAnonymous RzU94z100% (1)
- Math Practice Book AnswersDocument96 pagesMath Practice Book AnswersHaNoOsHa MoHdNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONMatt LamNo ratings yet
- Packet 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusDocument3 pagesPacket 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocument11 pagesPolynomial and Rational Functionsoana_brincoveanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document41 pagesChapter 1alexNo ratings yet
- Quiz Functions IDocument30 pagesQuiz Functions Icaleb castilloNo ratings yet
- Book Answers For CH 1Document20 pagesBook Answers For CH 1api-247437524No ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document16 pagesAlgebra 1sheheNo ratings yet
- Ib Grade 9 Math Book Chapter4Document52 pagesIb Grade 9 Math Book Chapter4TopDevelopersNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2-9 ReteachingDocument2 pagesAlgebra 2-9 Reteachingksimmons82No ratings yet
- Textbook Answers OddDocument47 pagesTextbook Answers OddOylaNo ratings yet
- g5 Multiplicative FunctionDocument45 pagesg5 Multiplicative FunctionMax PaineNo ratings yet
- Placement Test For Pre-AlgebraDocument1 pagePlacement Test For Pre-Algebraapi-232032459No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - DifferentiationDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - DifferentiationTOBY RANNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2-10 ReteachingDocument2 pagesAlgebra 2-10 Reteachingksimmons82No ratings yet
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Document9 pagesProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- BigIdeasMath Problems 15Document20 pagesBigIdeasMath Problems 15Puffy MathNo ratings yet
- Basic Discrete StructureDocument57 pagesBasic Discrete StructureAhmed Iqbal100% (1)
- CBSE 10 Maths Surface Areas and VolumesDocument33 pagesCBSE 10 Maths Surface Areas and VolumesAryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Lines and PlanesDocument16 pagesLines and PlanesNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Math Pre-Calculus - Semester Two Final: REVIEWDocument19 pagesMath Pre-Calculus - Semester Two Final: REVIEWKirby RoseNo ratings yet
- 2014 MCQ MTH 603Document5 pages2014 MCQ MTH 603Inocent NainaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differential Calculus ExerciseDocument17 pagesApplications of Differential Calculus ExerciseIsmail HashimNo ratings yet
- Maths F4 C2 Number BasesDocument79 pagesMaths F4 C2 Number Basesadampau1974No ratings yet
- Graphing QuadraticsDocument22 pagesGraphing QuadraticsMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- 11.1 - 11.3 Sequences and Series WorksheetDocument1 page11.1 - 11.3 Sequences and Series WorksheetDanalakshmi BharathiNo ratings yet
- Determining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5Document3 pagesDetermining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5api-288922072No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnswersDocument27 pagesChapter 7 Answersapi-247437524No ratings yet
- Text 8.6 - Scale DrawingsDocument4 pagesText 8.6 - Scale DrawingsAbdelaziz AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination: Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, IncDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Examination: Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, IncJoyce Ann SameraNo ratings yet
- Set-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsDocument19 pagesSet-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- DE - Modeling: Mixing Problem (Single Tank) Mixing Problem (Three Tank)Document11 pagesDE - Modeling: Mixing Problem (Single Tank) Mixing Problem (Three Tank)Laisa VittoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8: Conic Sections: H K y A XDocument2 pagesCh. 8: Conic Sections: H K y A XThanin KuphoonsapNo ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathneysaneptunex0% (1)
- Rise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSDocument2 pagesRise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSafzabbasi100% (1)
- 09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01Document1 page09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01sivsyadavNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Practice - BDocument2 pages2-1 Practice - BStanley50% (2)
- Linear Algebra Reivew: All Linear Algebra, So This Is A Fairly Serious Weakness. This Review IsDocument10 pagesLinear Algebra Reivew: All Linear Algebra, So This Is A Fairly Serious Weakness. This Review Isabo7999No ratings yet
- Basel Problem ProofDocument7 pagesBasel Problem ProofCody JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mcv4u TestDocument2 pagesMcv4u Testapi-483845268No ratings yet
- 16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsDocument21 pages16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsdevikaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math - Mock ExamDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Math - Mock ExamDawnNo ratings yet
- Shortcuts For MathDocument6 pagesShortcuts For Mathapi-27483824No ratings yet
- Math g8 m4 Mid Module AssessmentDocument11 pagesMath g8 m4 Mid Module AssessmentHrithik PeddireddyNo ratings yet
- Math g4 m1 End of Module AssessmentDocument8 pagesMath g4 m1 End of Module AssessmentRuselle N. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Precalculus m4 End of Module AssessmentDocument27 pagesPrecalculus m4 End of Module AssessmentMarina SmirnovaNo ratings yet
- Prescriptionand Administrationof Oxygen 201901Document26 pagesPrescriptionand Administrationof Oxygen 201901danasli7607245No ratings yet
- Surrogates For The Study of Norovirus Stability AnDocument6 pagesSurrogates For The Study of Norovirus Stability Andanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares Er IrDocument8 pagesVerbos Regulares Er Irdanasli7607245No ratings yet
- GUSTAR (Like) : Estudiar Espanol Dormir Temprano Comer Pizza Descansar en Casa Starbucks Vivir en CoreaDocument6 pagesGUSTAR (Like) : Estudiar Espanol Dormir Temprano Comer Pizza Descansar en Casa Starbucks Vivir en Coreadanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Classifying Numbers ReviewDocument10 pagesClassifying Numbers Reviewdanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Anchor Handling PDFDocument56 pagesAnchor Handling PDFEdwien Arif WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- PJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Document22 pagesPJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Ng Jia ChengNo ratings yet
- Physa S 20 02188Document20 pagesPhysa S 20 02188Mehmet ErtaşNo ratings yet
- Measurement Lesson Length1Document4 pagesMeasurement Lesson Length1api-242505437No ratings yet
- Tara Balam... : How To Caluculate Tarabalam?Document6 pagesTara Balam... : How To Caluculate Tarabalam?krishnaNo ratings yet
- Passing Select-Options To Smart Forms: by VenkatDocument43 pagesPassing Select-Options To Smart Forms: by VenkatsudhakpNo ratings yet
- Metric: Hex Nut Style 2 Class 12Document1 pageMetric: Hex Nut Style 2 Class 12Ankit LonareNo ratings yet
- Geometry Book-Chapter 5.2Document6 pagesGeometry Book-Chapter 5.2alternativoNo ratings yet
- Afm ButterflyDocument5 pagesAfm ButterflyAna-Maria MaticuNo ratings yet
- Pavers - ACN - PCN - The Pavement Classification NumberDocument2 pagesPavers - ACN - PCN - The Pavement Classification Numberphuong leNo ratings yet
- Wwkzii: Jan. 10, 1933. R. H. FarwellDocument3 pagesWwkzii: Jan. 10, 1933. R. H. Farwellmonem2014100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutTeshome Bekele100% (1)
- Codes TFM Webinar-DSDocument96 pagesCodes TFM Webinar-DSThành TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Zinn-Justin J. Quantum Field Theory and Critical Phenomena (3ed., Oxford, 1996) (150dpi) (L) (T) (517s) - PTqs - Cropped (Cut) - RedDocument1,033 pagesZinn-Justin J. Quantum Field Theory and Critical Phenomena (3ed., Oxford, 1996) (150dpi) (L) (T) (517s) - PTqs - Cropped (Cut) - RedBruno Da Fonseca GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SolidDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Solidatikah roshanNo ratings yet
- Power Pavilion Parfait Intel SKL / Kaby - H System DiagramDocument52 pagesPower Pavilion Parfait Intel SKL / Kaby - H System DiagramAbnesis NesisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3Abigail Jimenez100% (1)
- Properties of Moist AirDocument11 pagesProperties of Moist AirKarthik HarithNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology MBADocument3 pagesResearch Methodology MBAYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TUT2Document4 pagesTUT2Yogesh Israni ASET, NoidaNo ratings yet
- Homeinteriorpaint FractionsdecimalsandpercentsDocument4 pagesHomeinteriorpaint Fractionsdecimalsandpercentsapi-281744400No ratings yet
- Mozart Fantasie D Minor k397 Instructive All PDFDocument22 pagesMozart Fantasie D Minor k397 Instructive All PDFLiviu Pencea100% (1)
- Solving Multi-Dimensional Problems of Gas Dynamics Using MATLABDocument40 pagesSolving Multi-Dimensional Problems of Gas Dynamics Using MATLABMahmoud Abd El LateefNo ratings yet
- Hexagon MI Aerospace Smart Manufacturing Ebook A4 WEBDocument26 pagesHexagon MI Aerospace Smart Manufacturing Ebook A4 WEBLuis7929No ratings yet
- Applications of Algebra To A Problem in Topology - by Michael HopkinsDocument49 pagesApplications of Algebra To A Problem in Topology - by Michael HopkinsThe Simons Foundation100% (1)
- Tolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationDocument9 pagesTolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationCahyono IriawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer AnimationDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Computer Animationsanu222No ratings yet
- Nptel: Power Electronics Applications To Power Systems - Video CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: Power Electronics Applications To Power Systems - Video Courseprafful666No ratings yet
- Protective Paints For Heat Treatment of SteelsDocument4 pagesProtective Paints For Heat Treatment of SteelsMauricio Cesar DalzochioNo ratings yet
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Uploaded by
danasli7607245Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Material of Algebra For 8th Grade
Uploaded by
danasli7607245Copyright:
Available Formats
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
Name Date
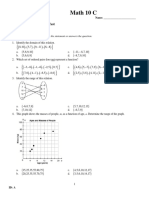
1. Use the graph below to answer parts (a)–(c).
a. Use any pair of points to calculate the slope of the line.
b. Use a different pair of points to calculate the slope of the line.
c. Explain why the slopes you calculated in parts (a) and (b) are equal.
Module 4: Linear Equations
495
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
2. Jeremy rides his bike at a rate of 12 miles per hour. Below is a table that represents the number of hours
and miles Kevin rides. Assume both bikers ride at a constant rate.
Time in Hours (𝒙) Distance in Miles (𝒚)
1.5 17.25
2 23
3.5 40.25
4 46
a. Which biker rides at a greater speed? Explain your reasoning.
Module 4: Linear Equations
496
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
b. Write an equation for a third biker, Lauren, who rides twice as fast as Kevin. Use 𝑦 to represent the
number of miles Lauren travels in 𝑥 hours. Explain your reasoning.
c. Create a graph of the equation in part (b).
d. Calculate the slope of the line in part (c), and interpret its meaning in this situation.
Module 4: Linear Equations
497
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
3. The cost of five protractors is $14.95 at Store A. The graph below compares the cost of protractors at
Store A with the cost at Store B.
Estimate the cost of one protractor at Store B. Use evidence from the graph to justify your answer.
Module 4: Linear Equations
498
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
4. Given the equation 3𝑥 + 9𝑦 = −8, write a second linear equation to create a system that:
a. Has exactly one solution. Explain your reasoning.
b. Has no solution. Explain your reasoning.
c. Has infinitely many solutions. Explain your reasoning.
d. Interpret the meaning of the solution, if it exists, in the context of the graph of the following system
of equations.
−5𝑥 + 2𝑦 = 10
{
10𝑥 − 4𝑦 = −20
Module 4: Linear Equations
499
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
5. Students sold 275 tickets for a fundraiser at school. Some tickets are for children and cost $3, while the
rest are adult tickets that cost $5. If the total value of all tickets sold was $1,025, how many of each type
of ticket was sold?
Module 4: Linear Equations
500
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
6.
a. Determine the equation of the line connecting the points (0, −1) and (2, 3).
b. Will the line described by the equation in part (a) intersect the line passing through the points
(−2, 4) and (−3, 3)? Explain why or why not.
Module 4: Linear Equations
501
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
7. Line 𝑙1 and line 𝑙2 are shown on the graph below. Use the graph to answer parts (a)–(f).
a. What is the 𝑦-intercept of 𝑙1 ?
b. What is the 𝑦-intercept of 𝑙2 ?
c. Write a system of linear equations representing lines 𝑙1 and 𝑙2 .
d. Use the graph to estimate the solution to the system.
Module 4: Linear Equations
502
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
e. Solve the system of linear equations algebraically.
f. Show that your solution from part (e) satisfies both equations.
Module 4: Linear Equations
503
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
A Progression Toward Mastery
STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 STEP 4
Assessment Missing or incorrect Missing or incorrect A correct answer A correct answer
Task Item answer and little answer but with some evidence supported by
evidence of evidence of some of reasoning or substantial
reasoning or reasoning or application of evidence of solid
application of application of mathematics to reasoning or
mathematics to mathematics to solve the problem, application of
solve the problem. solve the problem. OR an incorrect mathematics to
answer with solve the problem.
substantial
evidence of solid
reasoning or
application of
mathematics to
solve the problem.
1 a–b Student makes no Student computes the Student computes slope Student correctly
attempt to find the slope slope in parts (a) and (b) both times but may have computes the slope both
in part (a) and/or part but makes forgotten to include the 3
8.EE.B.5 times and finds 𝑚 = −
(b). computational errors negative sign or makes 2
(or an equivalent
leading to slopes that are another simple
fraction). Student finds
not equal. Student may computational error.
the slopes in both parts
have used the same two Student finds the slopes
(a) and (b) to be equal.
points for both parts (a) in both parts (a) and (b)
and (b). to be equal.
c Student makes no Student states that the Student makes a weak Student makes a
attempt to answer the slopes in parts (a) and (b) argument by stating that convincing argument
8.EE.B.6 question. are not equal. the slopes are equal and references similar
because the fractions are triangles to explain why
equal or that the the slopes between any
fractions representing two points on a line are
the slope are equivalent. equal.
2 a Student makes no Student writes an Student writes the Student writes the
attempt to answer the incorrect answer but correct answer that correct answer that
question or writes shows some evidence of Jeremy rides at a greater Jeremy rides at a greater
8.EE.B.5 “Kevin” or “Jeremy” with reasoning in the speed. Student speed. Student provides
no evidence of an explanation. explanation lacks a strong mathematical
application of precision or is incorrect. explanation as to which
mathematics to solve the For example, student biker rides at a greater
problem. may have written that speed by referencing a
Jeremy travels a farther graph (slopes of each
distance in two hours line where one slope is
instead of referencing steeper) or a numerical
the rates of each biker. comparison of their
rates.
Module 4: Linear Equations
504
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
b–d Student makes little or Student writes an Student correctly Student correctly writes
no attempt to complete incorrect equation in identifies the equation, the equation, 𝑦 = 23𝑥,
parts (b)–(d). Student part (b) and/or graphs graphs and calculates in part (b) or writes an
8.EE.B.5 may have plotted points the equation incorrectly the slope, and identifies equivalent equation.
on the graph with no and/or calculates the it as Lauren’s rate, but Student explains “twice
relevance to the slope incorrectly. the answer shows no as fast” in terms of
problem. Student does not evidence of reasoning in distance traveled for a
connect the slope of the part (b). given time interval
line to Lauren’s rate. OR compared to the data for
Student makes a mistake Kevin given in the table.
in writing the equation Student correctly graphs
for part (b), which leads the situation in part (c)
to an incorrect graph and correctly identifies
and slope in parts (c)– the slope of the line, 23,
(d). as the rate that Lauren
rides for part (d).
3 8.EE.B.5 Student makes no Student may or may not Student uses the Student uses the
attempt to answer the have correctly calculated information provided information provided
question. the unit rate of about Store A to about Store A to
OR protractors for Store A. determine the unit rate determine the unit rate
Student writes a dollar Student writes an of protractors but may of protractors and
amount with no estimate for Store B but have made a references the unit rate
explanation. does not justify the computational error at Store A in the
estimate using evidence leading to a poor justification of the
from the graph. estimate. Student may estimate. Student writes
or may not have used an estimate that makes
evidence from the graph sense (e.g., less than
to justify the estimate or Store A, about half as
makes a weak much) and uses evidence
connection between the from the graph in the
estimate and the graph. justification (e.g.,
comparison of slopes,
size of angles).
4 a–c Student makes no Student answers at least Student answers at least Student provides a
attempt to answer any one part of (a)–(c) two parts of (a)–(c) correct equation and
parts of (a)–(c). correctly. Student may correctly. Student may explanation for each of
8.EE.C.7a OR have left two parts have left one part blank. the parts of (a)–(c).
8.EE.C.8 Student only rewrites blank. Answer may or Student explains Specifically, for part (a),
the given equation as an may not show evidence reasoning in at least two an equation that
answer. of reasoning. parts of (a)–(c), noting represents a distinct line
the characteristics from the given equation
required to achieve the has a slope different
desired number of 1
from − ; for part (b), an
solutions. 3
equation that represents
a line parallel to the
given equation has the
same slope; and for part
(c), an equation that
represents the same line
as the given equation
whose graphs coincide.
Module 4: Linear Equations
505
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
d Student makes little or Student gives an Student may have tried Student correctly states
no attempt to answer incorrect answer. to find the solution that the graphs of the
the question. Student Student may have said algebraically. Student equations produce the
8.EE.C.8 does not provide a that the point of states that there are same line. Student
mathematical intersection of the lines infinitely many solutions explains that one
explanation or apply any is the solution to the to the system but may equation can be
mathematical reasoning system or that there is not have referenced obtained by the other by
to support the answer. no solution because the what the graph would multiplying the first
lines are parallel. look like (i.e., each equation by −2 or the
equation produced the 1
second equation by − .
same line on the graph). 2
OR
Student supplies weak
Student explains that
mathematical reasoning
both lines had the same
to support the answer. 5
slope of and the same
2
𝑦-intercept of (0, 5).
Student supplies strong
mathematical reasoning
to support the answer.
5 8.EE.C.8 Student makes little or Student may have Student correctly writes Student correctly writes
no attempt to write and written an incorrect a system of linear and solves a system of
solve a system of linear system of equations to equations to represent linear equations to solve
equations. represent the situation. the situation but makes the problem. Student
Student may or may not a computational error defines the variables
have defined the leading to an incorrect used in the system.
variables. Student may solution. Student states clearly
have used another OR that 175 children’s
strategy to determine Student correctly writes tickets and 100 adults’
the numbers of tickets of and solves a system but tickets were sold.
each type that were sold. does not define the
There is some evidence variables.
of mathematical
reasoning.
6 a Student makes little or Student incorrectly Student uses the points Student uses the points
no attempt to write the computes the slope of to correctly determine to determine the slope of
equation. the line as something the slope of the line as 2 the line and then writes
8.EE.C.8 other than 2. Student but may have written an the equation of the line
does not write the incorrect equation. passing through those
correct equation of the two points as 𝑦 = 2𝑥 − 1
line. or equivalent.
Module 4: Linear Equations
506
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
b Student makes little or Student incorrectly Student uses the points Students uses the points
no attempt to answer computes the slope of to correctly determine to determine the slope
the question. the line as something the slope of the line as 1 as 1 and correctly
8.EE.C.8 OR other than 1 and may or but makes an incorrect concludes that the lines
Student responds with may not have drawn an conclusion about intersect because the
yes or no only. incorrect conclusion whether or not the lines slopes are different.
about whether or not would intersect.
the lines would intersect. OR
Student makes a
computational error for
the slope and draws the
wrong conclusion about
the lines.
OR
Student says the lines
would intersect but does
not provide an
explanation.
7 a–b Student leaves both Student identifies one of Student identifies the Student correctly
parts (a) and (b) blank. the two 𝑦-intercepts but 𝑦-intercepts of 𝑙1 and 𝑙2 identifies the
OR may have inversed the but switches the 𝑦-intercepts of 𝑙1 and 𝑙2
8.EE.C.8 Student identifies coordinates. Student coordinates, i.e., (4, 0) as (0, 4) and (0, 2),
coordinates that do not leaves either (a) or (b) and (2, 0), or identifies respectively.
fall on either the 𝑥- or 𝑦- blank. the 𝑦-intercept of 𝑙1 as
axis. (0, 2) and 𝑙2 as (0, 4).
c–d Student leaves the item Student writes two Student writes a system Student correctly writes
blank. equations to represent of equations, but one of the system as
OR the system, but the the equations is written 𝑥 − 𝑦 = −2
8.EE.C.8 { or a system
Student only writes one equations do not incorrectly. Student 𝑥 + 2𝑦 = 8
equation that may or represent the lines on writes an estimate equivalent to this given
may not have the graph. Student may where the 𝑥-value is one. Student writes an
represented one of the or may not have written between 1 and 2 and the estimate where the
lines on the graph. an estimate or writes an 𝑦-value is between 3 and 𝑥-value is between 1 and
Student may or may not estimate where the 𝑥- 4. 2 and the 𝑦-value is
have written an estimate value is not between 1 between 3 and 4.
or writes an estimate and 2 and the 𝑦-value is
where the 𝑥-value is not not between 3 and 4.
between 1 and 2 and the
𝑦-value is not between 3
and 4.
e–f Student is unable to Student solves the Student solves the Student correctly solves
solve the system system algebraically but system but may have the system and identifies
algebraically. makes serious made a computational 4 10
8.EE.C.8 the solution as ( , ).
computational errors error leading to an 3 3
Student verifies the
leading to an incorrect incorrect 𝑥- or
solution in part (f).
solution. Student is 𝑦-coordinate. Student
unable to complete part verifies the solution in
(f) or notices an error part (f). Student makes a
and does not correct it. computational error and
believes the solution is
correct.
Module 4: Linear Equations
507
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
Name Date
1. Use the graph below to answer parts (a)–(c).
a. Use any pair of points to calculate the slope of the line.
b. Use a different pair of points to calculate the slope of the line.
c. Explain why the slopes you calculated in parts (a) and (b) are equal.
Module 4: Linear Equations
508
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
2. Jeremy rides his bike at a rate of 12 miles per hour. Below is a table that represents the number of hours
and miles Kevin rides. Assume both bikers ride at a constant rate.
Time in Hours (𝒙) Distance in Miles (𝒚)
1.5 17.25
2 23
3.5 40.25
4 46
a. Which biker rides at a greater speed? Explain your reasoning.
Module 4: Linear Equations
509
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
b. Write an equation for a third biker, Lauren, who rides twice as fast as Kevin. Use 𝑦 to represent the
number of miles Lauren travels in 𝑥 hours. Explain your reasoning.
c. Create a graph of the equation in part (b).
d. Calculate the slope of the line in part (c), and interpret its meaning in this situation.
Module 4: Linear Equations
510
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
3. The cost of five protractors is $14.95 at Store A. The graph below compares the cost of protractors at
Store A with the cost at Store B.
Estimate the cost of one protractor at Store B. Use evidence from the graph to justify your answer.
Module 4: Linear Equations
511
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
4. Given the equation 3𝑥 + 9𝑦 = −8, write a second linear equation to create a system that:
a. Has exactly one solution. Explain your reasoning.
b. Has no solution. Explain your reasoning.
c. Has infinitely many solutions. Explain your reasoning.
d. Interpret the meaning of the solution, if it exists, in the context of the graph of the following system
of equations.
Module 4: Linear Equations
512
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
5. Students sold 275 tickets for a fundraiser at school. Some tickets are for children and cost $3, while the
rest are adult tickets that cost $5. If the total value of all tickets sold was $1,025, how many of each type
of ticket was sold?
Module 4: Linear Equations
513
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
6.
a. Determine the equation of the line connecting the points (0, −1) and (2, 3).
b. Will the line described by the equation in part (a) intersect the line passing through the points
(−2, 4) and (−3, 3)? Explain why or why not.
Module 4: Linear Equations
514
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
7. Line 𝑙1 and line 𝑙2 are shown on the graph below. Use the graph to answer parts (a)–(f).
a. What is the 𝑦-intercept of 𝑙1 ?
b. What is the 𝑦-intercept of 𝑙2 ?
c. Write a system of linear equations representing lines 𝑙1 and 𝑙2 .
d. Use the graph to estimate the solution to the system.
Module 4: Linear Equations
515
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM End-of-Module Assessment Task 8•4
e. Solve the system of linear equations algebraically.
f. Show that your solution from part (e) satisfies both equations.
Module 4: Linear Equations
516
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org This work is licensed under a
This file derived from G8-M4-TE-1.3.0-09.2015 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
You might also like
- Korean Grammar in Use Beginner PDFDocument344 pagesKorean Grammar in Use Beginner PDFdanasli760724583% (6)
- AROC and IROC PracticeDocument4 pagesAROC and IROC PracticeAayan Khan100% (1)
- Chapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y IsDocument10 pagesChapter 8: Graphs of Functions (Practice Form 3) : 1. in The Figure Shown, When X 4, The Value of y Isunknown :)No ratings yet
- G7.M1.v3 Teacher EditionDocument224 pagesG7.M1.v3 Teacher EditionTuyếnĐặng67% (3)
- Volumes of A Revolution ExerciseDocument1 pageVolumes of A Revolution ExercisewolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- TAD1641GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineDocument2 pagesTAD1641GE: Volvo Penta Genset EnginesIMPEX sHARMANo ratings yet
- Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 2 Tips For ParentsDocument2 pagesEureka Math Grade 7 Module 2 Tips For ParentsEmily Greaves100% (1)
- Placement Test 1Document2 pagesPlacement Test 1GothamSchools.orgNo ratings yet
- Distributing Balls Into Boxes PDFDocument3 pagesDistributing Balls Into Boxes PDFPayashwini KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m3 Teacher MaterialsDocument374 pagesMath g7 m3 Teacher MaterialsMohammad Abdul OhabNo ratings yet
- MHF4U - Workbook 2022-2023Document91 pagesMHF4U - Workbook 2022-2023ashitha2goveasNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemDocument18 pagesAlgebra: Block Diagram of The Number SystemMichelle Corpuz IballaNo ratings yet
- A1AG12ADocument3 pagesA1AG12AAnonymous RzU94z100% (1)
- Math Practice Book AnswersDocument96 pagesMath Practice Book AnswersHaNoOsHa MoHdNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONMatt LamNo ratings yet
- Packet 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusDocument3 pagesPacket 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Polynomial and Rational FunctionsDocument11 pagesPolynomial and Rational Functionsoana_brincoveanuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document41 pagesChapter 1alexNo ratings yet
- Quiz Functions IDocument30 pagesQuiz Functions Icaleb castilloNo ratings yet
- Book Answers For CH 1Document20 pagesBook Answers For CH 1api-247437524No ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document16 pagesAlgebra 1sheheNo ratings yet
- Ib Grade 9 Math Book Chapter4Document52 pagesIb Grade 9 Math Book Chapter4TopDevelopersNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2-9 ReteachingDocument2 pagesAlgebra 2-9 Reteachingksimmons82No ratings yet
- Textbook Answers OddDocument47 pagesTextbook Answers OddOylaNo ratings yet
- g5 Multiplicative FunctionDocument45 pagesg5 Multiplicative FunctionMax PaineNo ratings yet
- Placement Test For Pre-AlgebraDocument1 pagePlacement Test For Pre-Algebraapi-232032459No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - DifferentiationDocument56 pagesChapter 4 - DifferentiationTOBY RANNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2-10 ReteachingDocument2 pagesAlgebra 2-10 Reteachingksimmons82No ratings yet
- Properties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1Document9 pagesProperties of Curves Worksheet Easy Problems 1V NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- BigIdeasMath Problems 15Document20 pagesBigIdeasMath Problems 15Puffy MathNo ratings yet
- Basic Discrete StructureDocument57 pagesBasic Discrete StructureAhmed Iqbal100% (1)
- CBSE 10 Maths Surface Areas and VolumesDocument33 pagesCBSE 10 Maths Surface Areas and VolumesAryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Lines and PlanesDocument16 pagesLines and PlanesNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Math Pre-Calculus - Semester Two Final: REVIEWDocument19 pagesMath Pre-Calculus - Semester Two Final: REVIEWKirby RoseNo ratings yet
- 2014 MCQ MTH 603Document5 pages2014 MCQ MTH 603Inocent NainaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differential Calculus ExerciseDocument17 pagesApplications of Differential Calculus ExerciseIsmail HashimNo ratings yet
- Maths F4 C2 Number BasesDocument79 pagesMaths F4 C2 Number Basesadampau1974No ratings yet
- Graphing QuadraticsDocument22 pagesGraphing QuadraticsMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- 11.1 - 11.3 Sequences and Series WorksheetDocument1 page11.1 - 11.3 Sequences and Series WorksheetDanalakshmi BharathiNo ratings yet
- Determining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5Document3 pagesDetermining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5api-288922072No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnswersDocument27 pagesChapter 7 Answersapi-247437524No ratings yet
- Text 8.6 - Scale DrawingsDocument4 pagesText 8.6 - Scale DrawingsAbdelaziz AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination: Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, IncDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Examination: Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, IncJoyce Ann SameraNo ratings yet
- Set-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsDocument19 pagesSet-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- DE - Modeling: Mixing Problem (Single Tank) Mixing Problem (Three Tank)Document11 pagesDE - Modeling: Mixing Problem (Single Tank) Mixing Problem (Three Tank)Laisa VittoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8: Conic Sections: H K y A XDocument2 pagesCh. 8: Conic Sections: H K y A XThanin KuphoonsapNo ratings yet
- MathDocument5 pagesMathneysaneptunex0% (1)
- Rise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSDocument2 pagesRise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSafzabbasi100% (1)
- 09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01Document1 page09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01sivsyadavNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Practice - BDocument2 pages2-1 Practice - BStanley50% (2)
- Linear Algebra Reivew: All Linear Algebra, So This Is A Fairly Serious Weakness. This Review IsDocument10 pagesLinear Algebra Reivew: All Linear Algebra, So This Is A Fairly Serious Weakness. This Review Isabo7999No ratings yet
- Basel Problem ProofDocument7 pagesBasel Problem ProofCody JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Mcv4u TestDocument2 pagesMcv4u Testapi-483845268No ratings yet
- 16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsDocument21 pages16 Quiz Review Quadratic EquationsdevikaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math - Mock ExamDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Math - Mock ExamDawnNo ratings yet
- Shortcuts For MathDocument6 pagesShortcuts For Mathapi-27483824No ratings yet
- Math g8 m4 Mid Module AssessmentDocument11 pagesMath g8 m4 Mid Module AssessmentHrithik PeddireddyNo ratings yet
- Math g4 m1 End of Module AssessmentDocument8 pagesMath g4 m1 End of Module AssessmentRuselle N. NavarroNo ratings yet
- Precalculus m4 End of Module AssessmentDocument27 pagesPrecalculus m4 End of Module AssessmentMarina SmirnovaNo ratings yet
- Prescriptionand Administrationof Oxygen 201901Document26 pagesPrescriptionand Administrationof Oxygen 201901danasli7607245No ratings yet
- Surrogates For The Study of Norovirus Stability AnDocument6 pagesSurrogates For The Study of Norovirus Stability Andanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares Er IrDocument8 pagesVerbos Regulares Er Irdanasli7607245No ratings yet
- GUSTAR (Like) : Estudiar Espanol Dormir Temprano Comer Pizza Descansar en Casa Starbucks Vivir en CoreaDocument6 pagesGUSTAR (Like) : Estudiar Espanol Dormir Temprano Comer Pizza Descansar en Casa Starbucks Vivir en Coreadanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Classifying Numbers ReviewDocument10 pagesClassifying Numbers Reviewdanasli7607245No ratings yet
- Anchor Handling PDFDocument56 pagesAnchor Handling PDFEdwien Arif WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- PJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Document22 pagesPJC H2 PHY 9646 Mid-Year Paper 2012Ng Jia ChengNo ratings yet
- Physa S 20 02188Document20 pagesPhysa S 20 02188Mehmet ErtaşNo ratings yet
- Measurement Lesson Length1Document4 pagesMeasurement Lesson Length1api-242505437No ratings yet
- Tara Balam... : How To Caluculate Tarabalam?Document6 pagesTara Balam... : How To Caluculate Tarabalam?krishnaNo ratings yet
- Passing Select-Options To Smart Forms: by VenkatDocument43 pagesPassing Select-Options To Smart Forms: by VenkatsudhakpNo ratings yet
- Metric: Hex Nut Style 2 Class 12Document1 pageMetric: Hex Nut Style 2 Class 12Ankit LonareNo ratings yet
- Geometry Book-Chapter 5.2Document6 pagesGeometry Book-Chapter 5.2alternativoNo ratings yet
- Afm ButterflyDocument5 pagesAfm ButterflyAna-Maria MaticuNo ratings yet
- Pavers - ACN - PCN - The Pavement Classification NumberDocument2 pagesPavers - ACN - PCN - The Pavement Classification Numberphuong leNo ratings yet
- Wwkzii: Jan. 10, 1933. R. H. FarwellDocument3 pagesWwkzii: Jan. 10, 1933. R. H. Farwellmonem2014100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutDocument25 pagesChapter 5 Auxiliary View - HandoutTeshome Bekele100% (1)
- Codes TFM Webinar-DSDocument96 pagesCodes TFM Webinar-DSThành TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Zinn-Justin J. Quantum Field Theory and Critical Phenomena (3ed., Oxford, 1996) (150dpi) (L) (T) (517s) - PTqs - Cropped (Cut) - RedDocument1,033 pagesZinn-Justin J. Quantum Field Theory and Critical Phenomena (3ed., Oxford, 1996) (150dpi) (L) (T) (517s) - PTqs - Cropped (Cut) - RedBruno Da Fonseca GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SolidDocument59 pagesChapter 3 Solidatikah roshanNo ratings yet
- Power Pavilion Parfait Intel SKL / Kaby - H System DiagramDocument52 pagesPower Pavilion Parfait Intel SKL / Kaby - H System DiagramAbnesis NesisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3Abigail Jimenez100% (1)
- Properties of Moist AirDocument11 pagesProperties of Moist AirKarthik HarithNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology MBADocument3 pagesResearch Methodology MBAYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- TUT2Document4 pagesTUT2Yogesh Israni ASET, NoidaNo ratings yet
- Homeinteriorpaint FractionsdecimalsandpercentsDocument4 pagesHomeinteriorpaint Fractionsdecimalsandpercentsapi-281744400No ratings yet
- Mozart Fantasie D Minor k397 Instructive All PDFDocument22 pagesMozart Fantasie D Minor k397 Instructive All PDFLiviu Pencea100% (1)
- Solving Multi-Dimensional Problems of Gas Dynamics Using MATLABDocument40 pagesSolving Multi-Dimensional Problems of Gas Dynamics Using MATLABMahmoud Abd El LateefNo ratings yet
- Hexagon MI Aerospace Smart Manufacturing Ebook A4 WEBDocument26 pagesHexagon MI Aerospace Smart Manufacturing Ebook A4 WEBLuis7929No ratings yet
- Applications of Algebra To A Problem in Topology - by Michael HopkinsDocument49 pagesApplications of Algebra To A Problem in Topology - by Michael HopkinsThe Simons Foundation100% (1)
- Tolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationDocument9 pagesTolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationCahyono IriawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer AnimationDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Computer Animationsanu222No ratings yet
- Nptel: Power Electronics Applications To Power Systems - Video CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: Power Electronics Applications To Power Systems - Video Courseprafful666No ratings yet
- Protective Paints For Heat Treatment of SteelsDocument4 pagesProtective Paints For Heat Treatment of SteelsMauricio Cesar DalzochioNo ratings yet