Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Company Makes Bicycles
A Company Makes Bicycles
Uploaded by
Nasir HussainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Company Makes Bicycles
A Company Makes Bicycles
Uploaded by
Nasir HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
A company makes bicycles. It produces 450 bicycles a month.
It buys the tires for bicycles from a
supplier at a cost of $20 per tire.
The company’s inventory carrying cost is estimated to be 15% of cost and the ordering is $50 per order.
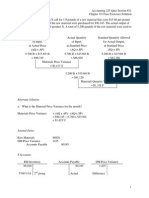
a. Calculate the EOQ In this problem:
D = annual demand = (2 tires per bicycle) x (450 bicycles per month) x (12 months in a year) =
10,800 tires
S = ordering cost = $50 per order
H = carrying cost = (15%) x ($20 per unit) = $ 3.00 per unit per year
EOQ = Square root of { (2 x 10,800 x $50) / $3 = Square root of 400,000 = 600 tires
The company should order about 600 tires each time it places an order.
b. What is the number of orders per year?
Number of orders per year = D / Q = 10,800 / 600 = 18 orders per year
c. Compute the average annual ordering cost.
Average annual ordering cost = (18 orders per year) x ($50 per order) = $900 per year
d. Compute the average inventory.
Average inventory = Q / 2 = 600 / 2 = 300 tires
e. What is the average annual carrying cost?
Average annual carrying cost = (average inventory) x (H) = (300 tires) x ( $3) = $900 per year
f. Compute the total cost. Total cost = (Average annual ordering cost) + (average annual carrying) =
($900) + ($900) = $1,800
You might also like
- Manegement Science Mod 1 M1L2Document8 pagesManegement Science Mod 1 M1L2Cher Na100% (2)
- Name:: MECH 6076 (Supply Chain Management For Engineers) Test IIDocument4 pagesName:: MECH 6076 (Supply Chain Management For Engineers) Test IIMarcus WallaceNo ratings yet
- Economics - FE Review Problems and Solutions 2012Document154 pagesEconomics - FE Review Problems and Solutions 2012Blake Reeves50% (2)
- Inventory Problems SolutionDocument8 pagesInventory Problems Solutionakash sam100% (1)
- Production Exercise 1Document8 pagesProduction Exercise 1Nasir Hussain100% (3)
- Problem 1 A Company Makes BicyclesDocument5 pagesProblem 1 A Company Makes BicyclesMajid Khan80% (5)
- 1 Ass-2Document13 pages1 Ass-2Kim SooanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - 12: Product Cost Flows Product Versus Period CostsDocument4 pagesExercise 1 - 12: Product Cost Flows Product Versus Period Costsmmdinar100% (3)
- Revise Mid TermDocument43 pagesRevise Mid TermThe FacesNo ratings yet
- Letter To An Employee Giving Notice of A Disciplinary Meeting DismissalDocument1 pageLetter To An Employee Giving Notice of A Disciplinary Meeting DismissalNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Homework AnswersDocument37 pagesHomework AnswersenergizerabbyNo ratings yet
- Problems EoqDocument2 pagesProblems EoqHoàng Ngọc LanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Exercises - BSCDocument4 pagesClassroom Exercises - BSCAdrian Gabriel Sincero LuceroNo ratings yet
- ACG 2071, Test 2-Sample QuestionsDocument11 pagesACG 2071, Test 2-Sample QuestionsCresenciano MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- Procurement and Inventory Management Partial Assignment On Inventory Management Uqba Imtiaz 20171-22152Document7 pagesProcurement and Inventory Management Partial Assignment On Inventory Management Uqba Imtiaz 20171-22152Aqba ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 7ADocument3 pagesProblem Sheet 7AMuztoba AliNo ratings yet
- ECON PS 1 With Soln by Julius GrazaDocument3 pagesECON PS 1 With Soln by Julius GrazaEzlan HarithNo ratings yet
- Ex 04 Inventory ManagementDocument4 pagesEx 04 Inventory ManagementZulhaily Suaille100% (1)
- CH 16Document4 pagesCH 16Riya Desai100% (5)
- Assignment #3 InventoryDocument13 pagesAssignment #3 InventoryAnkit SainiNo ratings yet
- Break EvenDocument2 pagesBreak EvenPia PeñaNo ratings yet
- 3 Relevant Costing Final PDFDocument31 pages3 Relevant Costing Final PDFmoss roffattNo ratings yet
- $70) ÷ $150 53.33%) - This May Suggest That D. LawranceDocument1 page$70) ÷ $150 53.33%) - This May Suggest That D. LawrancejppjelNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Kelompok 12 Bab 11 ADocument18 pagesPresentasi Kelompok 12 Bab 11 AsimsonNo ratings yet
- SCM Answer Case Harley-DavidsonDocument4 pagesSCM Answer Case Harley-DavidsonRobby SitorusNo ratings yet
- EOQ CalculationDocument2 pagesEOQ CalculationJustine WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 ExerciseDocument11 pagesModule 5 Exercisexxmbeta0% (1)
- Fourth Form Quiz 3 (Consumer Arithmetic) Name: - ClassDocument4 pagesFourth Form Quiz 3 (Consumer Arithmetic) Name: - ClassChet Ack100% (1)
- Homework Chapter 3Document3 pagesHomework Chapter 3cakesbybeth19No ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Economics Exercises)Document5 pagesAssignment 5 (Economics Exercises)OlyvianurmaharaniNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Homework 3: Student Name: Student IDDocument4 pagesEngineering Economy Homework 3: Student Name: Student IDMinh TríNo ratings yet
- BSAIS 3B MODULE 2 Unit 1 To 4 LUMAPAY ROSALIE Q. Cost Accounting and ControlDocument26 pagesBSAIS 3B MODULE 2 Unit 1 To 4 LUMAPAY ROSALIE Q. Cost Accounting and ControlNaruse JunNo ratings yet
- ZoroDocument11 pagesZoroDrinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Homework Manufacturing Economics and Computation Exercise With Solution CompressDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Homework Manufacturing Economics and Computation Exercise With Solution Compressngxbao0211suyaNo ratings yet
- Cost and IntaccDocument6 pagesCost and IntaccSAFLOR, Edlyn Mae A.No ratings yet
- ACC209 Assignment 2 AlternateDocument14 pagesACC209 Assignment 2 Alternatehtet aungNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document3 pagesHomework 2Genesis Carolina Castañeda VenturaNo ratings yet
- HomeWork Slide 7Document5 pagesHomeWork Slide 7Anisa Fitriani0% (1)
- Assignment Week 8Document1 pageAssignment Week 8Sandhya GoindaniNo ratings yet
- PPC ProblemDocument7 pagesPPC ProblemNiponIslamBeckham100% (1)
- Managment AssignmentDocument8 pagesManagment AssignmentMinilik MinilikNo ratings yet
- Final Practice SolutionsDocument15 pagesFinal Practice SolutionsMatthewLiuNo ratings yet
- Addtional ExercisesDocument36 pagesAddtional ExercisesGega XachidENo ratings yet
- 610 Midterm 2 S11 02 With SolDocument6 pages610 Midterm 2 S11 02 With SolabuzarNo ratings yet
- Life-Cycle CostingDocument12 pagesLife-Cycle CostingFahim MahmudNo ratings yet
- Assignment For EconomicsDocument5 pagesAssignment For EconomicstarekNo ratings yet
- Breakeven and EOQ Exercises (With Answers)Document6 pagesBreakeven and EOQ Exercises (With Answers)Charlene ChorNo ratings yet
- TT03 CVP1Document7 pagesTT03 CVP109-Cao Thị Mỹ LệNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document9 pagesClass 1hesham hassanNo ratings yet
- Purchase Cost 480,000.00Document9 pagesPurchase Cost 480,000.00Charisse Aro YcongNo ratings yet
- PPC Ec3r - QP AnsDocument12 pagesPPC Ec3r - QP AnsSWAROOPAN1No ratings yet
- Item Annual Demand Unit Cost (RS.)Document3 pagesItem Annual Demand Unit Cost (RS.)Manjita NyachhyonNo ratings yet
- Total Relevant Cost (TRC)Document7 pagesTotal Relevant Cost (TRC)LinhThùyNo ratings yet
- MGT Chap 6Document5 pagesMGT Chap 6tomNo ratings yet
- QS11 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument8 pagesQS11 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (2)
- Tutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet - 1 (UNIT-1)Frederick DugayNo ratings yet
- Inventory ModelsDocument38 pagesInventory ModelsAngela MenesesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Document8 pagesTutorial 8 Time Value Money 2021Hai Liang OngNo ratings yet
- OP QuestionsDocument14 pagesOP QuestionsAhmad EssamNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management AssignmentDocument6 pagesInventory Management Assignmenthanayuki_ghostNo ratings yet
- MAE - Inventory - Pratice SolutionDocument12 pagesMAE - Inventory - Pratice SolutionDhairya MudgalNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2: Theoritical Article: SummarizationDocument3 pagesAssignment # 2: Theoritical Article: SummarizationNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 SBPDocument6 pagesAssignment 03 SBPNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Annex-II - Draft HEC Policy On Drug and Tobacco Abuse in Higher Education Institutions (March 2021)Document11 pagesAnnex-II - Draft HEC Policy On Drug and Tobacco Abuse in Higher Education Institutions (March 2021)Nasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Case Study Part2-Industry and Market AnalysisDocument1 pageCase Study Part2-Industry and Market AnalysisNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Annex-I - HEC Policy For Students With Disabilities 2021 (Revised)Document11 pagesAnnex-I - HEC Policy For Students With Disabilities 2021 (Revised)Nasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Bera - A Real World Case StudyDocument2 pagesBera - A Real World Case StudyNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Animals Also Have RightsDocument1 pageAnimals Also Have RightsNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Translating Strategy Into HR Policies and Practices CaseDocument7 pagesCase Study: Translating Strategy Into HR Policies and Practices CaseNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Cranfield Superstore Case Study Part4Document8 pagesCranfield Superstore Case Study Part4Nasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Pricing in The Package Holiday MarketDocument3 pagesPricing in The Package Holiday MarketNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- PDF Startegic Management Analysis of Engro FoodsDocument38 pagesPDF Startegic Management Analysis of Engro FoodsNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- 1) - How Do Consumers Process and Evaluate Prices?Document4 pages1) - How Do Consumers Process and Evaluate Prices?Nasir HussainNo ratings yet
- CASE 9 AmazonDocument17 pagesCASE 9 AmazonNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix (Assignment)Document4 pagesBCG Matrix (Assignment)Nasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Can A Pessimistic Nation Be Led by An Optimistic LeaderDocument2 pagesCan A Pessimistic Nation Be Led by An Optimistic LeaderNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Project Idea ExerciseDocument4 pagesProject Idea ExerciseNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Renewable Energy OverviewDocument10 pagesChapter 1. Renewable Energy OverviewNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Childhood Domestic ViolenceDocument8 pagesChildhood Domestic ViolenceNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Nishat Mills Limited IntroductionDocument2 pagesNishat Mills Limited IntroductionNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- Marketing GENERAL Kotler (2006) Defined Marketing As The Social and Managerial Process by WhichDocument2 pagesMarketing GENERAL Kotler (2006) Defined Marketing As The Social and Managerial Process by WhichNasir HussainNo ratings yet
- MM Assignmet Solution - RAWDocument4 pagesMM Assignmet Solution - RAWNasir HussainNo ratings yet