Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Uploaded by
ShanpaulCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Efficiency Paradox - Niklas ModigDocument37 pagesThe Efficiency Paradox - Niklas ModiglawiNo ratings yet
- Basic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Document14 pagesBasic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Roxanne Forbes100% (1)
- History and Evolution of Psychiatric NursingDocument4 pagesHistory and Evolution of Psychiatric Nursingkaren carpio100% (2)
- Contoh KasusDocument6 pagesContoh KasusIndah Ratnasarii0% (3)
- Think CBT WorkbookDocument92 pagesThink CBT Workbooksindhu ponnusamy100% (1)
- Capgar Description 1Document4 pagesCapgar Description 1esbat07100% (2)
- Perspec've Taking Photo Cards Ac'vity #3 What Are They Feeling? Includes 30 Photo Ac'vity CardsDocument8 pagesPerspec've Taking Photo Cards Ac'vity #3 What Are They Feeling? Includes 30 Photo Ac'vity CardsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM 5 Section III PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM 5 Section III PDFraluca_ghigaNo ratings yet
- MyndLift Neurofeedback HandoutDocument2 pagesMyndLift Neurofeedback Handoutshaheenshaikh4940No ratings yet
- "A Critical Time": A Special Report On Emerging Adults Leaving Children's Services CareDocument56 pages"A Critical Time": A Special Report On Emerging Adults Leaving Children's Services CareEmily MertzNo ratings yet
- JAK Inhibitors For Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument7 pagesJAK Inhibitors For Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisMasithaNo ratings yet
- NURS 4369 Preceptor Packet Core 2013Document11 pagesNURS 4369 Preceptor Packet Core 2013Aruna Chezhian100% (1)
- Kate Nobles Linkedin ResumeDocument1 pageKate Nobles Linkedin Resumeapi-612399312No ratings yet
- Mindmap of Reproductive HealthDocument2 pagesMindmap of Reproductive Healthkabirp895No ratings yet
- Gastro BrochureDocument3 pagesGastro Brochuregus_lionsNo ratings yet
- Semu Web 2021 - 2022Document1 pageSemu Web 2021 - 2022Carol PhaswanaNo ratings yet
- School Medical Autism Review Team: A Virtual, Interdisciplinary Tool To Diagnose Children With Autism in Rural Washington State (Amy Carlsen)Document1 pageSchool Medical Autism Review Team: A Virtual, Interdisciplinary Tool To Diagnose Children With Autism in Rural Washington State (Amy Carlsen)AUCDNo ratings yet
- CHP Poster Final - April 2023Document1 pageCHP Poster Final - April 2023api-620860184No ratings yet
- Inclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)Document1 pageInclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)AUCDNo ratings yet
- Madhya Pradesh Medical Science University, Jabalpur (M.P.)Document78 pagesMadhya Pradesh Medical Science University, Jabalpur (M.P.)Vinay Mishra100% (1)
- Arunava Deb OJT Report 11909663Document34 pagesArunava Deb OJT Report 11909663nischal krishnaNo ratings yet
- Holahan Sloan Poster YaleDocument1 pageHolahan Sloan Poster Yaleapi-416977976No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Final Year Students Djerriwarrh Health ServicesDocument1 pageGuidelines For Final Year Students Djerriwarrh Health Servicessidney drecotteNo ratings yet
- 2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Document63 pages2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Taif SalimNo ratings yet
- Goldberg-HIV PosterDocument1 pageGoldberg-HIV PosterMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis Institute of Business Management Pune - Email: Placements@sibmpune - Edu.in - PH.: 020-28116071/72/73Document7 pagesSymbiosis Institute of Business Management Pune - Email: Placements@sibmpune - Edu.in - PH.: 020-28116071/72/73MeetaliSaxenaNo ratings yet
- Delgado Destiny ResumeDocument2 pagesDelgado Destiny Resumeapi-661552521No ratings yet
- CACTX BrochureDocument2 pagesCACTX BrochureAndrew BarlowNo ratings yet
- Change in Clinical Status and Side Effects of Patients Treated With Either Olanzapine or Risperidone 6-Month Results From IC-SOHODocument1 pageChange in Clinical Status and Side Effects of Patients Treated With Either Olanzapine or Risperidone 6-Month Results From IC-SOHOPedro GargoloffNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Interpersonal PsychotherapyDocument38 pagesLecture 9 Interpersonal PsychotherapyKar GayeeNo ratings yet
- E-Poster Enterics For Global Health Shigella Surveillance StudyDocument1 pageE-Poster Enterics For Global Health Shigella Surveillance StudyNeyama AlladinNo ratings yet
- Escala Del Dolor PPPDocument16 pagesEscala Del Dolor PPPMariana SuarezNo ratings yet
- First Bridge Centre ABA An IntroductionDocument70 pagesFirst Bridge Centre ABA An Introductionpsigrist100% (4)
- Figure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundDocument1 pageFigure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundAhmed Abd El AzizNo ratings yet
- Practicalskillschecklist 13Document15 pagesPracticalskillschecklist 13api-396515657No ratings yet
- Primary Care Entrepreneurship ModelsDocument60 pagesPrimary Care Entrepreneurship Modelssachin ganorkar100% (1)
- Malnutrition in Pakistan 20230418 FinalDocument1 pageMalnutrition in Pakistan 20230418 FinalZona AroojNo ratings yet
- O5 Vo4No4Document6 pagesO5 Vo4No4Muthanna Lo'ayNo ratings yet
- Final Compass Logic Model 8 MonthsDocument1 pageFinal Compass Logic Model 8 Monthsapi-256763045No ratings yet
- Register Kesehatan AnakDocument5 pagesRegister Kesehatan AnakSdnegeri LebakpasarNo ratings yet
- EMC Current State LoopsDocument1 pageEMC Current State LoopsGiovanni Lorenzoni AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 10 Day Course 2018Document2 pages10 Day Course 2018Niruj Kr DekaNo ratings yet
- Efectividad en Las Visitas DomicliariasDocument6 pagesEfectividad en Las Visitas DomicliariasJonathan Francisco Gomez SantelicesNo ratings yet
- ACCESSquality FINANCIAL PLAN TEMPLATEDocument15 pagesACCESSquality FINANCIAL PLAN TEMPLATEDulay RezzielNo ratings yet
- Fever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSDocument2 pagesFever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSnimraNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Nursing Management Round 5ad3bdbbDocument11 pagesOptimization of Nursing Management Round 5ad3bdbbsarvitaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Workplan 2023 2025Document12 pagesNutrition Workplan 2023 2025Rico Jay GrasparilNo ratings yet
- Fri 394 Ilc2022Document1 pageFri 394 Ilc2022rtthrtfhNo ratings yet
- Adventures in Parenting Rev PDFDocument67 pagesAdventures in Parenting Rev PDFjyzlle herrera100% (1)
- BudgetDocument3 pagesBudgetmalakdiabmed57No ratings yet
- Children Adopted From Eastern Europe EvoDocument1 pageChildren Adopted From Eastern Europe EvoDolores SeguraNo ratings yet
- Govph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaDocument29 pagesGovph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaCarol LaconsayNo ratings yet
- Annotated PDocument4 pagesAnnotated Papi-735789339No ratings yet
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionashish kuntewarNo ratings yet
- 1 - FORBESJHEPATOL2015 Cell Therapy en Enf HeaticasDocument13 pages1 - FORBESJHEPATOL2015 Cell Therapy en Enf HeaticasalexandresarradeyNo ratings yet
- 2011 Google Shopper Sciences Finance Credit Cards ZMOTDocument21 pages2011 Google Shopper Sciences Finance Credit Cards ZMOTangelo1boccola-1No ratings yet
- Are Asthma Programs Positioned For Impact Factors Associated With SuccessDocument1 pageAre Asthma Programs Positioned For Impact Factors Associated With SuccessCenter for Managing Chronic DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Elevate Effectiveness Study: Principal AuthorDocument7 pagesElevate Effectiveness Study: Principal Authorfederico torresNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Corrected 20pDocument5 pagesAnnotated-Corrected 20papi-735789339No ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument54 pagesEctopic PregnancyLawrence CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- KinsDocument2 pagesKinsapi-576274610No ratings yet
- Children 07 00064Document10 pagesChildren 07 00064zizee61No ratings yet
- Animal-Assisted Intervention in Dementia: Effects On Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and On Caregivers' Distress PerceptionsDocument8 pagesAnimal-Assisted Intervention in Dementia: Effects On Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and On Caregivers' Distress PerceptionsFelipe FookNo ratings yet
- India Heals 2020 - Indian ExhibitorsDocument2 pagesIndia Heals 2020 - Indian ExhibitorsRama VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Vbmapp FaqsDocument2 pagesVbmapp FaqsMonalisa Costa100% (2)
- DQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBDocument1 pageDQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBcococooleNo ratings yet
- Karlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleDocument1 pageKarlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleAfien MuktiNo ratings yet
- Procedure TempDocument2 pagesProcedure TempShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Up The Assessment Binder: SettingDocument9 pagesUp The Assessment Binder: SettingShanpaulNo ratings yet
- GRAPHICS by JW Illustrations ©Document4 pagesGRAPHICS by JW Illustrations ©ShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Ablls-R Visual Performance Section B8 Sort Non Identical ItemsDocument10 pagesAblls-R Visual Performance Section B8 Sort Non Identical ItemsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Roadmap 2 Evidence Based Social Emotional Curricula and Intervention Packages For Children 0 5 Years and Their Families PDFDocument21 pagesRoadmap 2 Evidence Based Social Emotional Curricula and Intervention Packages For Children 0 5 Years and Their Families PDFShanpaulNo ratings yet
- SOC - Games TA Musical ChairsDocument1 pageSOC - Games TA Musical ChairsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Ten Questions For John Rowan PDF PDFDocument3 pagesTen Questions For John Rowan PDF PDFtestNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lecture Materials: Human Behavior and VictimologyDocument64 pagesCompiled Lecture Materials: Human Behavior and Victimologyanna lei mazaredoNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy and AutismDocument4 pagesOccupational Therapy and AutismBetül Özsoy TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Final Mental Health Lit ReviewDocument116 pagesFinal Mental Health Lit ReviewDanny WamsleyNo ratings yet
- Read The Essay and Then Answer The QuestionsDocument4 pagesRead The Essay and Then Answer The QuestionsLINA MURILLONo ratings yet
- Why Is Mental Health Important? Mental Health Is Important Because It AffectsDocument1 pageWhy Is Mental Health Important? Mental Health Is Important Because It AffectsJellina Joya RosgaNo ratings yet
- NUR 3251 Module 10 Psychotherapeutic Agents Study GuideDocument6 pagesNUR 3251 Module 10 Psychotherapeutic Agents Study GuideWinnie MeiNo ratings yet
- Pola Komunikasi Guru Di Yayasan Peduli Autisme Bali Dalam Meningkatkan Interaksi Sosial Anak AutistikDocument14 pagesPola Komunikasi Guru Di Yayasan Peduli Autisme Bali Dalam Meningkatkan Interaksi Sosial Anak AutistikIntan HumaerohNo ratings yet
- Gemma Hardy Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument19 pagesGemma Hardy Post Traumatic AmnesiaAditya Pradana KNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes During MenopauseDocument48 pagesPsychological Changes During MenopauseSnow19987No ratings yet
- What To Expect - Chris Vanderwees, PHD, RPDocument1 pageWhat To Expect - Chris Vanderwees, PHD, RPGary FreedmanNo ratings yet
- The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)Document8 pagesThe Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)Wynda MuljonoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Child AbuseDocument4 pagesEffects of Child Abuselotusrai100% (2)
- Stress DiaryDocument2 pagesStress Diaryapi-217446206No ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety DisordersSantosh ParabNo ratings yet
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Skill Hebefrenic SchizophreniaDocument13 pagesSkill Hebefrenic SchizophreniasaidahrahmatNo ratings yet
- Drug Use Screening Tool - DUST 2Document4 pagesDrug Use Screening Tool - DUST 2TONIC100% (2)
- PSQIDocument6 pagesPSQINingsih An NajwaNo ratings yet
- Stress & Stress ManagementDocument19 pagesStress & Stress ManagementNawfal EddyaniNo ratings yet
- Child PsychiatrystudentbookletDocument83 pagesChild PsychiatrystudentbookletOana Popescu50% (2)
- The Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalDocument11 pagesThe Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalAdela100% (2)
- Jane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldDocument5 pagesJane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldCanola_Olive0% (1)
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Uploaded by
ShanpaulOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Therese Mathews Autism Care For Toddlers ACT Clinic
Uploaded by
ShanpaulCopyright:
Available Formats
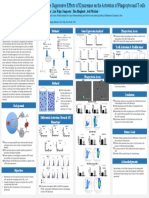
Autism Care for Toddlers (ACT) Clinic
Therese L. Mathews, Laura L. Needelman, Melissa L. King, Ashley M. Lugo, Leny D. Velasquez & Kiley J. Bliss
UNMC Department of Psychology, Munroe-Meyer Institute
Mission
To provide services to uninsured toddlers ages 18 to 36 months with autism and their families, train service providers in evidence-based early intervention procedures, and to conduct research.
Services Preliminary Findings:
The ACT clinic is a free-of-charge early intervention program for underinsured toddlers (ages 18-36 12-18-month
months) with a diagnosis of an Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in the Omaha area. The clinic seeks to
combine clinical service and research with interdisciplinary education to improve social communication, Evaluation Results
a
play, and adaptive skills through the use of techniques based on Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA).
VB-MAPP
The ACT Clinic opened its doors in September 2013 to three children with moderate to severe ASD three 160
VB-MAPP
mornings per week (i.e., 10.5 direct contact hours). Since then, we have expanded our services to serve 140
Baseline
a total of 27 children, and clinic services are provided 4 full days per week. 6-month
1-year
All participants had improved VB-MAPP scores in each
120 18-month
of the assessment periods.
Assessment/Outcome Measures Early Intervention Services The mean baseline score = 25, 6 months = 62, 12
100
Total Score
80 months=71, and 18 months = 82. (Higher score desired)
Several assessments are conducted with every child, prior to enrollment The ACT clinic provides early intervention services to target social 60
ADOS-2
in the clinic and every 6-months thereafter. communication, language, play skills, and maladaptive behavior. The 40
The mean scores for ADOS-2 at baseline =19, 6 months
Cognitive assessment (i.e., Mullen Scales of Early Learning; Cognitive Verbal Behavior (VB) approach to early intervention is used to guide
= 13, 12 months =15, and 18 months =19. (Lower score
Adaptive Test/Clinical Linguistic and Auditory Milestone Scale) individualized assessment and intervention to facilitate language 20
desired)
acquisition in early learners. 0
Functional assessment and/or analysis of challenging behavior 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Participant
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
ABAS-2
Direct clinic services include:
Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, 2nd Edition. The
1:1 discrete trial teaching targeting expressive and receptive No substantial differences were noted during the
ADOS-2 is a semi-structured standardized observation tool used to ADOS-2
language, imitation, social play, compliance, and preschool readiness assessment period.
measure autism symptoms in social relatedness, communication, play, 30
and repetitive behaviors. A higher total score indicates a higher skills COGNITIVE (Mullen & CAT/CLAMS)
Natural environment training to capture and contrive motivation to
Baseline
likelihood of autism
No significant differences were noted between
6-month
25 12-month
Adaptive Behavior Assessment System, 2nd Edition. The ABAS-II mand under natural contingencies and to promote generalization of 18-month
assessment periods.
is a rating form used to assess adaptive behavior in various domains, acquired skills 20
including: Communication, Community Use, Functional Academics, Functional assessment and/or analysis of problem behavior (e.g., self-
Autism Severity Score
Discussion
Home Living, Health and Safety, Leisure, Self-Care, Self-Direction, injurious behavior, aggression, tantrums) 15
Social and Work (optional subscale).
Parent Training
The Verbal Behavior-Milestones Assessment and Placement 10
Program. The VB-MAPP is an assessment tool and curriculum guide LIMITATIONS
used to assess and target early language and learning skills. As part of standard clinic services, collaboration between clinic staff and
5
Parent report may be biased on the ABAS-2 scores.
parents is ongoing. Additionally, in order to show improvement in adaptive
Student Training Opportunities
0
Parents are encouraged to meet on-site with their child’s case scores, the toddlers would be expected to make gains at a
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Participant 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
supervisor for 30-minutes every other week to discuss child’s progress faster rate than their peers.
and practice skills taught in their child’s individualized program. There was a change in ADOS-2 module from toddler to
Students are taught the basics of applied behavior analysis in order to Module 1 because of age change. Further, repetitive
In addition, parents attend one 1.5 hour group session per month ABAS-2
behaviors and restricted interests may emerge as the child
perform duties as behavior therapists. Multiple opportunities for growth 100
during which they are taught about general behavior principles and ages.
as future service providers are available, including: 90
techniques through the use of behavioral skills training There were different examiners for testing across
Training to become a Registered Behavior Technician 80 baseline
assessment tools and assessment periods.
Assessing preference and pairing 6-month
12-month
Learning to collect data and make data based decisions 70
Understanding behavior (e.g., the ABC’s & functions of behavior) CONSUMER SATISFACTION
Developing and implementing individualized interventions 60
Using positive reinforcement
Standard Score
Conducting applied research Overall, high levels of satisfaction are reported.
50
Teaching new skills (e.g., discrete trial teaching, how to use 40 “The impact that this program has had on our family is
Additionally, Licensed Psychologists and/or Board Certified Behavior effective prompting) immeasurable and we will reap benefits of the time that has
Analysts: 30
been invested in our son for his entire lifetime and beyond.”
Using differential attention
Oversee practicum opportunities for students in the field of applied –parent of a participant
20
Parents collect data on their in-home implementation of specific
behavior analysis and related fields 10
strategies and then meet individually with a parent training coordinator
Provide ongoing staff training and direct supervision between group sessions
0
GAC Conceptual
Composite
Social Practical
Current behavior therapist's have been recruited from local universities Individual follow-up meetings are provided with parents to review
(i.e., Creighton, College of St. Mary, University of Nebraska, AmeriCorps homework from the parent training program
at UNMC; St. Cloud State)
You might also like
- The Efficiency Paradox - Niklas ModigDocument37 pagesThe Efficiency Paradox - Niklas ModiglawiNo ratings yet
- Basic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Document14 pagesBasic Personality Inventory (Bpi)Roxanne Forbes100% (1)
- History and Evolution of Psychiatric NursingDocument4 pagesHistory and Evolution of Psychiatric Nursingkaren carpio100% (2)
- Contoh KasusDocument6 pagesContoh KasusIndah Ratnasarii0% (3)
- Think CBT WorkbookDocument92 pagesThink CBT Workbooksindhu ponnusamy100% (1)
- Capgar Description 1Document4 pagesCapgar Description 1esbat07100% (2)
- Perspec've Taking Photo Cards Ac'vity #3 What Are They Feeling? Includes 30 Photo Ac'vity CardsDocument8 pagesPerspec've Taking Photo Cards Ac'vity #3 What Are They Feeling? Includes 30 Photo Ac'vity CardsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM 5 Section III PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM 5 Section III PDFraluca_ghigaNo ratings yet
- MyndLift Neurofeedback HandoutDocument2 pagesMyndLift Neurofeedback Handoutshaheenshaikh4940No ratings yet
- "A Critical Time": A Special Report On Emerging Adults Leaving Children's Services CareDocument56 pages"A Critical Time": A Special Report On Emerging Adults Leaving Children's Services CareEmily MertzNo ratings yet
- JAK Inhibitors For Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument7 pagesJAK Inhibitors For Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisMasithaNo ratings yet
- NURS 4369 Preceptor Packet Core 2013Document11 pagesNURS 4369 Preceptor Packet Core 2013Aruna Chezhian100% (1)
- Kate Nobles Linkedin ResumeDocument1 pageKate Nobles Linkedin Resumeapi-612399312No ratings yet
- Mindmap of Reproductive HealthDocument2 pagesMindmap of Reproductive Healthkabirp895No ratings yet
- Gastro BrochureDocument3 pagesGastro Brochuregus_lionsNo ratings yet
- Semu Web 2021 - 2022Document1 pageSemu Web 2021 - 2022Carol PhaswanaNo ratings yet
- School Medical Autism Review Team: A Virtual, Interdisciplinary Tool To Diagnose Children With Autism in Rural Washington State (Amy Carlsen)Document1 pageSchool Medical Autism Review Team: A Virtual, Interdisciplinary Tool To Diagnose Children With Autism in Rural Washington State (Amy Carlsen)AUCDNo ratings yet
- CHP Poster Final - April 2023Document1 pageCHP Poster Final - April 2023api-620860184No ratings yet
- Inclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)Document1 pageInclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)AUCDNo ratings yet
- Madhya Pradesh Medical Science University, Jabalpur (M.P.)Document78 pagesMadhya Pradesh Medical Science University, Jabalpur (M.P.)Vinay Mishra100% (1)
- Arunava Deb OJT Report 11909663Document34 pagesArunava Deb OJT Report 11909663nischal krishnaNo ratings yet
- Holahan Sloan Poster YaleDocument1 pageHolahan Sloan Poster Yaleapi-416977976No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Final Year Students Djerriwarrh Health ServicesDocument1 pageGuidelines For Final Year Students Djerriwarrh Health Servicessidney drecotteNo ratings yet
- 2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Document63 pages2-3 - Oral & Esophageal Disorders 2Taif SalimNo ratings yet
- Goldberg-HIV PosterDocument1 pageGoldberg-HIV PosterMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis Institute of Business Management Pune - Email: Placements@sibmpune - Edu.in - PH.: 020-28116071/72/73Document7 pagesSymbiosis Institute of Business Management Pune - Email: Placements@sibmpune - Edu.in - PH.: 020-28116071/72/73MeetaliSaxenaNo ratings yet
- Delgado Destiny ResumeDocument2 pagesDelgado Destiny Resumeapi-661552521No ratings yet
- CACTX BrochureDocument2 pagesCACTX BrochureAndrew BarlowNo ratings yet
- Change in Clinical Status and Side Effects of Patients Treated With Either Olanzapine or Risperidone 6-Month Results From IC-SOHODocument1 pageChange in Clinical Status and Side Effects of Patients Treated With Either Olanzapine or Risperidone 6-Month Results From IC-SOHOPedro GargoloffNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Interpersonal PsychotherapyDocument38 pagesLecture 9 Interpersonal PsychotherapyKar GayeeNo ratings yet
- E-Poster Enterics For Global Health Shigella Surveillance StudyDocument1 pageE-Poster Enterics For Global Health Shigella Surveillance StudyNeyama AlladinNo ratings yet
- Escala Del Dolor PPPDocument16 pagesEscala Del Dolor PPPMariana SuarezNo ratings yet
- First Bridge Centre ABA An IntroductionDocument70 pagesFirst Bridge Centre ABA An Introductionpsigrist100% (4)
- Figure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundDocument1 pageFigure 1. POLARIS Study Design: BackgroundAhmed Abd El AzizNo ratings yet
- Practicalskillschecklist 13Document15 pagesPracticalskillschecklist 13api-396515657No ratings yet
- Primary Care Entrepreneurship ModelsDocument60 pagesPrimary Care Entrepreneurship Modelssachin ganorkar100% (1)
- Malnutrition in Pakistan 20230418 FinalDocument1 pageMalnutrition in Pakistan 20230418 FinalZona AroojNo ratings yet
- O5 Vo4No4Document6 pagesO5 Vo4No4Muthanna Lo'ayNo ratings yet
- Final Compass Logic Model 8 MonthsDocument1 pageFinal Compass Logic Model 8 Monthsapi-256763045No ratings yet
- Register Kesehatan AnakDocument5 pagesRegister Kesehatan AnakSdnegeri LebakpasarNo ratings yet
- EMC Current State LoopsDocument1 pageEMC Current State LoopsGiovanni Lorenzoni AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 10 Day Course 2018Document2 pages10 Day Course 2018Niruj Kr DekaNo ratings yet
- Efectividad en Las Visitas DomicliariasDocument6 pagesEfectividad en Las Visitas DomicliariasJonathan Francisco Gomez SantelicesNo ratings yet
- ACCESSquality FINANCIAL PLAN TEMPLATEDocument15 pagesACCESSquality FINANCIAL PLAN TEMPLATEDulay RezzielNo ratings yet
- Fever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSDocument2 pagesFever PrimaryCommunityCare Dec 16 FINAL VSnimraNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Nursing Management Round 5ad3bdbbDocument11 pagesOptimization of Nursing Management Round 5ad3bdbbsarvitaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Workplan 2023 2025Document12 pagesNutrition Workplan 2023 2025Rico Jay GrasparilNo ratings yet
- Fri 394 Ilc2022Document1 pageFri 394 Ilc2022rtthrtfhNo ratings yet
- Adventures in Parenting Rev PDFDocument67 pagesAdventures in Parenting Rev PDFjyzlle herrera100% (1)
- BudgetDocument3 pagesBudgetmalakdiabmed57No ratings yet
- Children Adopted From Eastern Europe EvoDocument1 pageChildren Adopted From Eastern Europe EvoDolores SeguraNo ratings yet
- Govph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaDocument29 pagesGovph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaCarol LaconsayNo ratings yet
- Annotated PDocument4 pagesAnnotated Papi-735789339No ratings yet
- NutritionDocument2 pagesNutritionashish kuntewarNo ratings yet
- 1 - FORBESJHEPATOL2015 Cell Therapy en Enf HeaticasDocument13 pages1 - FORBESJHEPATOL2015 Cell Therapy en Enf HeaticasalexandresarradeyNo ratings yet
- 2011 Google Shopper Sciences Finance Credit Cards ZMOTDocument21 pages2011 Google Shopper Sciences Finance Credit Cards ZMOTangelo1boccola-1No ratings yet
- Are Asthma Programs Positioned For Impact Factors Associated With SuccessDocument1 pageAre Asthma Programs Positioned For Impact Factors Associated With SuccessCenter for Managing Chronic DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Elevate Effectiveness Study: Principal AuthorDocument7 pagesElevate Effectiveness Study: Principal Authorfederico torresNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Corrected 20pDocument5 pagesAnnotated-Corrected 20papi-735789339No ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument54 pagesEctopic PregnancyLawrence CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- KinsDocument2 pagesKinsapi-576274610No ratings yet
- Children 07 00064Document10 pagesChildren 07 00064zizee61No ratings yet
- Animal-Assisted Intervention in Dementia: Effects On Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and On Caregivers' Distress PerceptionsDocument8 pagesAnimal-Assisted Intervention in Dementia: Effects On Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and On Caregivers' Distress PerceptionsFelipe FookNo ratings yet
- India Heals 2020 - Indian ExhibitorsDocument2 pagesIndia Heals 2020 - Indian ExhibitorsRama VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Vbmapp FaqsDocument2 pagesVbmapp FaqsMonalisa Costa100% (2)
- DQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBDocument1 pageDQC24 Tableau Medicaments EN WEBcococooleNo ratings yet
- Karlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleDocument1 pageKarlien Vanhouteghem, Annelies Aerssens, Dirk Ommeslag, Jerina Boelens, Steven Callens, Anne-Marie Van Den AbeeleAfien MuktiNo ratings yet
- Procedure TempDocument2 pagesProcedure TempShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Up The Assessment Binder: SettingDocument9 pagesUp The Assessment Binder: SettingShanpaulNo ratings yet
- GRAPHICS by JW Illustrations ©Document4 pagesGRAPHICS by JW Illustrations ©ShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Ablls-R Visual Performance Section B8 Sort Non Identical ItemsDocument10 pagesAblls-R Visual Performance Section B8 Sort Non Identical ItemsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Roadmap 2 Evidence Based Social Emotional Curricula and Intervention Packages For Children 0 5 Years and Their Families PDFDocument21 pagesRoadmap 2 Evidence Based Social Emotional Curricula and Intervention Packages For Children 0 5 Years and Their Families PDFShanpaulNo ratings yet
- SOC - Games TA Musical ChairsDocument1 pageSOC - Games TA Musical ChairsShanpaulNo ratings yet
- Ten Questions For John Rowan PDF PDFDocument3 pagesTen Questions For John Rowan PDF PDFtestNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lecture Materials: Human Behavior and VictimologyDocument64 pagesCompiled Lecture Materials: Human Behavior and Victimologyanna lei mazaredoNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy and AutismDocument4 pagesOccupational Therapy and AutismBetül Özsoy TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Final Mental Health Lit ReviewDocument116 pagesFinal Mental Health Lit ReviewDanny WamsleyNo ratings yet
- Read The Essay and Then Answer The QuestionsDocument4 pagesRead The Essay and Then Answer The QuestionsLINA MURILLONo ratings yet
- Why Is Mental Health Important? Mental Health Is Important Because It AffectsDocument1 pageWhy Is Mental Health Important? Mental Health Is Important Because It AffectsJellina Joya RosgaNo ratings yet
- NUR 3251 Module 10 Psychotherapeutic Agents Study GuideDocument6 pagesNUR 3251 Module 10 Psychotherapeutic Agents Study GuideWinnie MeiNo ratings yet
- Pola Komunikasi Guru Di Yayasan Peduli Autisme Bali Dalam Meningkatkan Interaksi Sosial Anak AutistikDocument14 pagesPola Komunikasi Guru Di Yayasan Peduli Autisme Bali Dalam Meningkatkan Interaksi Sosial Anak AutistikIntan HumaerohNo ratings yet
- Gemma Hardy Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument19 pagesGemma Hardy Post Traumatic AmnesiaAditya Pradana KNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes During MenopauseDocument48 pagesPsychological Changes During MenopauseSnow19987No ratings yet
- What To Expect - Chris Vanderwees, PHD, RPDocument1 pageWhat To Expect - Chris Vanderwees, PHD, RPGary FreedmanNo ratings yet
- The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)Document8 pagesThe Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ)Wynda MuljonoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Child AbuseDocument4 pagesEffects of Child Abuselotusrai100% (2)
- Stress DiaryDocument2 pagesStress Diaryapi-217446206No ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety DisordersSantosh ParabNo ratings yet
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Skill Hebefrenic SchizophreniaDocument13 pagesSkill Hebefrenic SchizophreniasaidahrahmatNo ratings yet
- Drug Use Screening Tool - DUST 2Document4 pagesDrug Use Screening Tool - DUST 2TONIC100% (2)
- PSQIDocument6 pagesPSQINingsih An NajwaNo ratings yet
- Stress & Stress ManagementDocument19 pagesStress & Stress ManagementNawfal EddyaniNo ratings yet
- Child PsychiatrystudentbookletDocument83 pagesChild PsychiatrystudentbookletOana Popescu50% (2)
- The Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalDocument11 pagesThe Wisdom of Trauma Booklet - FinalAdela100% (2)
- Jane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldDocument5 pagesJane R. Wheatley-Crosbie - Healing Traumatic Reenactment: Psyche's Return From Soma's UnderworldCanola_Olive0% (1)