Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Servomotor 161204090653
Servomotor 161204090653
Uploaded by
Shreyansh Porwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesA servomotor consists of an electric motor, feedback device, and electronic controller. It allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. Servomotors can use AC or DC motors that are 1 or 3 phase, and DC motors can be brushed or brushless. Feedback is typically provided by an encoder or resolver built into the motor. A servomotor uses position control with pulse width modulation to vary the angular position of the motor based on the width of the control pulse. Servomotors are used in applications like robotics, conveyor belts, CNC machines, antenna positioning, and metal cutting machines to provide accurate control of motion.
Original Description:
Servo motor ppy
Original Title
servomotor-161204090653
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA servomotor consists of an electric motor, feedback device, and electronic controller. It allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. Servomotors can use AC or DC motors that are 1 or 3 phase, and DC motors can be brushed or brushless. Feedback is typically provided by an encoder or resolver built into the motor. A servomotor uses position control with pulse width modulation to vary the angular position of the motor based on the width of the control pulse. Servomotors are used in applications like robotics, conveyor belts, CNC machines, antenna positioning, and metal cutting machines to provide accurate control of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesServomotor 161204090653
Servomotor 161204090653
Uploaded by
Shreyansh PorwalA servomotor consists of an electric motor, feedback device, and electronic controller. It allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. Servomotors can use AC or DC motors that are 1 or 3 phase, and DC motors can be brushed or brushless. Feedback is typically provided by an encoder or resolver built into the motor. A servomotor uses position control with pulse width modulation to vary the angular position of the motor based on the width of the control pulse. Servomotors are used in applications like robotics, conveyor belts, CNC machines, antenna positioning, and metal cutting machines to provide accurate control of motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Sai kumar
A servomotor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows
for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and
acceleration.
Essentially, it consists of an
1. electric motor,
2. feedback device,
3. electronic controller.
Motors can be either AC or DC
Can be of 1 phase or 3 phase.
DC motors can be brushed or brushless.
Brushless DC motors are more expensive, drives are more
complex, but are more reliable and maintenance free.
Feedback device for servomotors is typically an encoder or
resolver built into the motor frame.
Control circuitry is a motion controller (generates motion) and
a drive to supply power to the motor
AC servo motor
Dc servo motor
Continuous rotation servo motor
Linear servo motor
PLC (transistor
type)
contactor
Power Servo drive
source
Servo motor Load
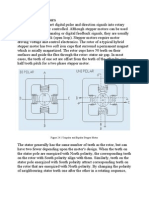
Position control using Pulse Width Modulation Technique.
The width of the pulse applied to the motor is varied and send
for a fixed amount of time.
The pulse width determines the angular position of the servo
motor.
For example
a pulse width of 1 ms -a angular position of 0 degrees,
a pulse width of 2 ms - a angular width of 180 degrees.
Electronic amplifier used to power electric
servomechanisms.
A servo drive monitors the feedback signal
from the servomechanism and continually
adjusts for deviation from expected behaviour.
linear relationship b/n speed and electric control signal
Steady state stability
Wide range of speed control
Low mechanical and electrical inertia
Fast response
Robotics
Conveyor belts
Camera auto focus
Robotic vehicles
Solar tracking system
CNC machines
Antenna positioning
Metal cutting & metal forming m/c – millimg m/c, lathe,
grinding, pressing, punching, bending in metal fabrication.
Textiles
Printers
Automatic door openers
Thank you….
You might also like
- Servo MotorDocument3 pagesServo Motormuneeb saeedNo ratings yet
- Sarvan KumarDocument11 pagesSarvan KumarsarvankumarNo ratings yet
- Servomotors: by Joseph M Abraham Aeronautical DeptDocument17 pagesServomotors: by Joseph M Abraham Aeronautical DeptibrahimNo ratings yet
- Servo Motors Types and ApplicationsDocument22 pagesServo Motors Types and ApplicationsJavierNo ratings yet
- CNC MachinesDocument52 pagesCNC Machinespranav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Types of MotorsDocument15 pagesTypes of Motorskbp qawaNo ratings yet
- Theory DC ServoMDocument3 pagesTheory DC ServoMKaustubh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Servo MoDocument10 pagesServo MonatiNo ratings yet
- Report of Servo MotorDocument3 pagesReport of Servo MotorMUHAMMAD KASHIFNo ratings yet
- What Is Servo Motor Servomotor: Rotary Actuator Linear ActuatorDocument11 pagesWhat Is Servo Motor Servomotor: Rotary Actuator Linear ActuatorThe-kiros HadushNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Control Using Arduino: 1) IntroductionDocument10 pagesDC Motor Control Using Arduino: 1) IntroductionSoeAyeNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Product Finder Home PageDocument6 pagesTechnical Information: Product Finder Home PageawemetalNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Control: Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurHassnain MohdNo ratings yet
- Computer Numeric ControlDocument48 pagesComputer Numeric Controlabdifatah.nadir.snu.eduNo ratings yet
- BLDC Motor: 4 Pole 2 Phase Motor OperationDocument10 pagesBLDC Motor: 4 Pole 2 Phase Motor OperationG.R.AzhaguvelSaranya Professor MechanicalNo ratings yet
- ActuatorDocument61 pagesActuatorforeverdieselNo ratings yet
- Control Theory 31 PDFDocument44 pagesControl Theory 31 PDFAmit TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Steeper and Servo MotorsDocument3 pagesSteeper and Servo MotorsIan Justine JornalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DC MotorsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To DC Motorsmanishwakade73No ratings yet
- Microprocessor PP TDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor PP Tmanishwakade73No ratings yet
- Servo Motor - Types, Construction, Working, Controlling & ApplicationsDocument7 pagesServo Motor - Types, Construction, Working, Controlling & ApplicationsAHMED YOUSEFNo ratings yet
- Eceg-5401 2Document37 pagesEceg-5401 2Kide Bay0% (1)
- Special Electrical Machines: Permanent Magnet Brushless DC MotorsDocument35 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines: Permanent Magnet Brushless DC MotorsRozitarmizi MohammadNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: DR D Y Patil School of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 02: DR D Y Patil School of Engineering & Technologypradnya sadigaleNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: DR D Y Patil School of Engineering & TechnologyDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 02: DR D Y Patil School of Engineering & Technologypradnya sadigaleNo ratings yet
- Ac-Dc-Servomotor-Net NotesDocument9 pagesAc-Dc-Servomotor-Net NotesDINESHKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- DC Servomotors Assignment 02Document5 pagesDC Servomotors Assignment 02Saad BhattiNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors For RoboticsDocument16 pagesElectric Motors For RoboticsMunindar KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDocument6 pagesUniversity of Kirkuk College of Engineering Mechanical Departmentعبدالمؤمن خالد محمود100% (1)
- Servo MotorDocument11 pagesServo MotorBotlhe SomolekaeNo ratings yet
- Control System - by Rakesh KumarDocument6 pagesControl System - by Rakesh KumarRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- This Video Discusses Servo Motors and How They WorkDocument2 pagesThis Video Discusses Servo Motors and How They WorkĐăng DuyNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC MotorDocument19 pagesBrushless DC MotorSanjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- 11 Additional Reading - CNCDocument49 pages11 Additional Reading - CNCAnoop kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology and InstrumentationDocument53 pagesEngineering Metrology and InstrumentationRam SethuNo ratings yet
- Machines AssignmentDocument7 pagesMachines AssignmentCharles MuneneNo ratings yet
- ServomotorsDocument17 pagesServomotorsVi GaneshNo ratings yet
- Servomechanism: Application of Servo MechanismDocument6 pagesServomechanism: Application of Servo MechanismJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- of BLDCDocument45 pagesof BLDCsmhbNo ratings yet
- Motors Encoders EtcDocument9 pagesMotors Encoders Etcaqtu12fucNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Drive SystemDocument84 pagesUnit-II Drive SystemSatheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Robot Drive Systems and End EffectorsDocument81 pagesUnit-II: Robot Drive Systems and End EffectorsSatheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument12 pagesDC Motorsmuletola7No ratings yet
- BLDCDocument45 pagesBLDCthulasi_krishna75% (4)
- DC Servo MotorsDocument19 pagesDC Servo MotorsSoumitri JenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4udayoleti21005a0406No ratings yet
- Servo MotorDocument9 pagesServo Motoramanda christineNo ratings yet
- DC ServomotorDocument3 pagesDC ServomotorAshutosh Prakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Controlling Stepper/DC/Servo Motors With Arduino/NI DAQ/PMACDocument17 pagesControlling Stepper/DC/Servo Motors With Arduino/NI DAQ/PMACandita ranniNo ratings yet
- Automation System Design - 2 - 1709737440783Document37 pagesAutomation System Design - 2 - 1709737440783Vaishnavi CharyaNo ratings yet
- ECNG-4010 Lecture 05Document37 pagesECNG-4010 Lecture 05Abel BatuNo ratings yet
- Actuators: Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Iit BombayDocument36 pagesActuators: Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Iit BombayMohd Sazli SaadNo ratings yet
- Overview of Industrial Motor Control SystemsDocument8 pagesOverview of Industrial Motor Control Systemsiwuo4797No ratings yet
- DC Serv O-Mo TOR: Engr. M.BILALDocument28 pagesDC Serv O-Mo TOR: Engr. M.BILALBilalNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument12 pagesDC MotorsJamie Ray DalisayNo ratings yet
- The Basic DC MotorDocument22 pagesThe Basic DC MotortamilselviNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentgeraldjetjetNo ratings yet